Human monoclonal antibody against Hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HBVSAG)
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
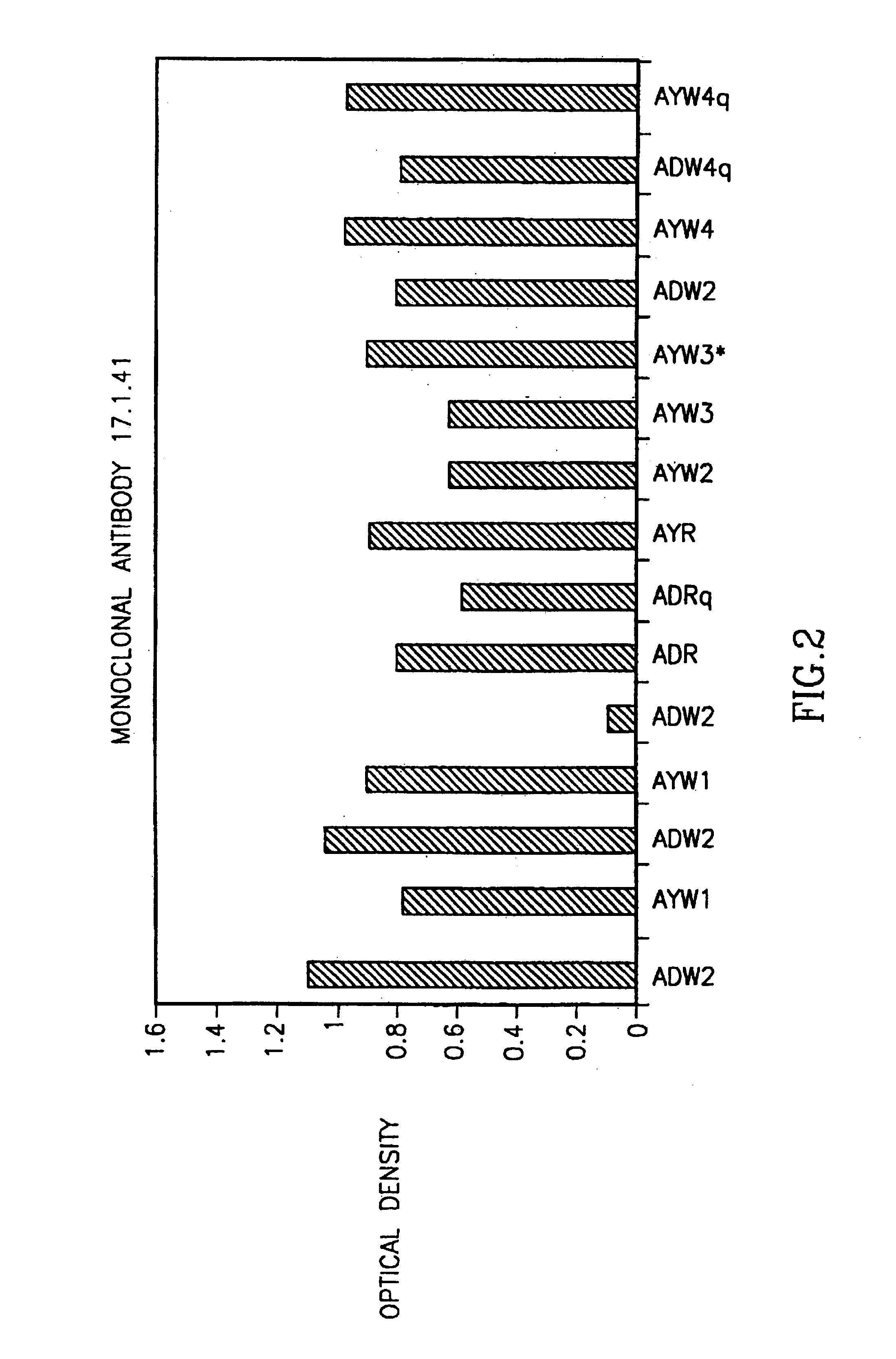
[0050]Human peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL) from donors positive for anti HBVs antibodies were obtained and activated in vitro with PWM as described above. The cells were then fused with a human mouse heteromyeloto form hybridoma cell lines. One stable hybridoma clone secreting specific human anti HBVsAg designated 17.1.41 was characterized. The antibodies secreted by the above clone were purified on a protein A column as well as on an anti human Ig-agarose column and were found to be of the IgG1 Vκ type. The affinity constant of the antibodies to HBVsAg was 1.34×10−9. Specificity was tested by competitive inhibition assay using HBV surface antigen of the ad-ay (1:1).
