Cylindrical roller stent crimper apparatus with radiation shield
a technology of crimper and cylindrical roller, which is applied in the direction of prosthesis, manufacturing tools, blood vessels, etc., can solve the problems of stent and/or balloon catheter damage, stent reclosure or restnosis, and insufficient performance of these tools
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
second embodiment
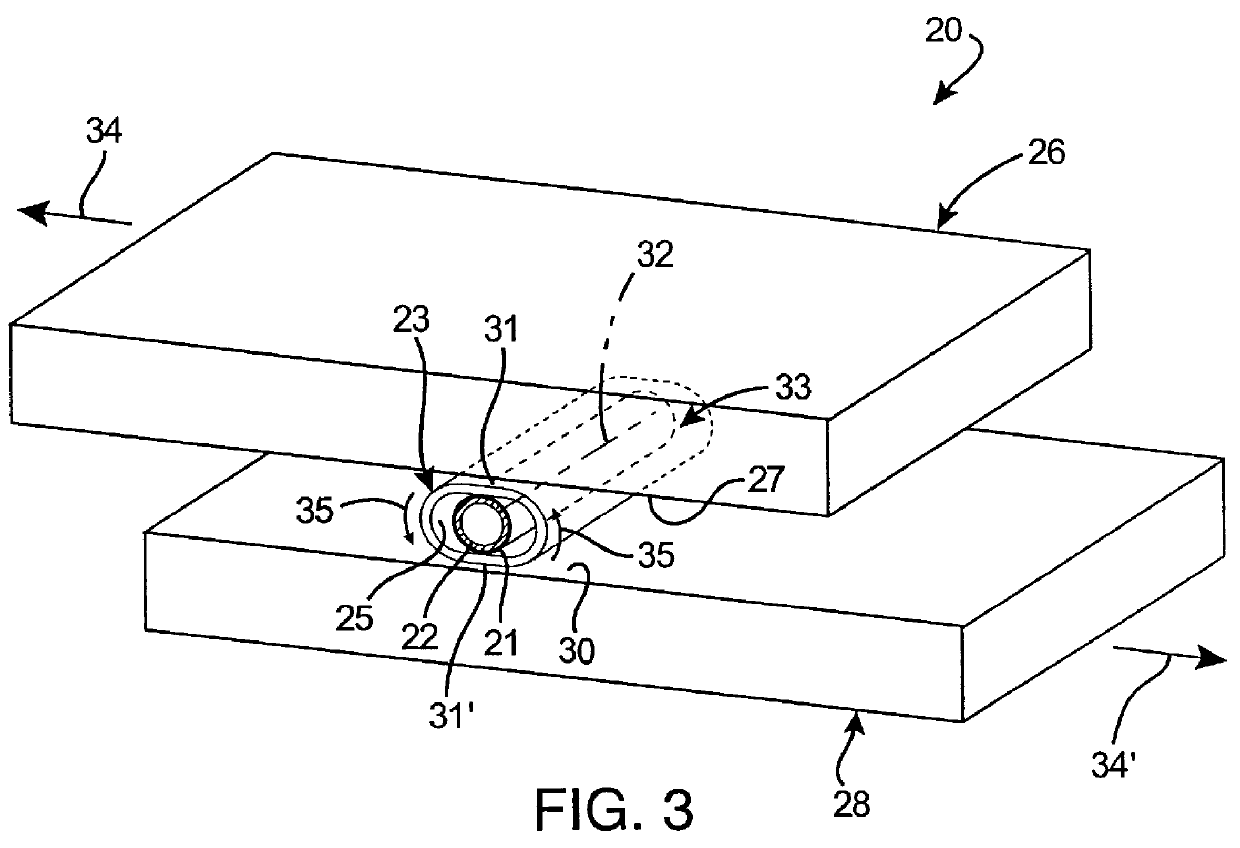
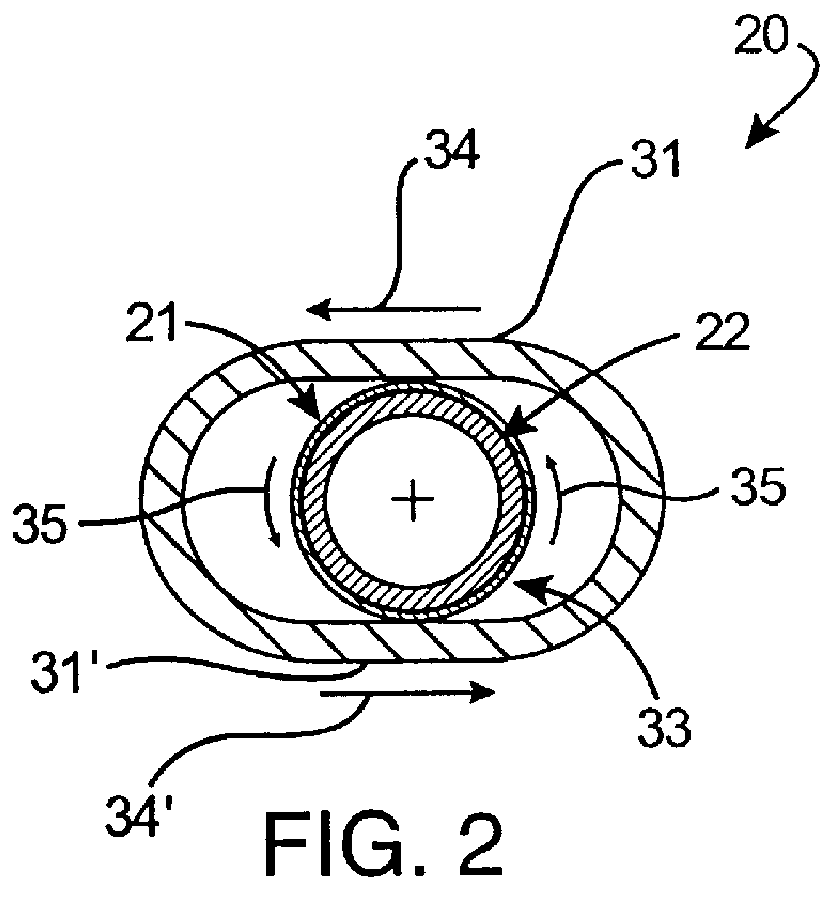
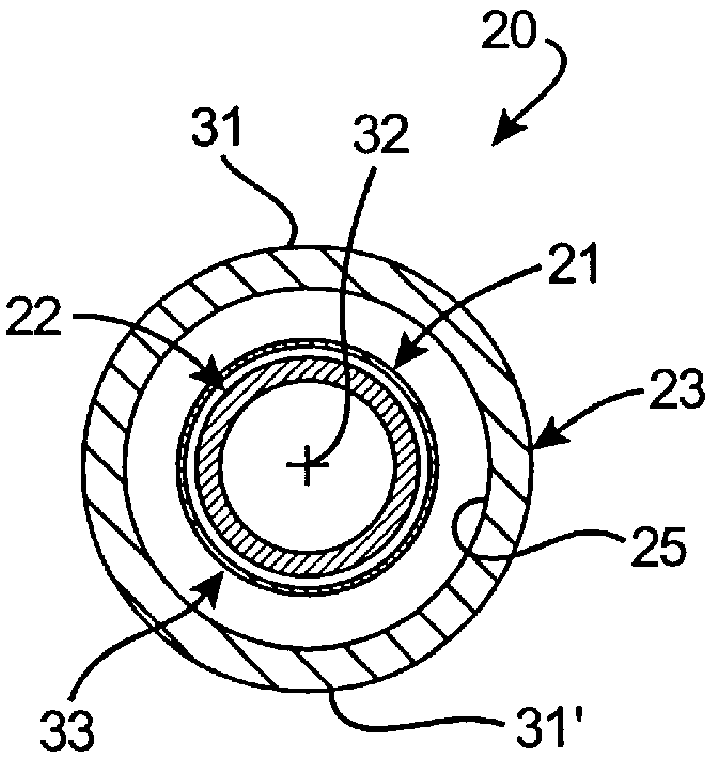
Referring now to FIGS. 4-5C, the stent loading apparatus 20 of the present invention is illustrated for loading a deformable stent 21 onto a deployment device 22. In this embodiment, the first member 26 is provided a crimper body, generally designated 36, having a curvilinear first compression region, preferably wall 27, defining a bore portion 37; and a spindle member 38 having a curvilinear second compression region, preferably wall 30, extending into the bore portion 37 adjacent the first compression wall 27. Collectively, these opposed first and second compression walls define an annular gap 40 between the rotating components where the crimp is to be performed. The spindle member 38 is rotatably coupled to the crimper body 36 for relative rotation of the first compression wall 27 and the second compression wall 30 between a first position (FIGS. 4 and 5A) and a second position (FIGS. 5B and 5C). In the first position, the first compression wall 27 and the second compression wall...
first embodiment
Accordingly, the stent 21 is caused to be radially compressed and simultaneously rolled about its longitudinal axis during the relative rotational movement between first compression wall 27 and second compression wall 30. Analogous to the first embodiment, the first member is provided by