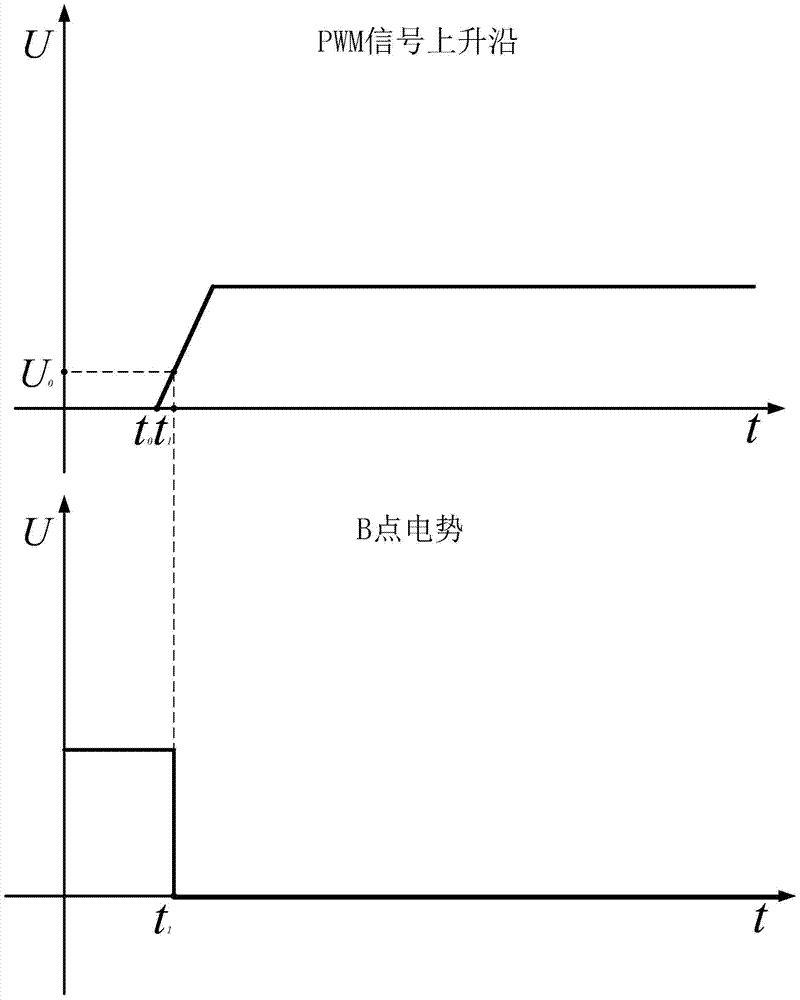
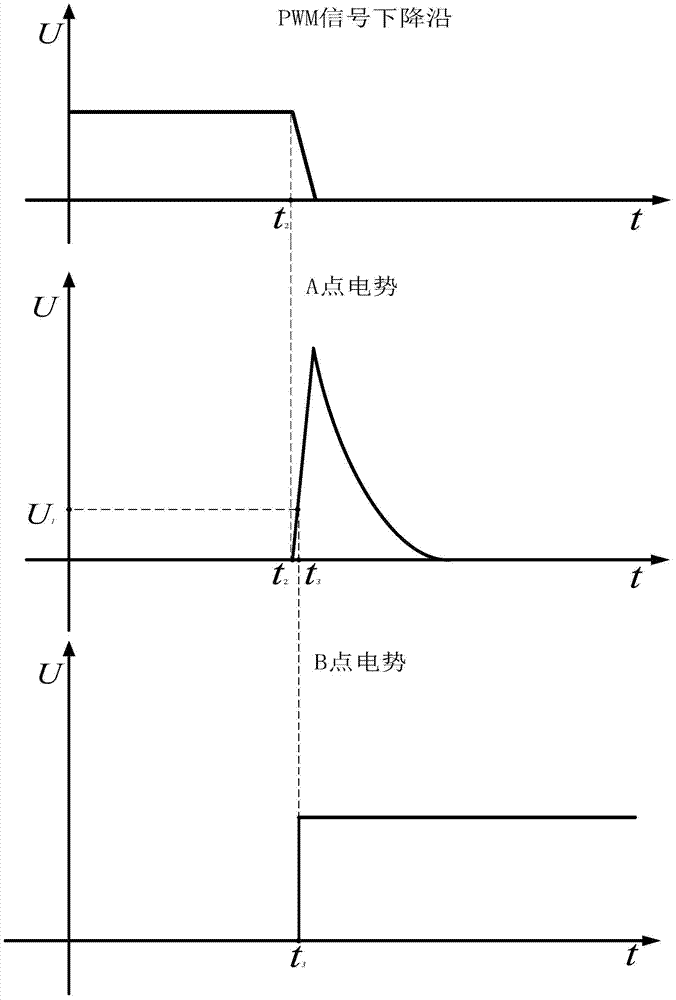
Patents
Literature
36 results about "Microwave transistors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
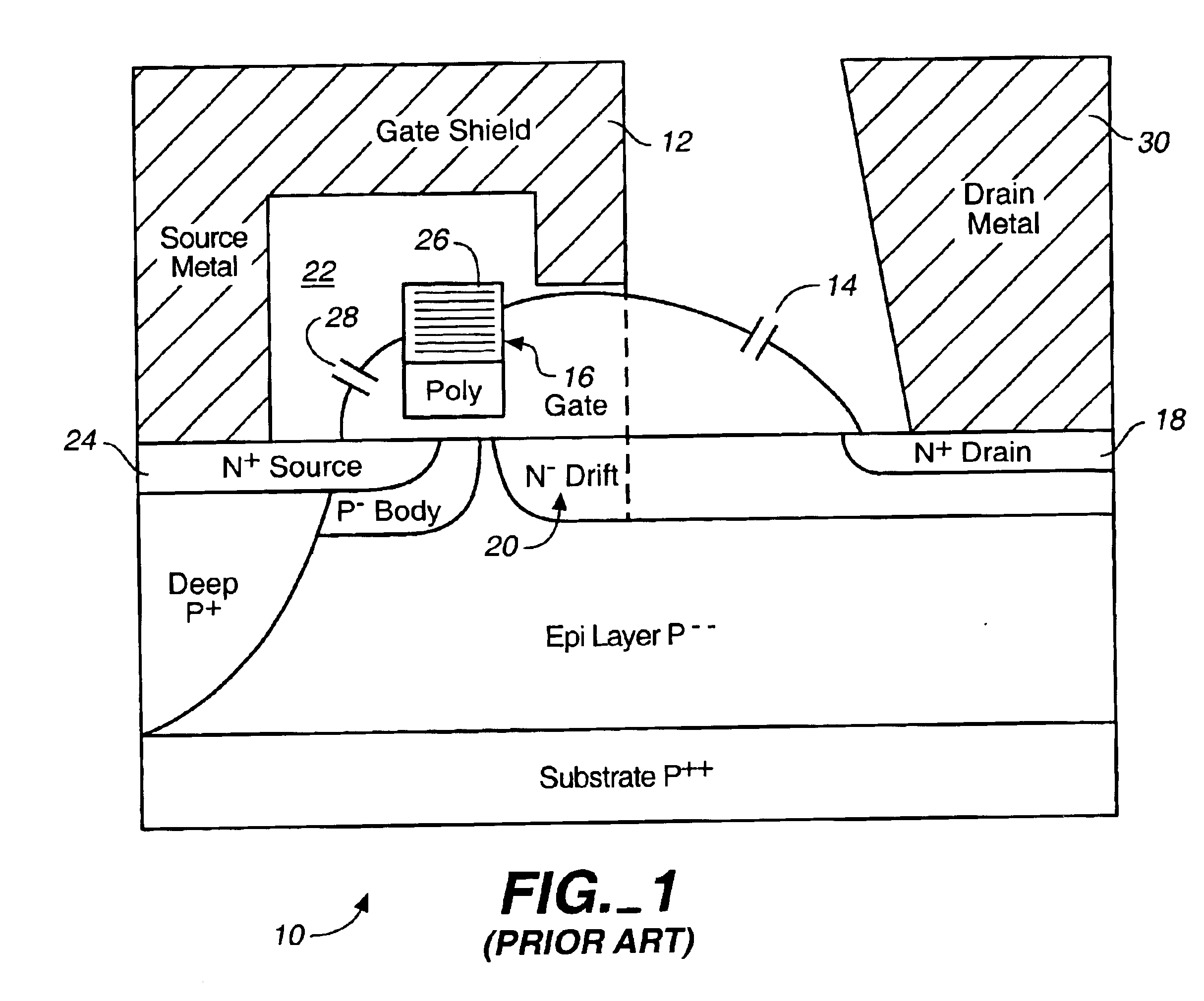
Microwave transistor is made to operate in microwave frequency unlike normal BJT. They are with typically 5 watts at the frequency of 3GHz with a gain of 5dB.
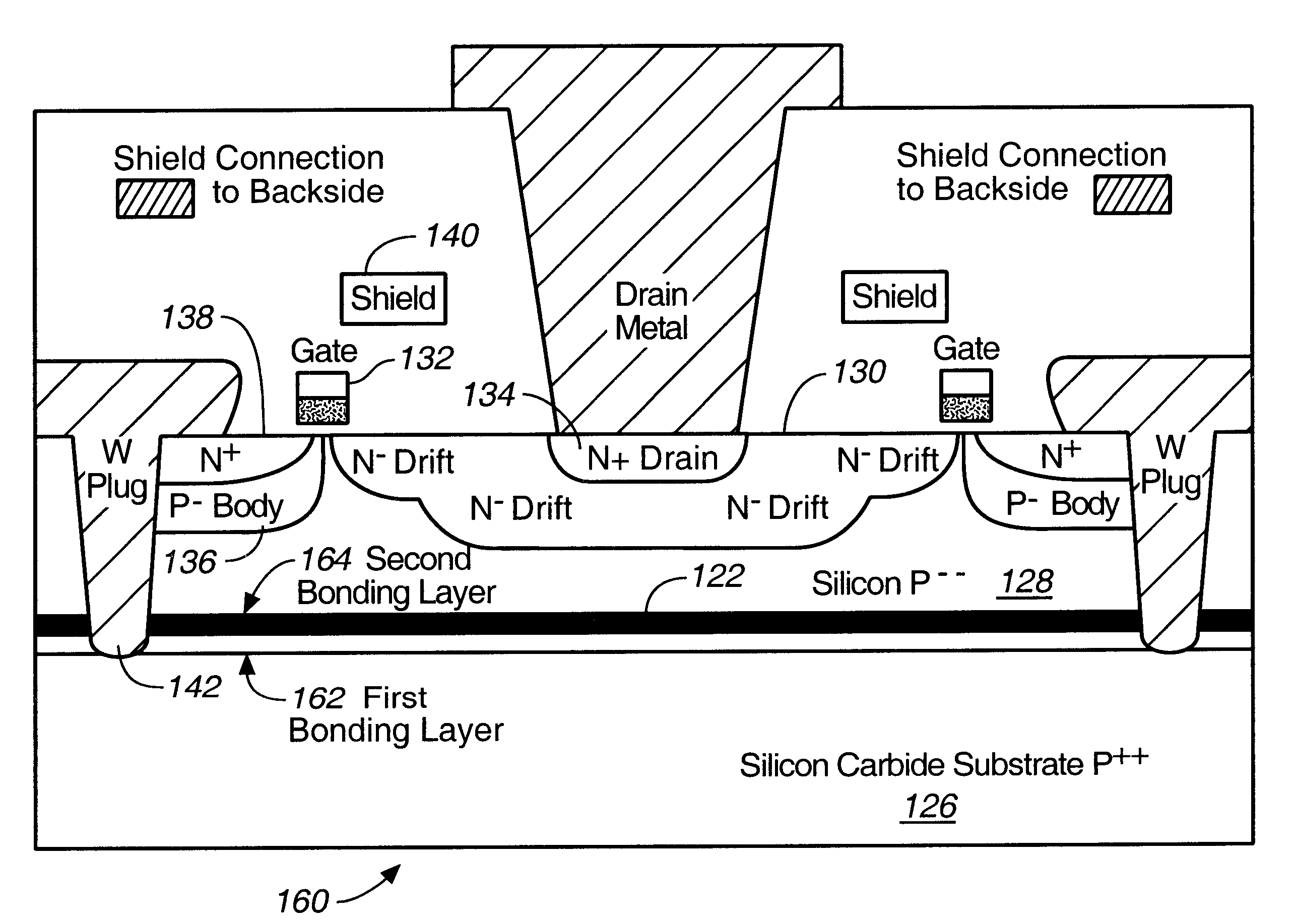
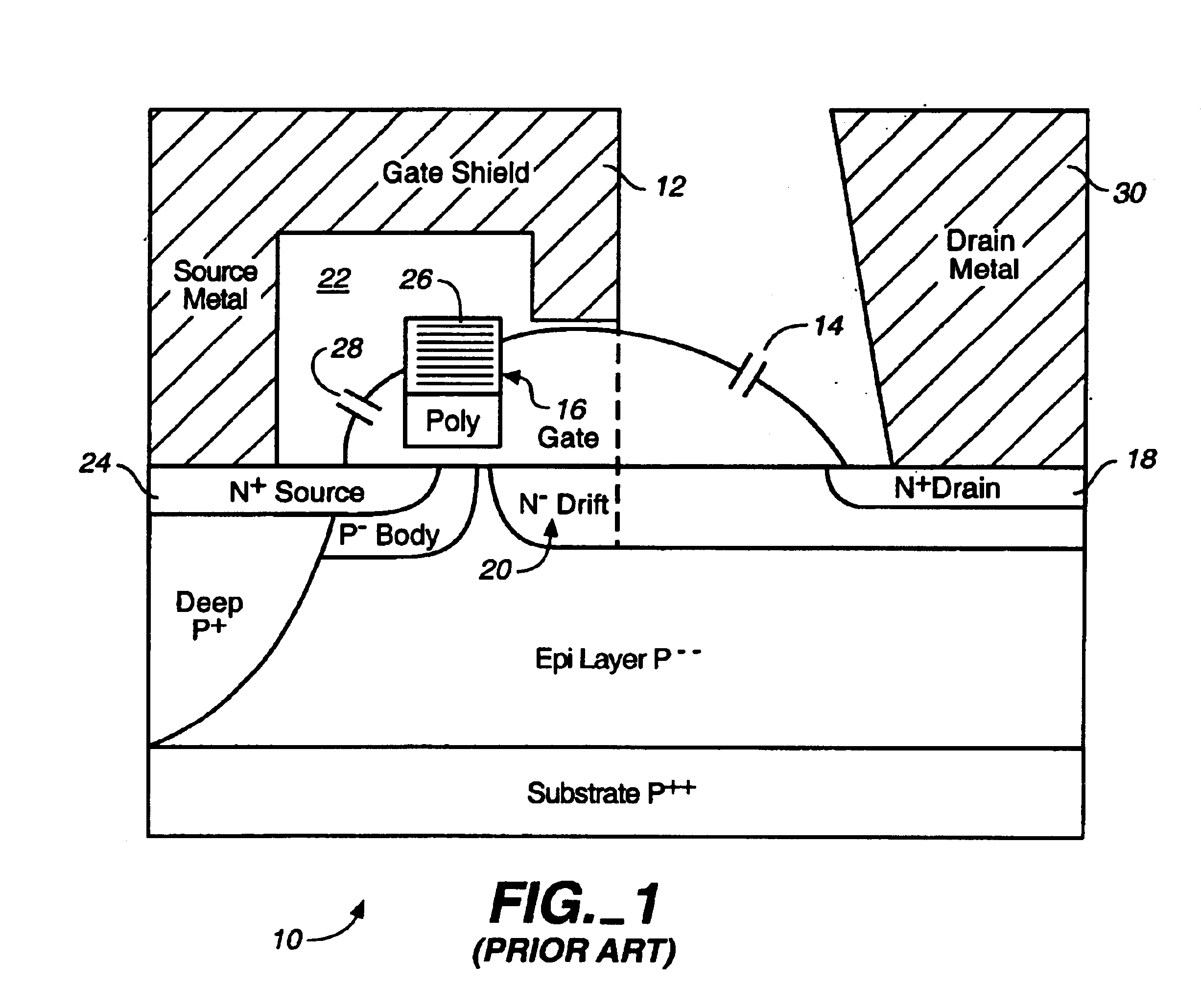
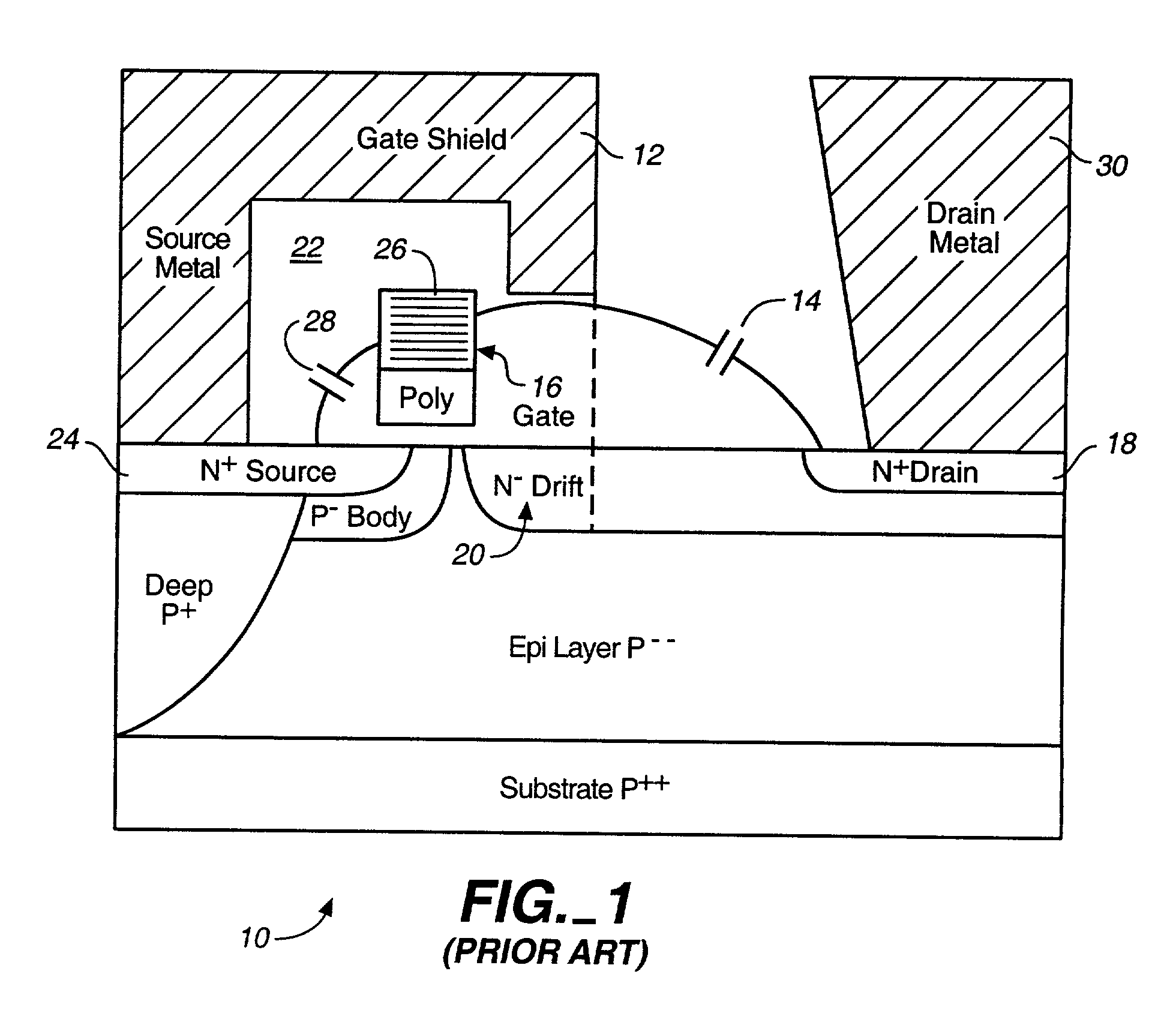
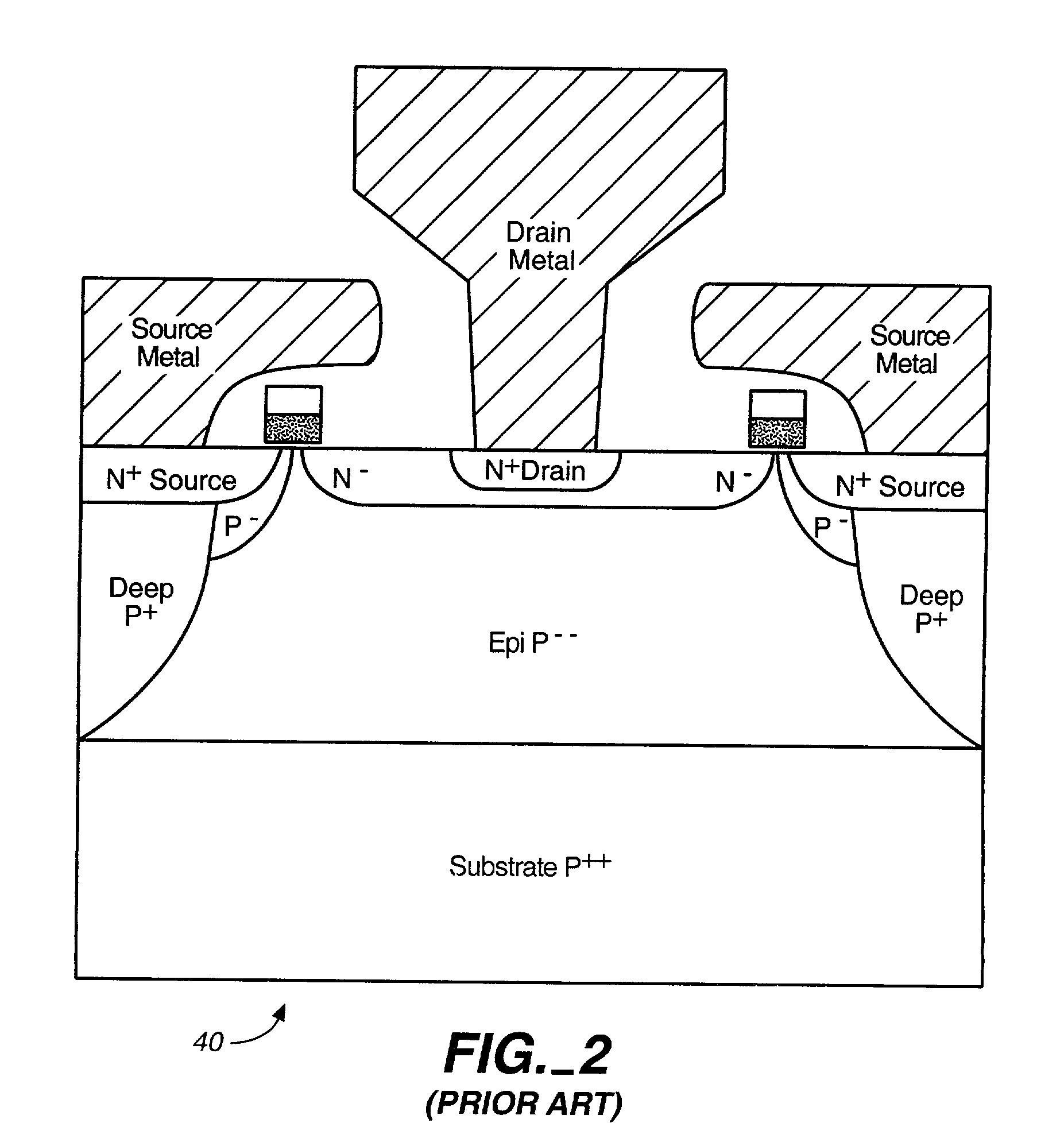
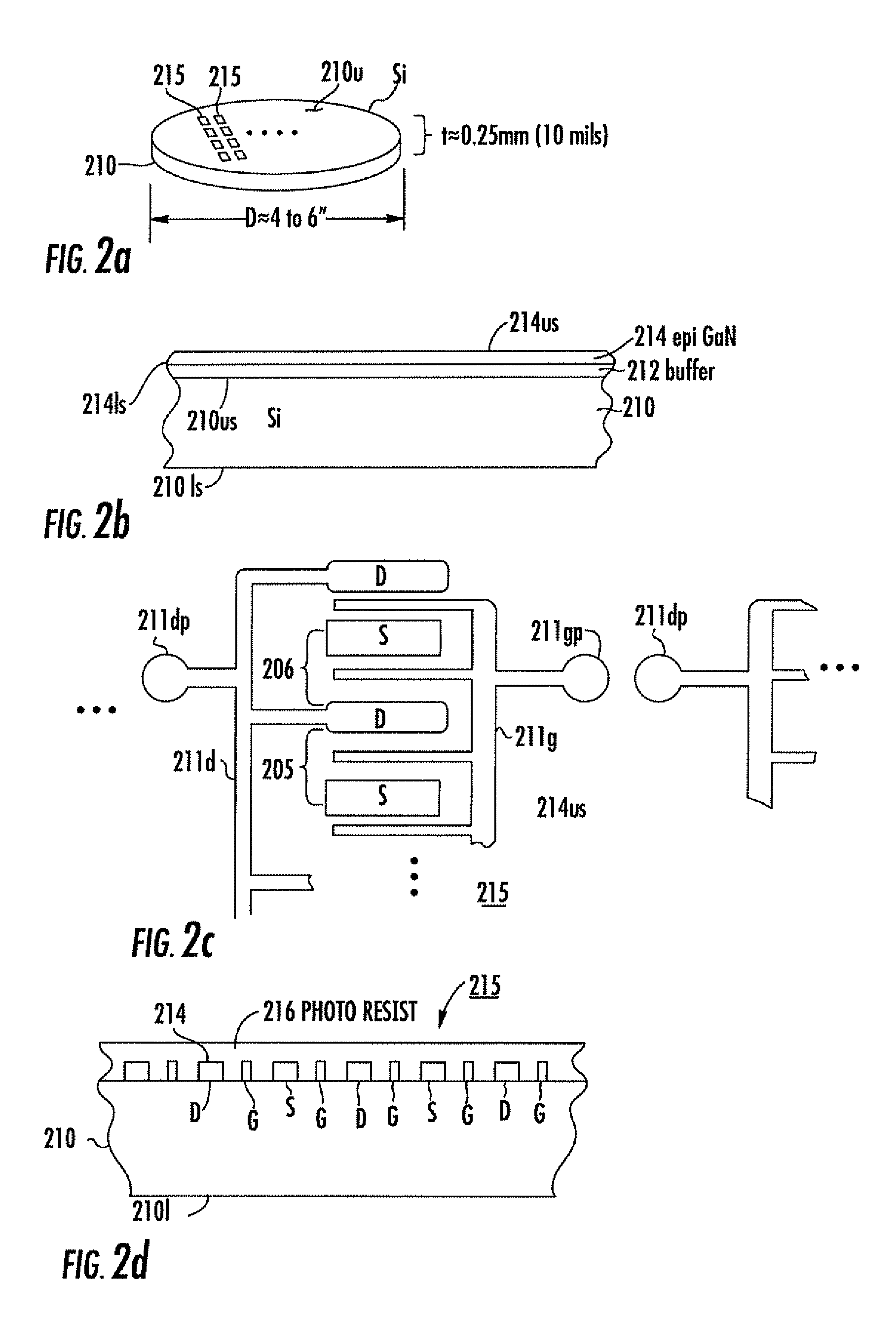
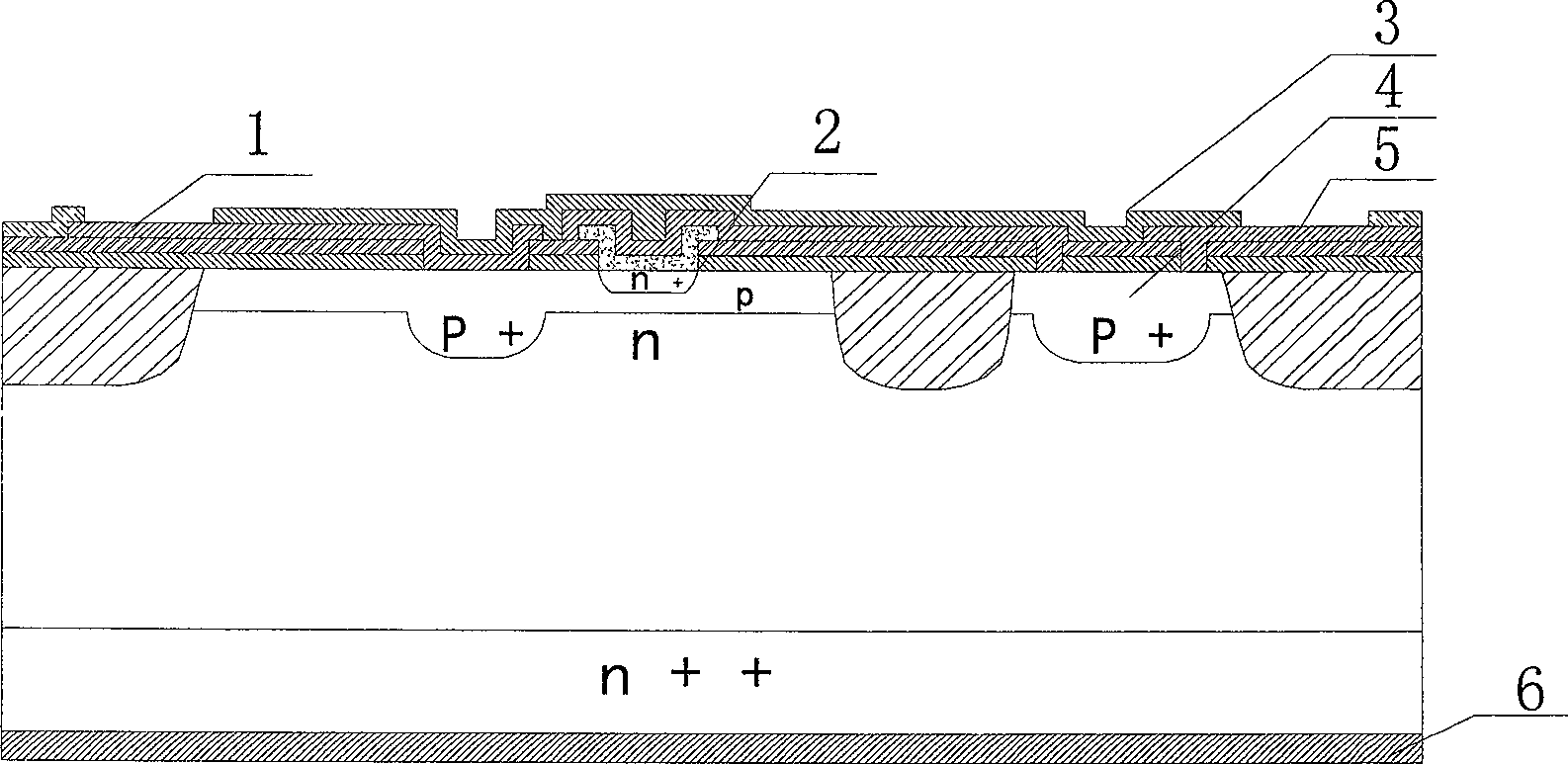
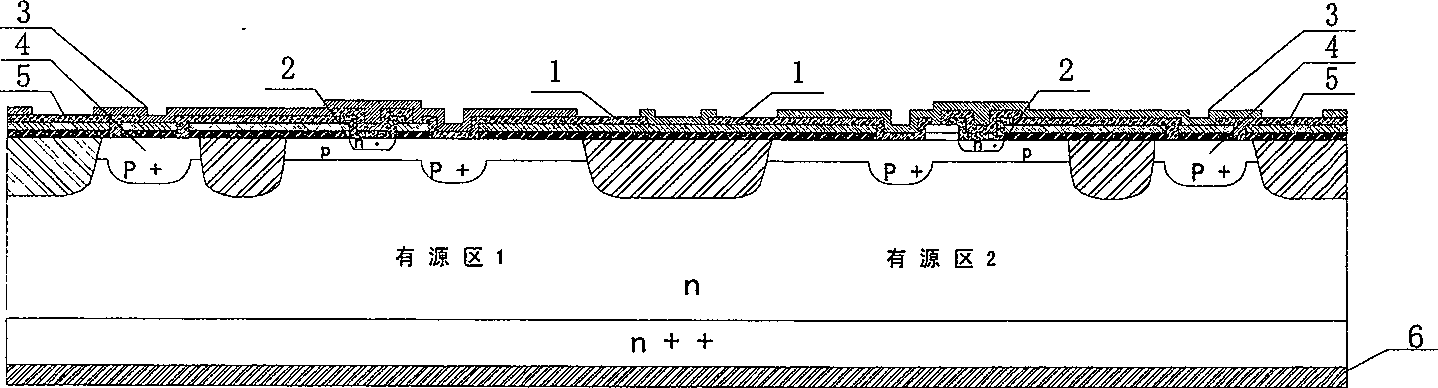
Microwave field effect transistor structure on silicon carbide substrate
InactiveUS6521923B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDopantSemiconductor materials
A microwave transistor structure comprising: (a) a SiC substrate having a top surface; (b) a silicon semiconductor material of a first conductivity type overlaying the top surface of the semiconductor substrate and having a top surface; (c) a conductive gate overlying and insulated from the top surface of the silicon semiconductor material; (d) a channel region of the first conductivity type formed completely within the silicon semiconductor material including a channel dopant concentration; (e) a drain region of the second conductivity type formed in the silicon semiconductor material and contacting the channel region; (f) a body region of the first conductivity type and having a body region dopant concentration formed in the silicon semiconductor material under the conductive gate region; (g) a source region of the second conductivity type and having a source region dopant concentration formed in the silicon semiconductor material within the body region; (h) a shield plate region being adjacent and being parallel to the drain region formed on the top surface of the silicon semiconductor material over a portion of the channel region; wherein the shield plate region is adjacent and parallel to the conductive gate region; and wherein the shield plate extends above the top surface of the silicon semiconductor material to a shield plate height level, and is insulated from the top-surface of the silicon semiconductor material; and (i) a conductive plug region formed in the body region of the silicon semiconductor material to connect a lateral surface of the body region to the top surface of the substrate.
