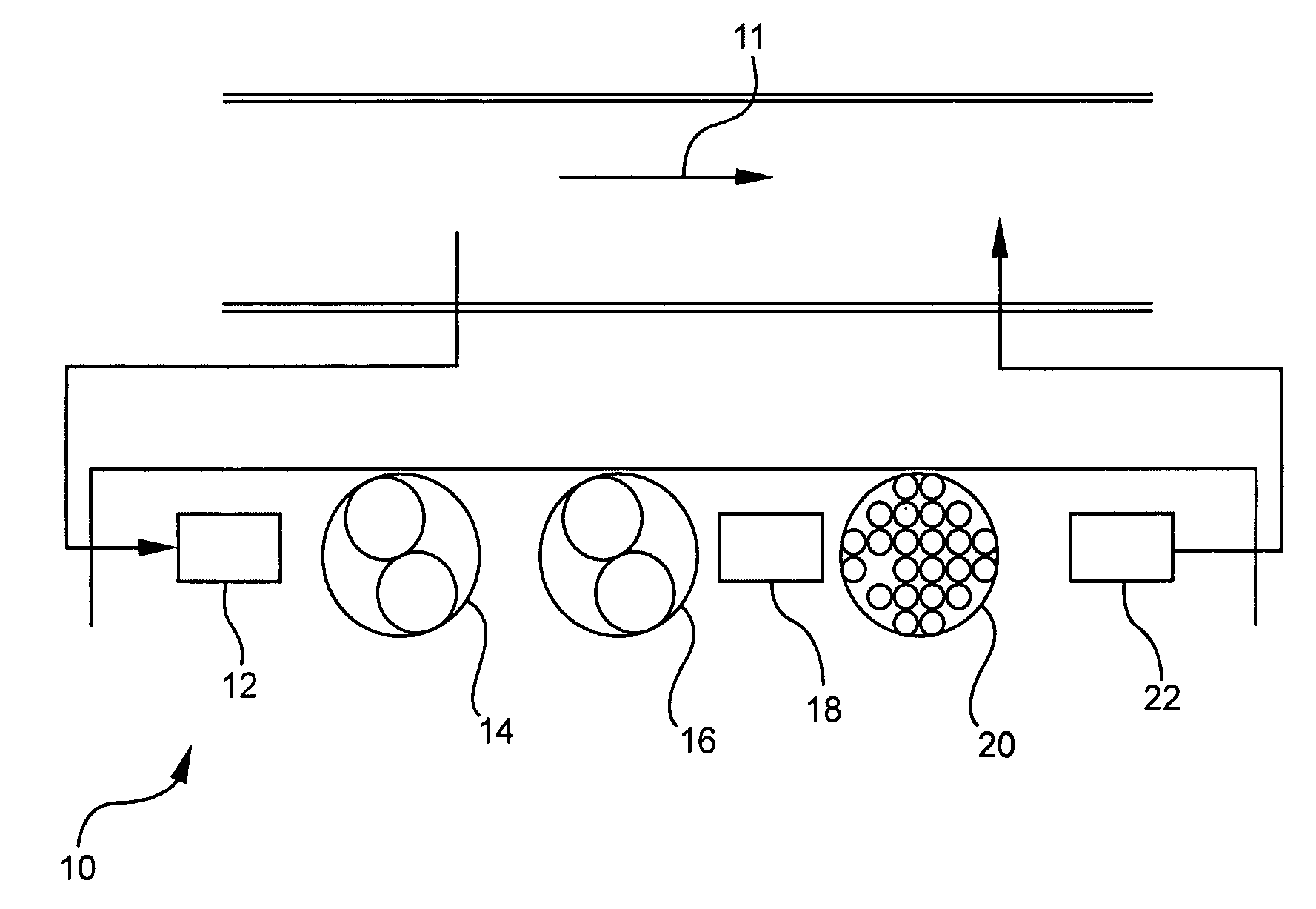
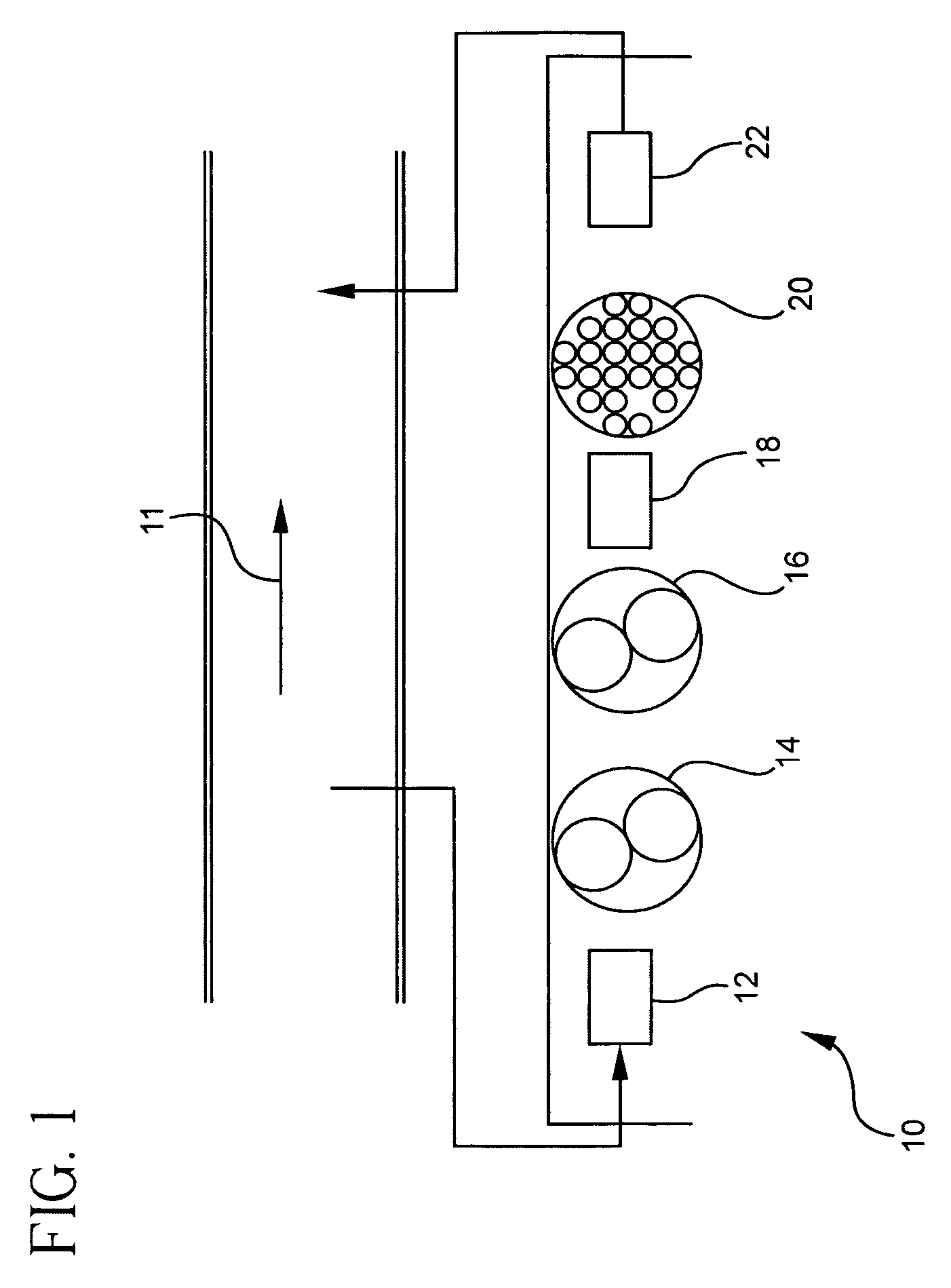
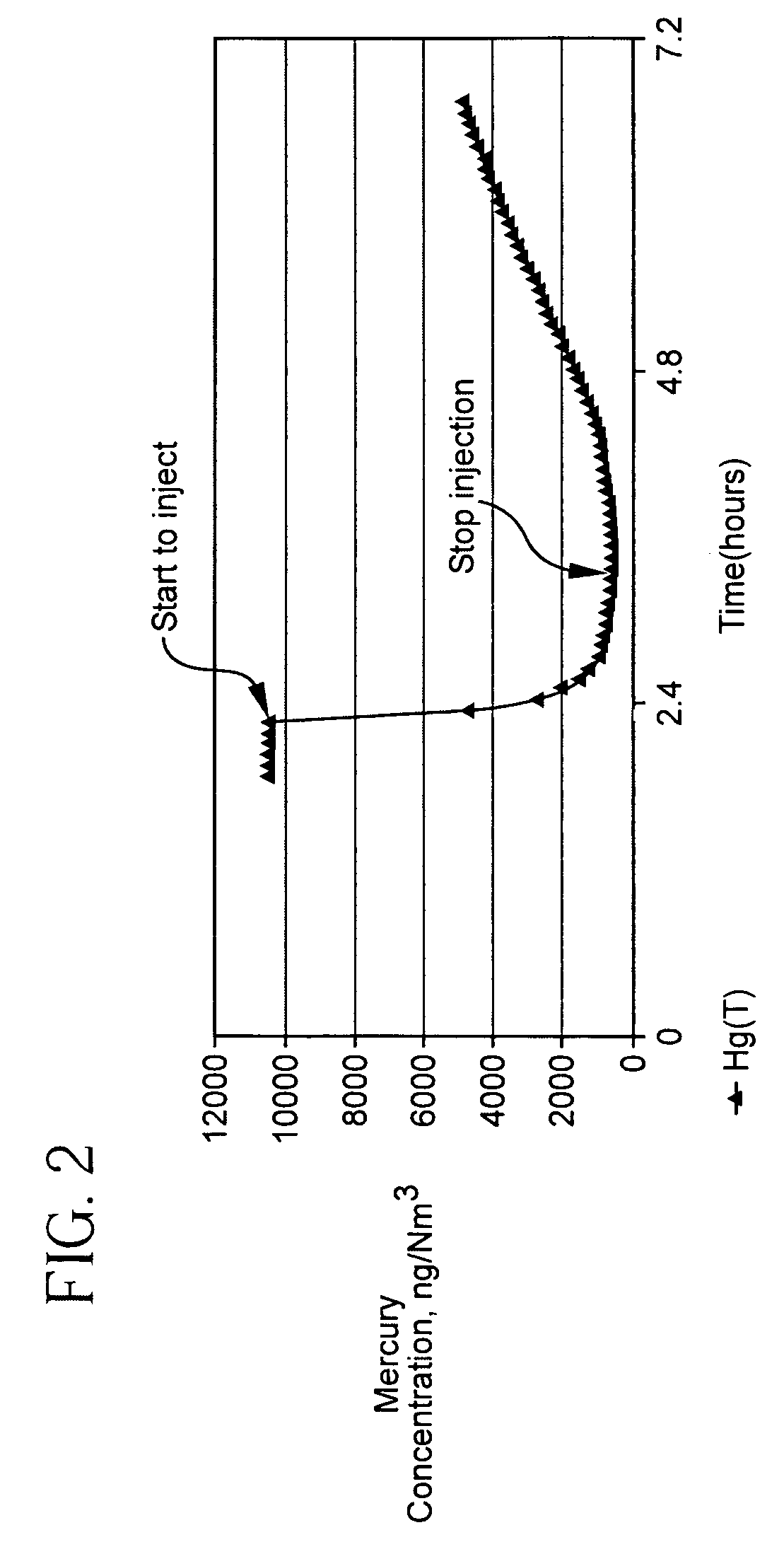
Pollutant emission control sorbents and methods of manufacture
a technology of sorbents and pollutants, applied in the field of pollution emission control sorbents, can solve the problems of reducing the performance of activated carbon, introducing significantly higher costs, and not being as effective with elemental mercury, and achieving the effect of reducing the particle size of particles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of CuS / Fly Ash Sorbent (3% Cu) via Reactive Grinding
[0036]First, 0.29 g CuCl2.2H2O, 0.87 g CuSO4.5H2O and 10 g fly ash were ground together, ensuring that the copper salts are fully mixed with fly ash. Then, 1.25 g Na2S.9H2O was added to the above mixture and the mixture was ground again. The mixture became