example 2
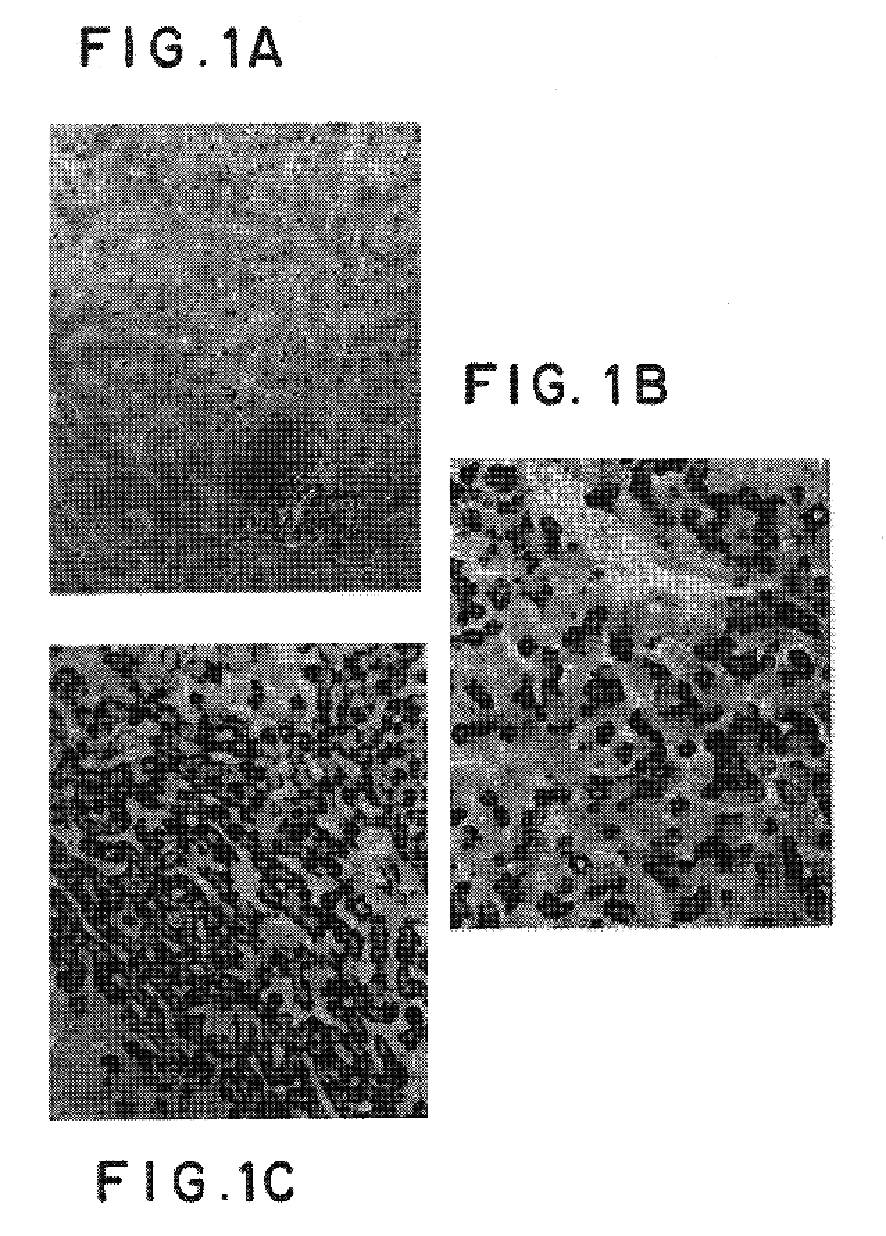
[0051]The 17.1.41 antibodies were used for staining human liver fragments as described above. As seen in FIG. 1, the 17.1.41 antibodies were able to detect HBV particles present in the infected liver fragments.
[0052]The gene encoding the variable region of Ab 17.1.41 was isolated, fully sequenced, and its subgroups and CDRs were determined.
[0053]The antibody has a fully human Ig gene sequence as determined by alignment to Genebank sequences and Kabat protein sequences. FIG. 8 shows the nucleotide sequence of the cDNA encoding the light chain of the variable region of Ab 17.1.41 and its corresponding amino acid sequence (Sequence identification nos. I and 3). FIG. 9 shows the nucleotide sequence of the cDNA encoding the heavy chain of the variable region of Ab17.1.41 and its corresponding amino acid sequence (Sequence identification nos. 2 and 4).
[0054]The sequencing data revealed that the variable region of Ab 17.1.41 consists of the subgroups VH3, JH6, VK2 and JK2.
