Method of adjusting axial direction of monitoring apparatus
a technology of axial direction and monitoring apparatus, which is applied in the direction of distance measurement, instruments, and using reradiation, etc., can solve the problems of large error between the measured position of the monitoring apparatus and the actual position, the relative positional relationship between the radar and the camera may become inappropriate, and the error accumulation between the sensors, etc., to achieve the effect of mass production of vehicles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
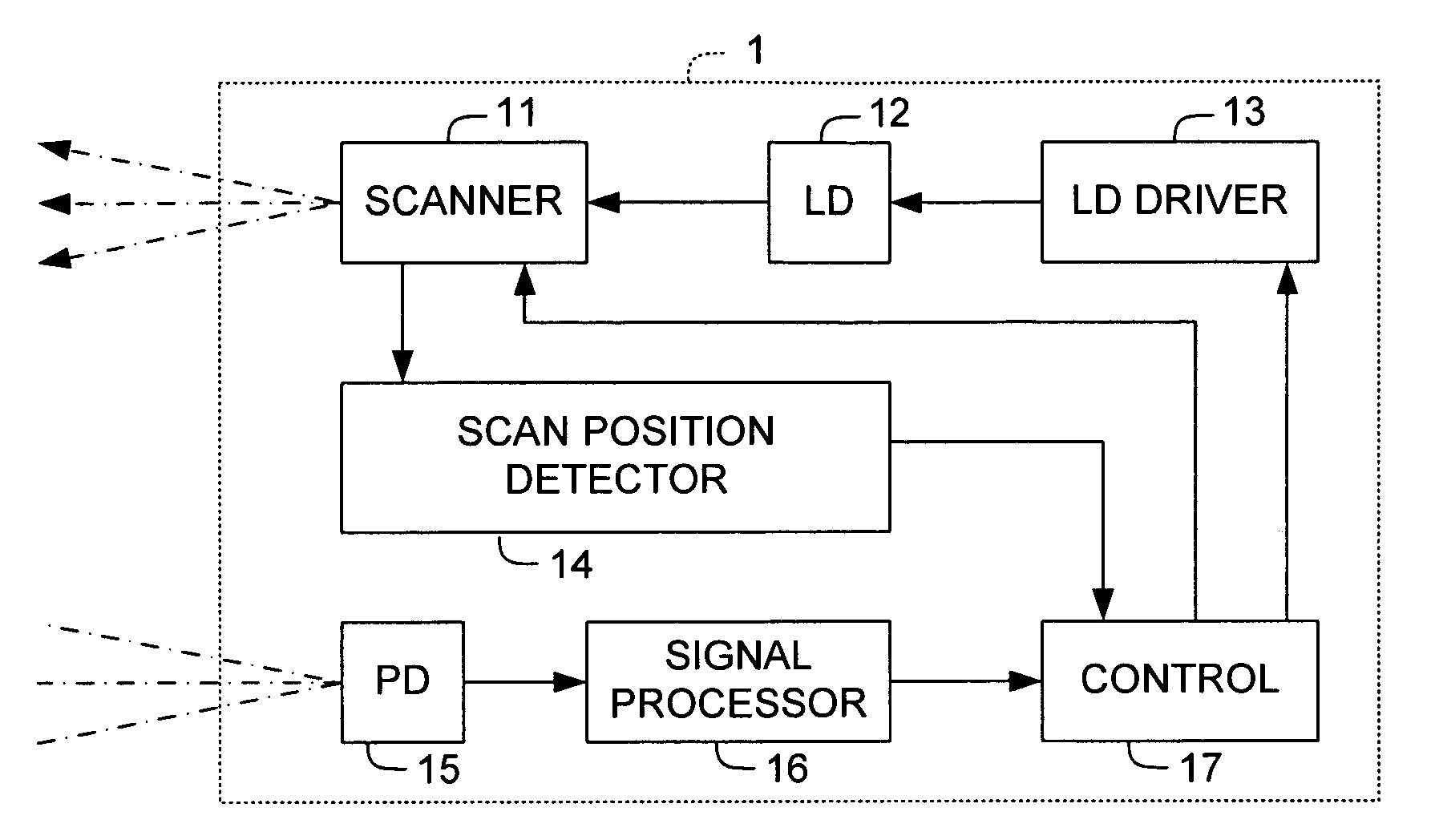
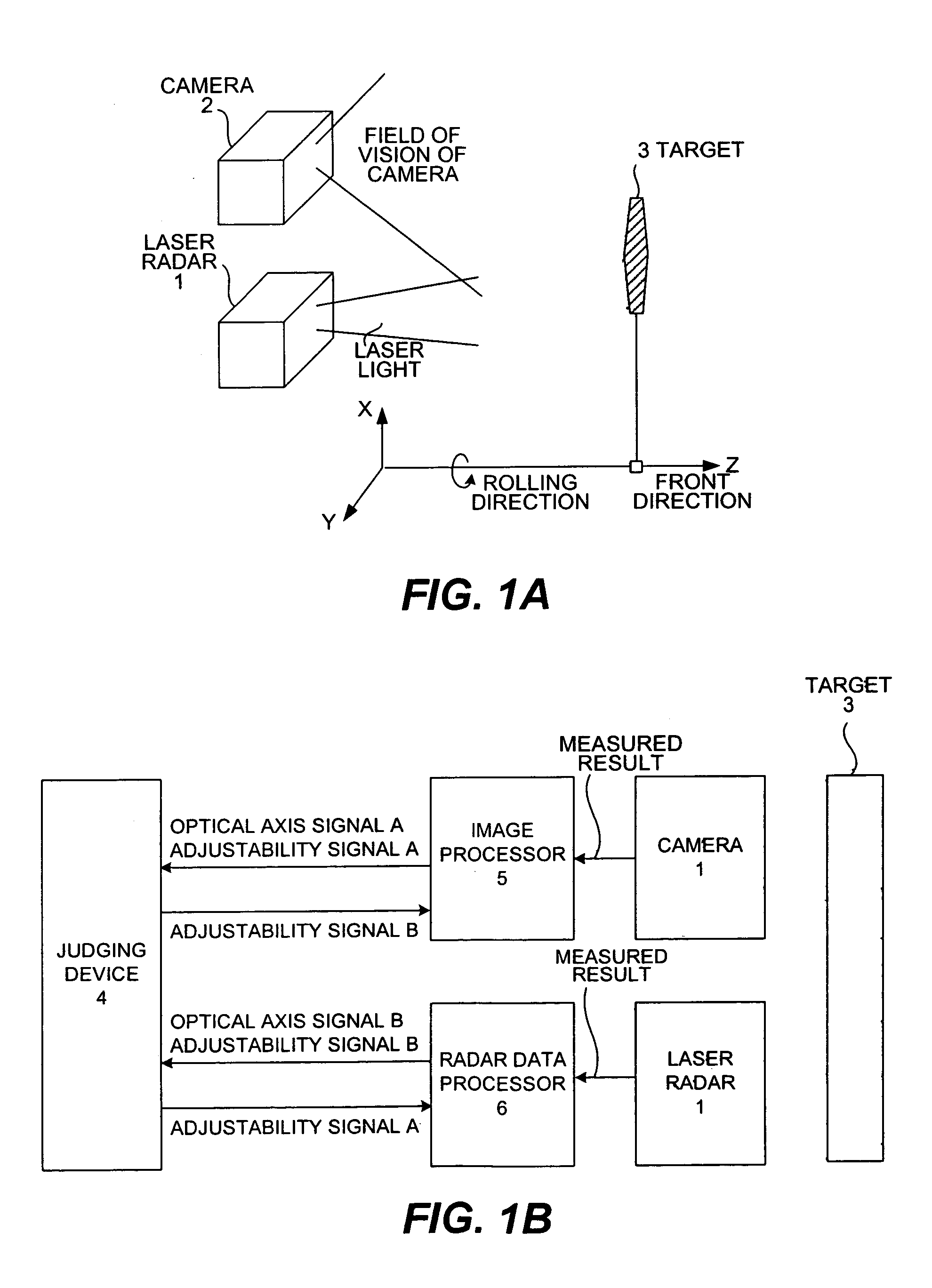
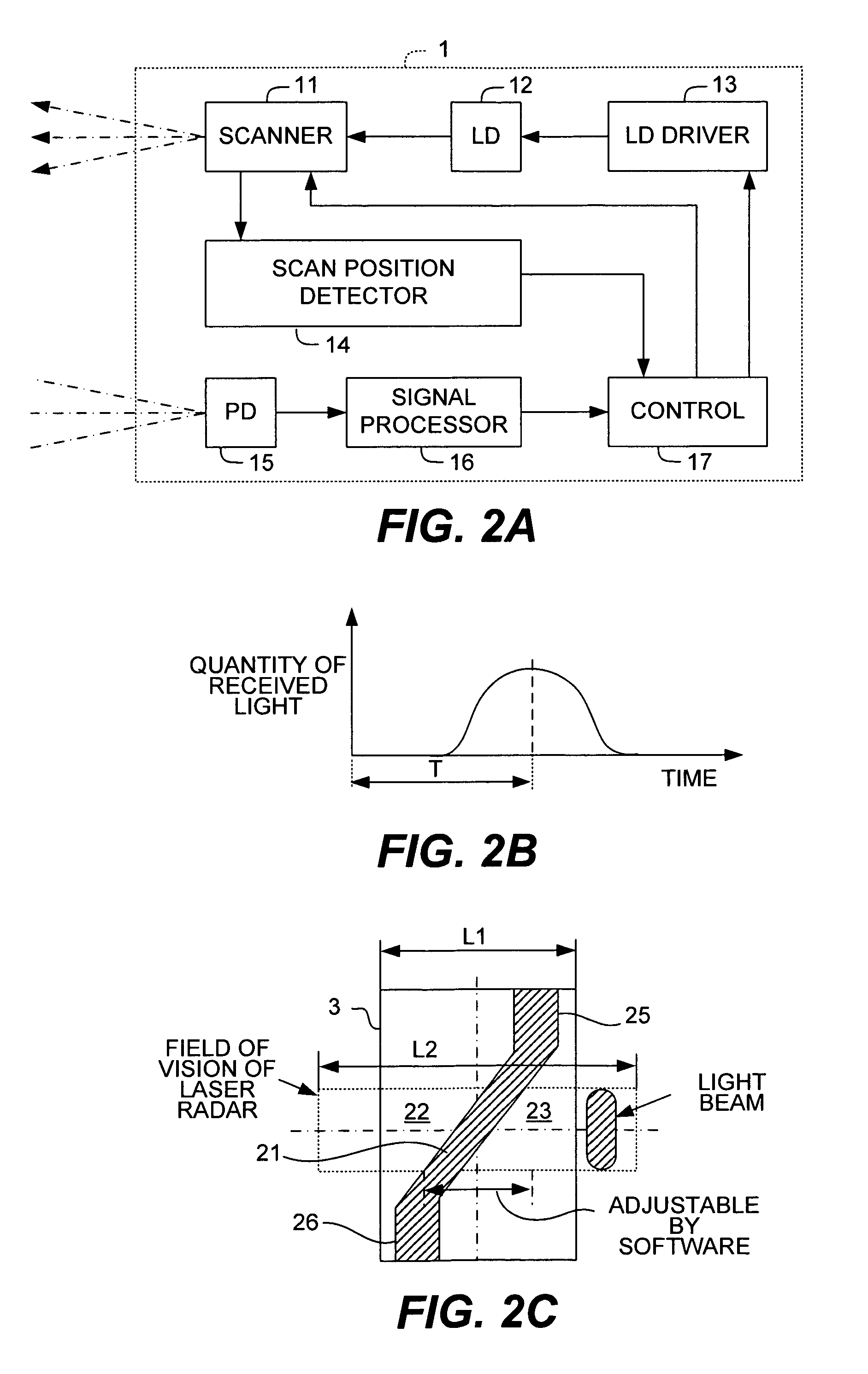
[0053]FIGS. 1A, 1B, 2A, 2B and 2C show the structure of a system including a monitoring apparatus provided with a laser radar and a camera to be mounted to a vehicle on which a method embodying this invention may be carried out, FIG. 1A showing its main structure, FIG. 1B being a block diagram of the control system of the monitoring apparatus, FIG. 2A being a block diagram of the laser radar, FIG. 2B being a drawing for explaining the principle of measurement by the laser radar, and FIG. 2C being a front view of a target used for the adjustment.
[0054]FIG. 1A shows a laser radar (hereinafter referred to simply as the radar) 1 and a camera 2 both mounted to a vehicle. The radar 1 is of a type for scanning both in the horizontal and vertical directions (respectively the standard and perpendicular directions). Numeral 3 indicates a target used for the adjustment. X, Y and Z in FIG. 1A indicates a coordinate system fixed to the vehicle, the X-axis being in the vertical direction, the Y-a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com