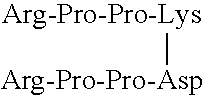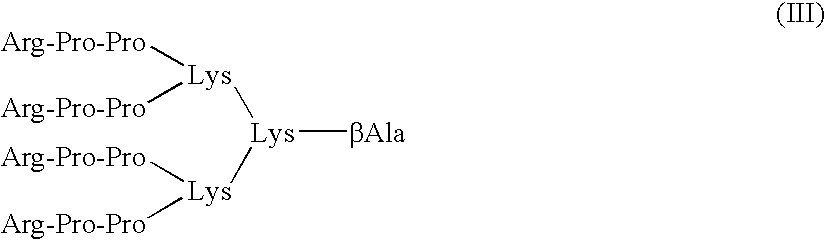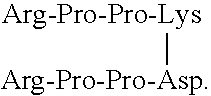Bradykinin analogs as selective inhibitors of cell activation
a thrombin-induced cell and analog technology, applied in the direction of peptide/protein ingredients, extracellular fluid disorder, peptide sources, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the safety of patients, high reocclusion rate, and high complication rate, and achieve the effect of inhibiting thrombin-induced platelet and preventing platelet aggregation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
In Vitro Functional Assays
[0101]Functional assays are used to evaluate the relative inhibitory efficacies of the methods and compounds according to the invention. In these assays, native BK (SEQ ID NO:5), the BK fragment Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe (SEQ ID NO:7), or another BK analog, may be used as a positive control peptide.
A. Inhibition of Platelet Aggregation
[0102]For human platelet aggregation studies, 50 ml human blood was collected into a syringe containing 5 ml of 0.013 M sodium citrate. The anticoagulated blood was centrifuged at 180 xg for 10 minutes at room temperature and the platelet-rich plasma was the supernatant. Platelet aggregation studies in platelet-rich plasma were performed in the cuvette of an aggregometer using γ-thrombin (Haematologic Technologies, Essex Junction, Vt.). After standardization of the aggregometer, the threshold dose of γ-thrombin, defined as the minimal concentration that will induce full platelet aggregation, was ascertained for each preparation of p...
example 2
Binding Assays
[0120]Binding assays are used to show protein-protein interactions, and can be used to determine which domains of proteins participate in the binding and to ascertain the relative binding affinity of various domains. Binding assays are also used to screen large numbers of peptides, such as those in a combinatorial library. It is particularly useful to screen peptides for the ability to bind to the NAT12 peptide or to the thrombin receptor. Peptides that show activity in one or more of the binding assays are also tested in one or more of the in vitro functional assays, such as those described in Example 1. A combination of binding and functional assays can be used to identify compounds that selectively inhibit thrombin-induced platelet and other cell activation.
A. Assay for Binding to the NAT12 Peptide
[0121]Peptides from a combinatorial library are linked to microtiter plates and the wells are blocked with 1% BSA. Biotinylated-NAT12 is incubated with the microtiter plat...
example 3
In Vivo Clearance and Function: Correlation With In Vitro Results
[0123]Clearance studies were performed in New Zealand white rabbits weighing between 2.0 and 2.5 kg. Rabbits were premedicated according to the method of Michelson et al., J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 20, 547 (1988) with 10 mg / kg 1 M xylazine and 10 mg / kg 1 M ketamine. After tracheostomy, intubation, and positive pressure ventilation done with room air (Harvard instruments), stage III surgical anesthesia was maintained with 20 mg / ml of intravenous pentobarbital. A carotid artery and a jugular vein were then exposed. A catheter was inserted into the exposed carotid artery for withdrawal of blood samples and monitoring the animal's blood pressure (Gould, Inc., Cardiovascular Products, Oxnard. Calif.). In a similar manner, a catheter was inserted into the exposed jugular vein for administering the anesthetic and BK analog.
[0124]A single intravenous infusion of BK analog was injected. The amount of BK analog injected was calculat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com