Photocatalytic electrode for water splitting and water splitting device
a photocatalytic electrode and water splitting technology, applied in the direction of electrolysis components, electrolysis coatings, physical/chemical process catalysts, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient onset potential and insatisfactory performance of water splitting devices, and achieve excellent onset potential
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
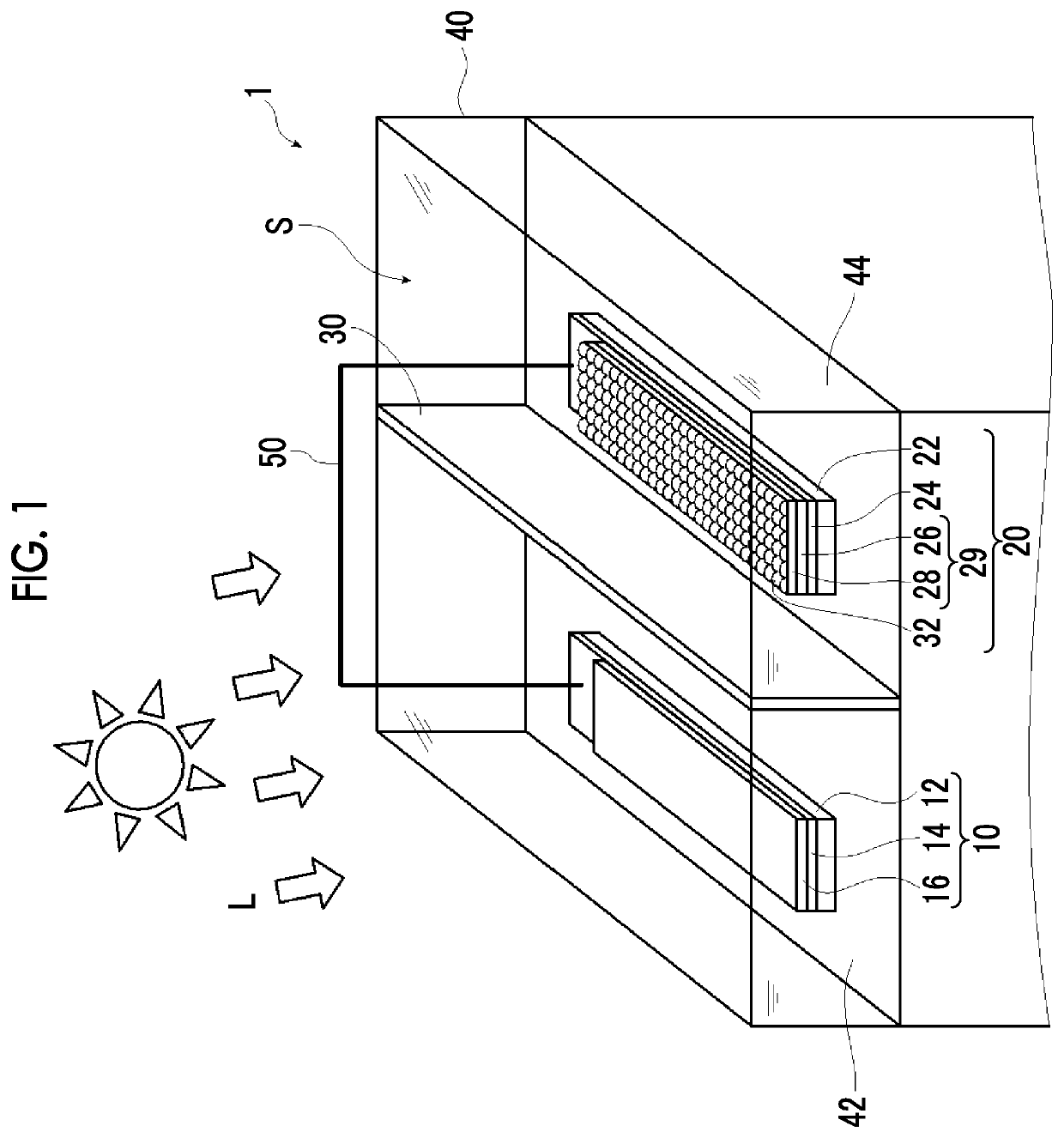
[0037]In one embodiment of a water splitting device of the present invention, the water splitting device generates gases from a photocatalytic electrode for hydrogen generation and a photocatalytic electrode for oxygen generation by irradiating the photocatalytic electrode for hydrogen generation and the photocatalytic electrode for oxygen generation with light, and includes a bath to be filled with an electrolytic aqueous solution and the photocatalytic electrode for hydrogen generation and the photocatalytic electrode for oxygen generation each disposed in the bath, in which the photocatalytic electrode for hydrogen generation has a p-type semiconductor layer, an n-type semiconductor layer provided on the p-type semiconductor layer, and a co-catalyst provided on the n-type semiconductor layer, the p-type semiconductor layer is a semiconductor layer containing a CIGS compound semiconductor containing Cu, In, Ga, and Se, and a molar ratio of Ga to a total molar amount of Ga and In i...