Owner:QORVO US INC
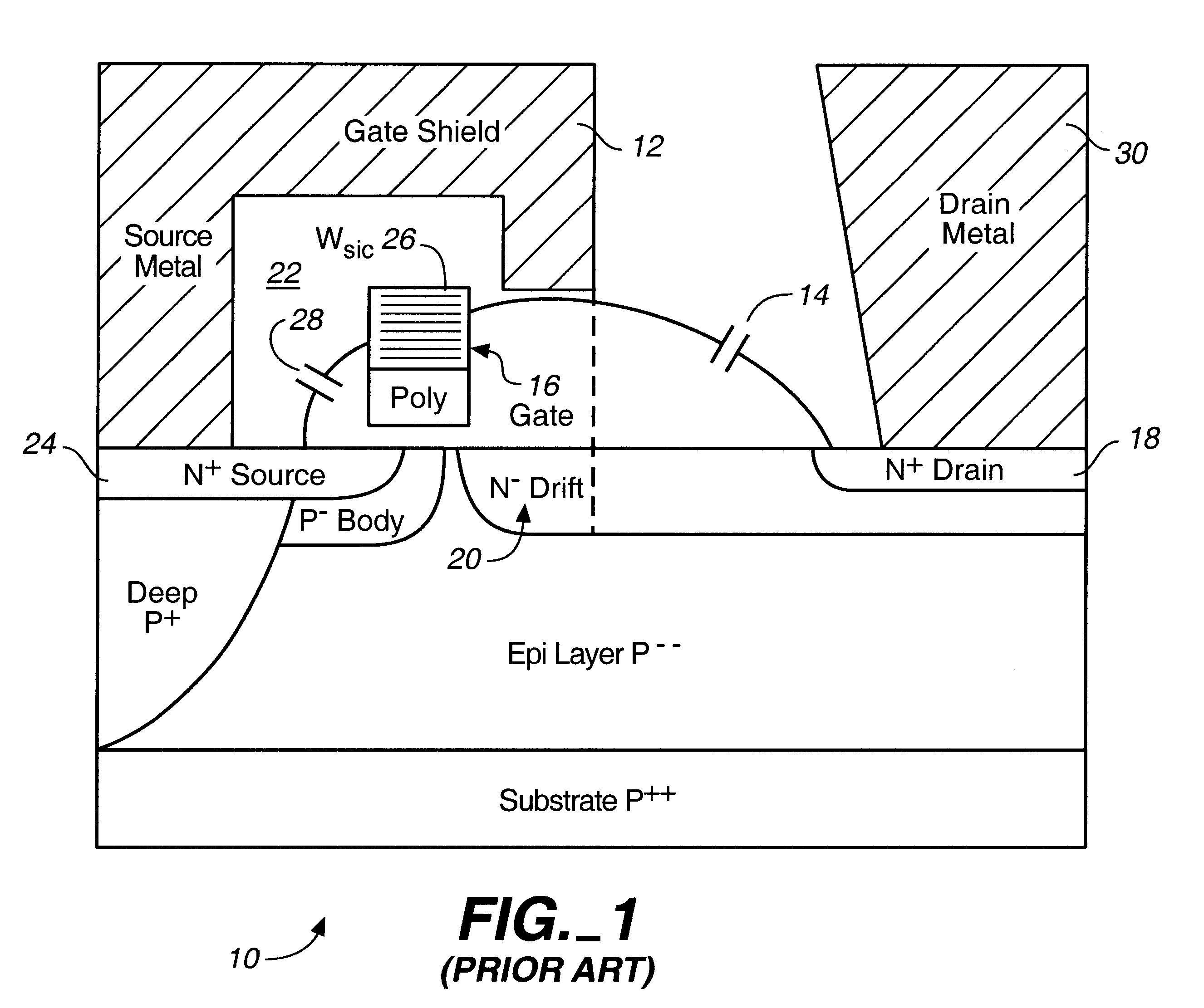
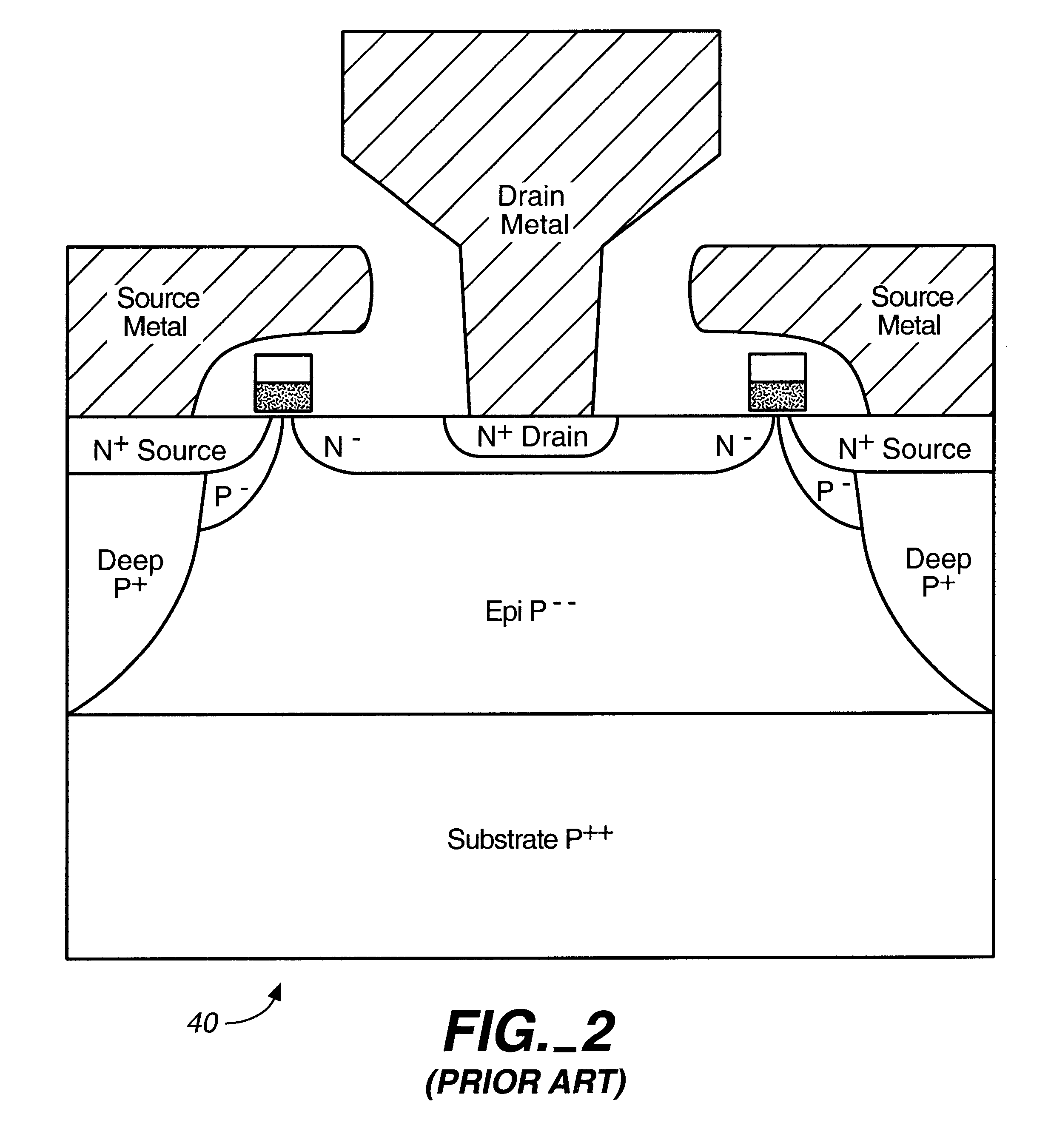
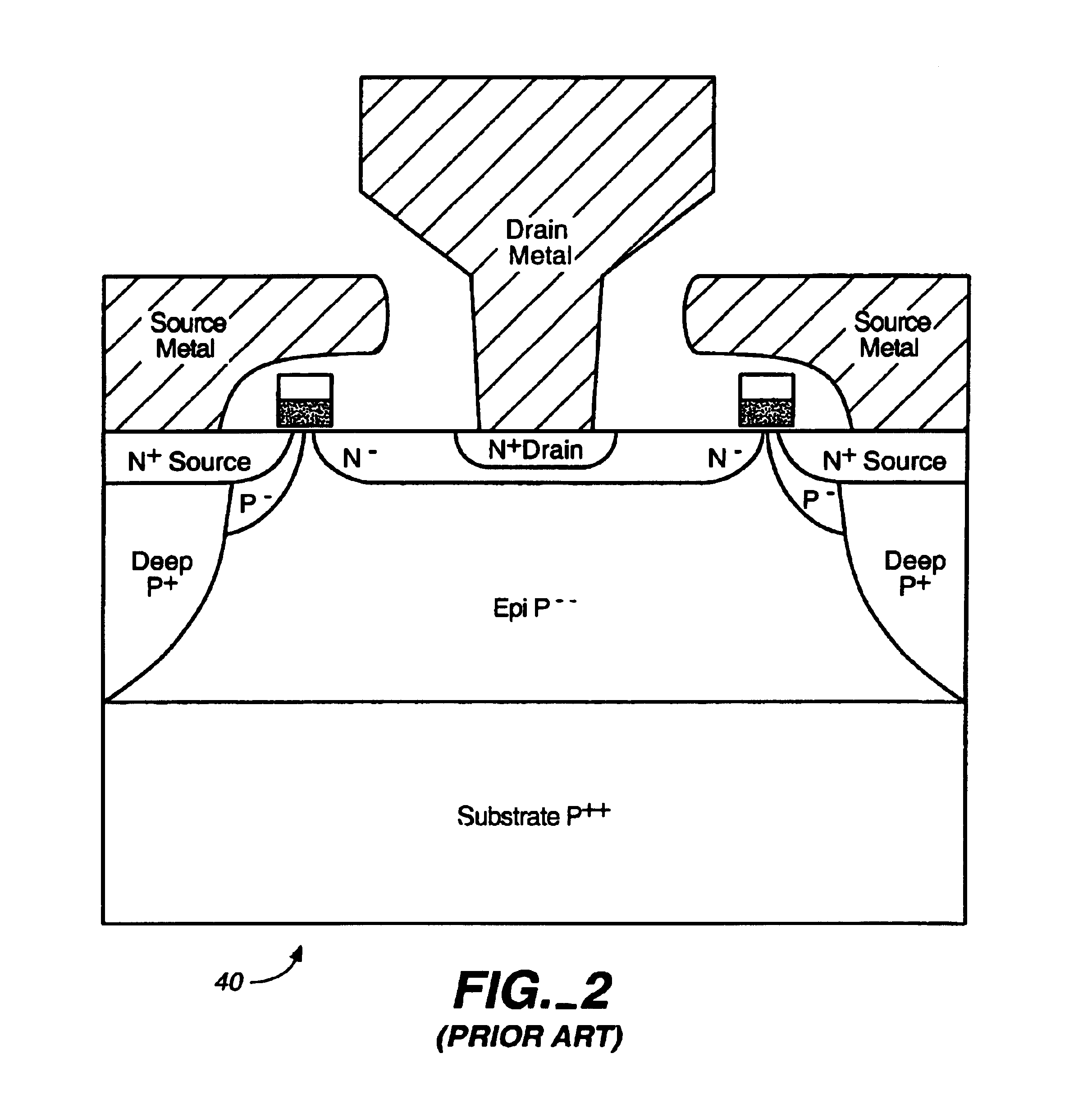
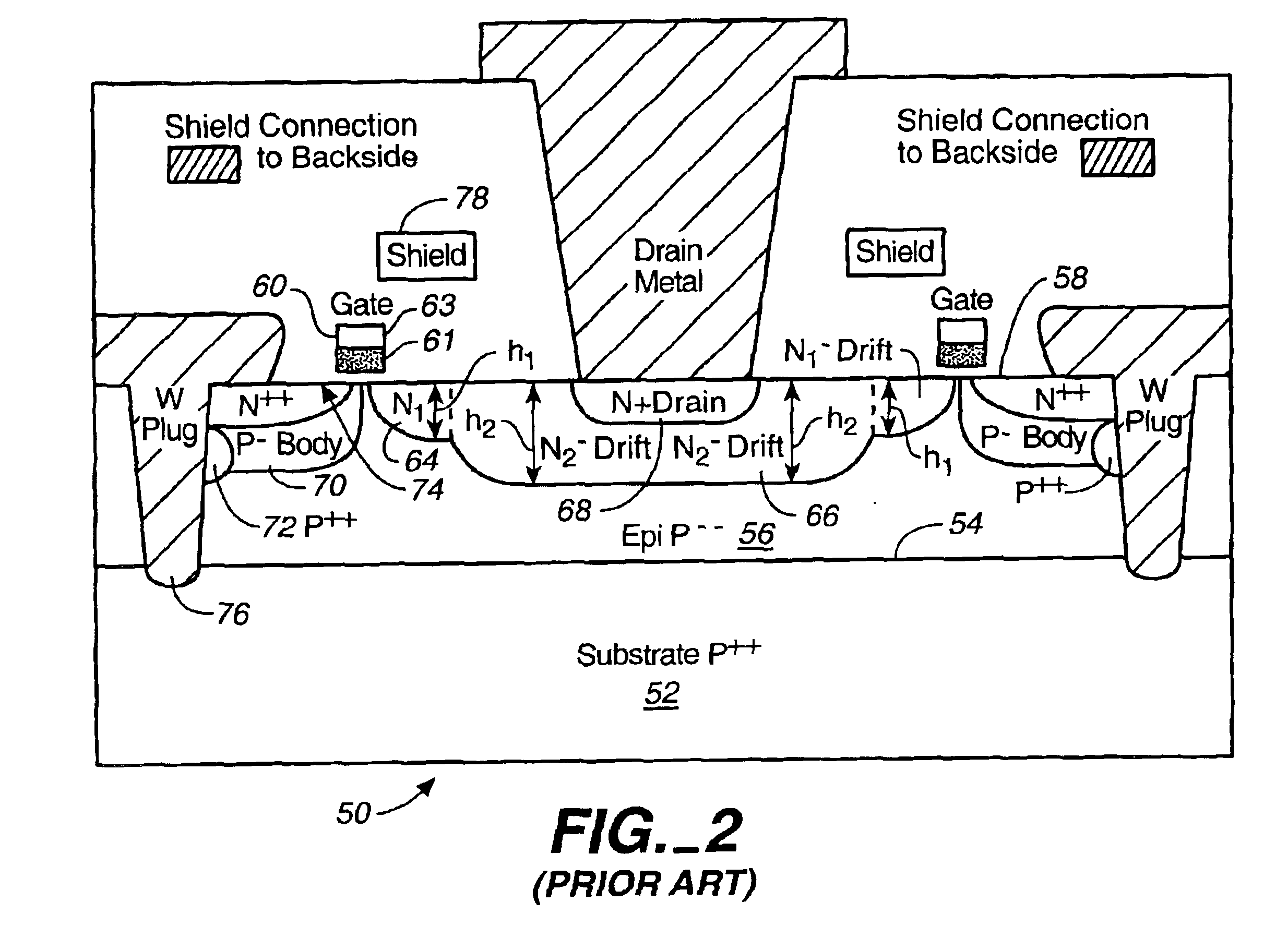
Microwave field effect transistor structure
InactiveUS6831332B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsMicrowave
Owner:QORVO US INC
Microwave field effect transistor structure
InactiveUS20030218209A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantMicrowave
A microwave transistor structure comprising: (1) a substrate having a top surface; (2) a silicon semiconductor material of a first conductivity type, having a first dopant concentration and a top surface; (3) a conductive gate overlying and insulated from the top surface of the silicon semiconductor material; (4) a channel region of a second conductivity type and having a channel dopant concentration; (5) a drain region of the second conductivity type and having a drain dopant concentration greater than the channel region dopant concentration; (6) a body of the first conductivity type and having a body region dopant concentration; (7) a source region of the second conductivity type and having a source region dopant concentration; (8) a shield plate region formed on the top surface of the silicon semiconductor material over a portion of the channel region, wherein the shield plate is adjacent and parallel to the drain region, and to the conductive gate region; and wherein the shield plate extends above the top surface of the silicon semiconductor material to a shield plate height level; and wherein the shield plate is insulated from the top surface of the silicon semiconductor material; and (9) a conductive plug region formed in the body region of the silicon semiconductor material, wherein the conductive plug region connects a lateral surface of the body region to the top surface of the substrate.
