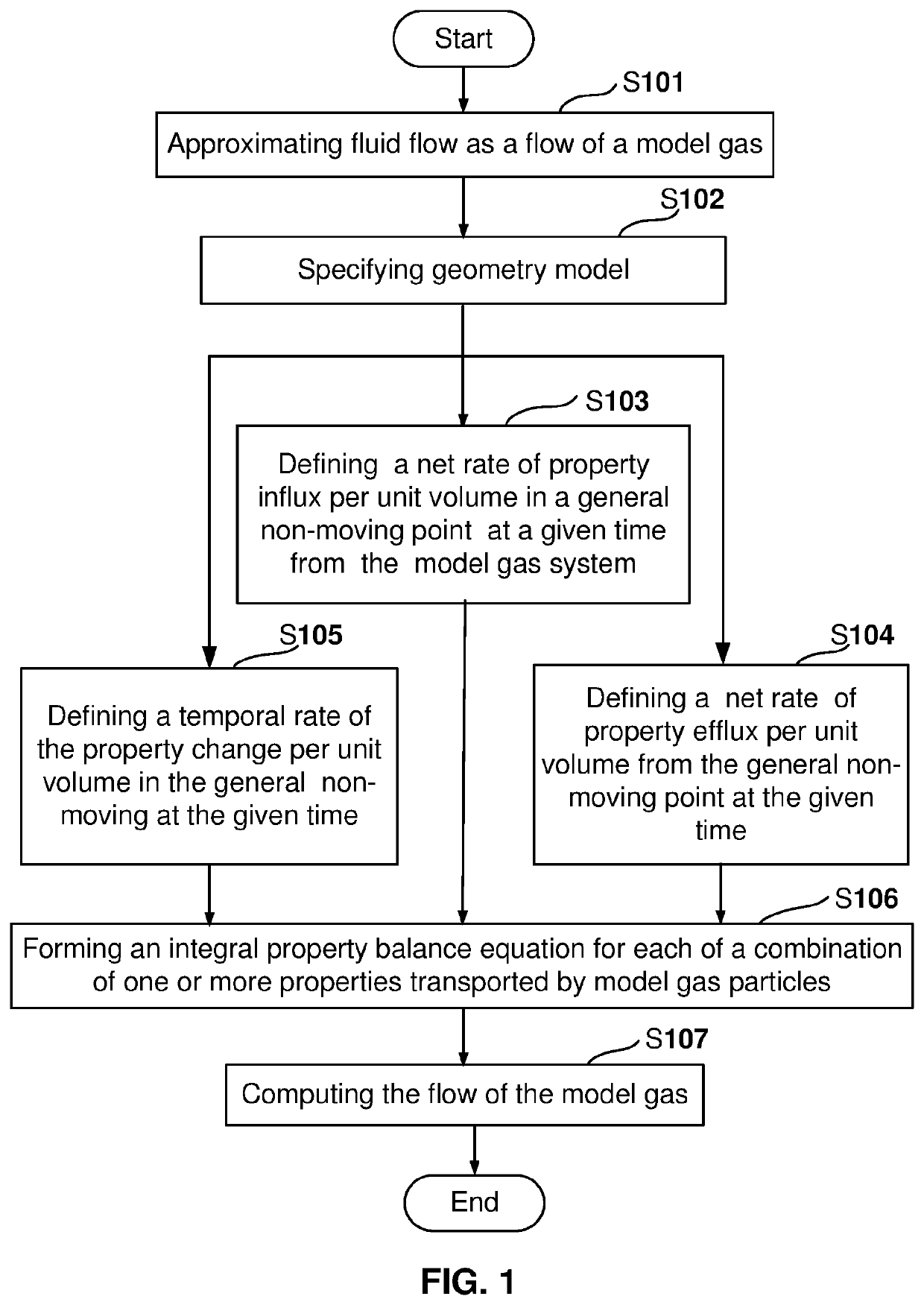
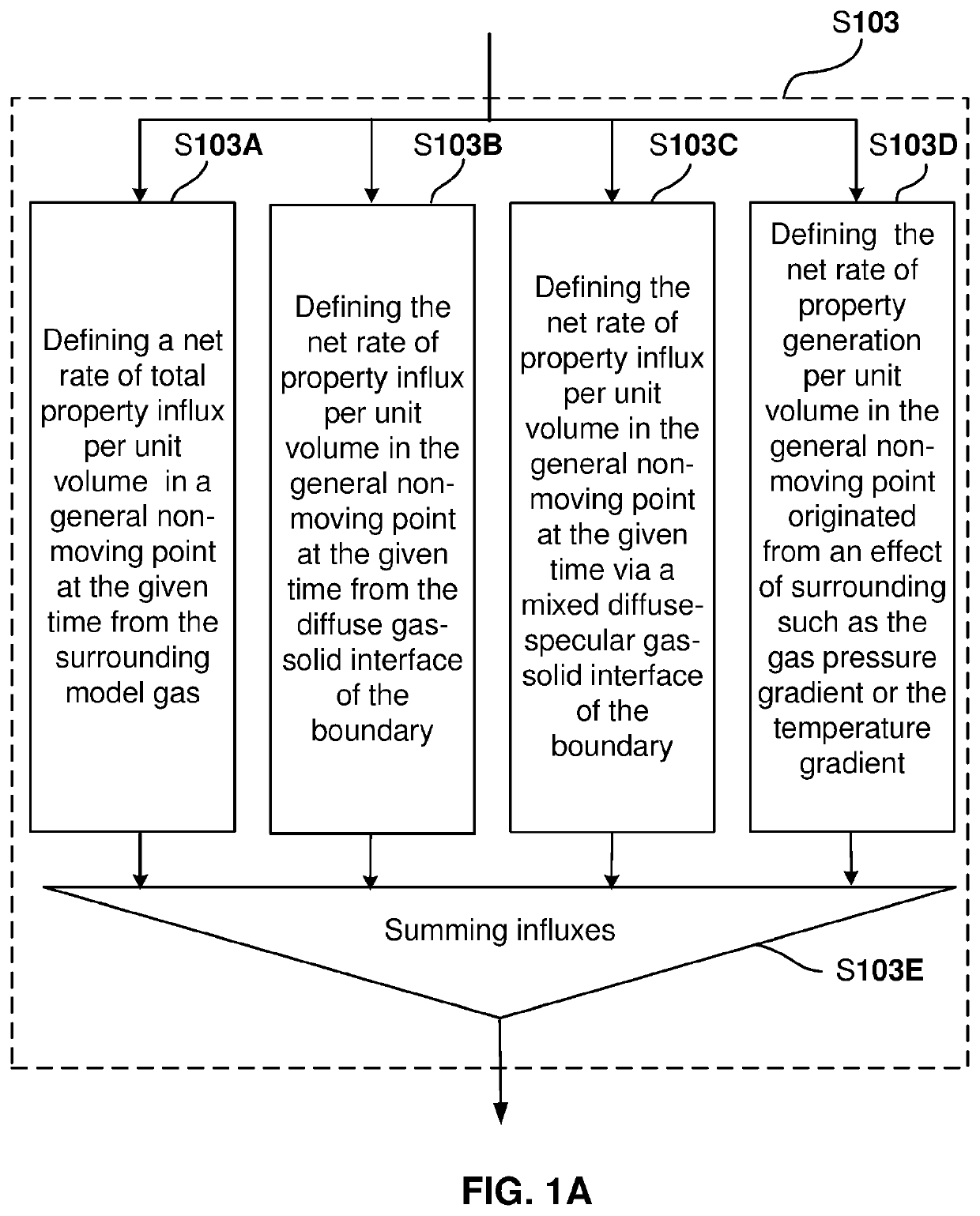
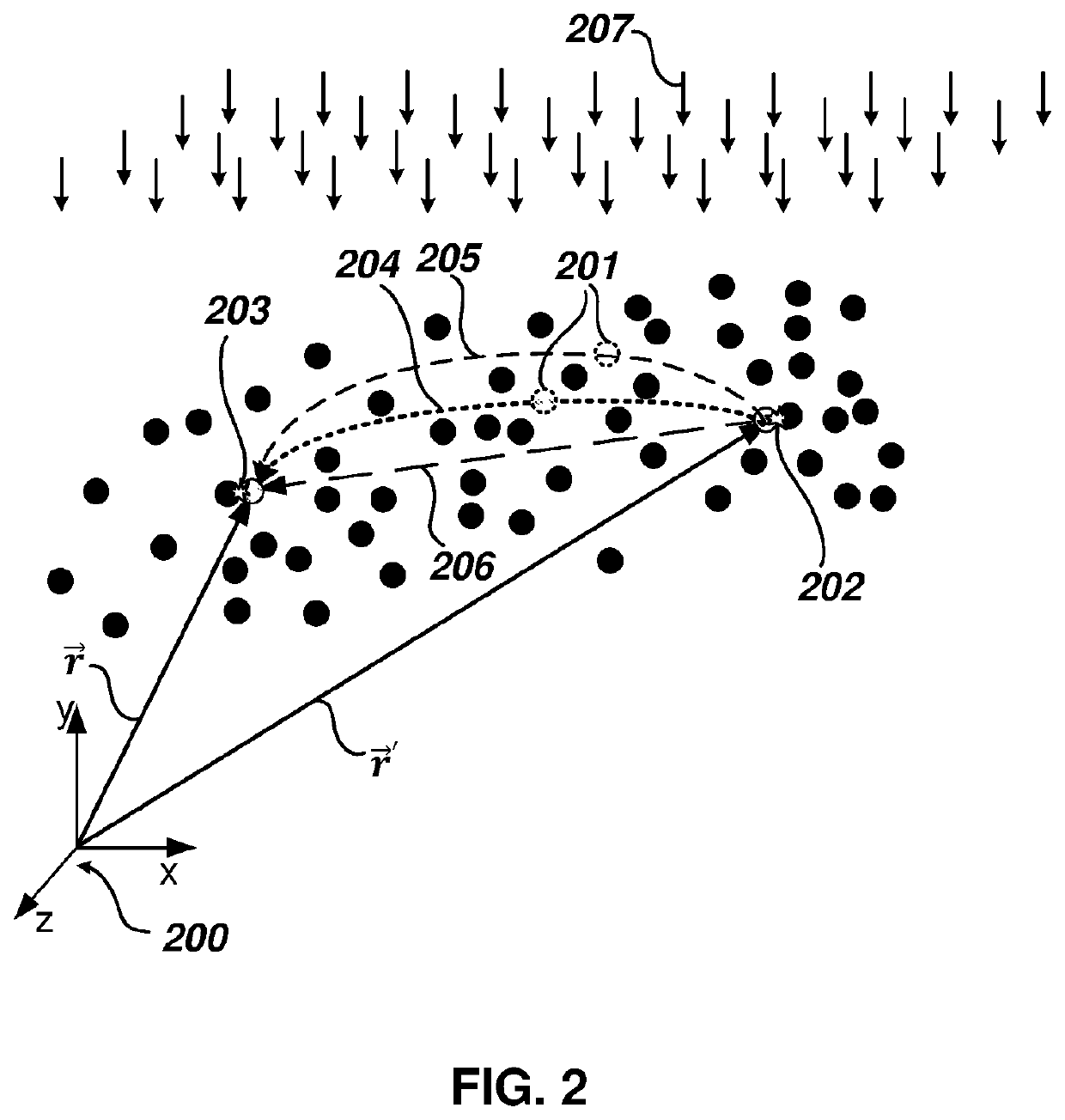
Analytical Tools and Method for Modeling Transport Processes in Fluids
a technology of fluids and analytical tools, applied in the field of analytical tools and methods for modeling transportation processes in fluids, can solve the problems of affecting the usefulness of computation results, affecting the accuracy of fluid modeling, so as to improve the time resolution of computations, increase the operable range of knudsen numbers, and expand the horizon of cfd applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
2.1 Simulation 1
[0427]In the first simulation, Simulation 1, transient plane Couette flow is calculated.
[0428]FIG. 6 is a schematic view in section of a Newtonian model gas between parallel infinite plates in the open channel at uniform temperature and no