second embodiment
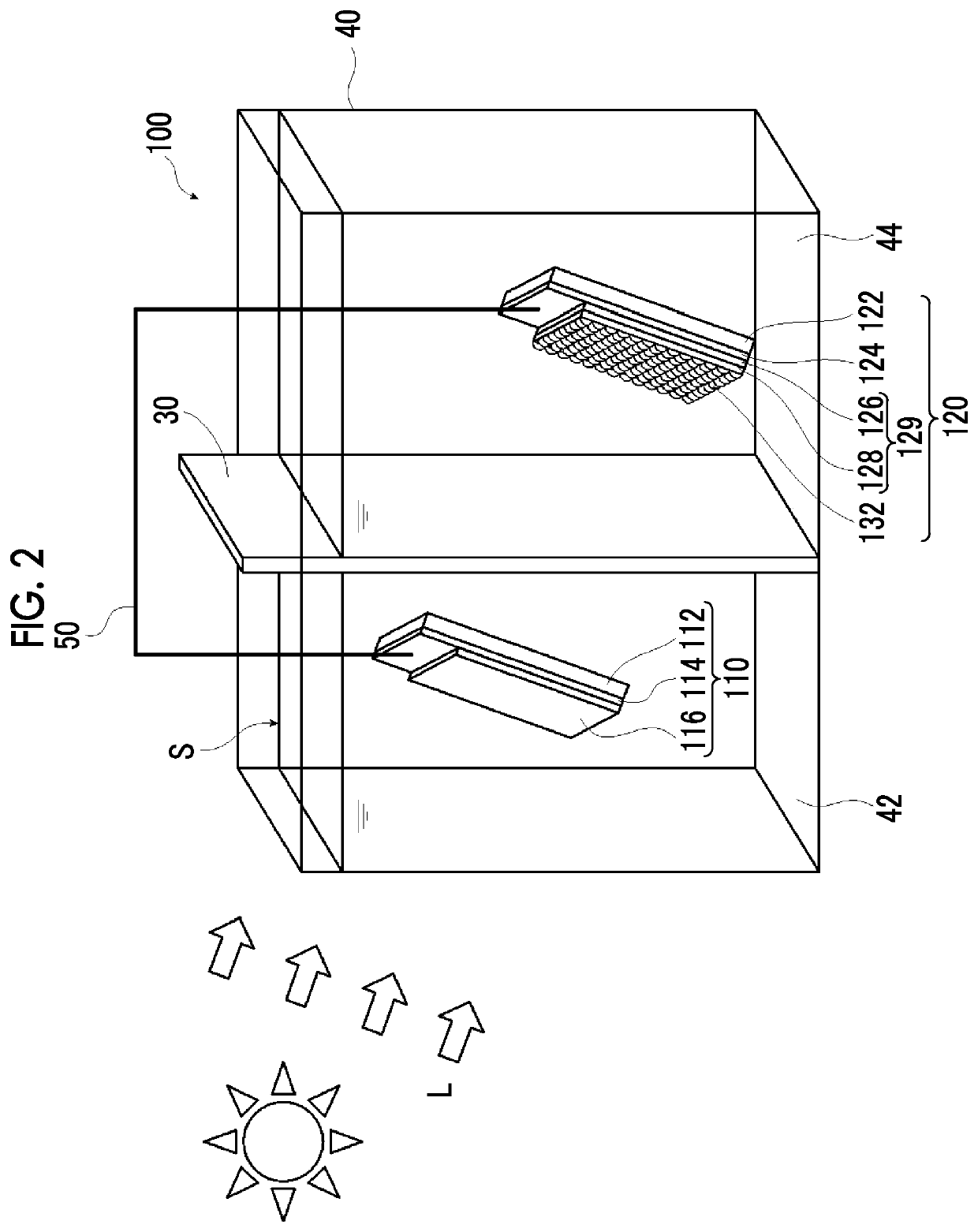
[0141]In one embodiment of a water splitting device of the present invention, the water splitting device generates gases from a photocatalytic electrode for hydrogen generation and a photocatalytic electrode for oxygen generation by irradiating the photocatalytic electrode for hydrogen generation and the photocatalytic electrode for oxygen generation with light, and includes a bath to be filled with an electrolytic aqueous solution and the photocatalytic electrode for hydrogen generation and the photocatalytic electrode for oxygen generation each disposed in the bath, in which the photocatalytic electrode for hydrogen generation has a p-type semiconductor layer, an n-type semiconductor layer provided on the p-type semiconductor layer, and a co-catalyst provided on the n-type semiconductor layer, and a band offset ΔE which is a difference between a potential p-CBM at a lower end of a conduction band of the p-type semiconductor layer and a potential n-CBM at a lower end of a conductio...
example 1
[0149]A photocatalytic electrode of Example 1 was produced as follows.
[0150]First, a layer (conductive layer) having a thickness of 600 nm and formed of Mo was formed on the surface of a soda-lime glass substrate (insulating substrate) by a direct current (DC) magnetron sputtering method using a magnetron sputtering apparatus (product name “CFS-12P”, manufactured by Shibaura Eletech Corporation).
[0151]Next, a layer (p-type semiconductor layer) formed of a CIGS compound semiconductor having a thickness of 2 μm was formed on the surface of the conductive layer by a three-step method using a multi-source vapor deposition apparatus (product name “EW-10”, manufactured by EIKO Engineering Corporation). Specifically, Cu, In, Ga, and Se were used as vapor deposition sources, the substrate temperature of the first step was set to 400° C., and the substrate temperatures of the second and third steps were set to 520° C. The Ga ratio (Ga / (Ga+In)) was adjusted by controlling the vapor deposition...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molar ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molar ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com