Owner:QORVO US INC
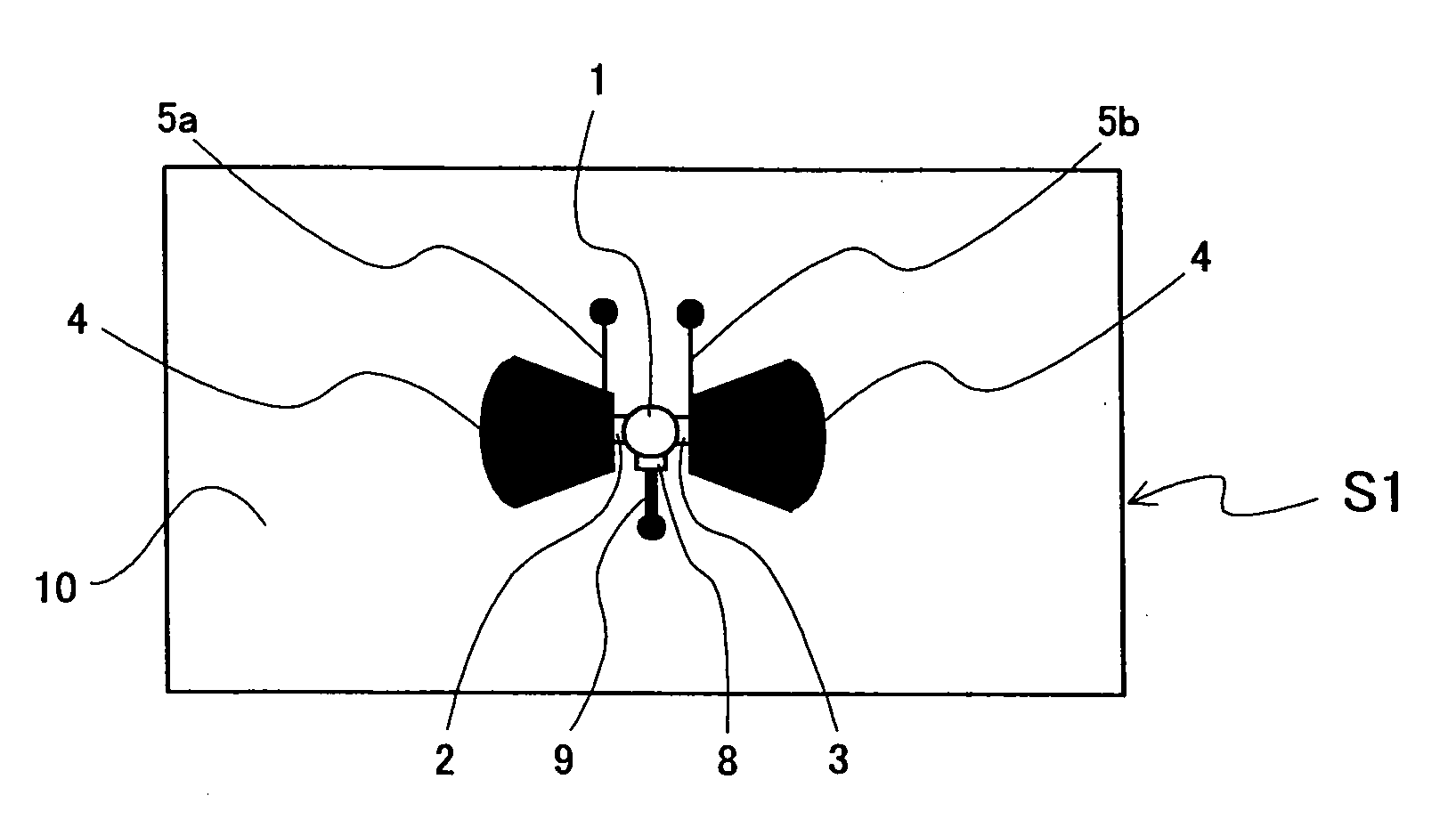
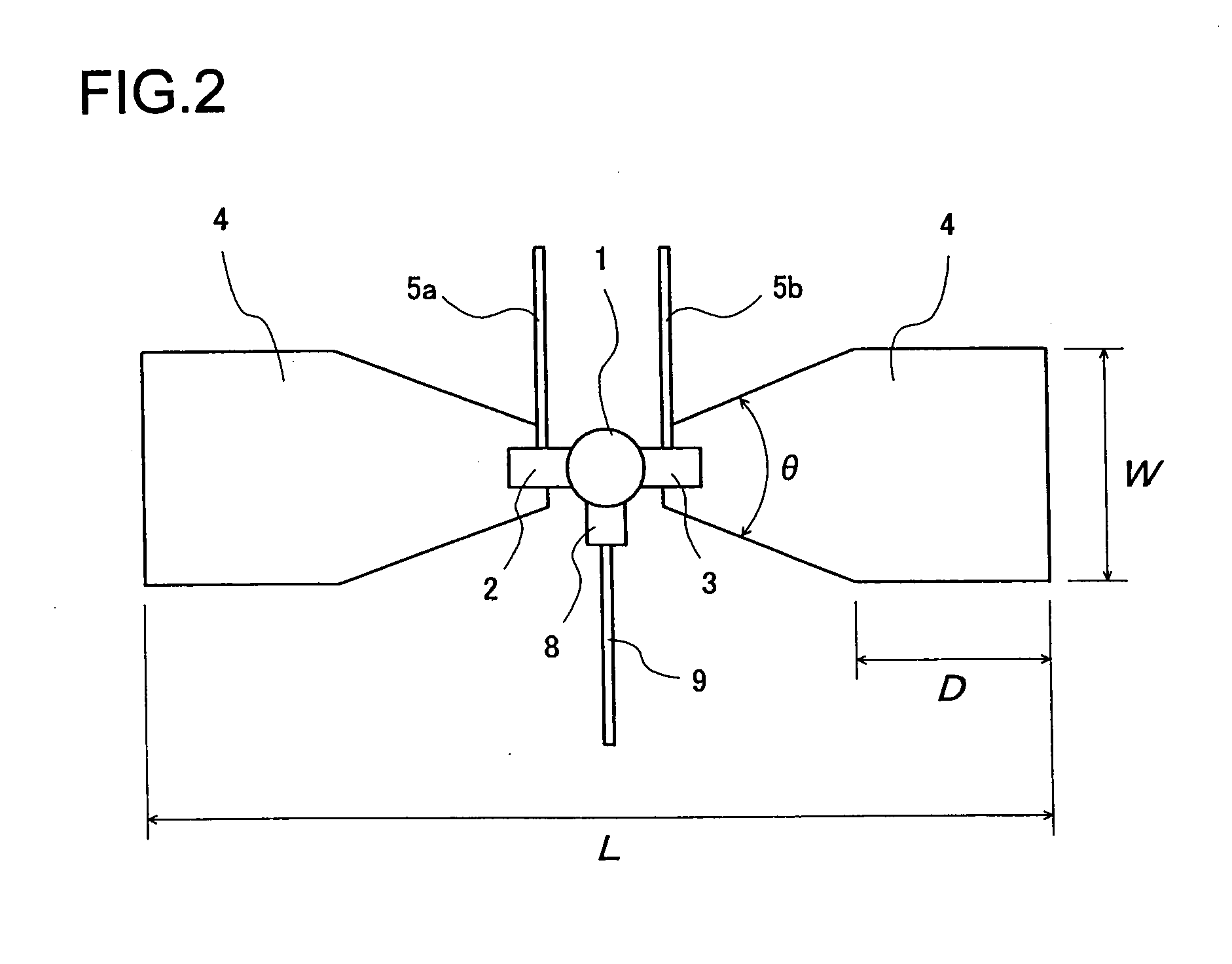
Microwave/millimeter wave sensor apparatus
ActiveUS20100117891A1Simple structureHigh detection sensitivityOscillations generatorsElectrically short antennasElectricityMicrowave
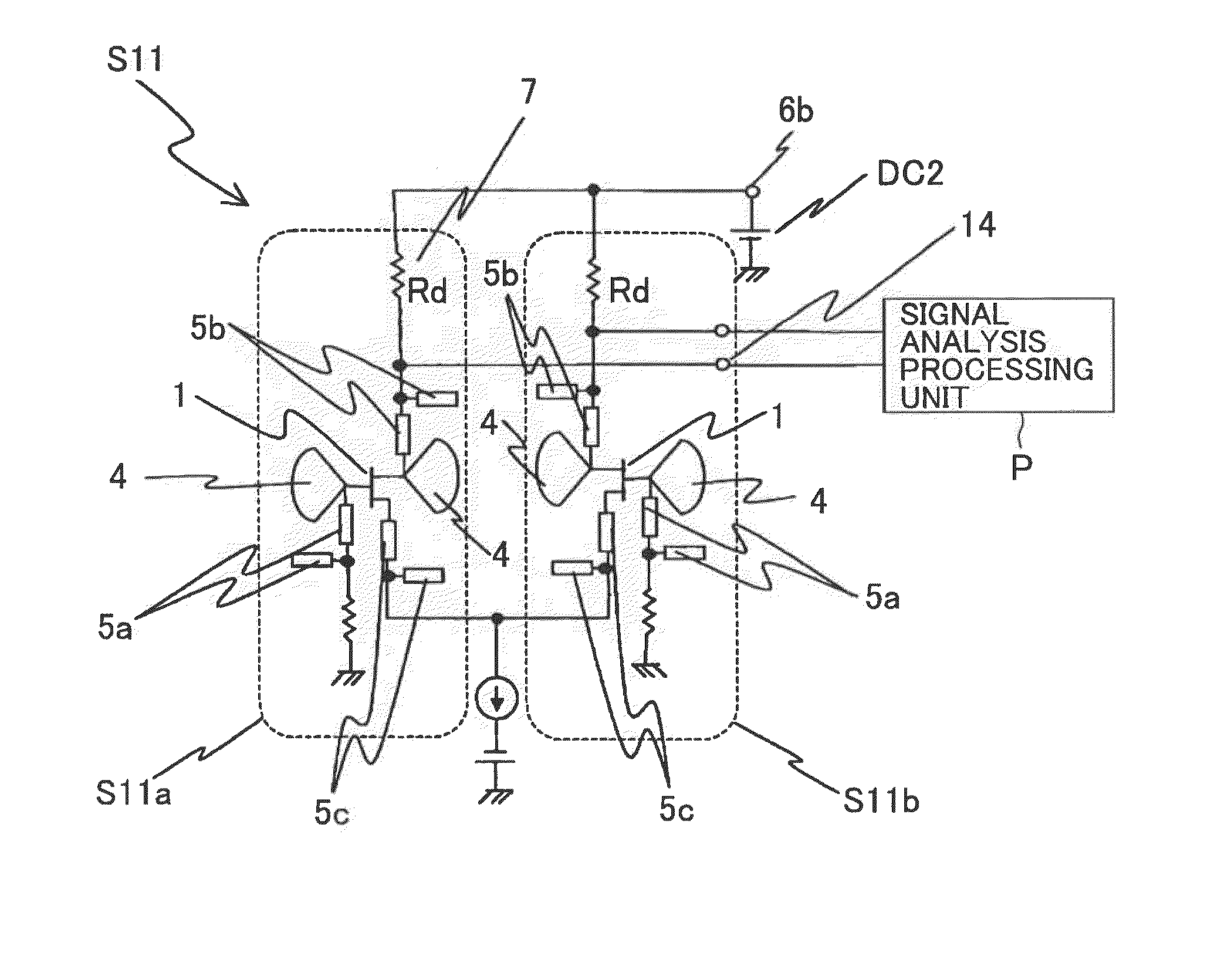
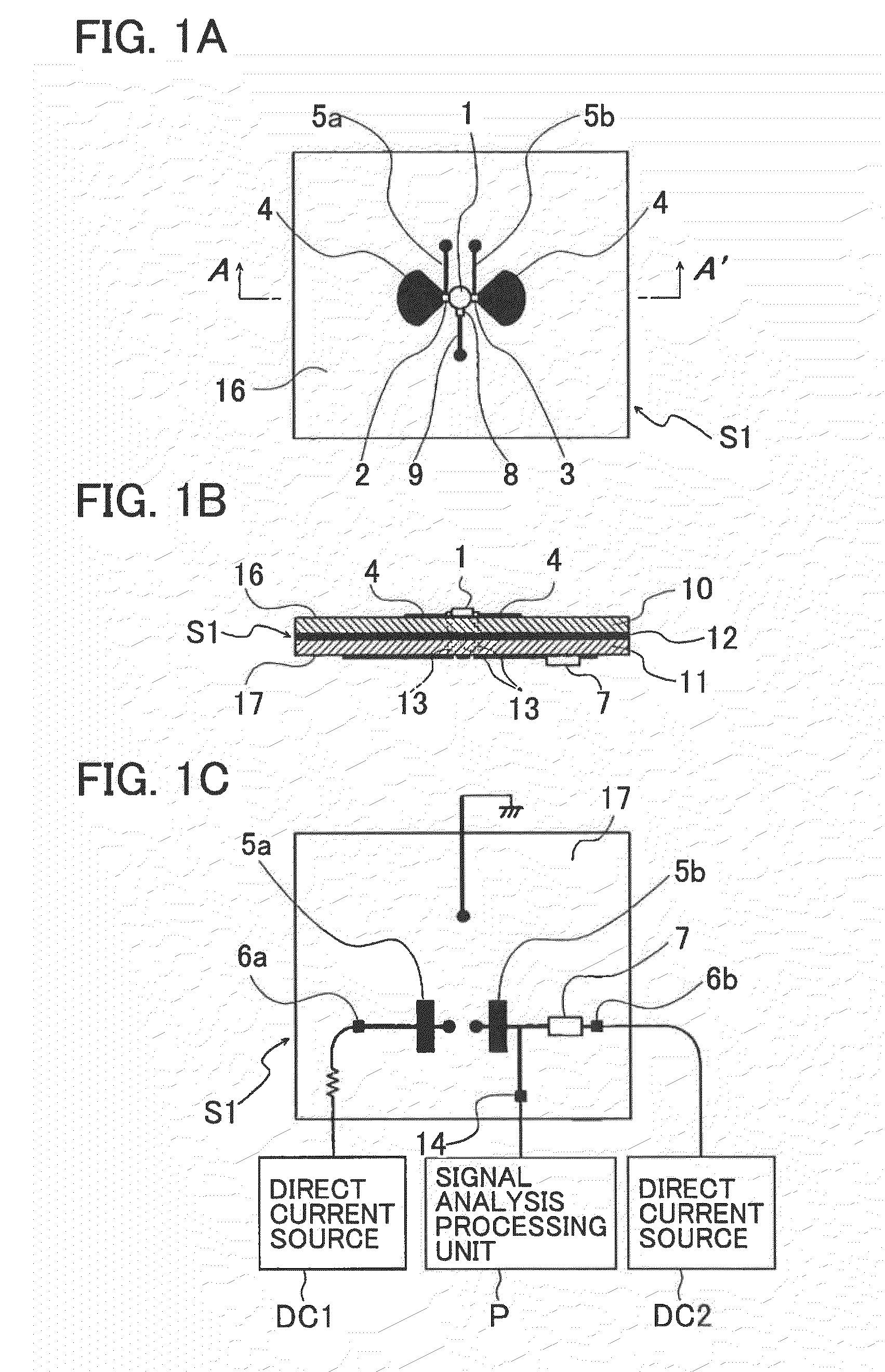
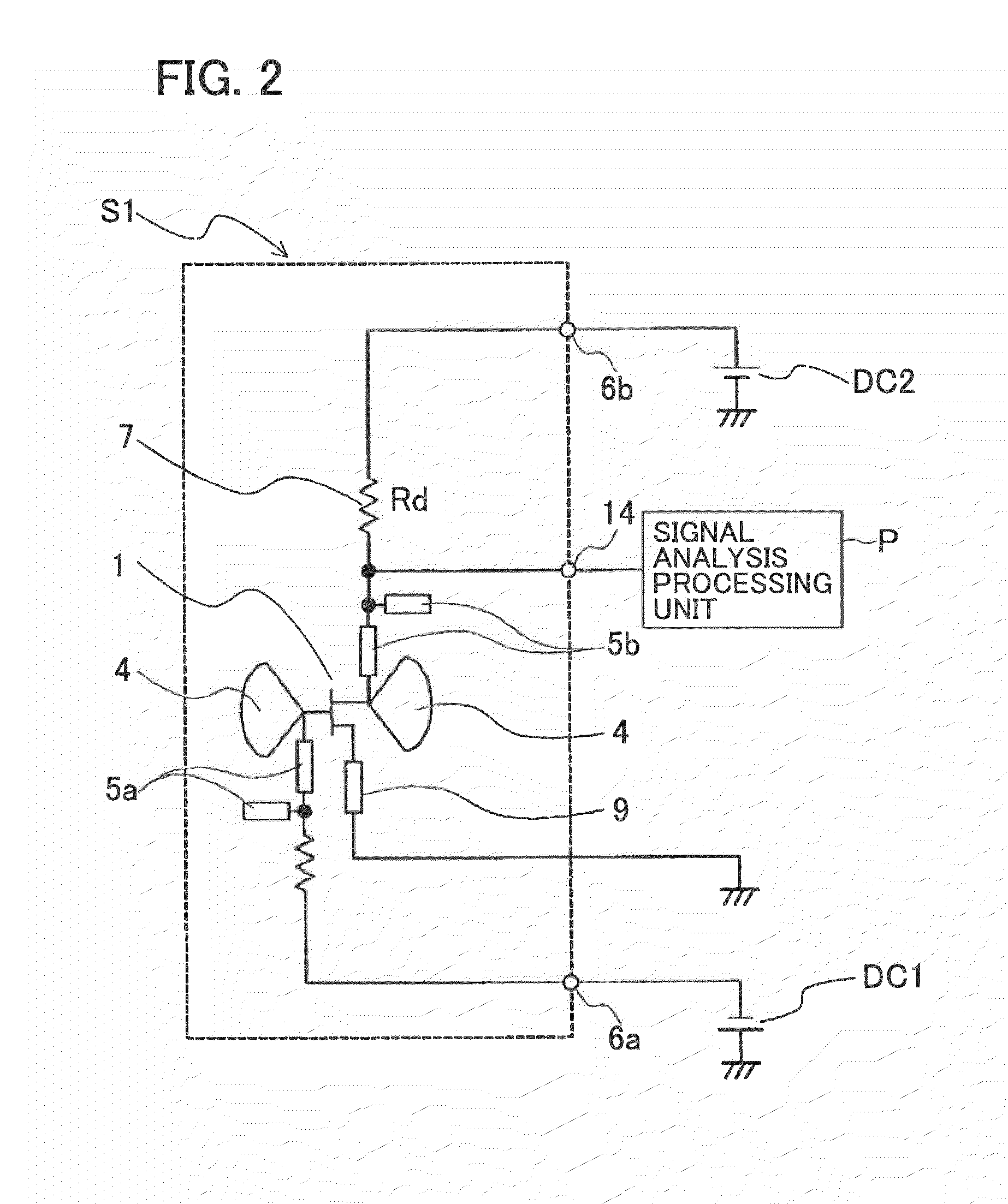
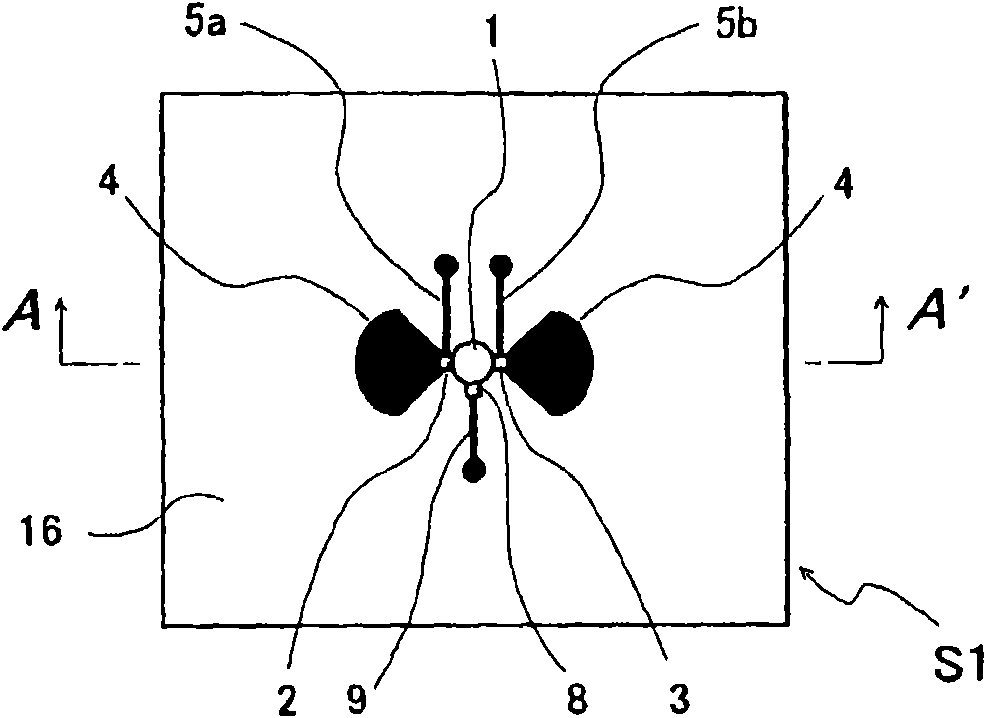
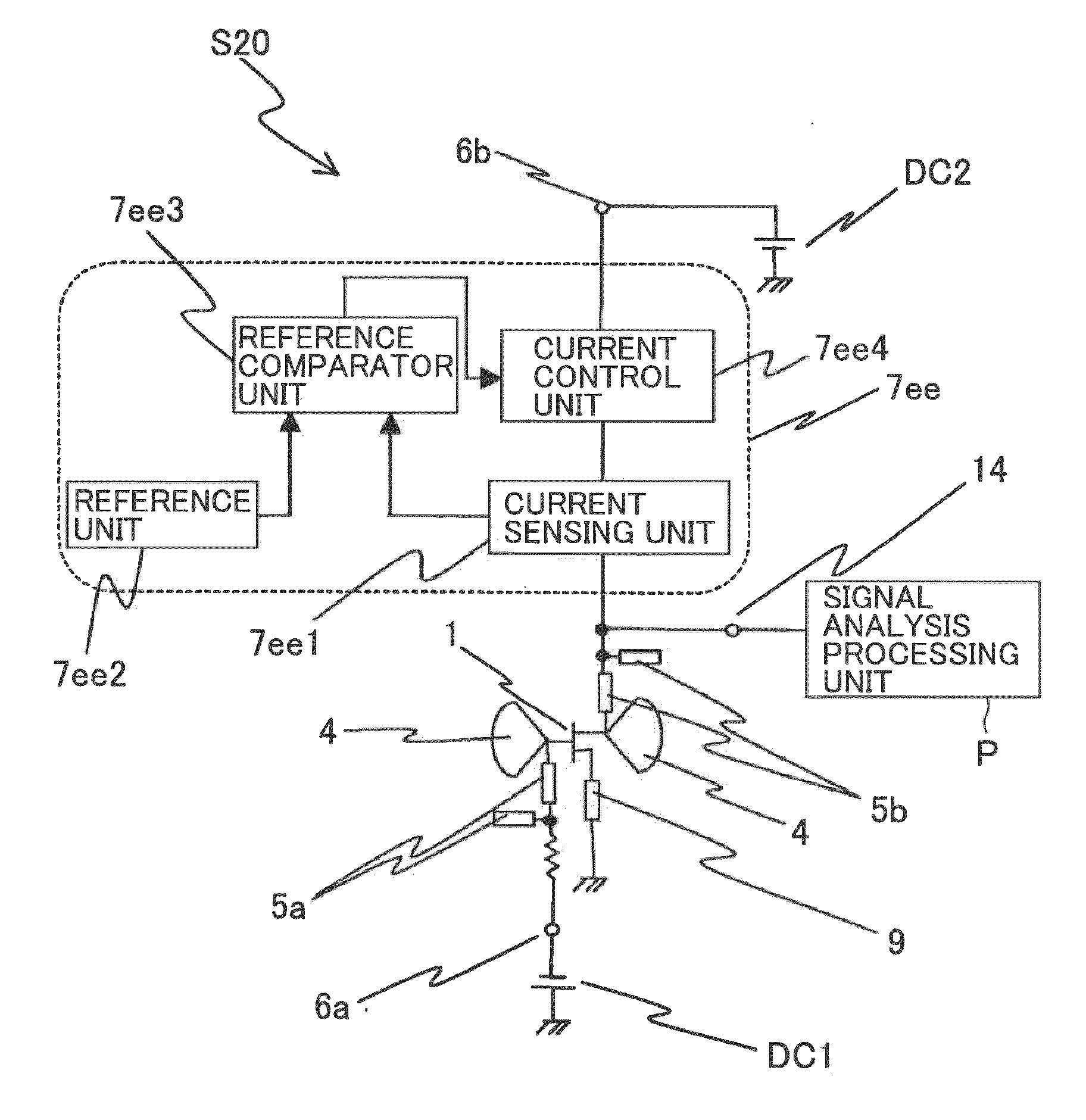
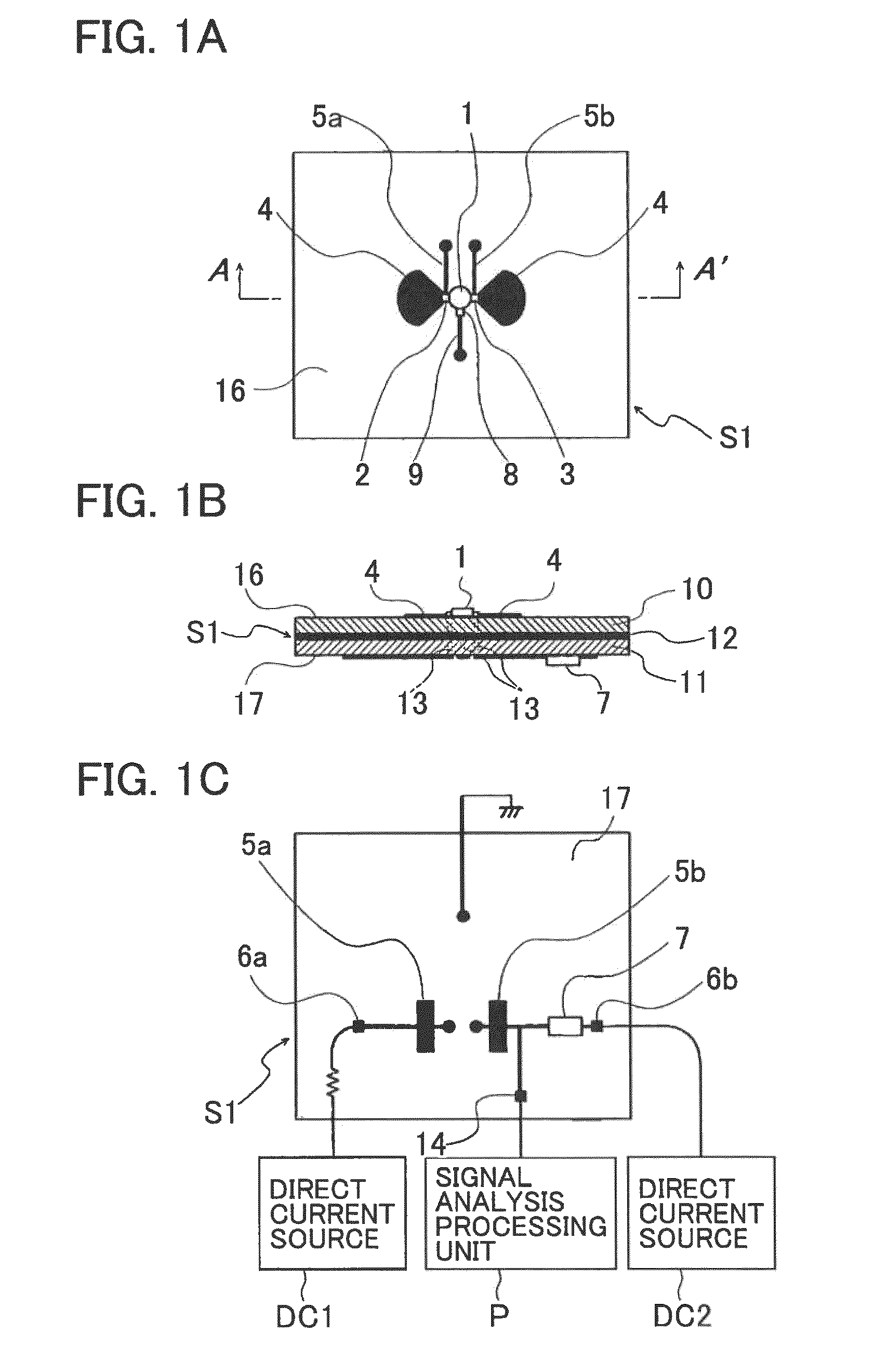
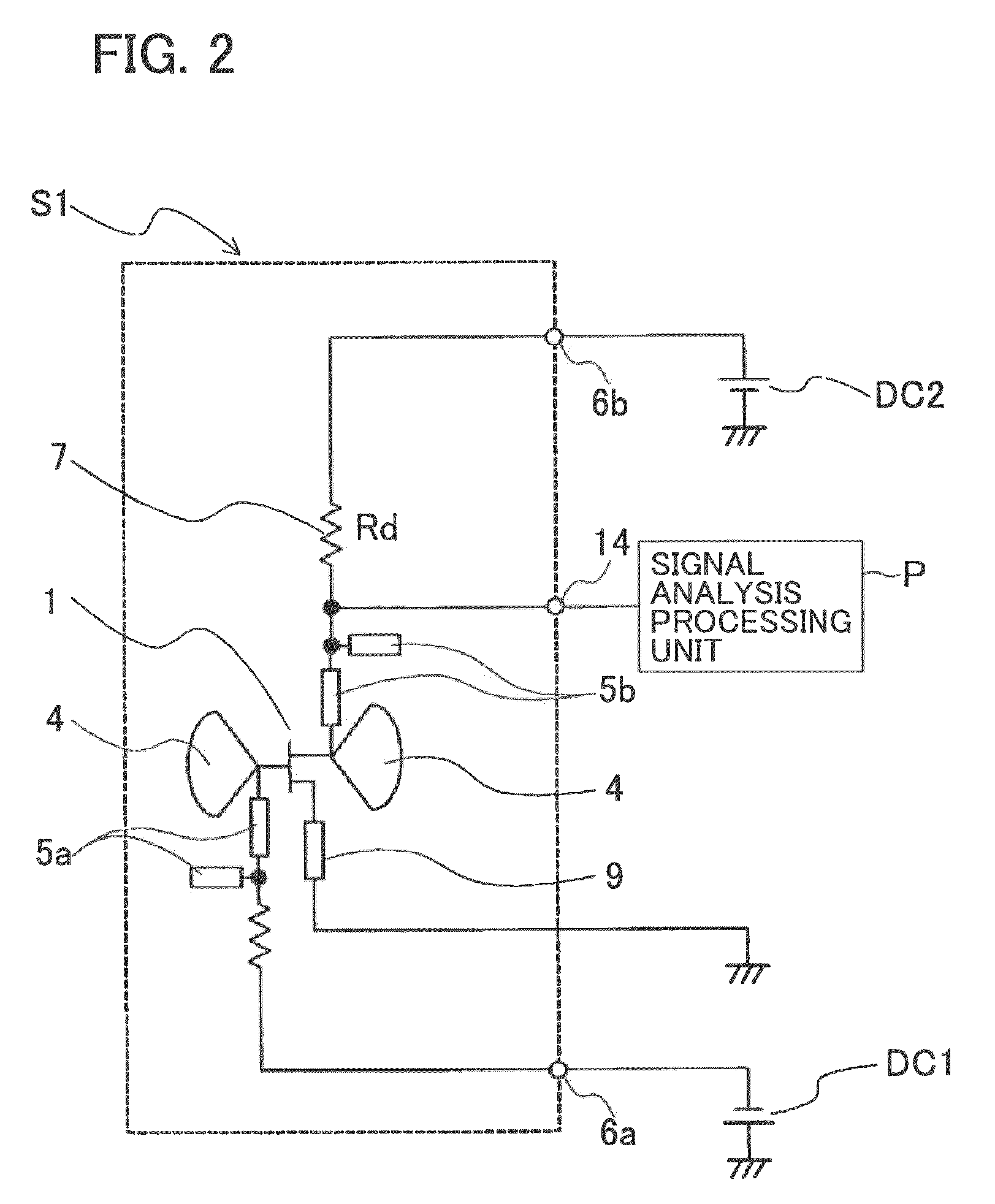
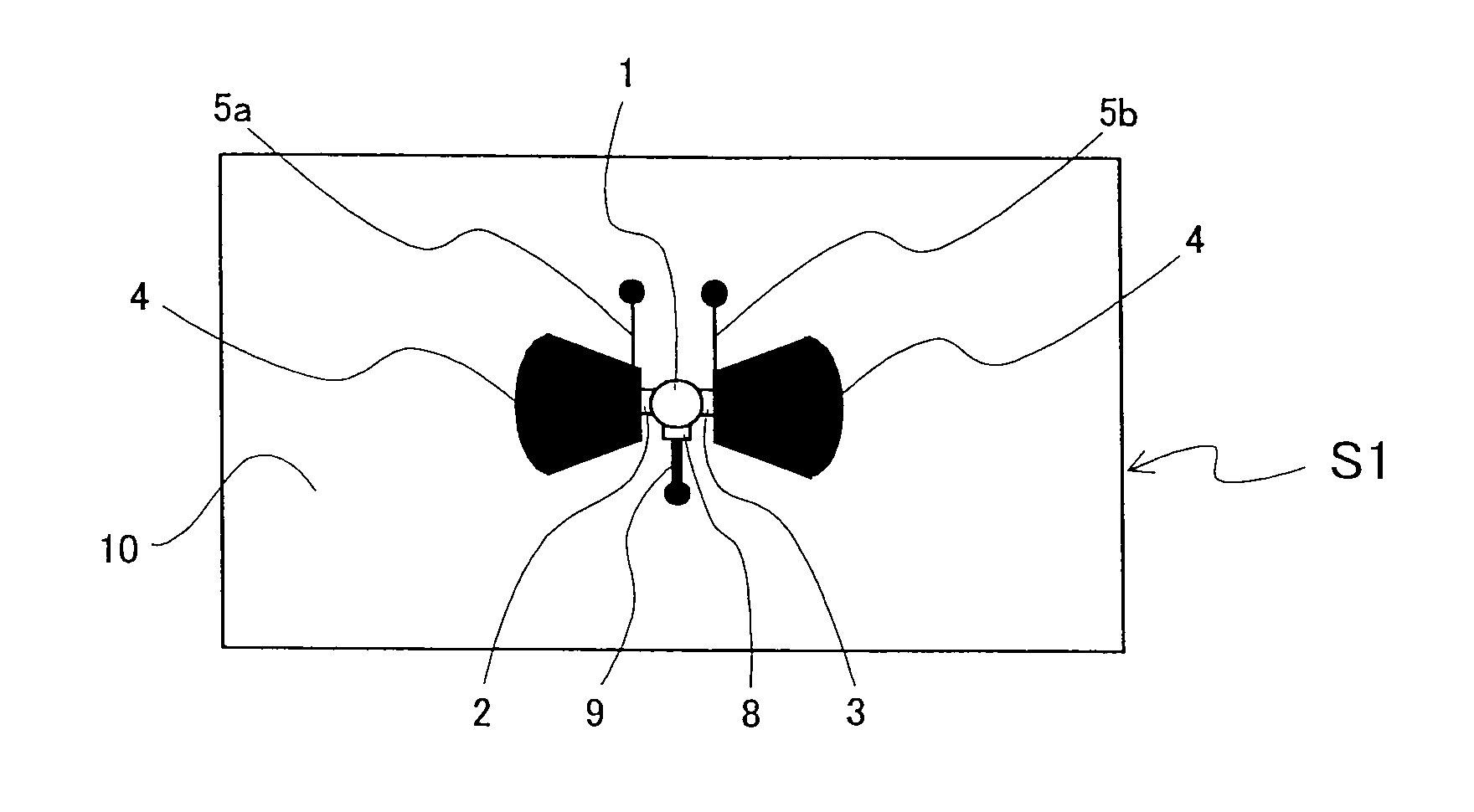
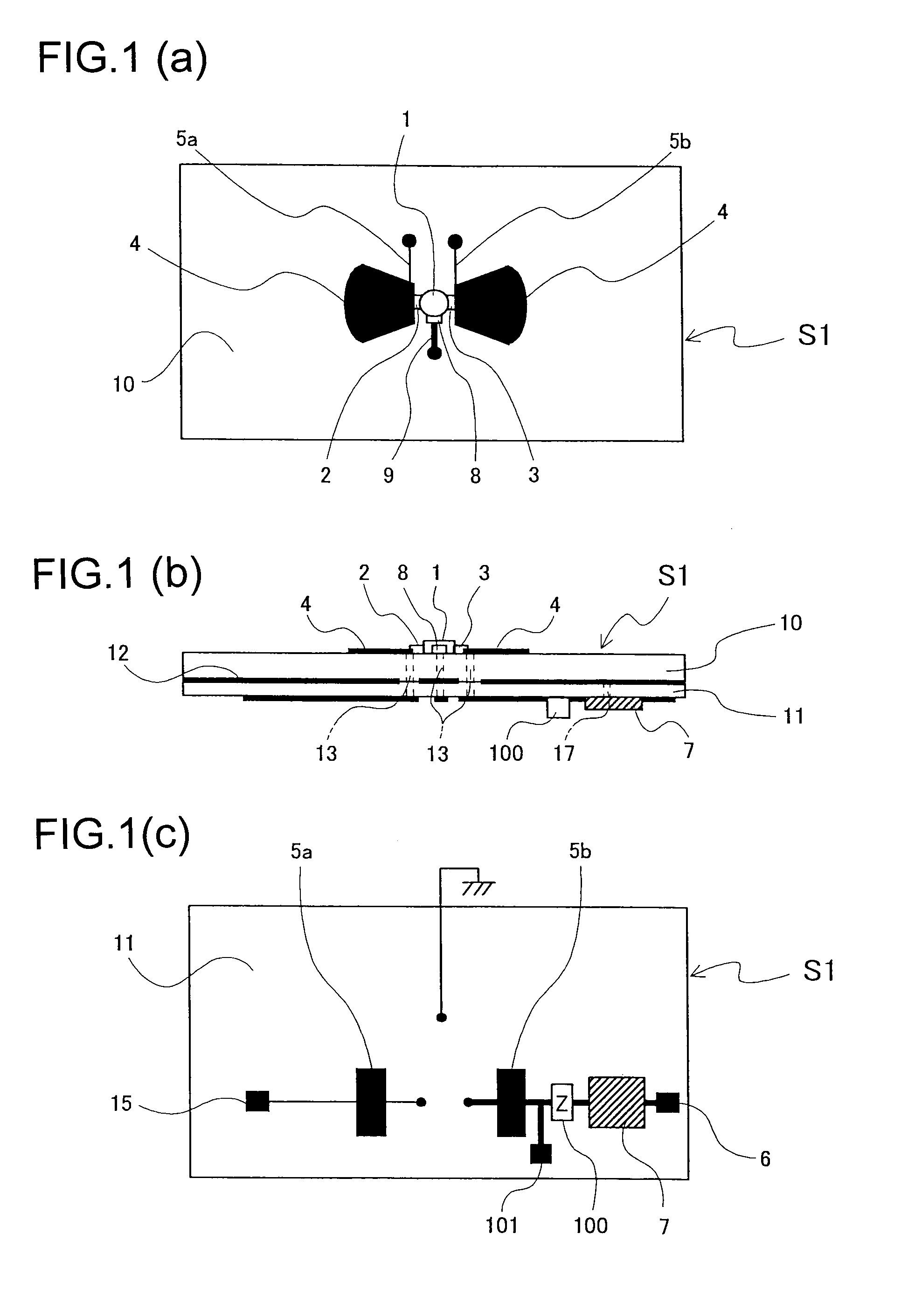
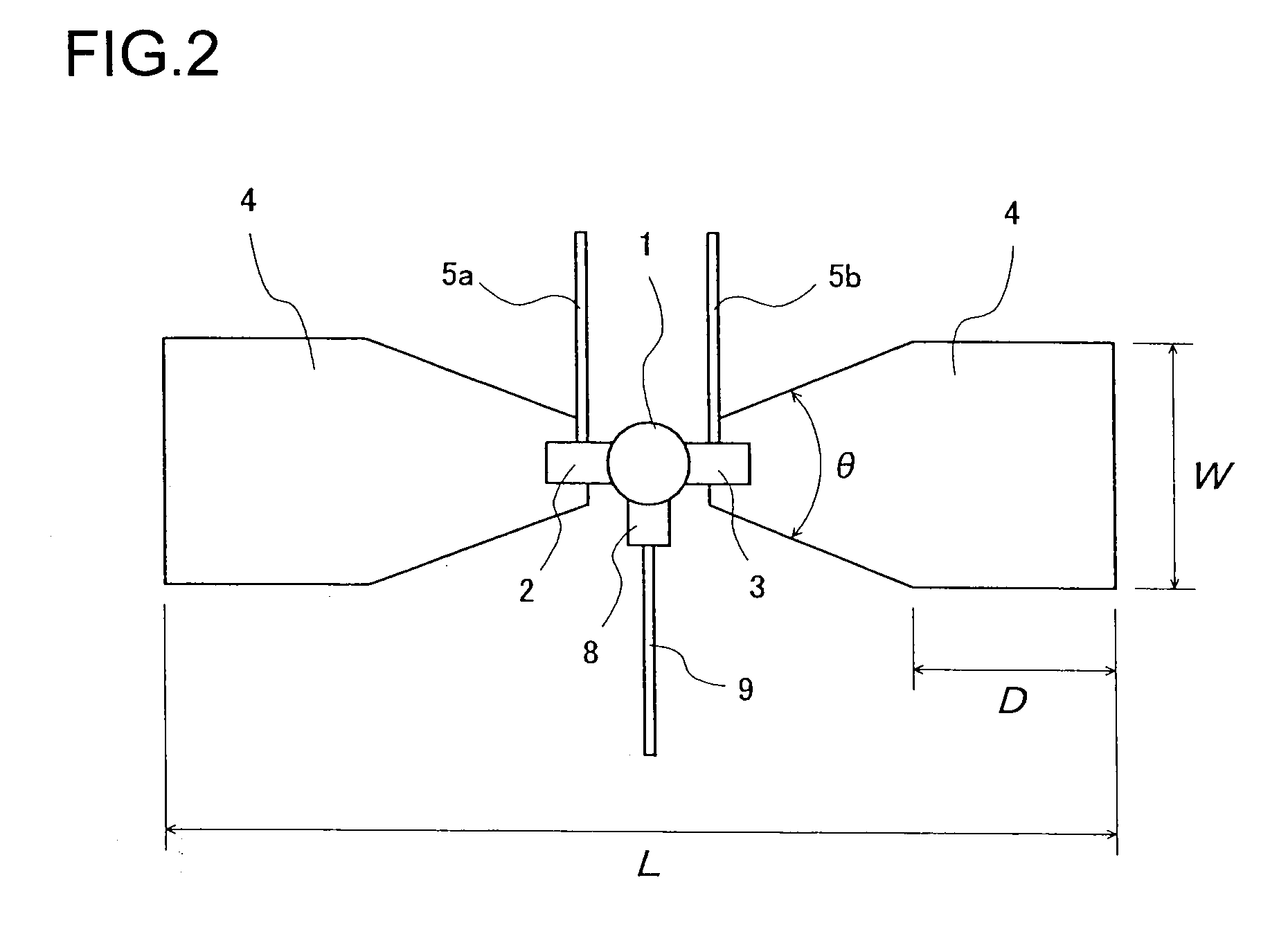
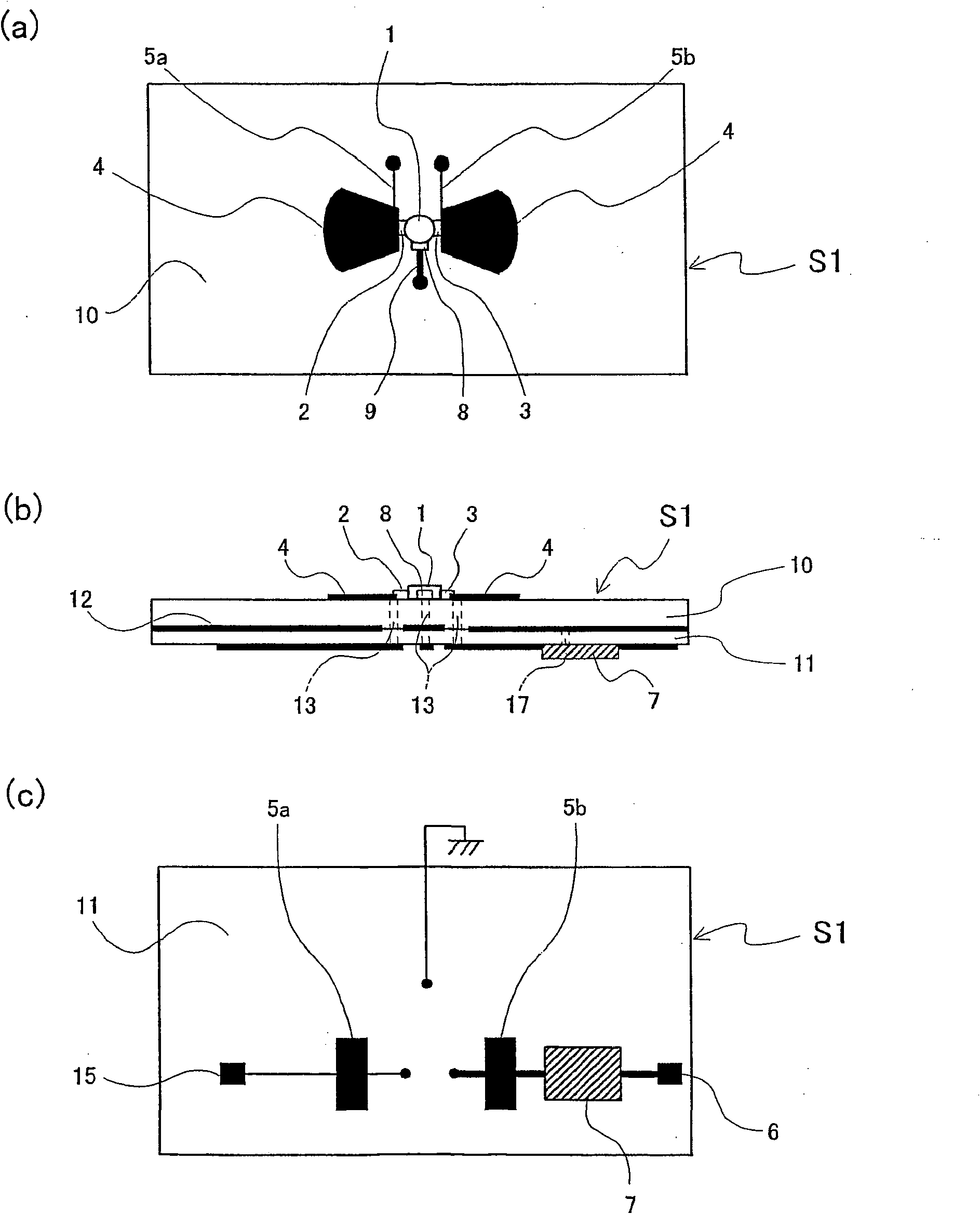
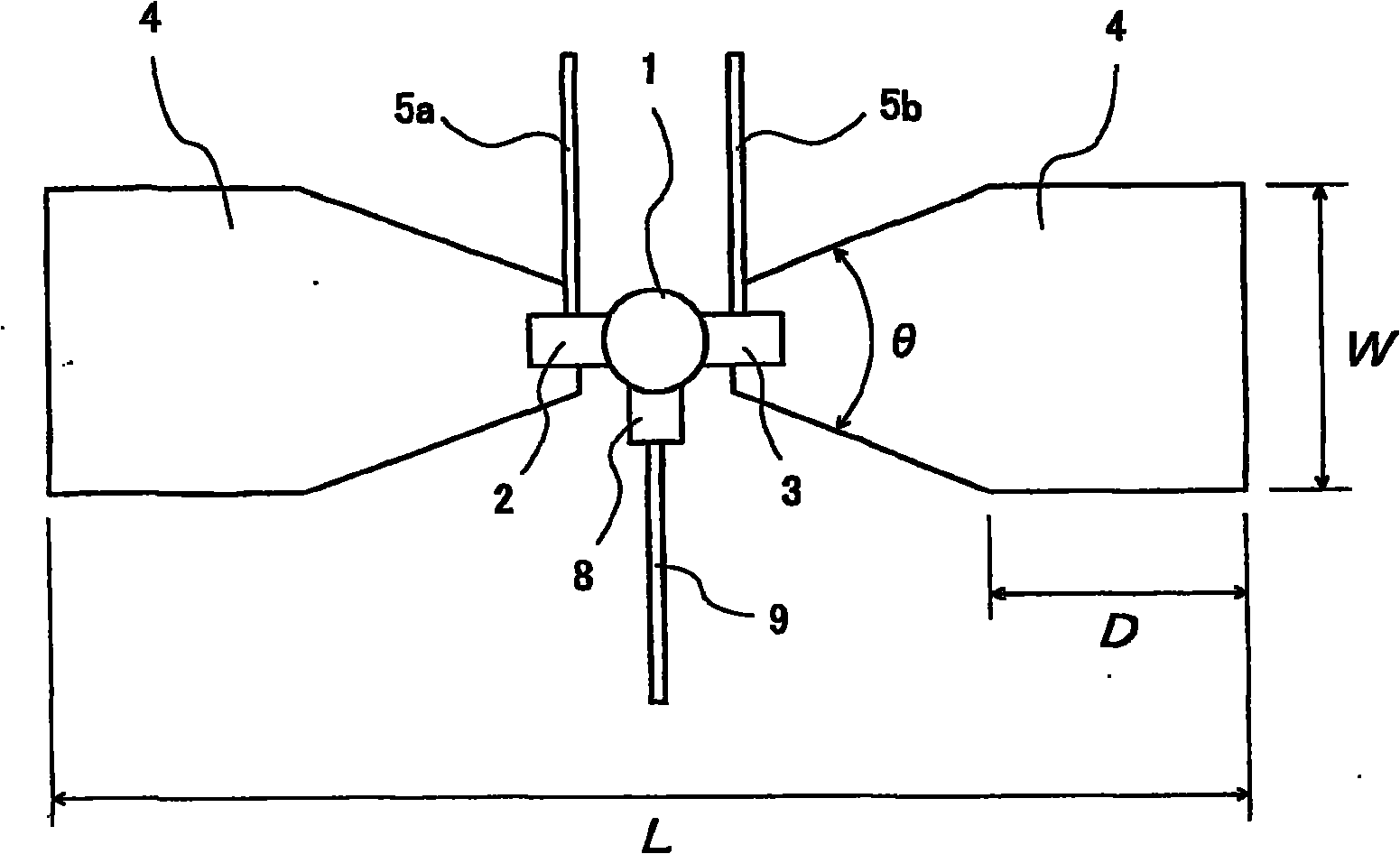
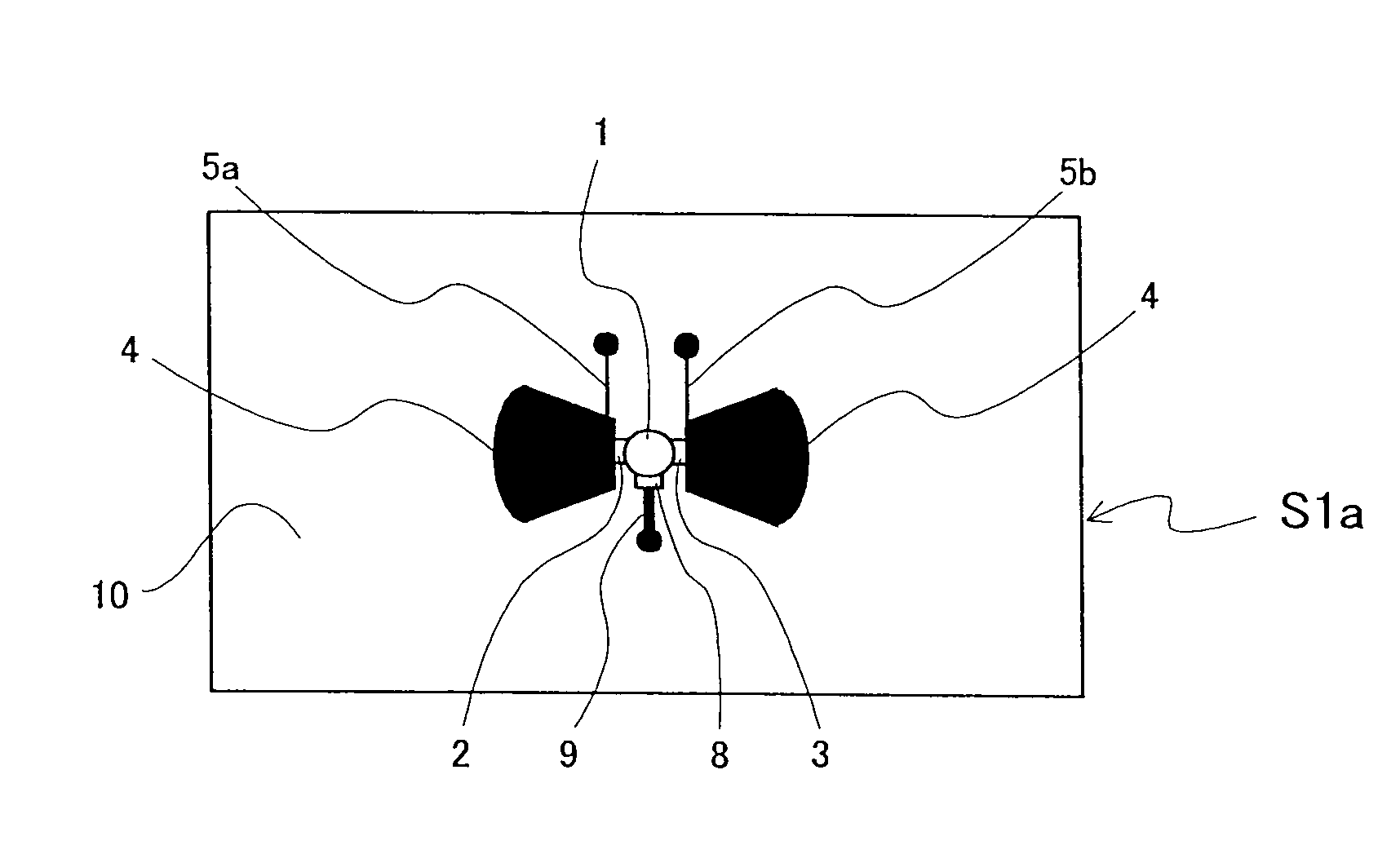
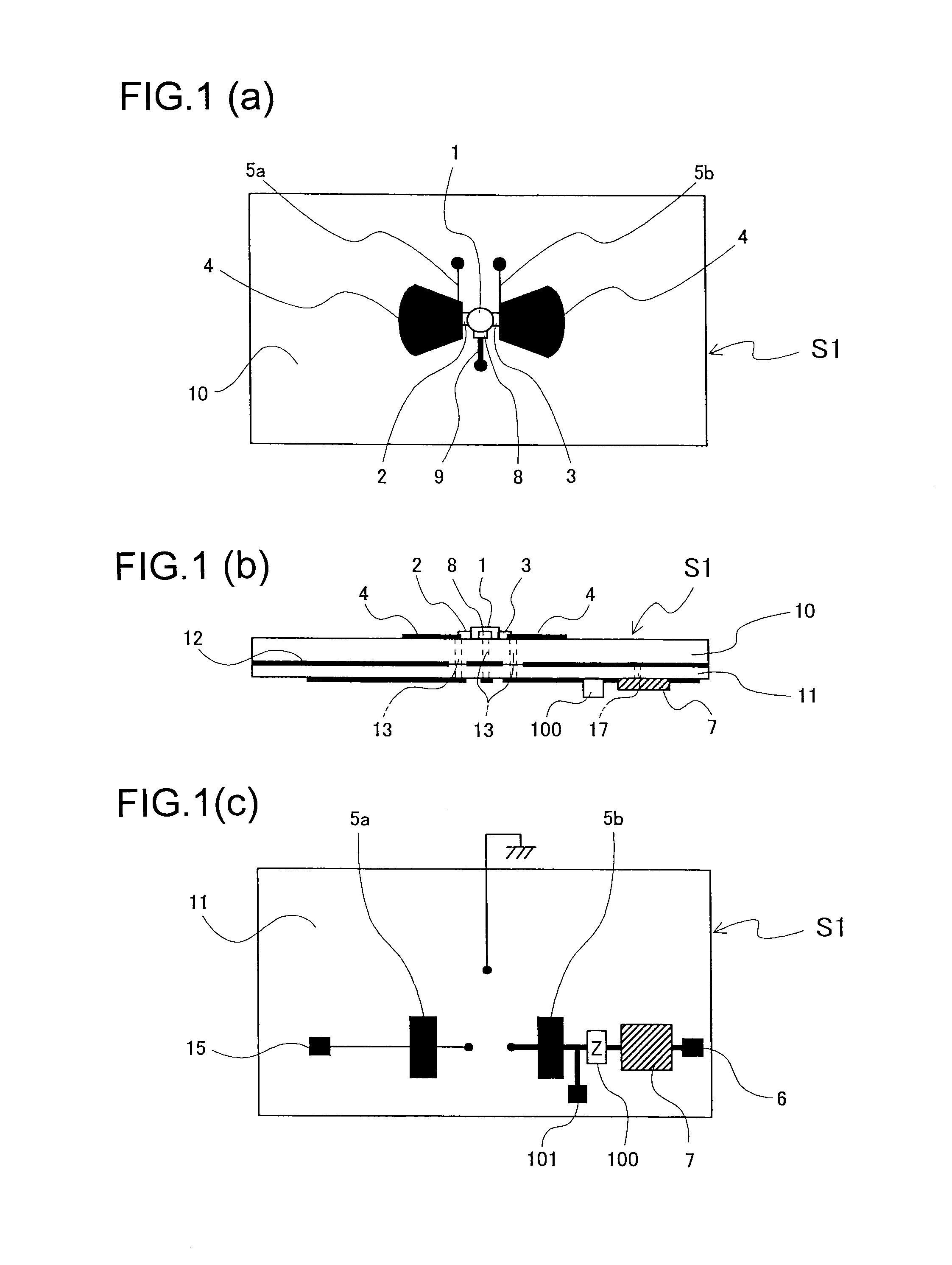
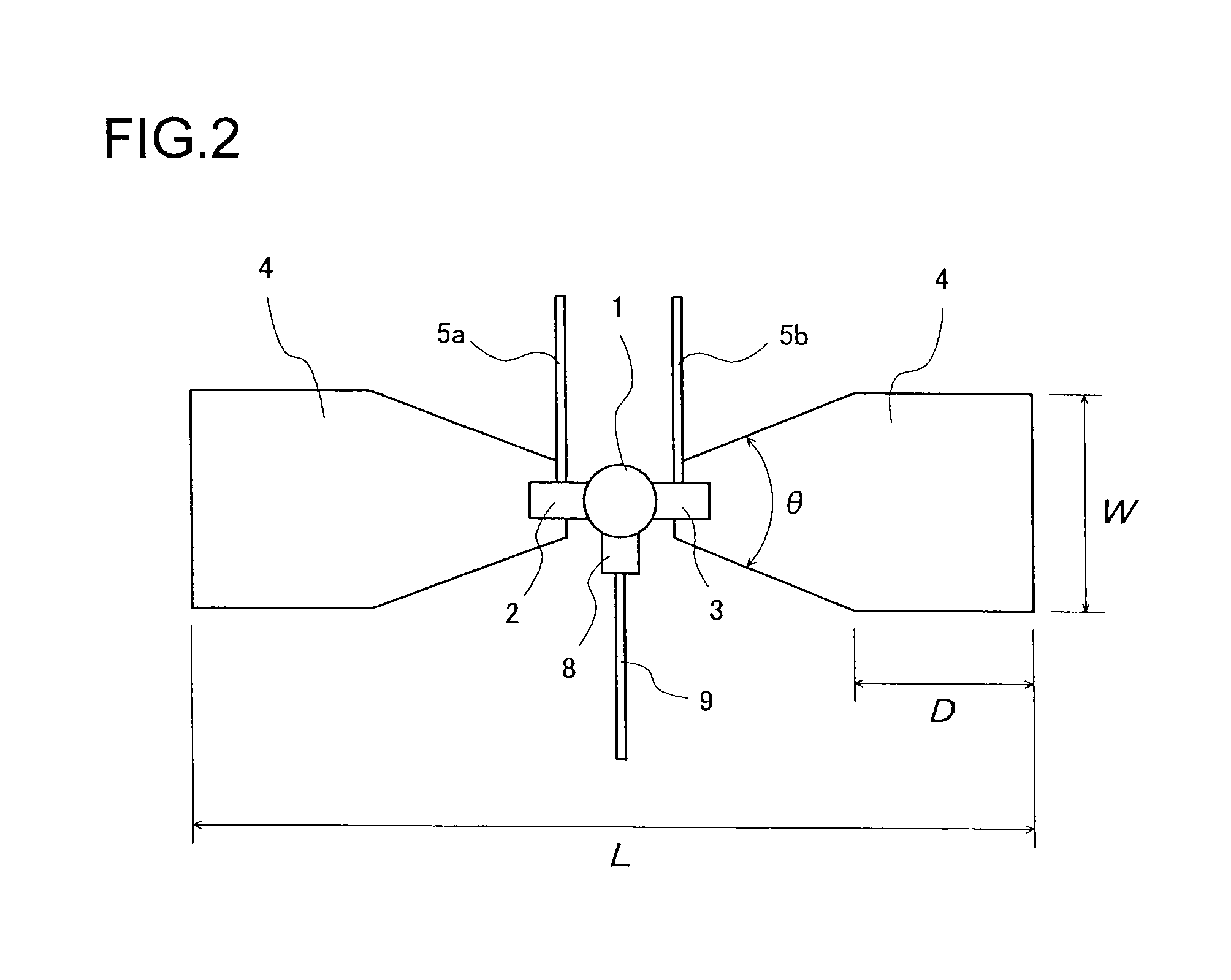
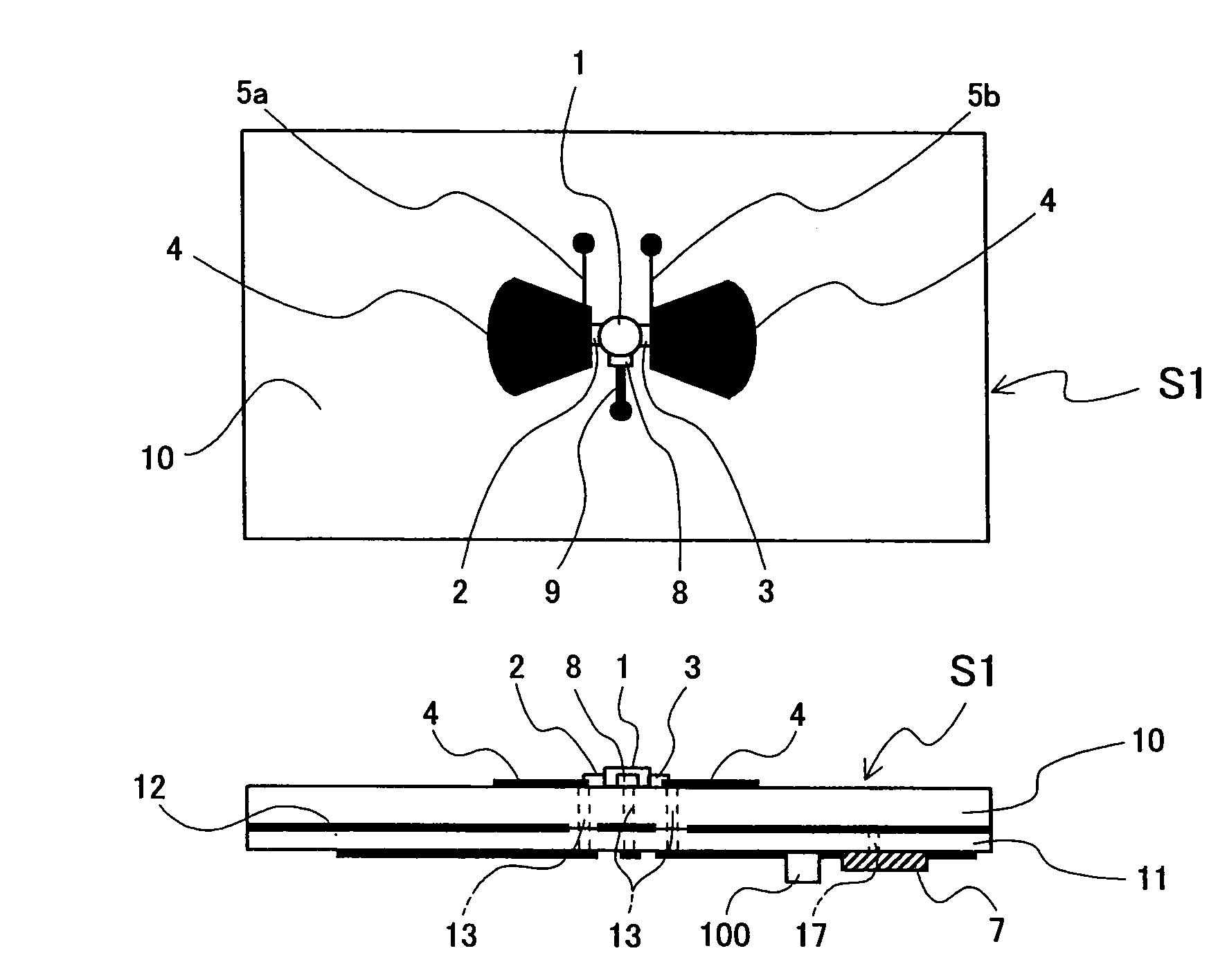
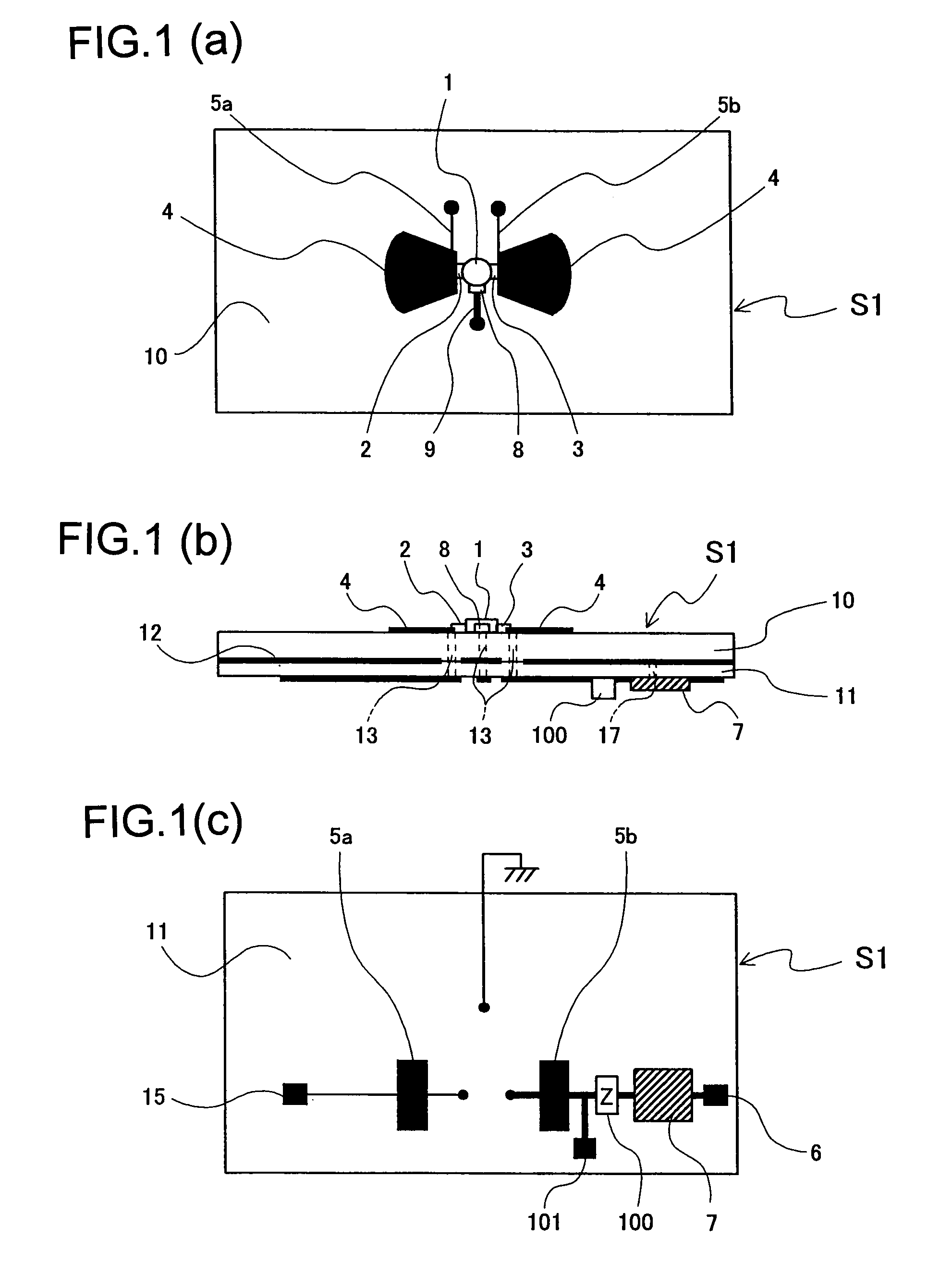
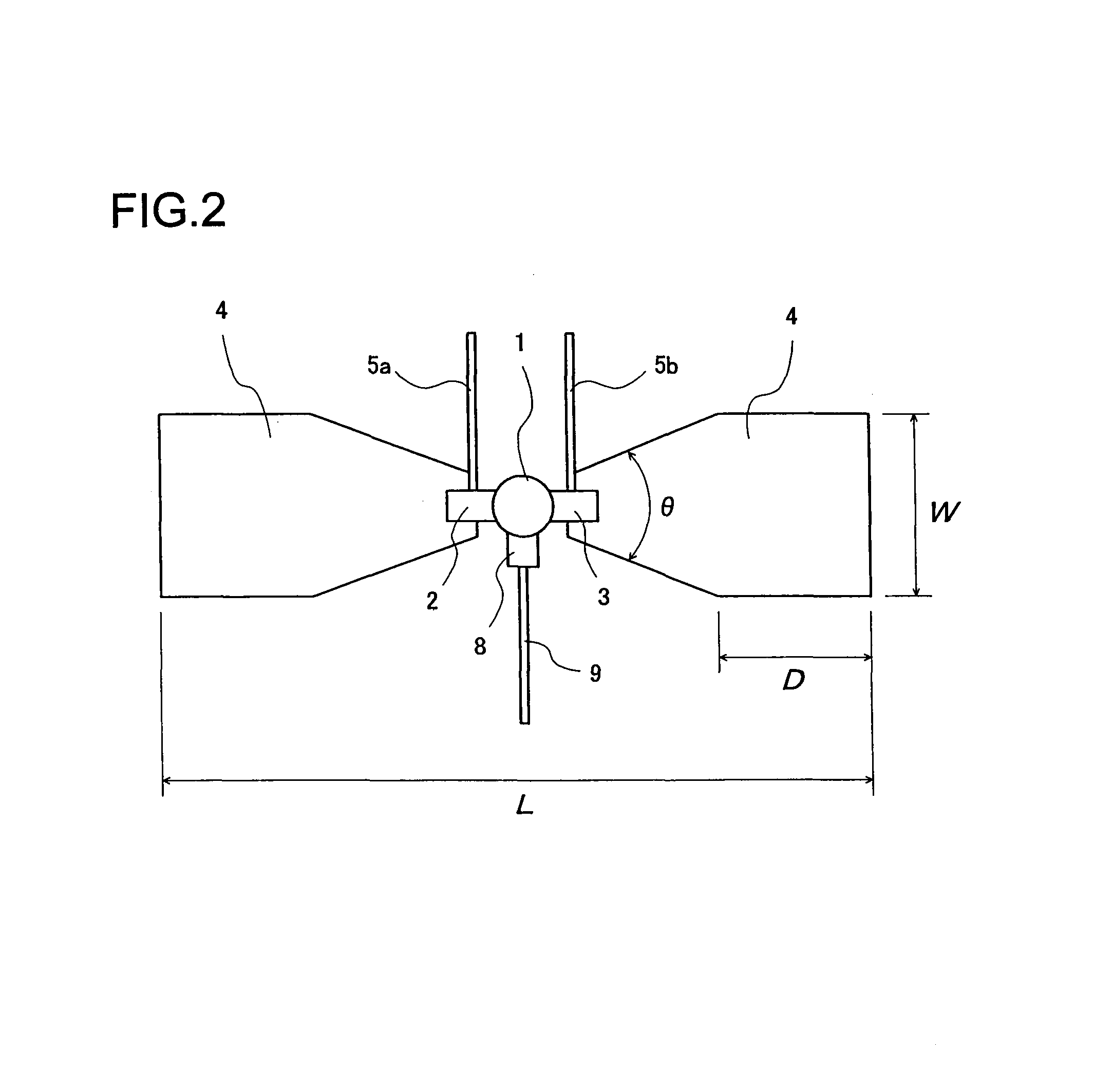
A microwave / millimeter wave sensor apparatus including a planar radiation type oscillator substrate having an inner-layer GND interposed between a front surface side dielectric substrate and a rear surface side dielectric substrate and a pair of conductor patches in an axis-symmetric manner on the side of the front surface layer. A gate and drain of a microwave transistor are respectively connected to the conductor patches to supply power to the gate and the drain of the microwave transistor through a gate-side RF choke circuit and a drain-side RF choke circuit. An impedance line satisfying an oscillation condition is connected to a source and a transmit RF signal in an RF zone as a planar radiation type oscillator is transmitted and a receive RF signal as reflected waves is received from a measured object, thus obtaining an IF signal as the sensing information through homodyne mixing.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH
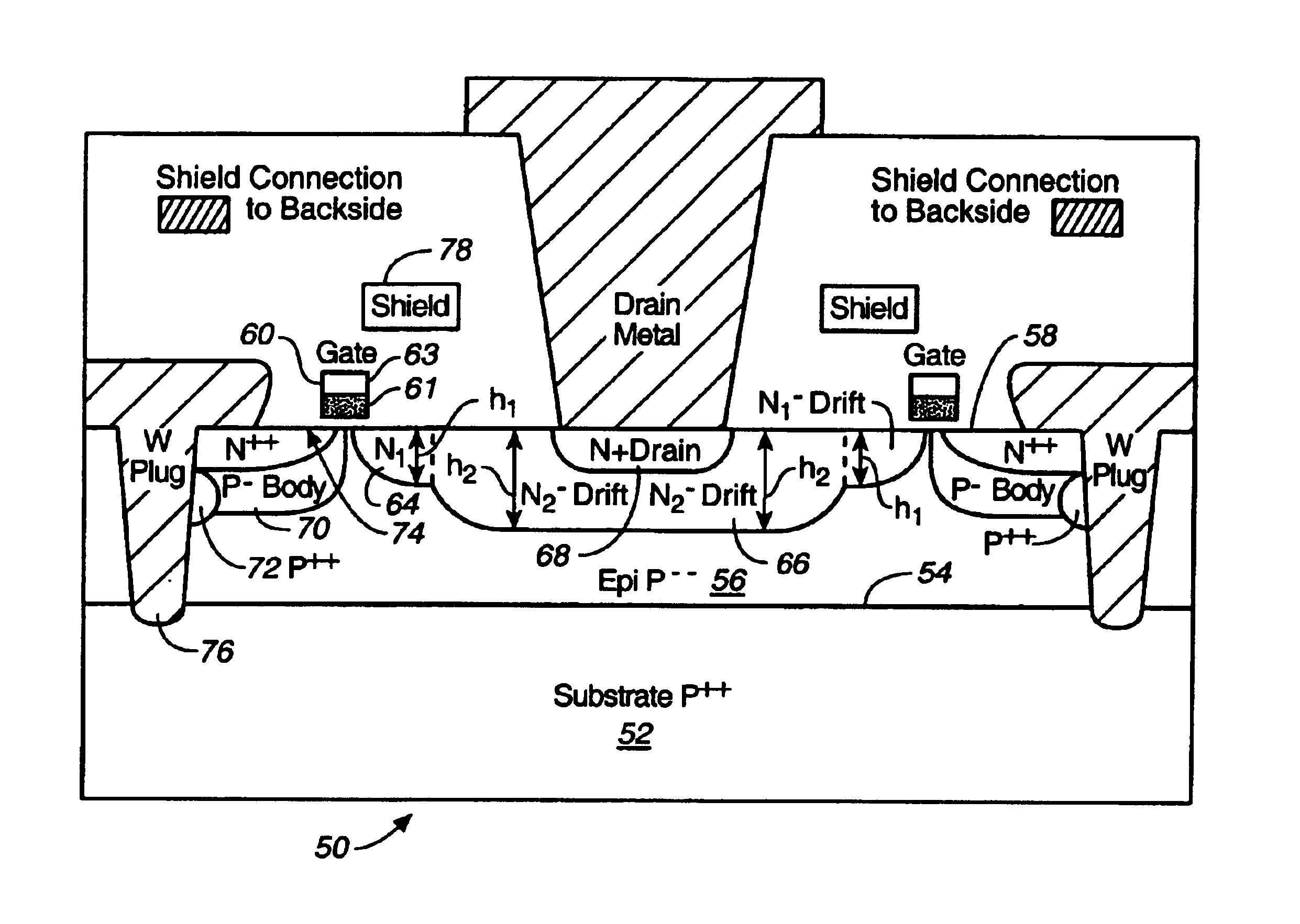
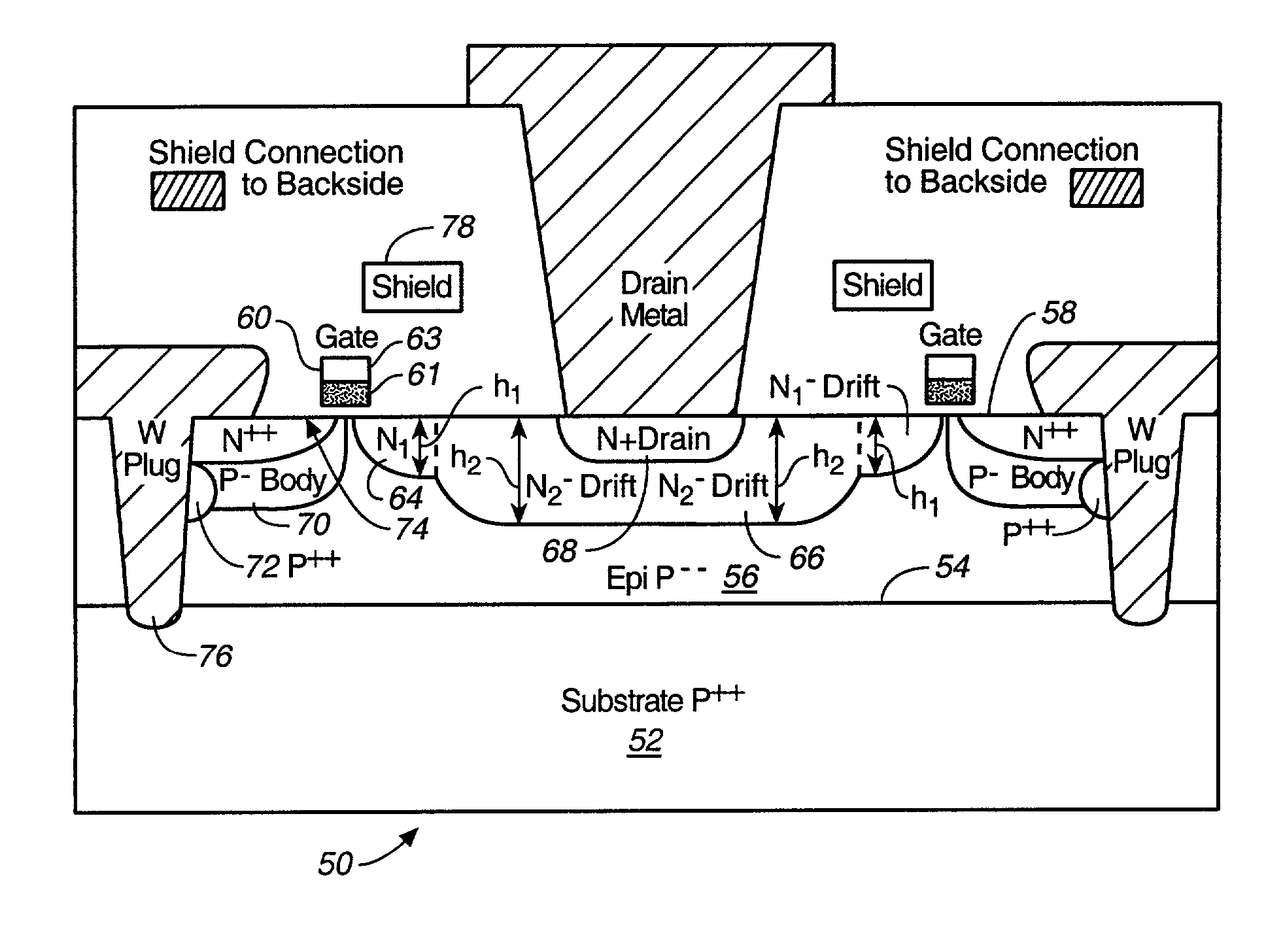
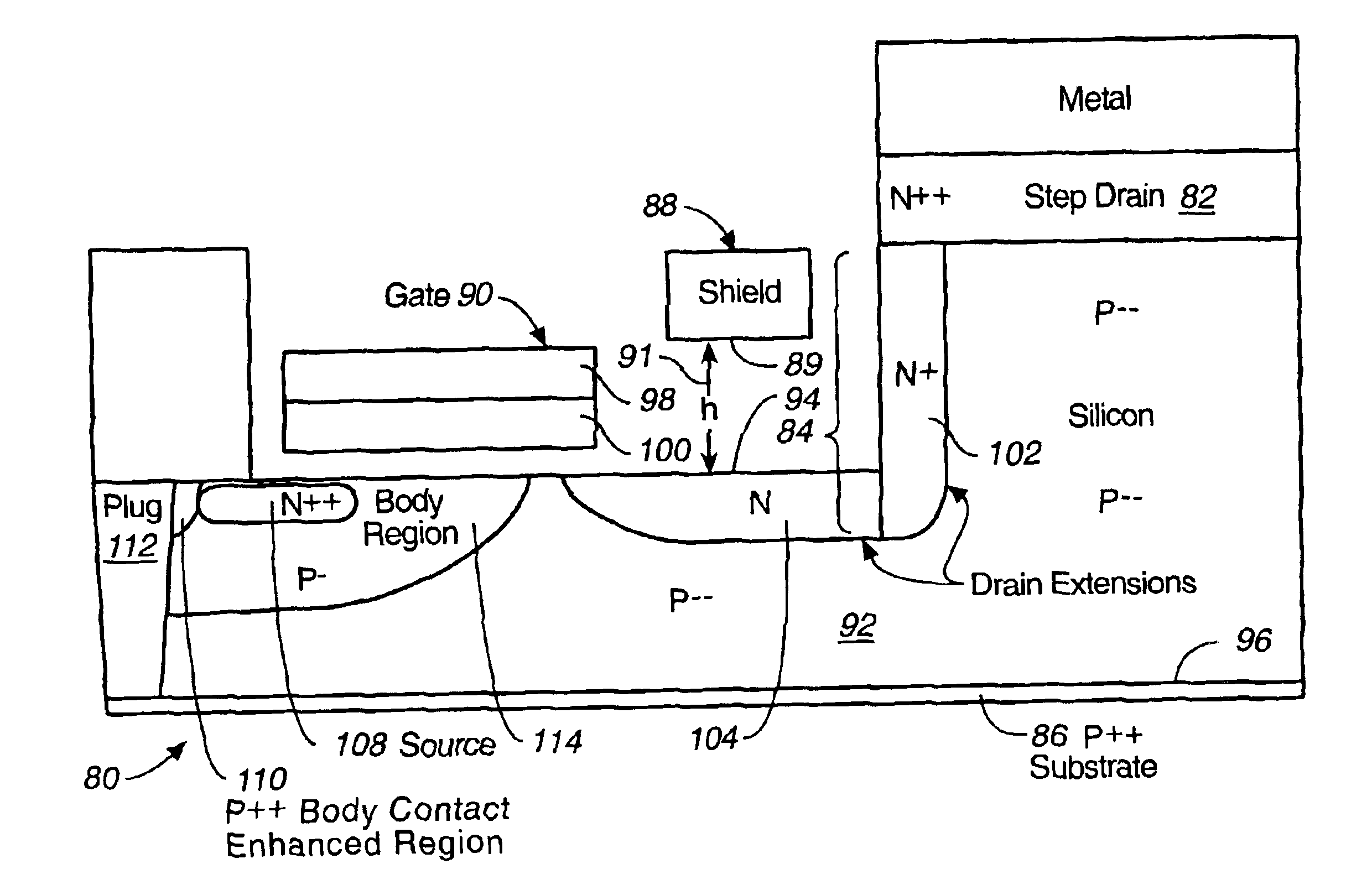
Microwave transistor structure having step drain region
InactiveUS6838731B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDopantMicrowave
A microwave transistor structure having a step drain region comprising: (A) a substrate having a top surface; (B) a silicon semiconductor material of a first conductivity type, having a first dopant concentration and a top surface; (C) a conductive gate overlying and insulated from the top surface of the silicon semiconductor material; (D) at least one horizontal drain extension region of a second conductivity type and having a horizontal drain extension dopant concentration; (E) a