[0055]HBV genomes...
example 3
[0056]The biological activity of Ab 17.1.41 was characterized using the following HBV animal model: a mouse was treated so as to allow the stable engraftment of human liver fragments. The treatment included intensive irradiation followed by transplantation of scid (severe combined immunodeficient) mice bone marrow. Viral infection of human liver fragments was performed ex-vivo using HBV positive human serum (EP 699 235).
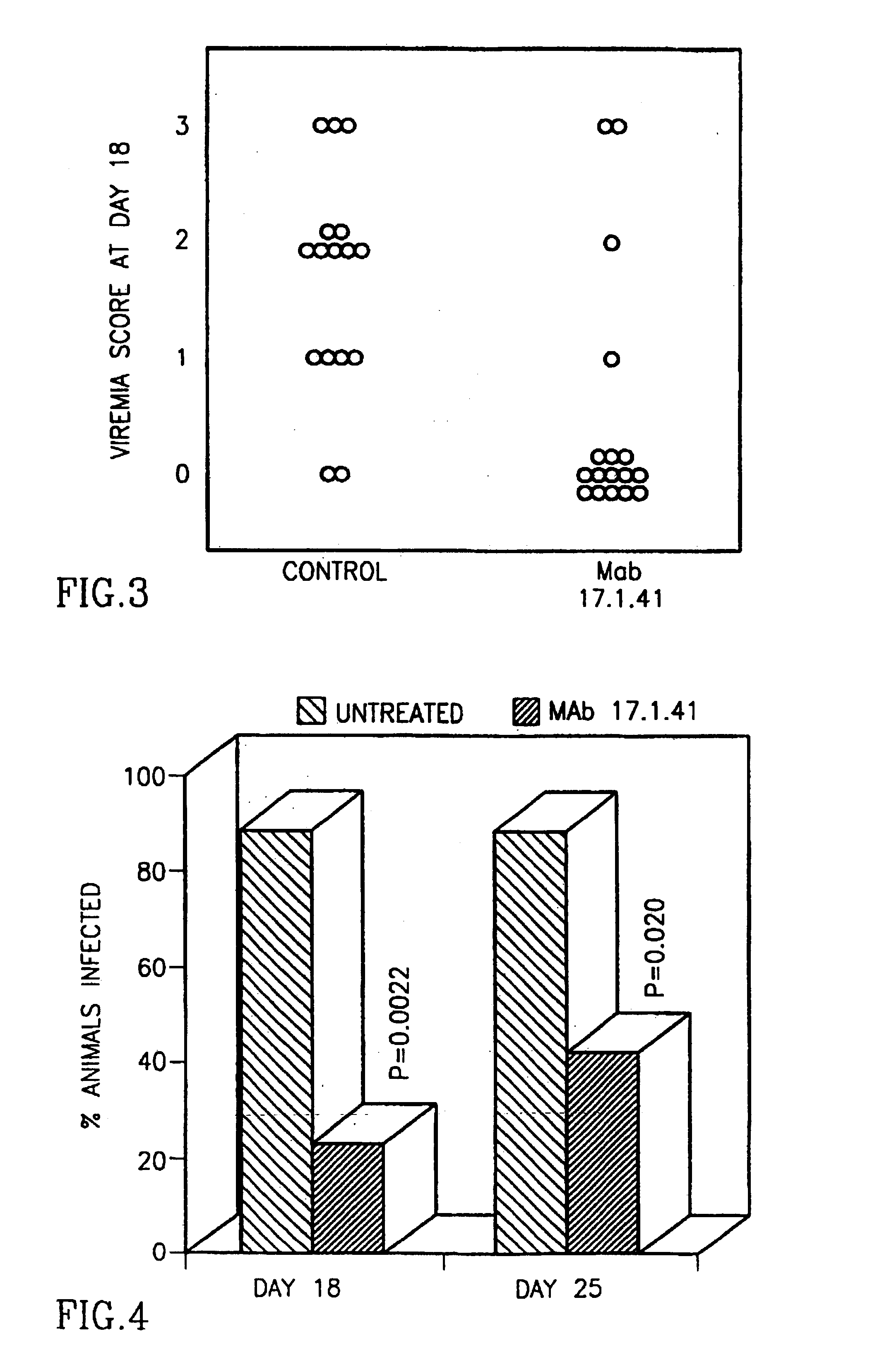
[0057]The animal model was used in three different modes representing various potential uses of the antibodies: treatment mode, combined prophylaxis / inhibition mode and combined inhibition / treatment.[0058]1. Treatment mode—This model demonstrates the ability to use the antibody to treat chronic HBV infection. Mice were transplanted with HBV infected human liver fragments. The mice were treated with Ab 17.1.41 at days 16, and 17 post liver transplantation. HBV DNA was tested on days 18 and 25. The number of HBV DNA copies (the viral load) in mouse sera was determined ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com