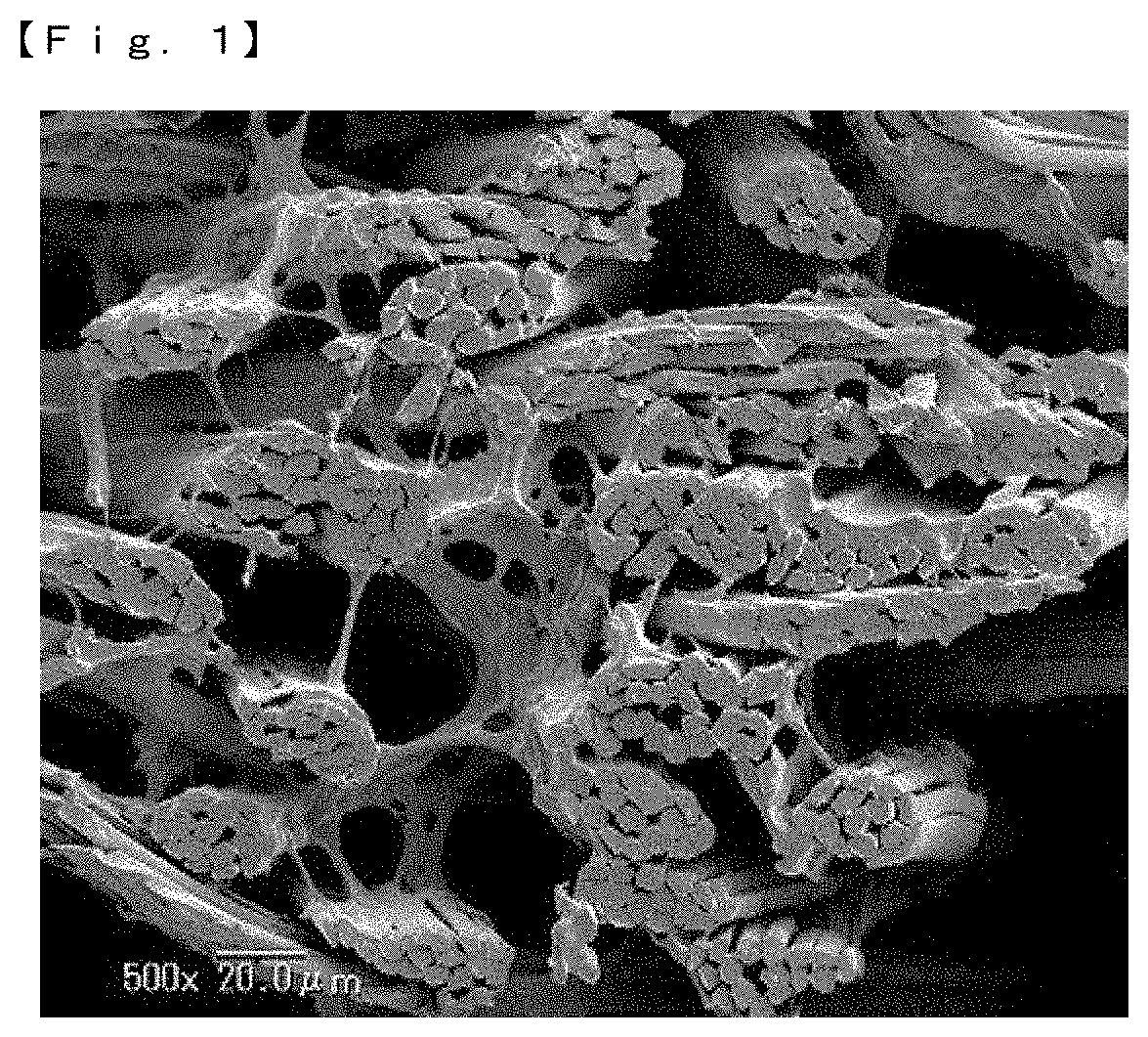
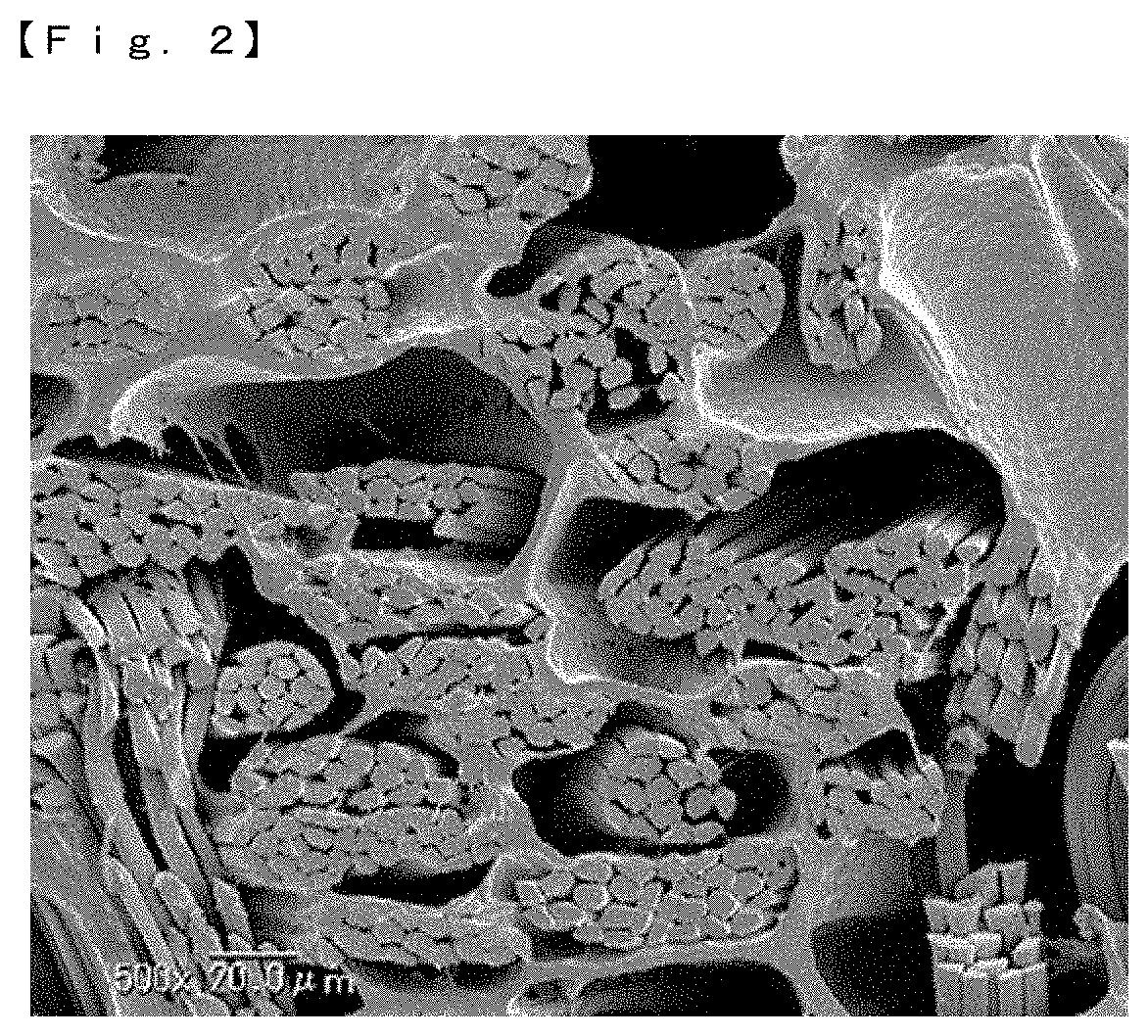
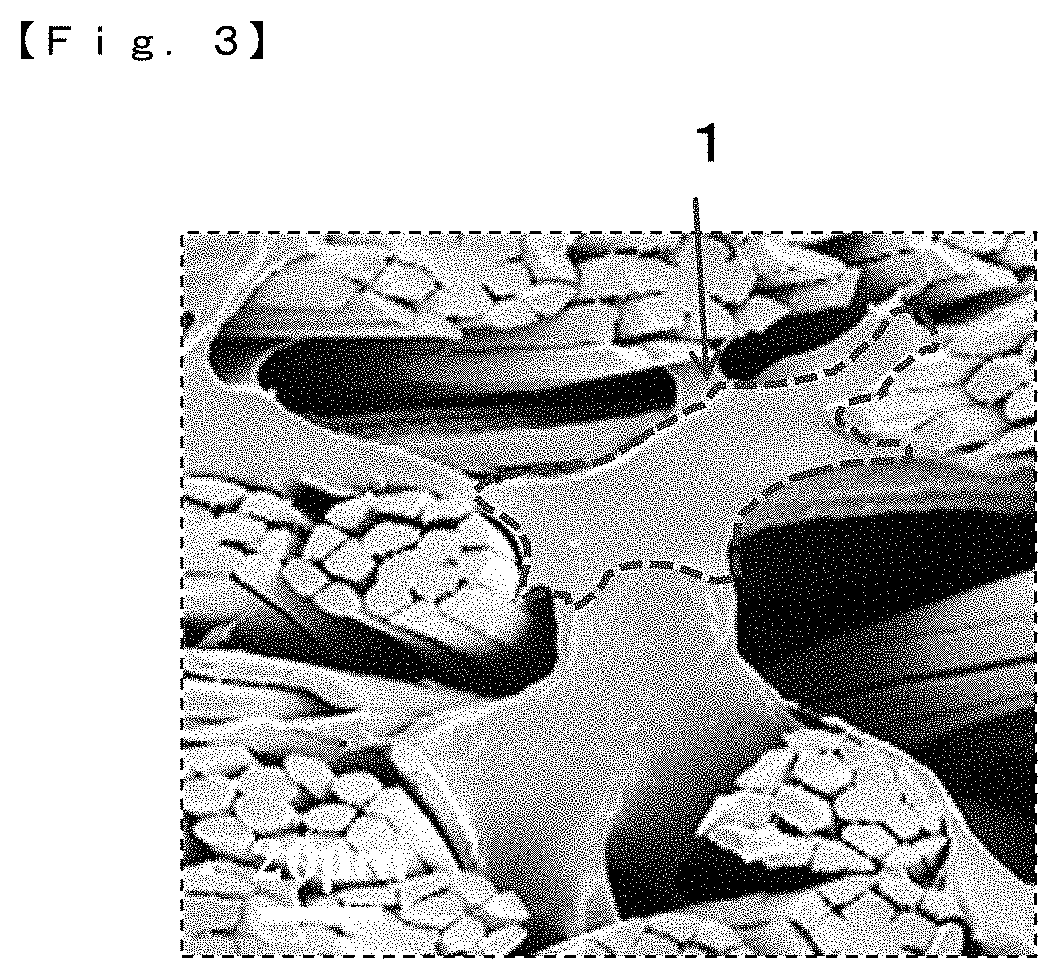
Sheet-like article and a production method therefor
a production method and technology of a sheet-like article, applied in the field of environmental protection production methods of sheet-like articles, can solve the problems of poor softness of texture, high harmfulness of organic solvents to the human body and the environment, and stiff texture of coagulating polyurethane, etc., to achieve elegant surface quality, fold and crease recovery and flexibility, and dense fiber feel
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0193]Polyethylene terephthalate copolymerized with 8 mol % sodium 5-sulfoisophthalate was used as sea component and polyethylene terephthalate was used as island component to produce an island-in-sea type composite fiber in which the composition ratio was 20 mas % sea component and 80 mas % island component, the number of islands was 16 islands / filament, and the average filament diameter was 20 μm. The island-in-sea type composite fiber obtained was cut into pieces with a fiber length of 51 mm to provide staple. It was then passed through a card and a cross lapper to form a fiber web, which was subjected to needle punching to produce a non-woven fabric.