step drain region formed in the silicon semiconductor material, and contacting the horizontal drain extension region; (F) a body region of the first conductivity type and having a body region dopant concentration; (G) a source region of the second conductivity type and having a source region dopant concentration; (H) a shield plate region formed on the top surface of the silicon semiconductor material over a portion of the horizontal drain extension region, the shield plate being adjacent and parallel to the horizontal drain extension region; the shield plate being adjacent and parallel to the conductive gate region; and (I) a conductive plug region.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Microwave/millimeter wave sensor apparatus
InactiveCN101680945AImprove conversion efficiencyImprove comprehensivenessOscillations generatorsElectrically short antennasElectricityElectrical conductor
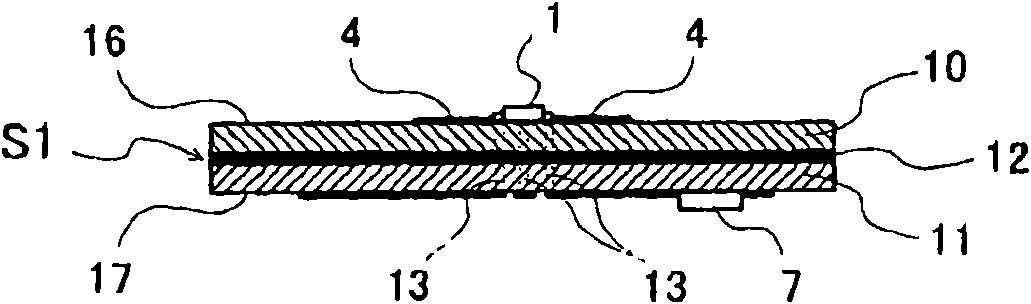
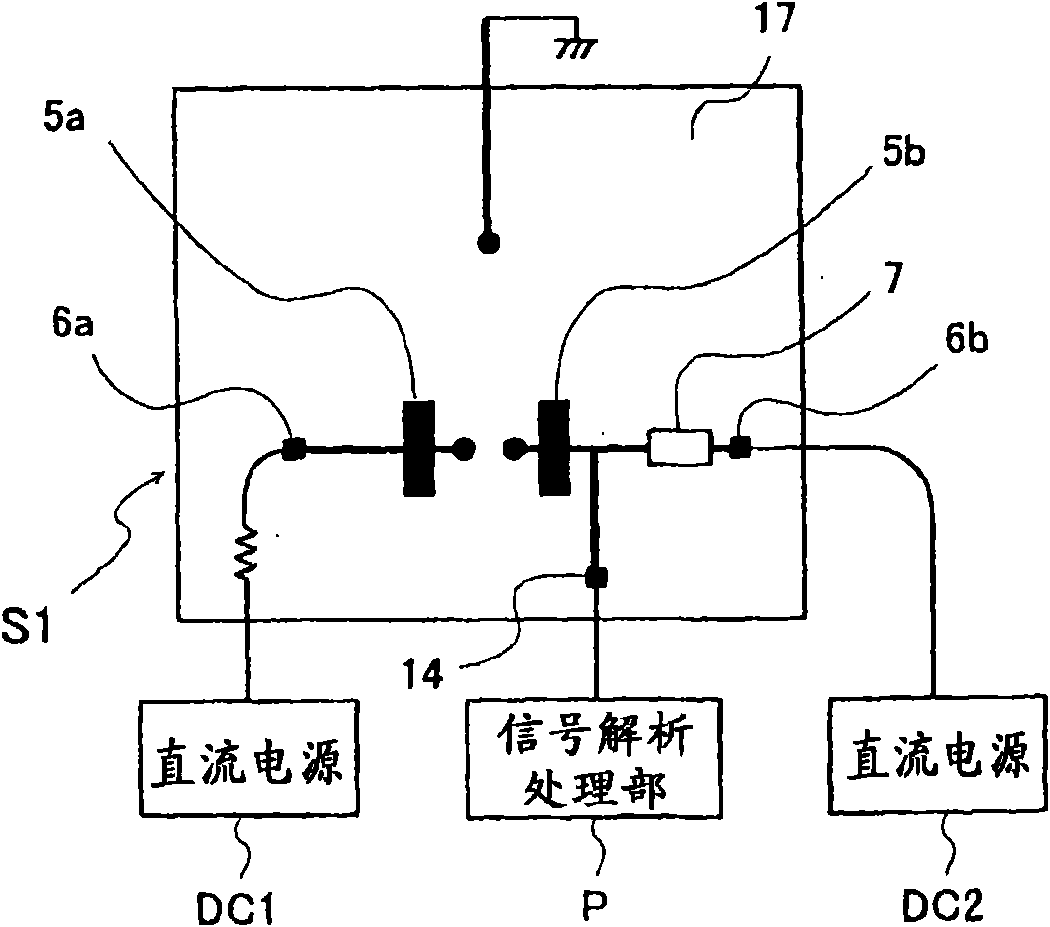
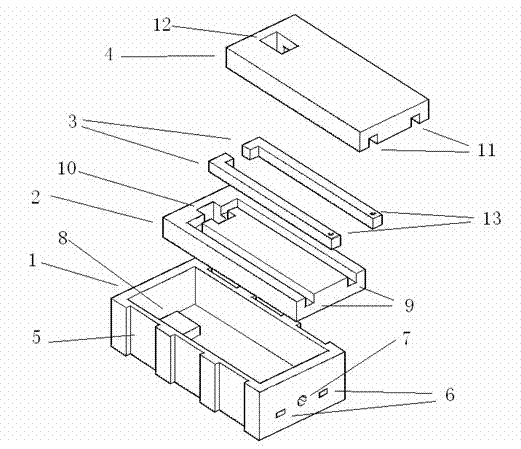
A microwave / millimeter wave sensor apparatus can obtain sensitive detected information while attaining a simple constitution, low costs and high efficiency of power. In the sensor apparatus, a planar radiation type oscillator substrate (S1) having an inner layer GND (12) interposed between a front surface side dielectric substrate (10) and a rear surface side dielectric substrate (11) has a pair of conductor patches (4, 4) axisymmetrically on the side of a front surface layer (16). A gate (2) and a drain (3) of a microwave transistor (1) are respectively connected to the conductor patches (4,4) to supply power to the gate (2) and the drain (3) of the microwave transistor (1) by a gate-side RF choke circuit (5a) and a drain-side RF choke circuit (5b). An impedance line (9) satisfying an oscillation condition is connected to a source (8) to transmit a transmission RF signal in an RF zone as a planar radiation type oscillator and to receive a reception RF signal as reflected waves from a matter to be measured, thus obtaining an IF signal as detected information by homodyne mixing.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH
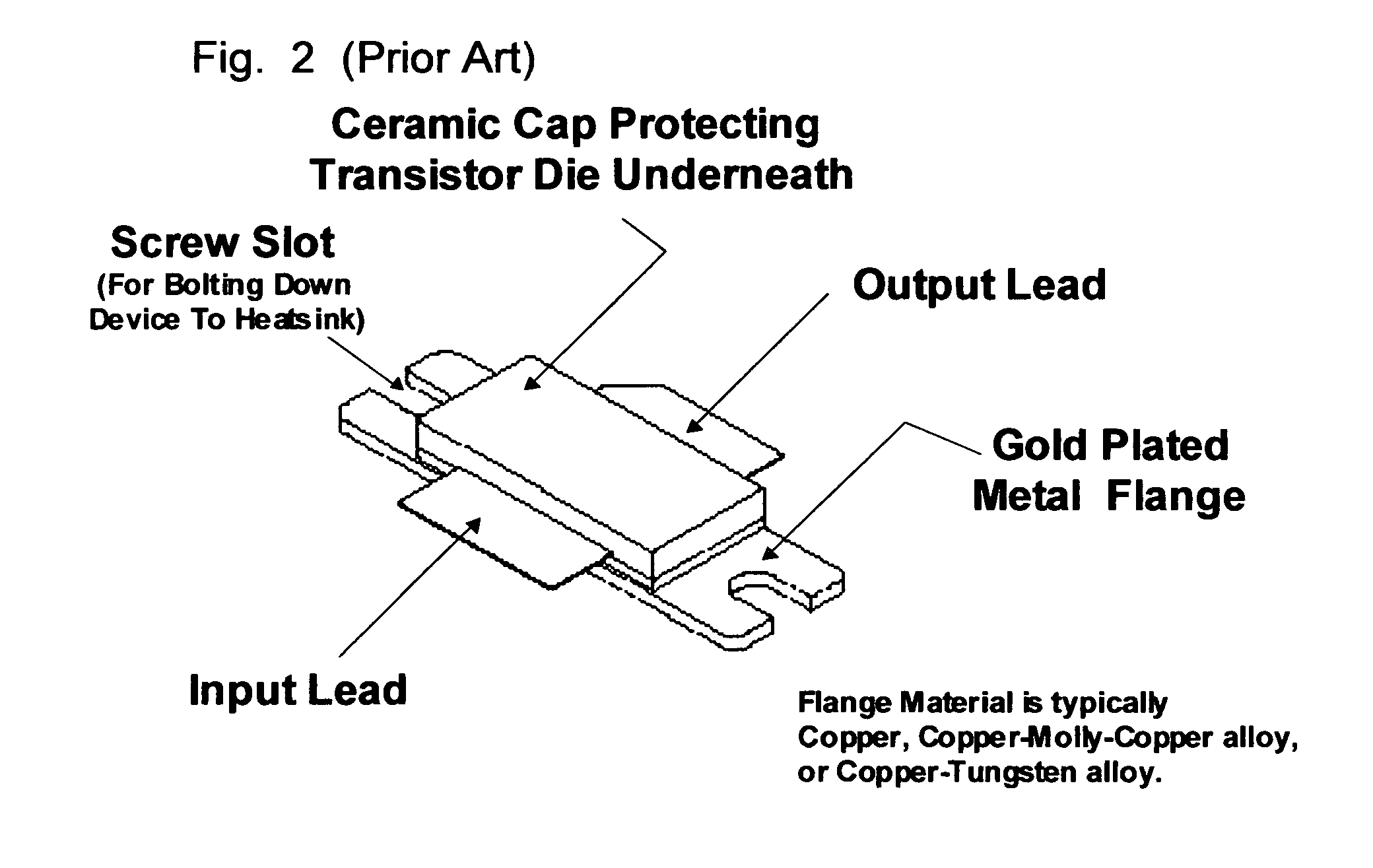
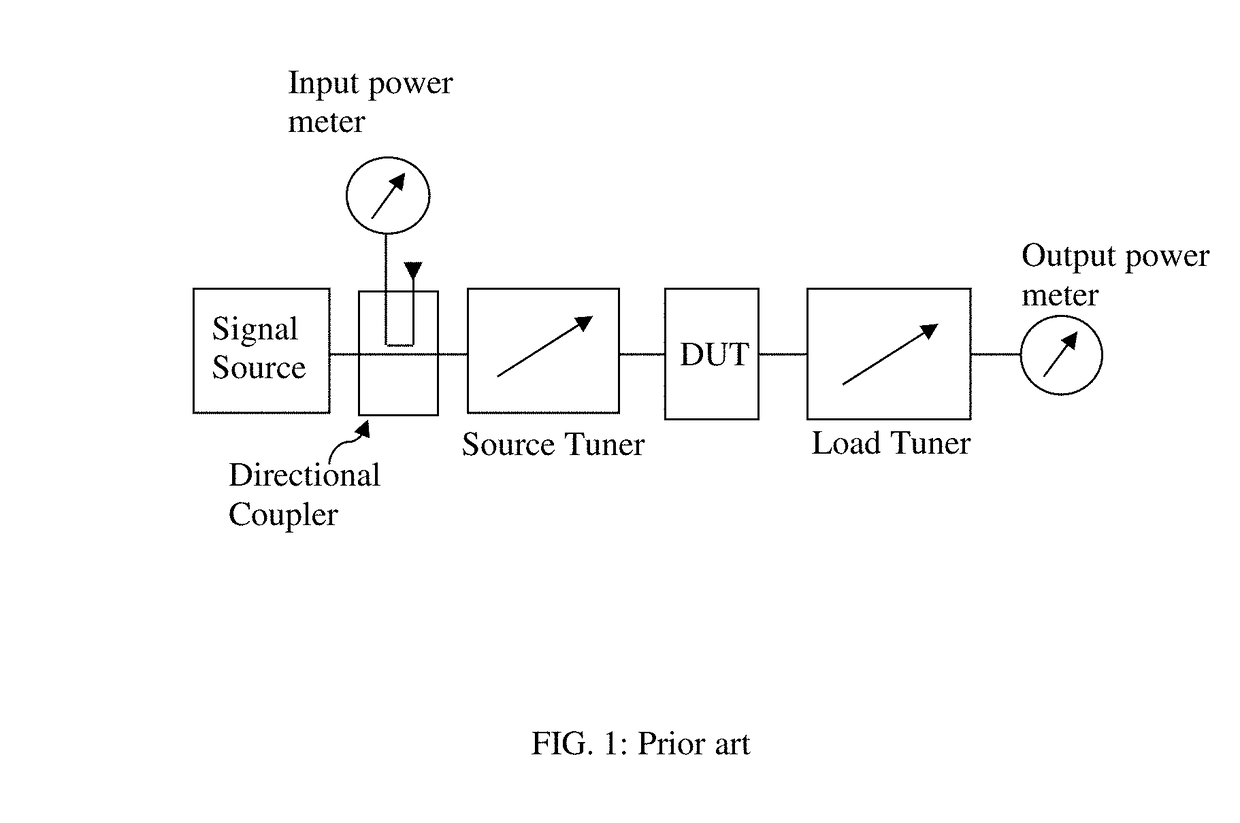
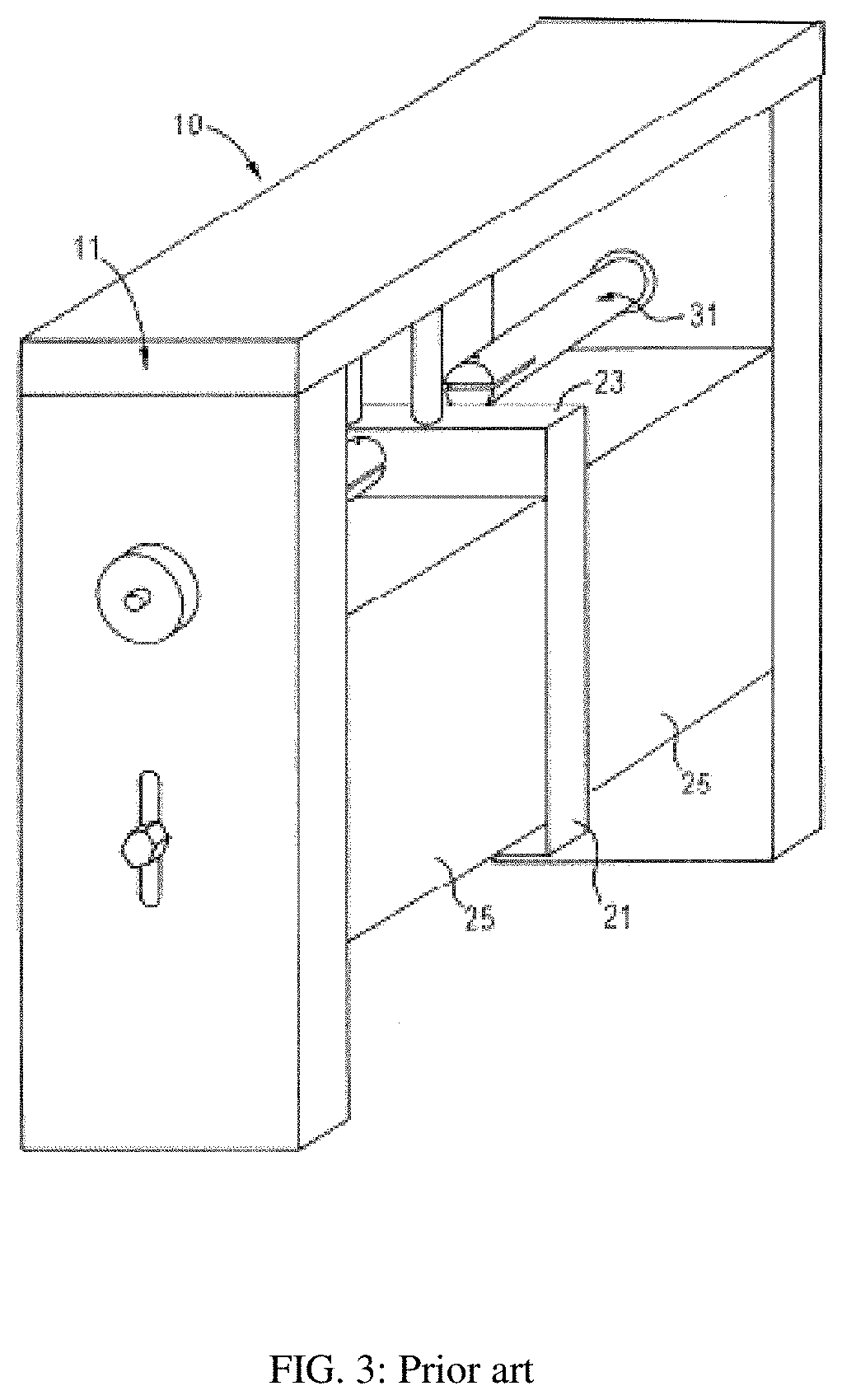
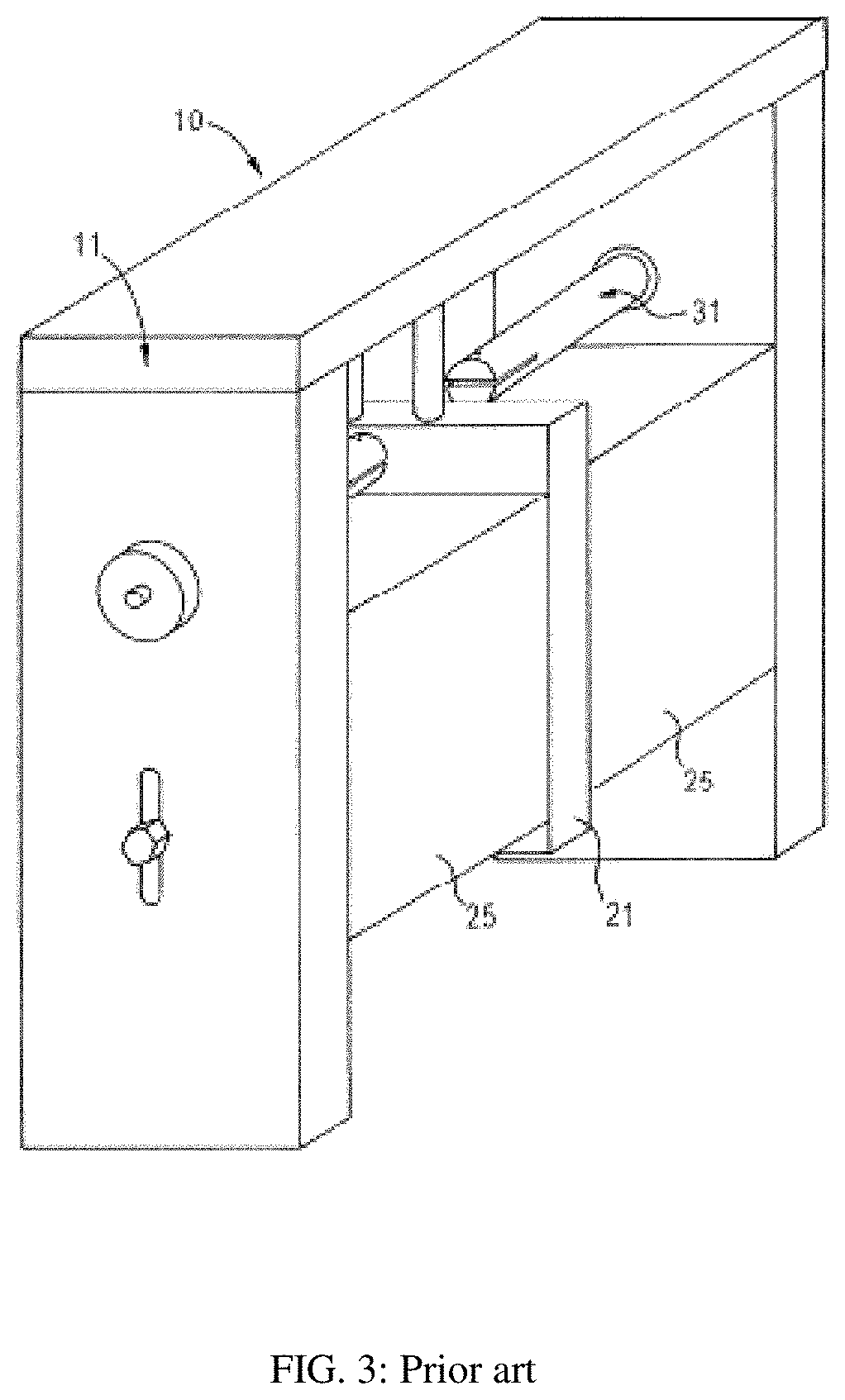
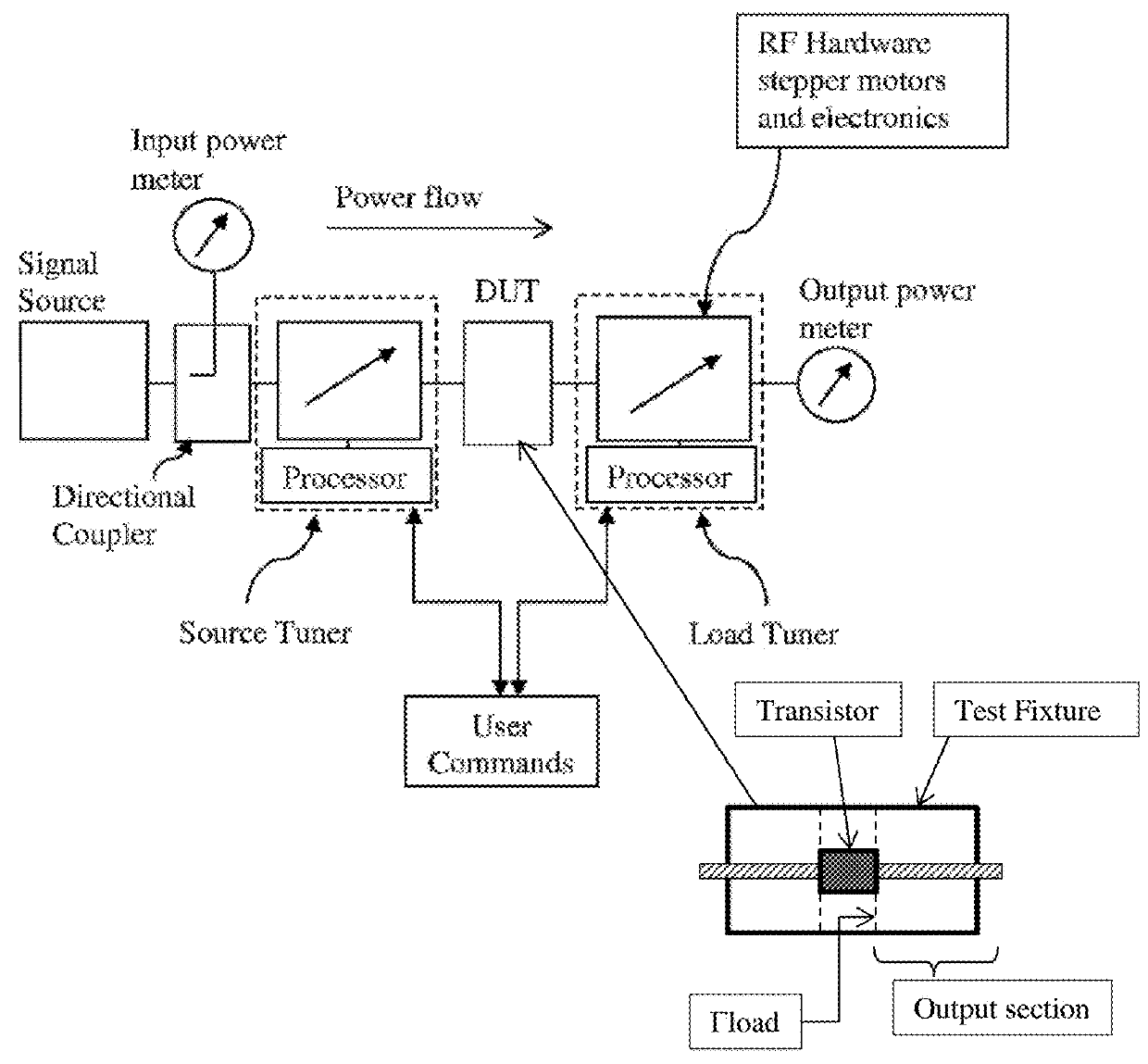
Universal test fixture for high-power packaged transistors and diodes
InactiveUS20110080188A1Maximum heat transferGood thermal contactElectrical measurement instrument detailsFault location by increasing destruction at faultEngineeringThermal contact