the crimper body 36 defining the first compression wall 27, while the second member is provided by the spindle member 38. During relative rotational movement between the crimper body 36 and the spindle member 38, the substantially cylindrical first compression wall 27 rotates relative the cylindrical second compression wall 30 in a manner compressing and rotating the elastic tube 23 therebetween from the first position (FIGS. 4 and 5A) to the second position (FIGS. 5B and 5C) to compressively crimp the stent assembly 33.
Briefly, while the application of the present invention is primarily described and illustrated in connection with the elastic tube embodiment, it will be appreciated that this tube m...
fourth embodiment
Turning now to FIGS. 9-11B, the stent loading of the present invention is illustrated having a planetary gear assembly, generally designated 68, which enables smooth and accurate rotation of the spindle member 38 relative the crimper body 36. This gear assembly 68 further facilitates rolling transport of the stent assembly, the catheter, the crimp tube and the radiation shield about the annular gap 40 at a substantially similar rate and distance, and in a longitudinal orientation between the first and second compression walls.
As shown in FIGS. 11A and 11B gear assembly 68 is configured to cooperate with the crimper body 36, the spindle member 38 and the deployment device 22 to provide rolling support for the stent assembly 33 between the first position (FIGS. 9, 10A and 11A) and the second position (FIGS. 10B and 11B). The planetary gear assembly 68 preferably includes a drive gear 70 fixedly coupled to the proximal end of crimp roller 28 through post portion 71. Positioned circumfe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Elasticity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com