external field of force applied in y direction and a lack of internal aging processes, namely, λ=0, each particle conserves properties acquired by it at a point and time of the original collision and deliver that properties unchanged to another location upon its final collision with another particle in a point sink. The following simulation is shown to illustrate the inventive approach in determining velocity profiles ux(y,t) or velocity distribution across the space between the plates.
[0429]A simulation is performed for incompressible model gas expanding in the y-direction between parallel infinite plates being spaced at the distance H in the open channel at the uniform temperature where the top and bottom plates and the model ga...
example 2
2.2 Simulation 2
[0473]In the second simulation, Simulation 2, the steady velocity profile across between the parallel plates with mixed diffuse and specular particles scatterings from the plates being at rest is calculated.
[0474]The particular embodiment is limited to a simulation of incompressible stable model gas flow confined in the y-direction between parallel infinite plates at a uniform temperature with no external field of the force applied in y-direction where the top and bottom plates are at rest. However, the method can be generalized to the model gas flow affected by the external field of force or kept at non-uniform temperature with no difficulty, as apprehended by those skilled in the art. The pressure gradient is constant along with the model gas flow in he x-direction. The velocity profile induced in the model gas due to the pressure gradient is to be determined. Referring to FIG. 14, more detailed description of the steps of performing flow calculation by the comput...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com