A ballasting resistor structure of microwave power transistor dynamic emitter electrode
A microwave power and ballast resistance technology, which is applied in the manufacture of transistors, semiconductor/solid-state devices, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient thermal coupling of ballast resistance, loss of microwave power gain of devices, and limiting additional ballast effect. Meet the requirements of microwave performance and reliability, reduce parasitic capacitance and chip area, and increase the effect of additional ballast effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
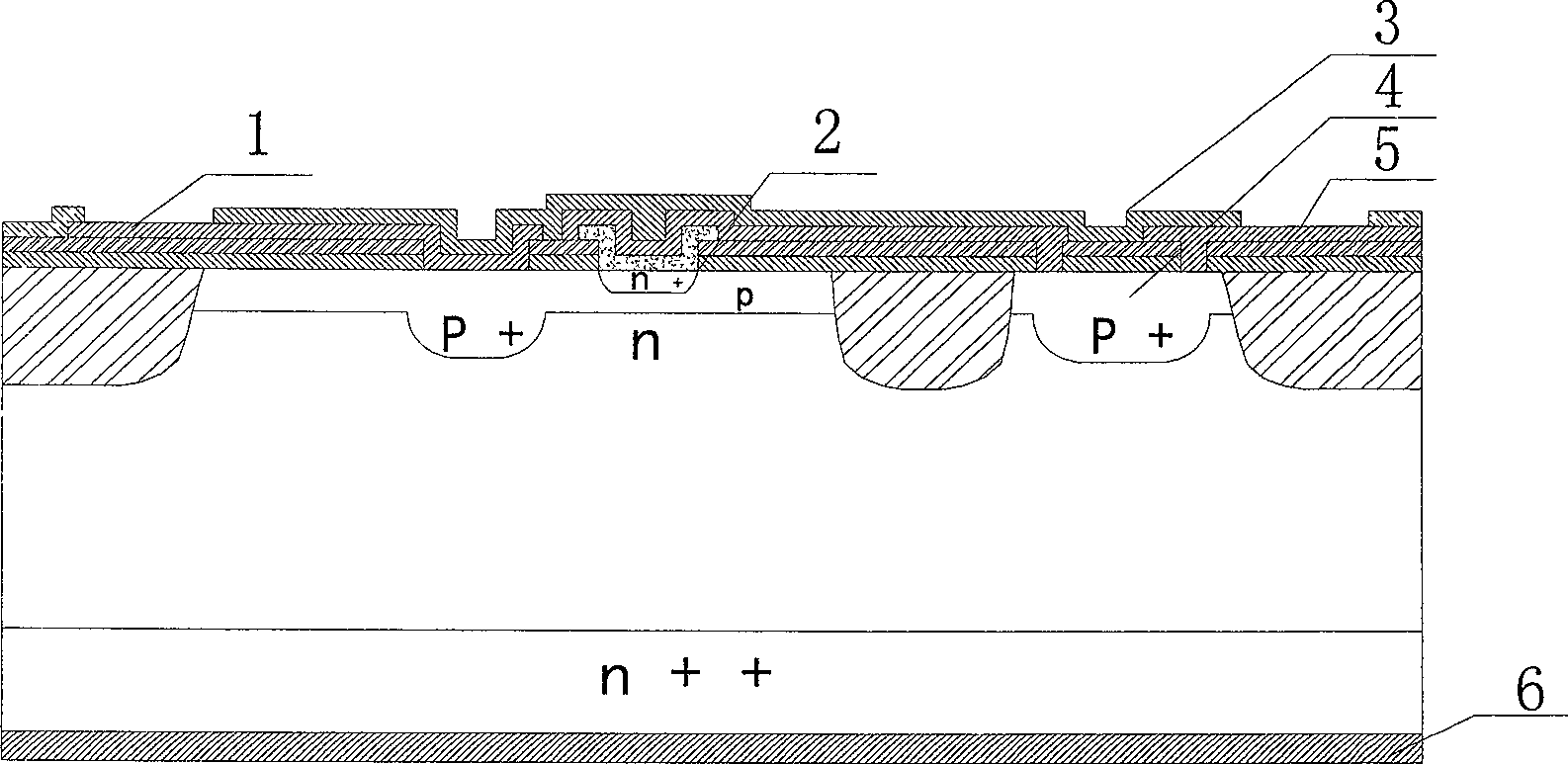
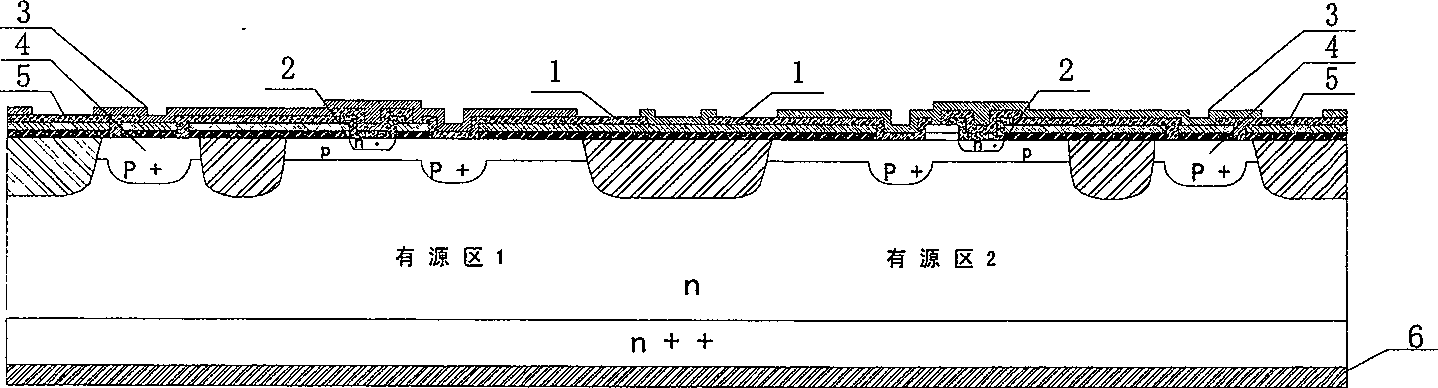
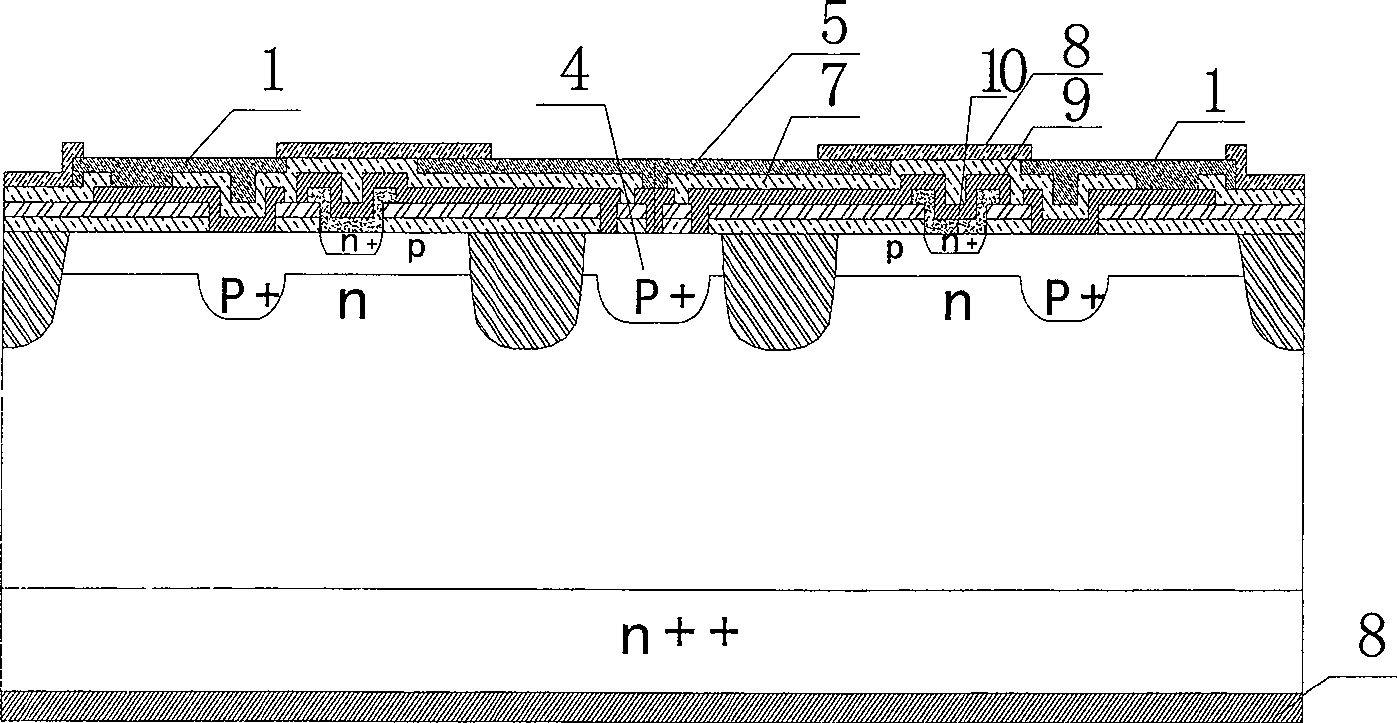
[0059] 1 in the figure is the base metal bonding region; 2 is the n+ doped emitter region, and the emitter region and its corresponding p-type base region and n-type collector region together form the active region; 3 is the passivation dielectric film on the metal surface; 4 is the P+ doped emitter ballast resistance area, with a thickness of 1μm-2μm; 5 is the emitter metal bonding area; 6 is the collector; n ++ for the silicon substrate. The thickness of p region is 0.3μm-0.4μm; n + The thickness of the region is 0.1μm-0.2μm; the thickness of the n-type silicon epitaxial layer is 3μm-14μm; n ++ The thickness of the silicon substrate material is 380 μm-560 μm. 7 is an isolation dielectric film between double-layer metals; 8 is a passivation layer on the metal surface. 9 is the interconnection metal of the emitter window and the ballast resistor window; 10 is n + launch area, n + The emitter region and its corresponding p-type base region and n-type collector region toget...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com