A universal test fixture for testing and characterization of high-power flange-packaged RF and microwave transistors and diodes includes a precision-machined heat sink having a built-in center cavity with a finger catch on either side of the cavity which uses a plurality of matching modules that are installed in the center cavity and designed as transistor or diode carrier modules to provide mounting for the high-power packaged RF and microwave devices in a wide variety of flange type packages, an adjustable clamping structure connected to a movable arm, and a plurality of non-conductive high temperature pressure clamps. Each carrier module is made of a gold-plated rectangular aluminum block having a center cavity that is machined to the package outline. A non-conductive black-anodized high-temperature resistant pressure clamp machined to the package outline holds the packaged device in the carrier module. When clamped down using the clamping structure, the pressure clamp holds the package leads on a printed circuit board ensuring excellent electrical contact between package leads and circuit traces and surrounding ground planes, obviating soldering and desoldering the leads to the circuit board. The pressure clamp also produces pressure along the device package to hold the packaged device to the carrier module which houses the device and which itself is bolted to the heat sink resulting in excellent thermal contact under the device.
Owner:AESTECH
Microwave/millimeter wave sensor apparatus
ActiveUS8212718B2Improve directivityHigh detection sensitivityOscillations generatorsElectrically short antennasElectricitySurface layer
A microwave / millimeter wave sensor apparatus including a planar radiation type oscillator substrate having an inner-layer GND interposed between a front surface side dielectric substrate and a rear surface side dielectric substrate and a pair of conductor patches in an axis-symmetric manner on the side of the front surface layer. A gate and drain of a microwave transistor are respectively connected to the conductor patches to supply power to the gate and the drain of the microwave transistor through a gate-side RF choke circuit and a drain-side RF choke circuit. An impedance line satisfying an oscillation condition is connected to a source and a transmit RF signal in an RF zone as a planar radiation type oscillator is transmitted and a receive RF signal as reflected waves is received from a measured object, thus obtaining an IF signal as the sensing information through homodyne mixing.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH
Pulse radar device
ActiveUS20110260906A1Low costQuality improvementElectrically short antennasSlot antennasElectrical resistance and conductanceResonant cavity
