Stacked pixel for high resolution CMOS image sensor
a stacked, image sensor technology, applied in the field of solid-state image sensors, can solve the problems of sacrificing resolution, reducing the resolution of stacked pixels, and reducing the number of transistors in each pixel, so as to achieve the effect of reducing the loss of light sensitivity, reducing the loss of resolution, and simplifying and more practical solutions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
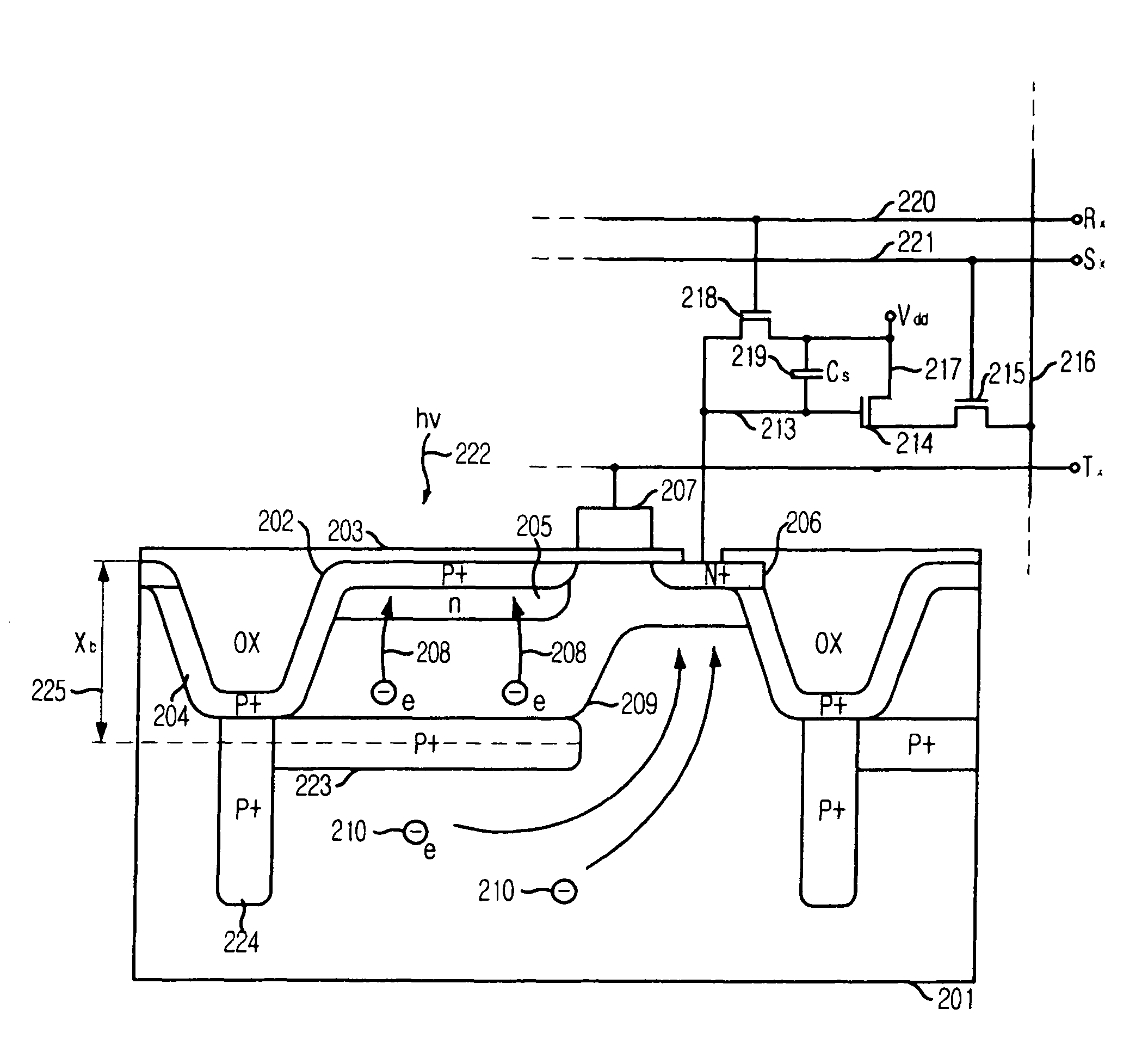
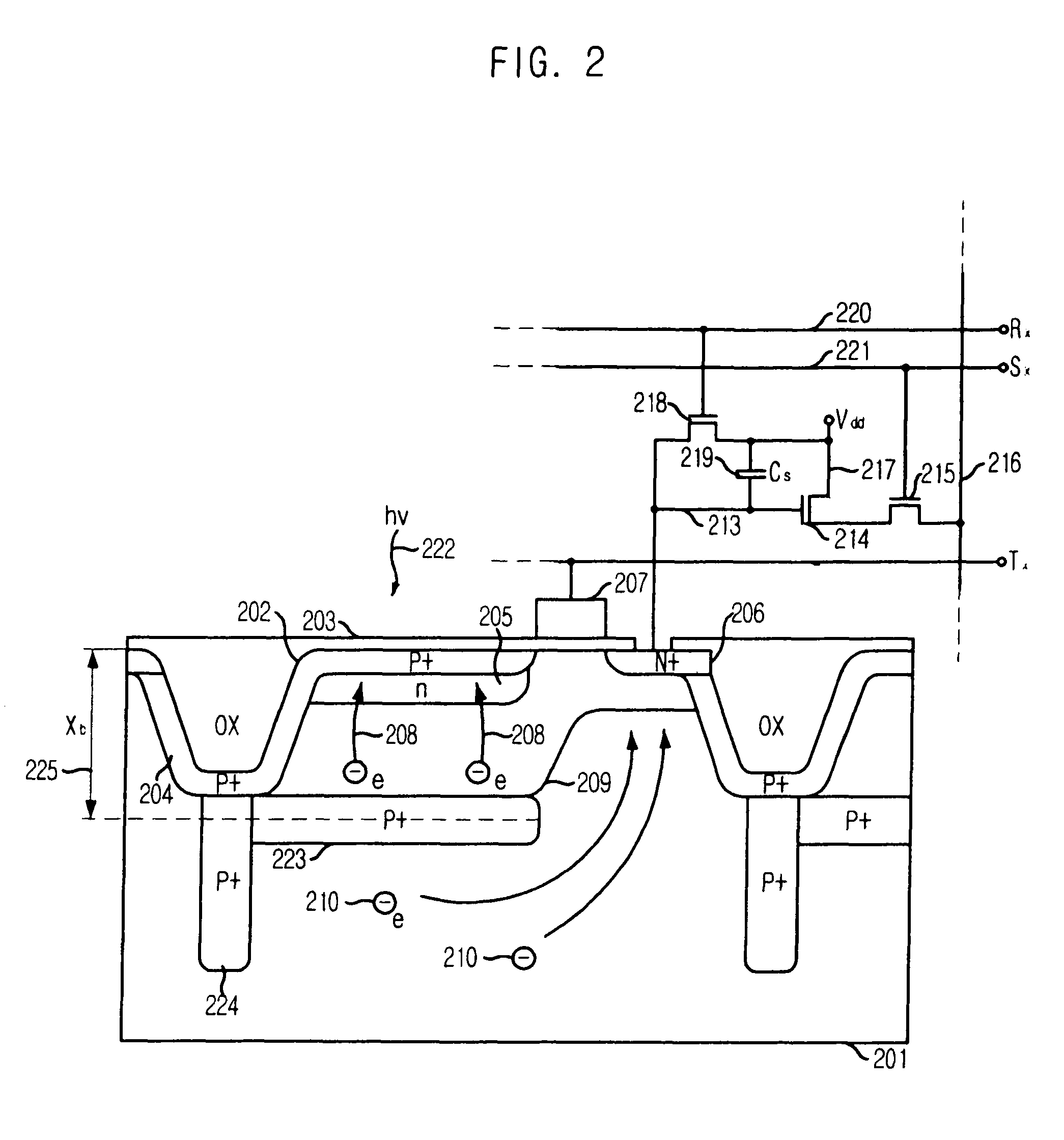
[0027]FIG. 2 is a simplified cross-sectional view illustrating a pixel with a stacked photo-site and a potential barrier and readout circuits associated with the pixel in accordance with the present invention.
[0028]According to the first embodiment of the present invention, the pixel has an ability to separate charge according to the depth of charge generation and thus sense color. A substrate 201 has a shallow STI region 202, obtained by forming a trench through etching the substrate 201 to a certain depth and filling the trench with a silicon dioxide layer 203. The silicon dioxide layer 203 also covers the entire surface of the pixel. Herein, the substrate 201 is a p-type silicon substrate. A shallow p+-type doped region 204 passivates the walls and the bottom of the STI region 202 as well as the surface of the pixel to minimize a dark current generation. However, in this pixel, a p+-type doped barrier 223 is placed into the pixel at a depth Xb 225. This p+-type doped barrier 223 ...
second embodiment
[0034]There are many other combinations of the pinned photodiode arrangements and charge storage wells that can be used with the pixel according to the present invention. For the simplicity of description one such possibility and another embodiment of the present invention is shown only in a simplified circuit diagram form in FIG. 4.
[0035]FIG. 4 is a simplified circuit diagram illustrating a stacked pixel where charge from a shallow depleted region is stored in a pinned photodiode 401 and charge from a deep undepleted region is directed to another pinned photodiode 402. The pinned photodiodes 401 and 402 interface with a common FD charge detection node 408 via respective charge transfer gates 403 and 404. The rest of the circuit is the same as in the first and second embodiments where transistors 405, 406 and 407 are a SF transistor 405, an address transistor and a reset transistor, respectively. Control signals are supplied to the pixel via a reset gate bus Rx 410, an address gate ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com