[0194]The non-woven fabric obtained in this manner was shrunk by immersing it in hot water at a temperature of 97° C. for 2 minutes, and then dried at a temperature of 100° C. for 5 minutes. Subsequently, the resulting nonwoven fabric was impregnated with a dispersion liquid prepared by adjusting water-dispersed polyurethane dispersi...
example 2
[0196]Except that the same nonwoven fabric as in Example 1 was impregnated with a dispersion liquid prepared by adjusting water-dispersed polyurethane dispersion liquid A to a solid content of 20%, adding an epoxy based crosslinking agent [CR-5L, manufactured by DIC] to an effective component content of 5 mass % relative to the polyurethane solid content, adding an association type viscosity improver [Thickner 627N, manufactured by San Nopco Limited] to an effective component content of 4 mass % relative to the polyurethane solid content, and adding magnesium sulfate to 1.2 mass % relative to the polyurethane solid content, the same procedure as in Example 1 was carried out to provide artificial leather with a metsuke of 223 g / m2. The falling-off rate of polyurethane during the water-dispersed polyurethane coagulation step in hot water was as small as 0.1%, suggesting scarce occurrence. The resulting artificial leather had good appearance quality and good texture free of a paper-lik...
example 3
[0197]Polyethylene terephthalate copolymerized with 8 mol % sodium 5-sulfoisophthalate was used as sea component and polyethylene terephthalate was used as island component to produce an island-in-sea type composite fiber in which the composition ratio was 20 mas % sea component and 80 mas % island component, the number of islands was 16 islands / filament, and the average filament diameter was 20 μm. The island-in-sea type composite fiber obtained was cut into pieces with a fiber length of 51 mm to provide staple. It was then passed through a card and a cross lapper to form a fiber web, which was subjected to needle punching to produce a non-woven fabric.
[0198]The non-woven fabric obtained in this manner was shrunk by immersing it in hot water at a temperature of 97° C. for 5 minutes, and then dried at a temperature of 100° C. for 10 minutes. Subsequently, an aqueous solution containing 10 mass % (solid content) of PVA with a degree of saponification of 99% and a degree of polymeriza...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com