A radiation type oscillator including a radiation type oscillator substrate including a microwave transistor for generating negative resistance by short-duration operation and a resonant cavity structure; a high-frequency pulse signal of an oscillation frequency / frequency bandwidth determined by negative resistance produced by the short-duration operation of the microwave transistor and the resonant cavity structure is generated as a transmitted RF signal and simultaneously radiated into space. The radiation type oscillator performs oscillating operation when a received RF signal that is a reflected wave of the transmitted RF signal from an object of detection enters the radiation type oscillator, an IF signal is acquired from an IF signal output terminal owing to homodyne mixing by the radiation type oscillator itself, and this is analyzed and processed to detect the object of detection.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH +1
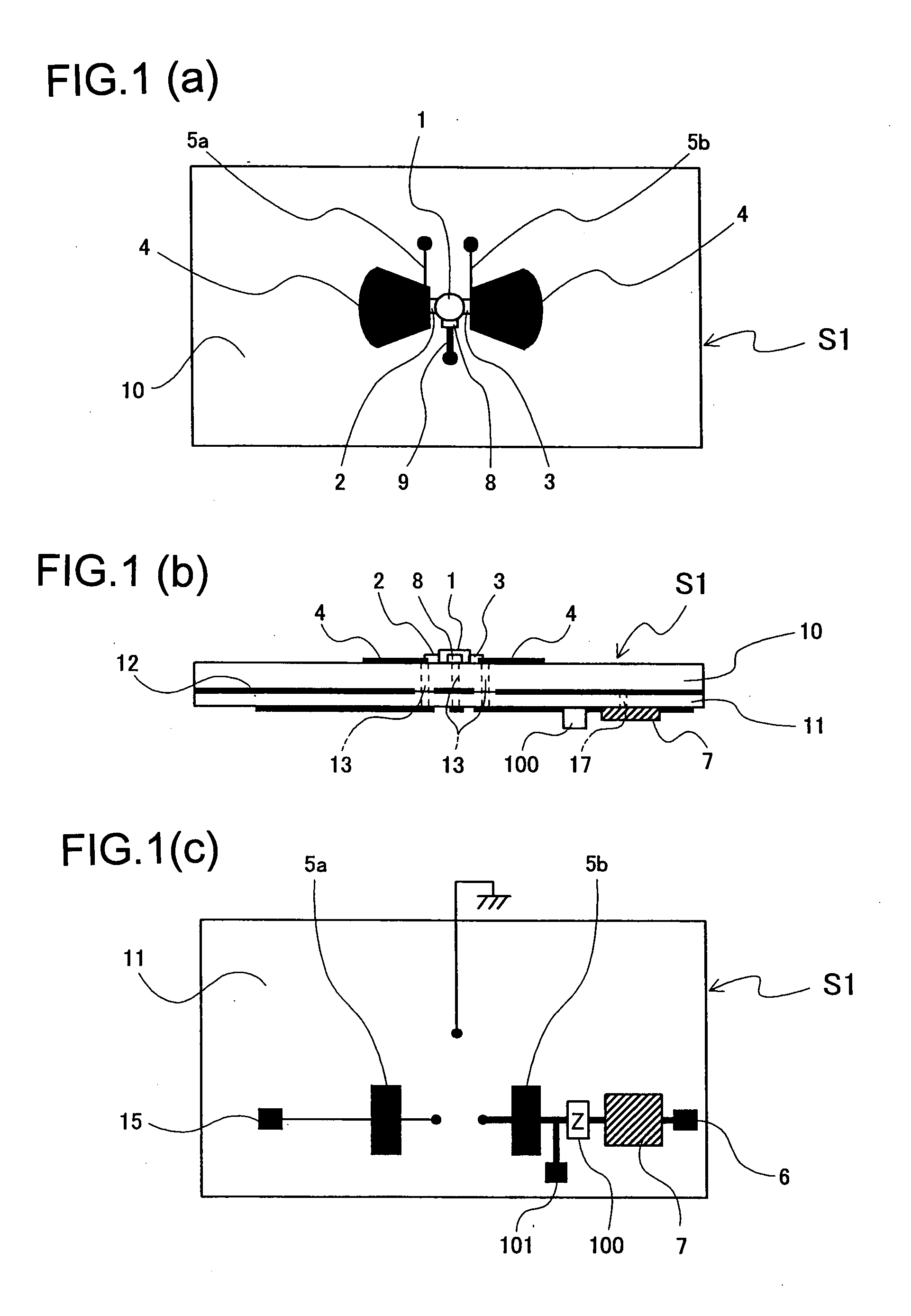
Pulse signal generation device
ActiveCN102210060AImprove yieldImprove reliabilitySimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsElectrical conductorDielectric substrate
Provided is a microwave-, milliwave-band, high-frequency pulse signal generation device which makes it possible to achieve a simpler structure, improved performance, smaller integration, easier design, lower power consumption, and lower cost. A planar radiation oscillator substrate (S1) having an inner layer (GND12) interposed between a front dielectric substrate (10) and a back dielectric substrate (11) is provided with a pair of axially-symmetrical conductive patches (4, 4) in the radiating surface. A gate electrode (2) and a drain electrode (3) of a microwave transistor (1) are connected to each of the conductive patches (4, 4). A DC bias is supplied through an RF choke circuit (5a) to the gate electrode (2). A monopulse is supplied from a monopulse generation circuit (7) through an RF choke circuit (5b) to the drain electrode (3). An impedance line (9) which satisfies the oscillation conditions is connected to a source electrode (8). A high-frequency pulse signal, having an oscillation frequency and frequency bandwidth which are determined on the basis of the negative resistance generated by the short-time operation of the microwave transistor (1) and a resonant cavity structure, radiates into space simultaneous to being generated.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH +1
Hybrid microwave integrated circuit
ActiveUS7391067B1Less power capabilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsAudio power amplifierMicrowave
