Process employing hydrogen to strip dissolved hydrogen sulfide from the liquid effluent of a petroleum distillate hydrotreater
a technology of hydrotreater and hydrotreater, which is applied in the field of stripping of hydrogen sulfide from the effluent of a petroleum distillate hydrotreater, can solve the problems of environmental and pollution problems, corrosion of pipes and vessels, and significant energy required for the circulation and heating of water to form steam
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0052]In order to demonstrate the use and benefits of hydrogen stripping in accordance with the process of the present disclosure, a computer simulation employing Aspen HYSYS® V10.0 was conducted using a diesel stream containing 1.0 W % of sulfur as a feed to the hydrotreating zone to remove the sulfur.
[0053]Table 1 shows the mass balance and properties of the feedstream employed in the simulation included a diesel feed flow of 1.0 m3 / h and a hydrogen gas flow rate of 316 Sm3 / h providing a ratio of H2-to-oil for hydrotreating of 316 Sm3 / m3 of oil.
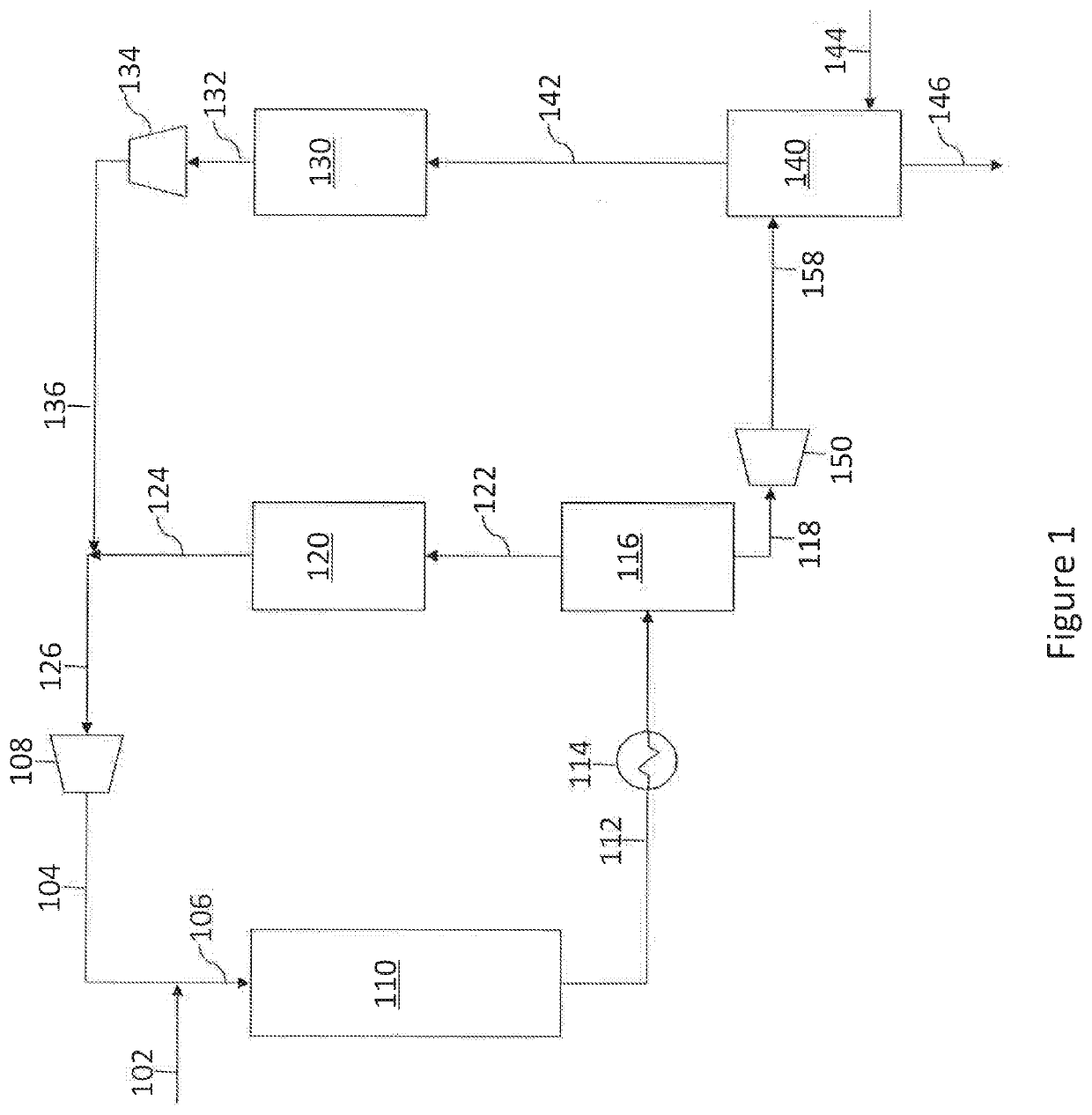
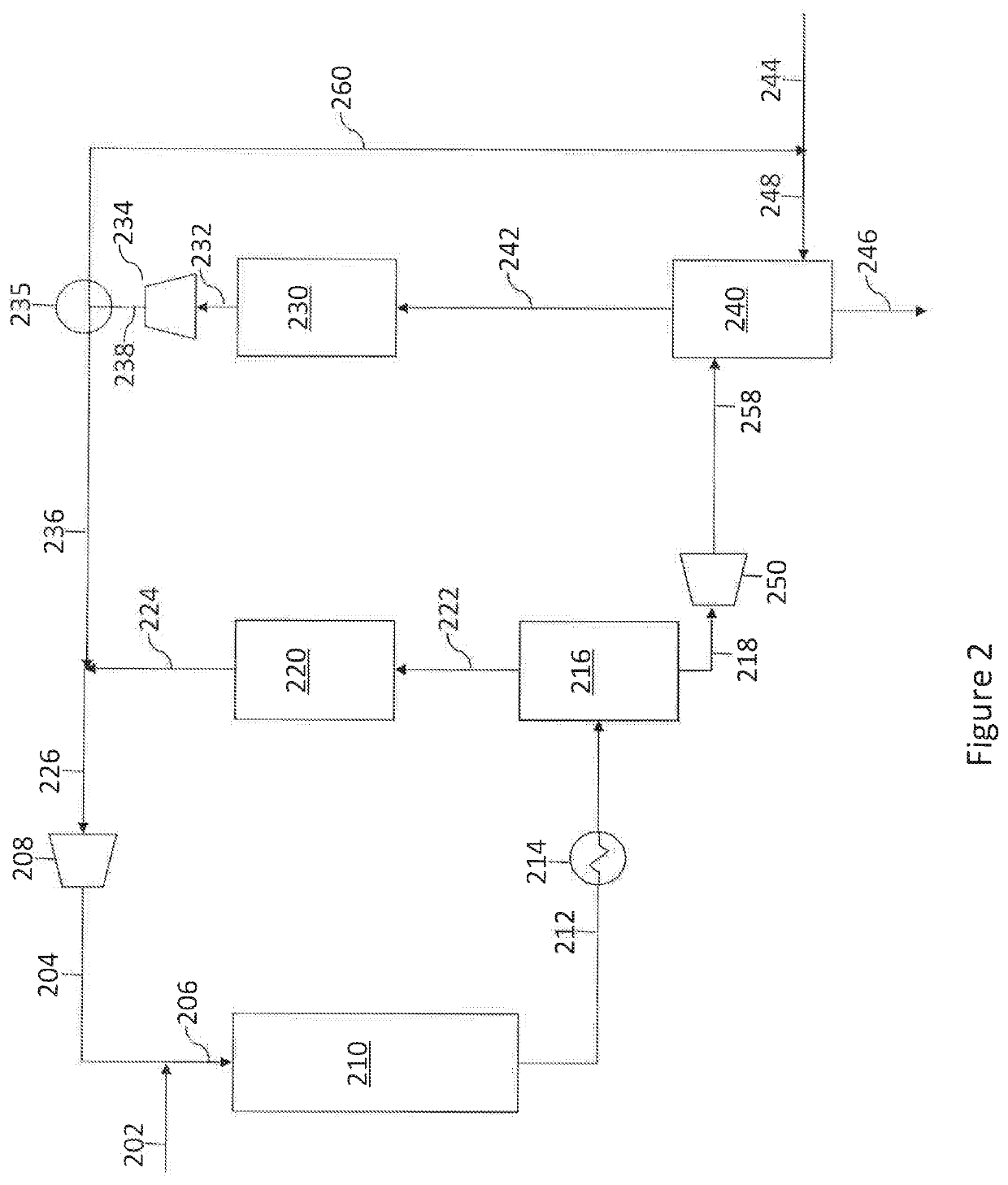
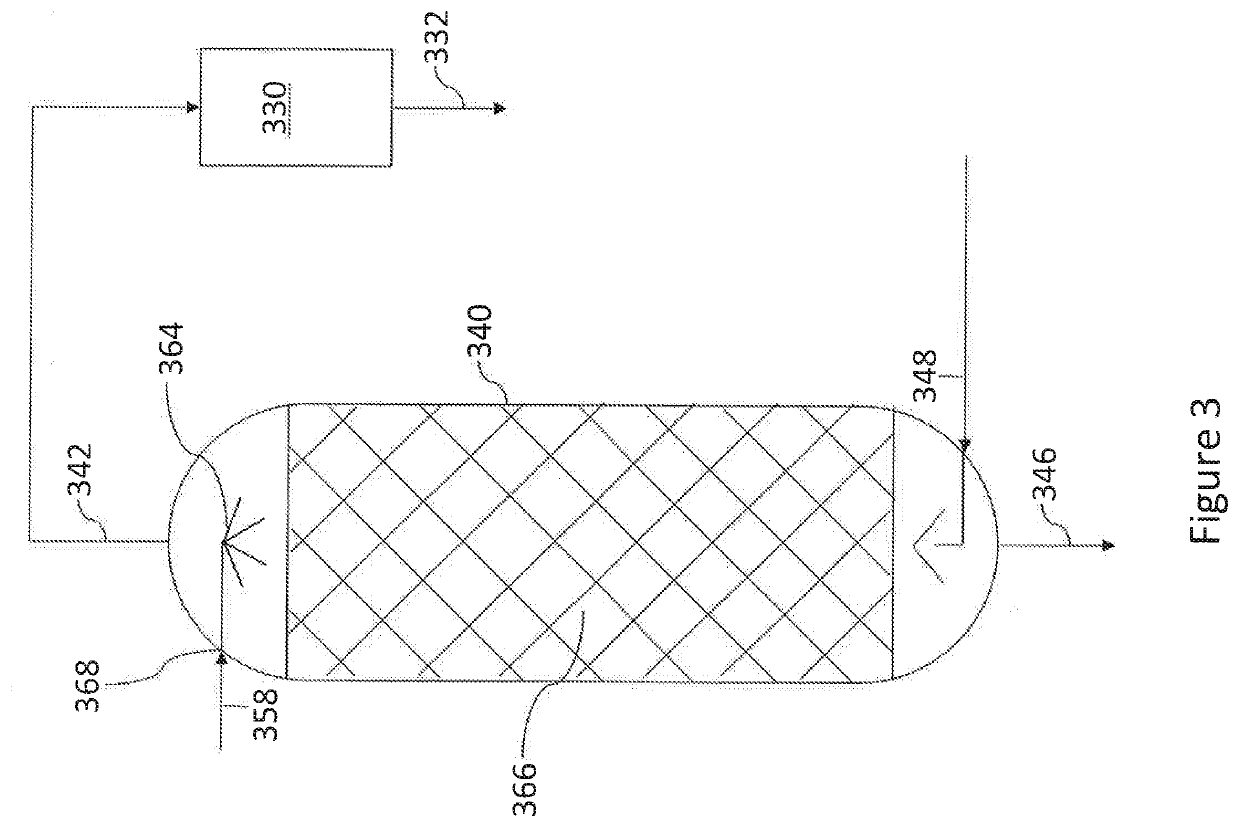
[0054]In the simulation, the hydrotreater and high-pressure separator units produced a stream, i.e., the cooled and low-pressure stream (158), that contains 2690 ppm of H2S. The effluent is introduced into the top of the stripper via a distribution device. Make-up hydrogen gas is injected into the bottom of the stripper via a conventional distribution manifold. The flow rate of make-up hydrogen stream (144) is determined by the consumption ...
example 2
[0055]In this Example, the ratio of make-up hydrogen flow-to-feed oil was varied from Example 1 in order to illustrate how the flow rate of H2 stripping gas affects the removal of dissolved H2S in the hydrotreated diesel product of the HYSYS simulation. The results are presented in Table 2. It can be seen that the lowest ratio of hydrogen stripping gas to liquid feed required to obtain a final product containing less than 1 ppm Wt of H2S is 15 Sm3 / m3 of oil.
TALBE 2Ratio of Flow of Make-up H2 to HydrotreatedLiquid Feed to Diesel H2Sstripper, Sm3 / m3content, ppmCaseof oilWtCase 151444.11Case 2 1027.49Case 3150.88Case 4200.063Case 5250.008Case 6300.001Case7353.07E−04Case 8408.42E−05Case 9452.68E−05Case 10509.59E−06
example 3
[0056]In this Example, Case 10 from Example 2, i.e., with a ratio of hydrogen stripping gas flow to liquid feed of 50 Sm3 / m3 was investigated to determine the impact of the number of theoretical plates required in order to obtain a final hydrotreated product containing less than about 1 ppm of dissolved H2S. As shown by the results in Table 3, the minimum number theoretical plates required is 4.
TABLE 3Number ofH2S Content inTheoretical Plates inHydrotreated Diesel,CaseStripping Columnppm WtCase 1232.88Case 234.01Case 340.49Case 450.06Case 560.007
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com