moist and turned dark as heat was released as a result of Reaction 1. Grinding was stopped when there was no more physical change. The sample was then dried at 110° C. until the free moisture was completely removed. The sample was then ground to pass through a 325 mesh sieve.
example 2
Preparation of CuS / Fly Ash Sorbent (1% Cu) via Incipient Wetness
[0037]First, 0.097 g CuCl2.2H2O, 0.29 g CuSO4.5H2O and 10 g fly ash were ground together, ensuring that the copper salts are fully mixed with the fly ash. Then, 0.416 g Na2S.9H2O was mixed in 1.60 g DI-H2O to provide a solution. The solution was added to the solid mixture drop-wise while stirring the solid vigorously. The mixture moistened and turned dark as heat was released as a result of Reaction 1. Mixing was stopped when there was no more physical change. The sample was dried at 110° C. until the free moisture was completely removed. The dried sample was ground to pass through a 325 mesh sieve.
example 3
Preparation of CuS / Bentonite Sorbent (5% Cu) via Reactive Grinding
[0038]First, 0.49 g CuCl2.2H2O, 1.45 g CuSO4.5H2O and 10 g bentonite were mixed together to ensure that the copper salts were fully mixed with the clay. Then, 2.08 g Na2S.9H2O was added to the above mixture, and the mixture was ground again. The mixture moistened and turned dark as heat was released as a result of Reaction 1. Grinding was stopped when there was no more physical change. The sample was dried at 110° C. until the free moisture was completely removed. The dried sample was ground to pass through a 325 mesh sieve.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| weight percent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight percent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com