An integrated microwave transistor amplifier includes a AlGaN / GaN active transistor arrangement on a thinned Si 1-mil heat spreader. Elongated, plated-through vias extend from the source portions of the transistor arrangement through the spreader to a thick gold supporting layer. A matching circuit is defined on a four-mil GaAs substrate, also with a thick gold support layer. A stepped heat sink supports the matching circuit and the active transistor with surfaces coplanar. Bond wires interconnect the matching circuit with the gate or drain connections of the transistor.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Pulse wireless communication device
ActiveUS20110255634A1Simple structureLow costWaveguide hornsEnergy efficient ICTCommunication deviceWireless communication systems
To provide a microwave / milliwave UWB pulse wireless communication device that enables realization of structural simplification, high performance, compact integration, easy design, low power consumption, and low cost. A radiation type oscillator is configured by a radiation type oscillator substrate S1 equipped with a microwave transistor 1 for generating negative resistance by short-duration operation and a resonant cavity structure, a high-frequency pulse signal of an oscillation frequency / frequency bandwidth determined based on negative resistance produced by the short-duration operation of the microwave transistor 1 and the resonant cavity structure is generated as a transmitted RF signal and simultaneously radiated into space, and the radiation type oscillator is caused to perform oscillating operation when a received RF signal arriving from an external wireless communication device enters the radiation type oscillator, whereby a received data signal is established based on acquisition of an IF signal owing to mixing by the radiation type oscillator itself.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH +1
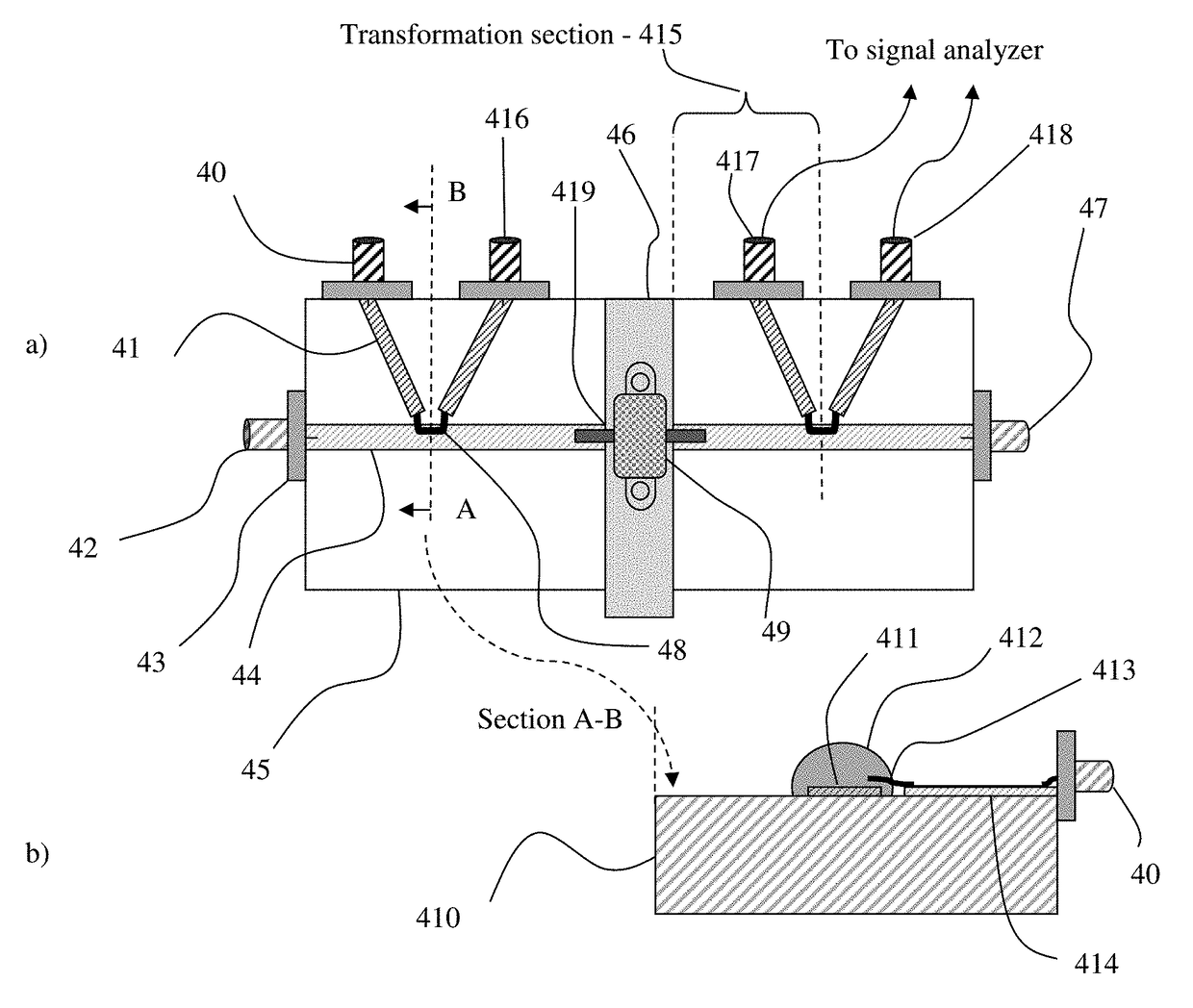
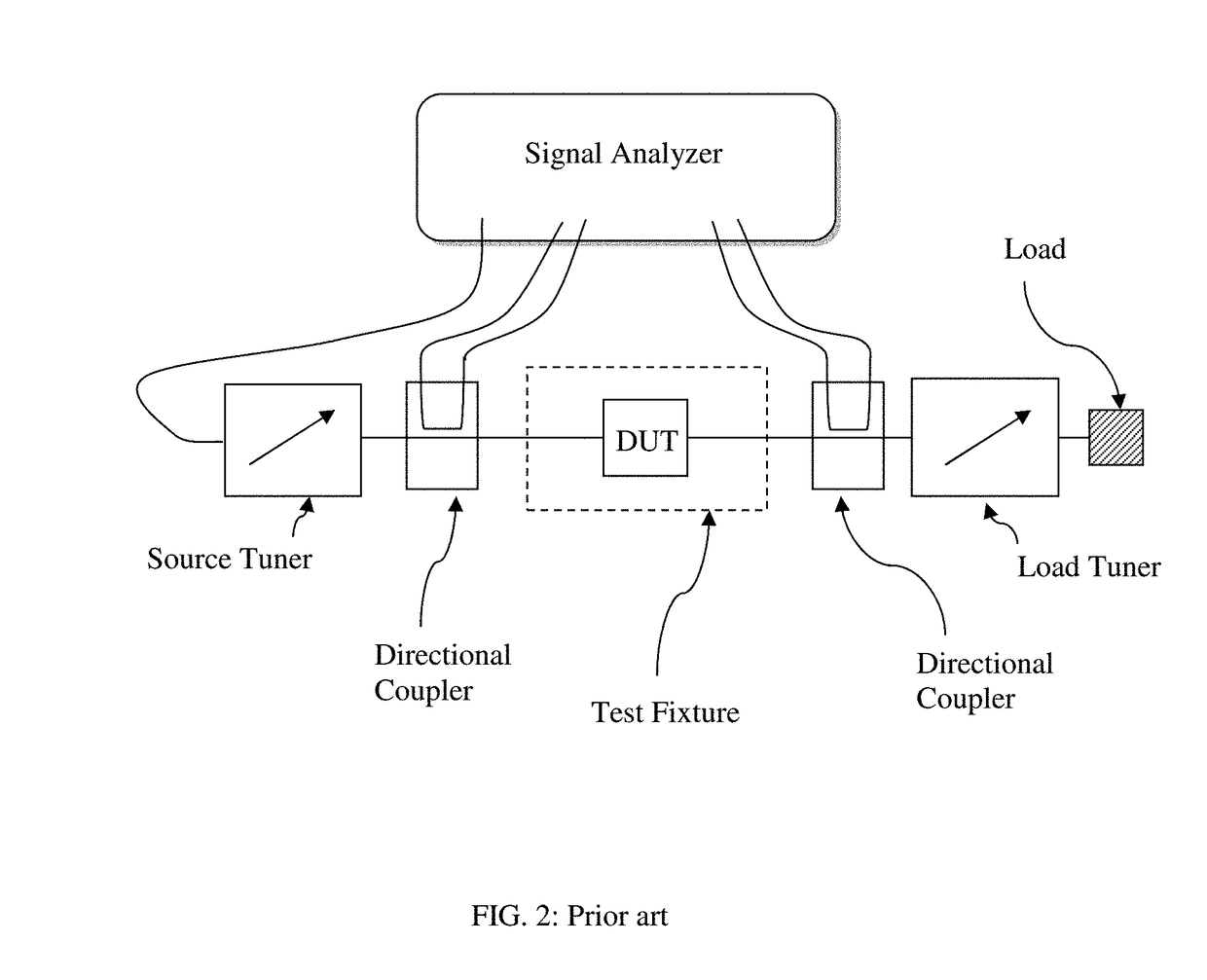
Transistor test fixture with integrated couplers and method
ActiveUS10001521B1Electrical measurement instrument detailsMaterial analysis using microwave meansCoaxial cableHarmonic
Microwave transistor test fixtures, both micro-strip and coaxial, include integrated wideband directional signal sensors / couplers and allow the detection of the main signal and its harmonic components, injected into and delivered by a transistor in high power operation mode, by using a phase-calibrated network or signal analyzer and allows this way the reproduction of real time signal waveforms. The fixtures are best calibrated using equivalent TRL calibrated fixtures allowing overcoming the incompatibility of the internal ports connecting to the transistor terminals with coaxial cables attached to VNA.
