Wireless receiving microelectronic mechanical microwave power sensor and manufacturing method therefor
A micro-electromechanical and microwave power technology, applied in the direction of electromagnetic field characteristics, can solve the problems that microwave power cannot be directly received, and achieve the effects of widening the microwave measurement frequency band, reducing return loss, and realizing impedance matching
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] specific implementation plan
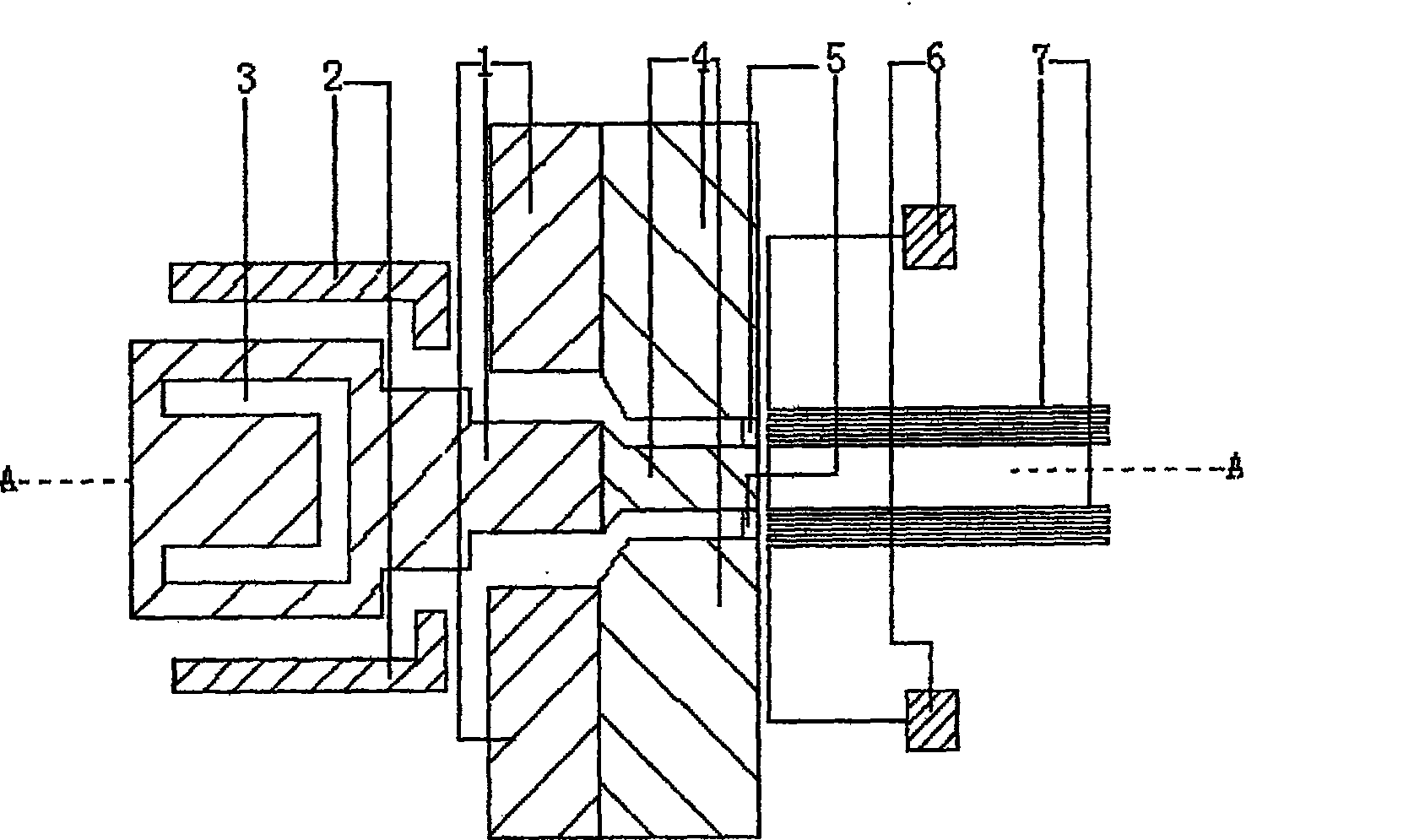
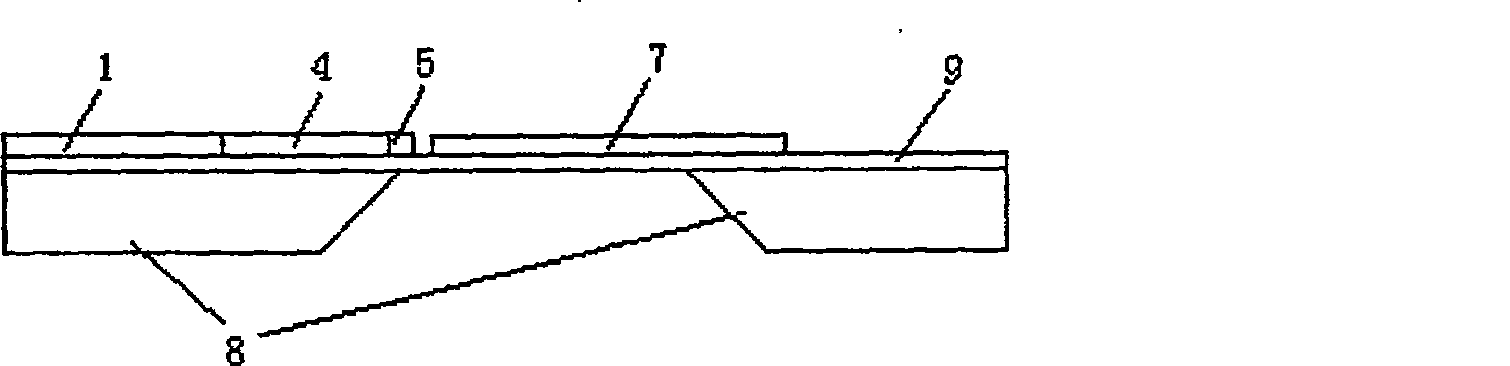
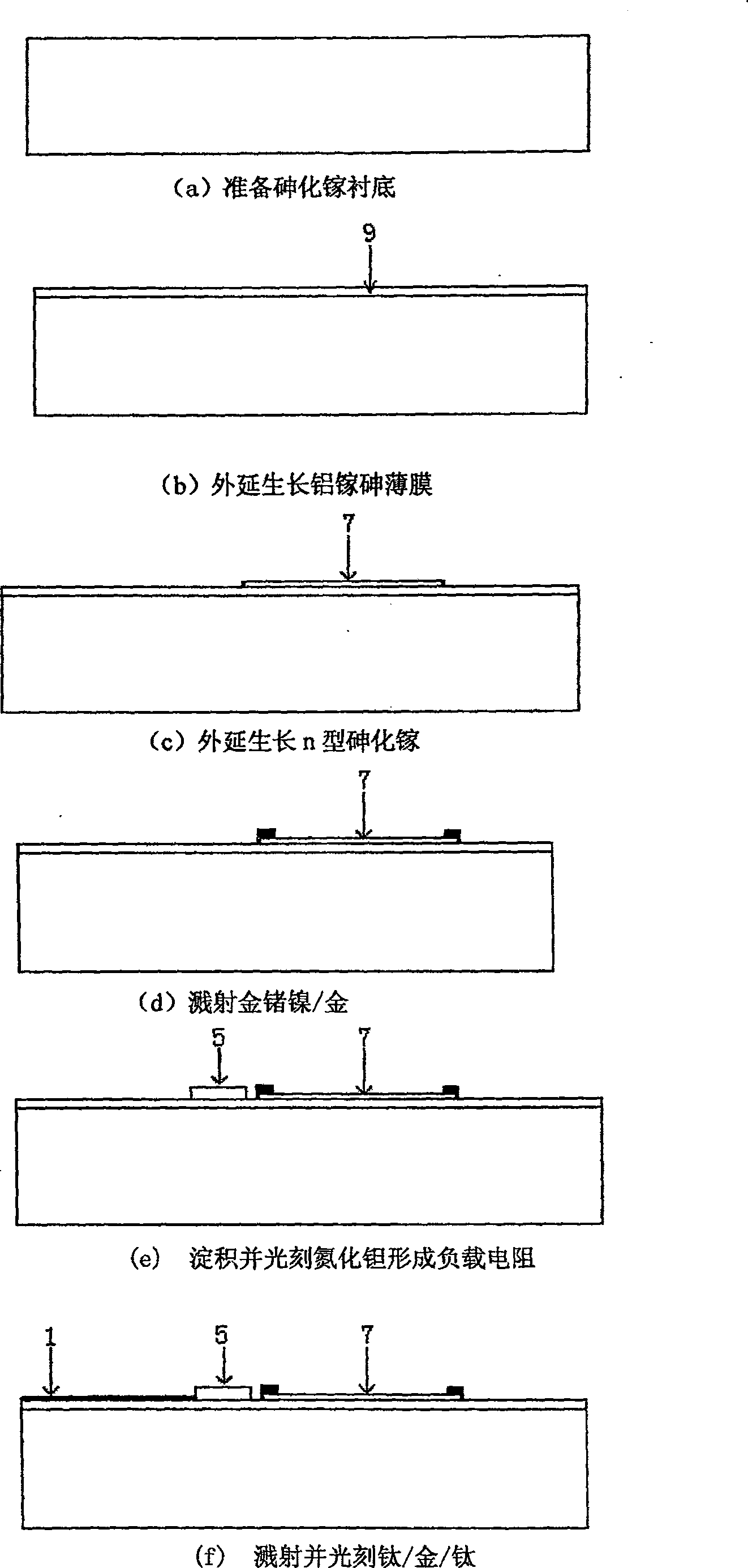
[0032] The sensor uses gallium arsenide as the substrate 8, on the gallium arsenide substrate 8 there is a layer of AlGaAs thin film 9, on the AlGaAs thin film 9 there is a layer of coplanar waveguide antenna 1, and a section of the antenna is etched away The U-shaped slot 3 has a parasitic element patch 2 on both sides of the antenna, the end of the coplanar waveguide antenna 1 is connected to the coplanar waveguide transmission line 4, and there are two parallel load resistors at the end of the coplanar waveguide transmission line 4, and the load resistor 5 The outer side of the thermopile is correspondingly provided with a thermopile 7, and the two ends of the thermopile 7 are connected to the two pressure welding blocks 6 through wires. The present invention receives the microwave signal from the outside through the special structure coplanar waveguide antenna at the front end, and then transmits the microwave signal to the terminal th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com