Owner:TSIRONIS CHRISTOS
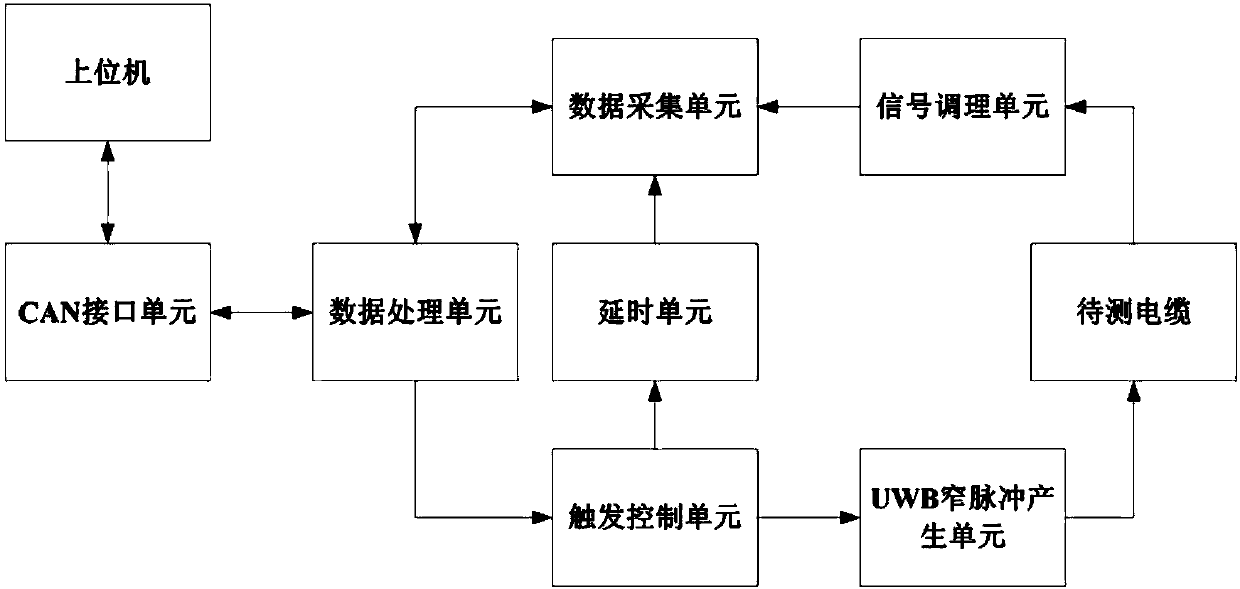
Airplane cable fault locating device
InactiveCN107861027AShort lifeRapid positioningFault location by conductor typesFault location by pulse reflection methodsEnvironmental noiseEngineering
The invention provides an aircraft cable fault location device, comprising a data processing unit, a trigger control unit, a UWB narrow pulse generating unit, a signal conditioning unit, a delay unit, a data acquisition unit and a CAN interface unit; the UWB narrow pulse generating unit Utilizing the avalanche switching characteristics of the microwave transistor working in the avalanche area, combined with the basic working principle of the MARX circuit, a narrow pulse transmitting signal with ns level rising edge is generated and sent to the cable to be tested. The invention utilizes the low-voltage pulse reflection method to inject narrow-band pulses into the cable to be tested, adopts equivalent sampling to collect the pulse echo signal, and processes the collected data through DSP to realize fast and accurate positioning of the fault point of the cable to be tested, so as to reduce maintenance work The number of wrong disassembly and assembly in the cable can avoid the reduction of cable life due to wrong disassembly and assembly, and it will not be disturbed by environmental noise.
Owner:HUZHOU YOUCHUANG TECH CO LTD
Universal test fixture for high-power packaged transistors and diodes
InactiveUS7982477B2High temperature resistance pressureGood thermal contactElectrical measurement instrument detailsFault location by increasing destruction at faultEngineeringThermal contact
A universal test fixture for testing and characterization of high-power flange-packaged RF and microwave transistors and diodes includes a precision-machined heat sink having a built-in center cavity with a finger catch on either side of the cavity which uses a plurality of matching modules that are installed in the center cavity and designed as transistor or diode carrier modules to provide mounting for the high-power packaged RF and microwave devices in a wide variety of flange type packages, an adjustable clamping structure connected to a movable arm, and a plurality of non-conductive high temperature pressure clamps. Each carrier module is made of a gold-plated rectangular aluminum block having a center cavity that is machined to the package outline. A non-conductive black-anodized high-temperature resistant pressure clamp machined to the package outline holds the packaged device in the carrier module. When clamped down using the clamping structure, the pressure clamp holds the package leads on a printed circuit board ensuring excellent electrical contact between package leads and circuit traces and surrounding ground planes, obviating soldering and desoldering the leads to the circuit board. The pressure clamp also produces pressure along the device package to hold the packaged device to the carrier module which houses the device and which itself is bolted to the heat sink resulting in excellent thermal contact under the device.
Owner:AESTECH
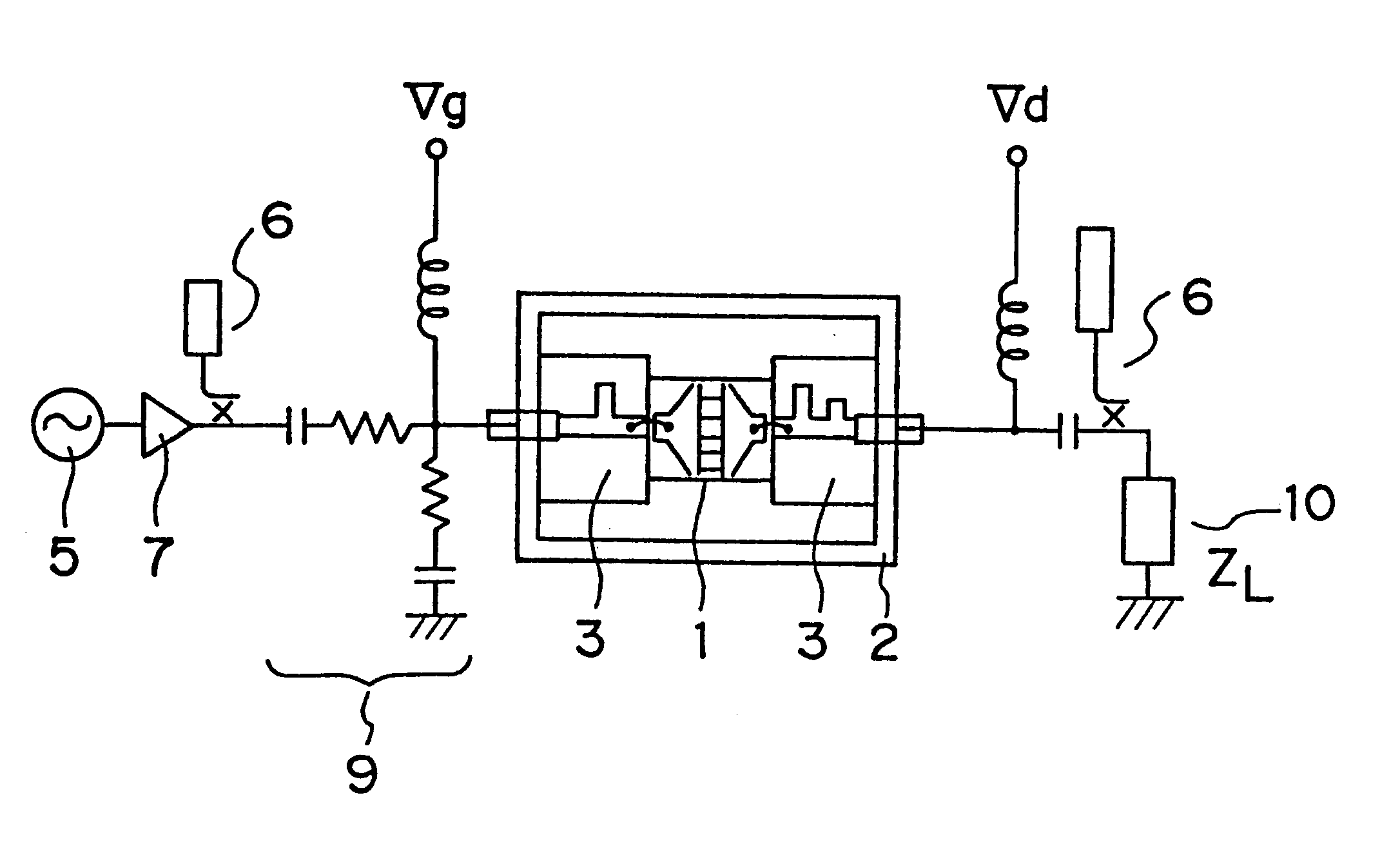
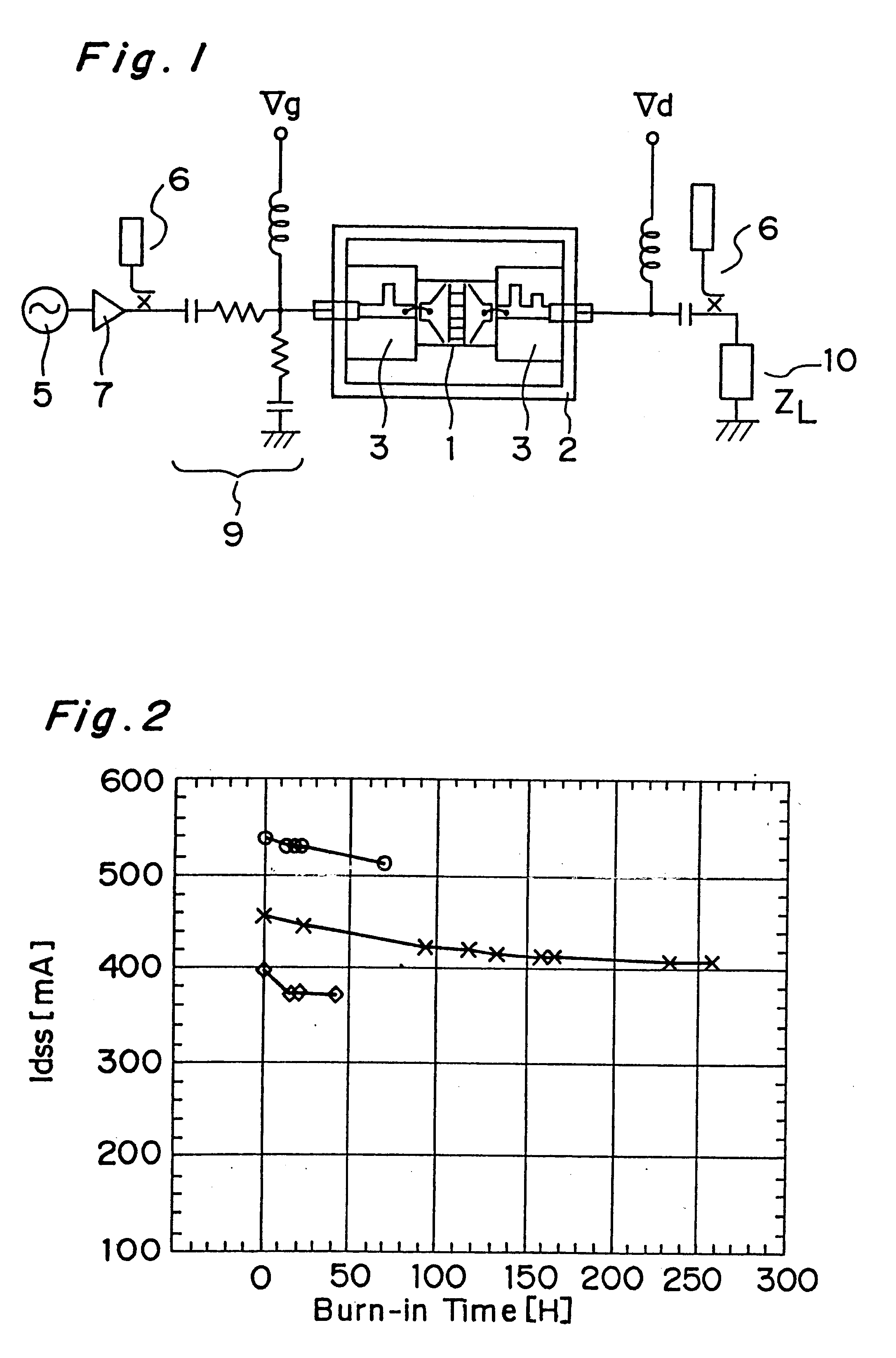
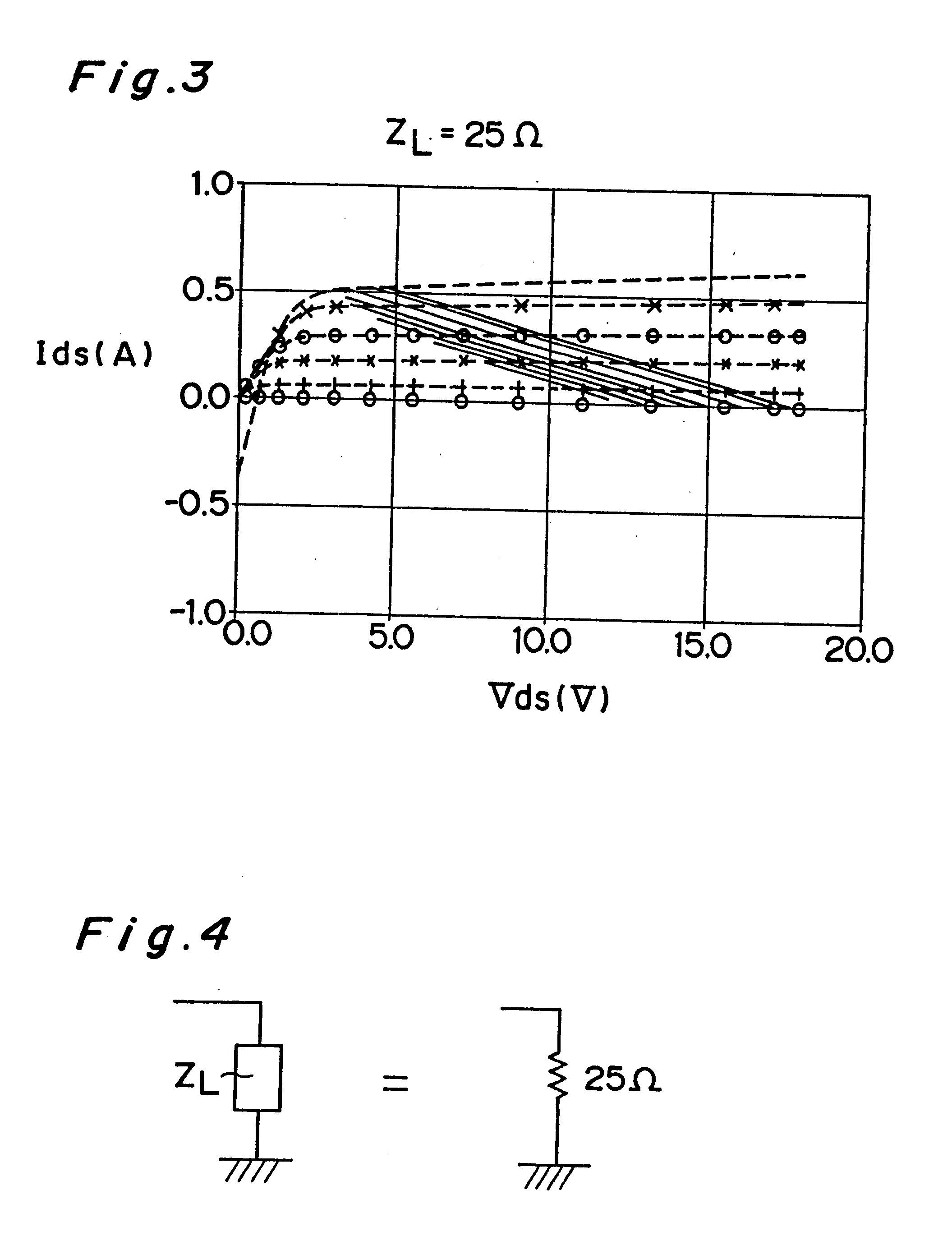
Microwave transistor subjected to burn-in testing
InactiveUS6507076B2Improve reliabilityIncandescent ignitionSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMicrowaveResponse Frequency
A semiconductor transistor which is burned in by a burn-in signal having a burn-in frequency higher than a thermal transient response frequency of a transistor used at an operating frequency in the microwave region, and supplying the burn-in signal to the transistor, wherein the burn-in signal has a frequency lower than the operating frequency of the transistor and higher than a response frequency of impurities included in the transistor, and the operating frequency is higher than 1 GHz.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
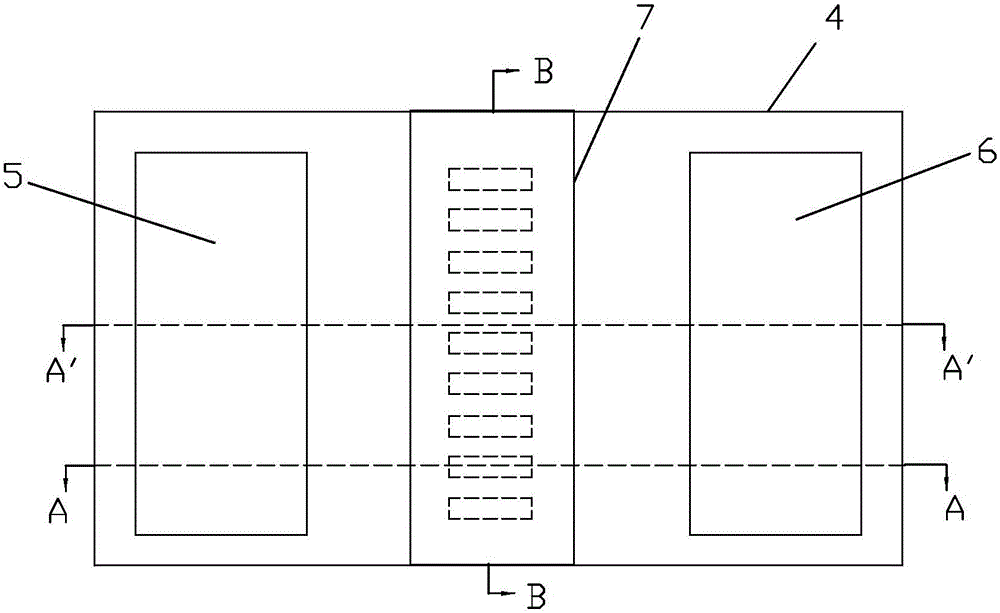
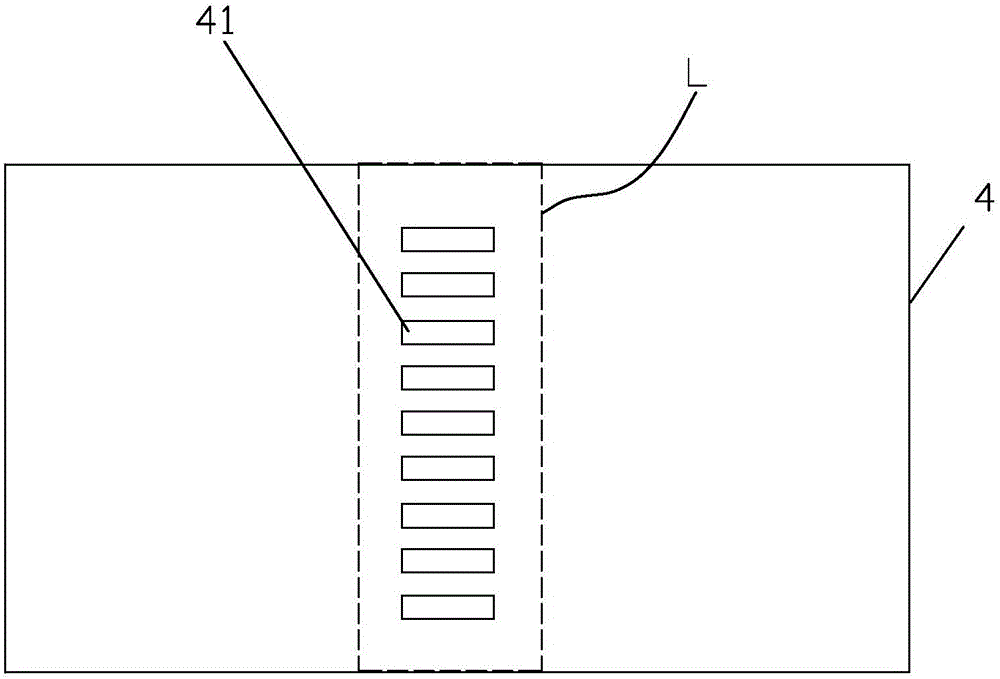
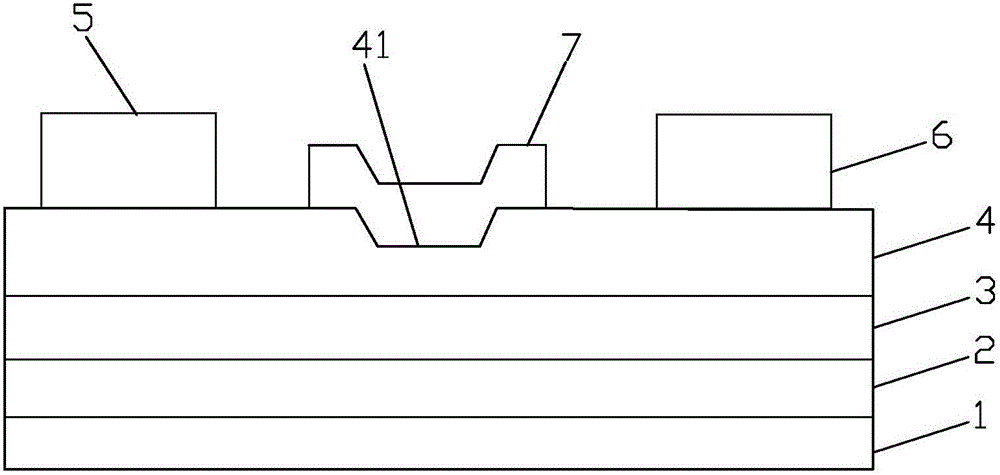
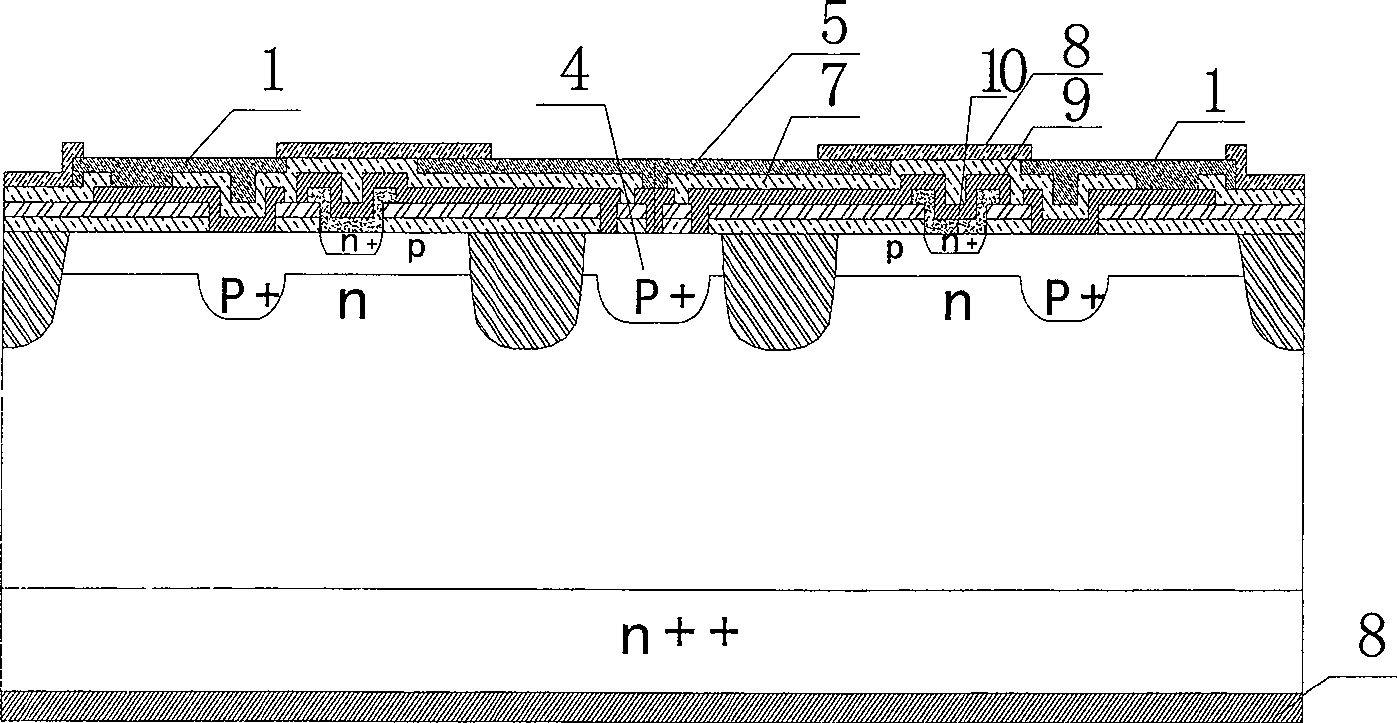
Microwave transistor of patterned grid structure and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN106024880AImprove gate control abilityGuaranteed current output capabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDensity reductionMicrowave
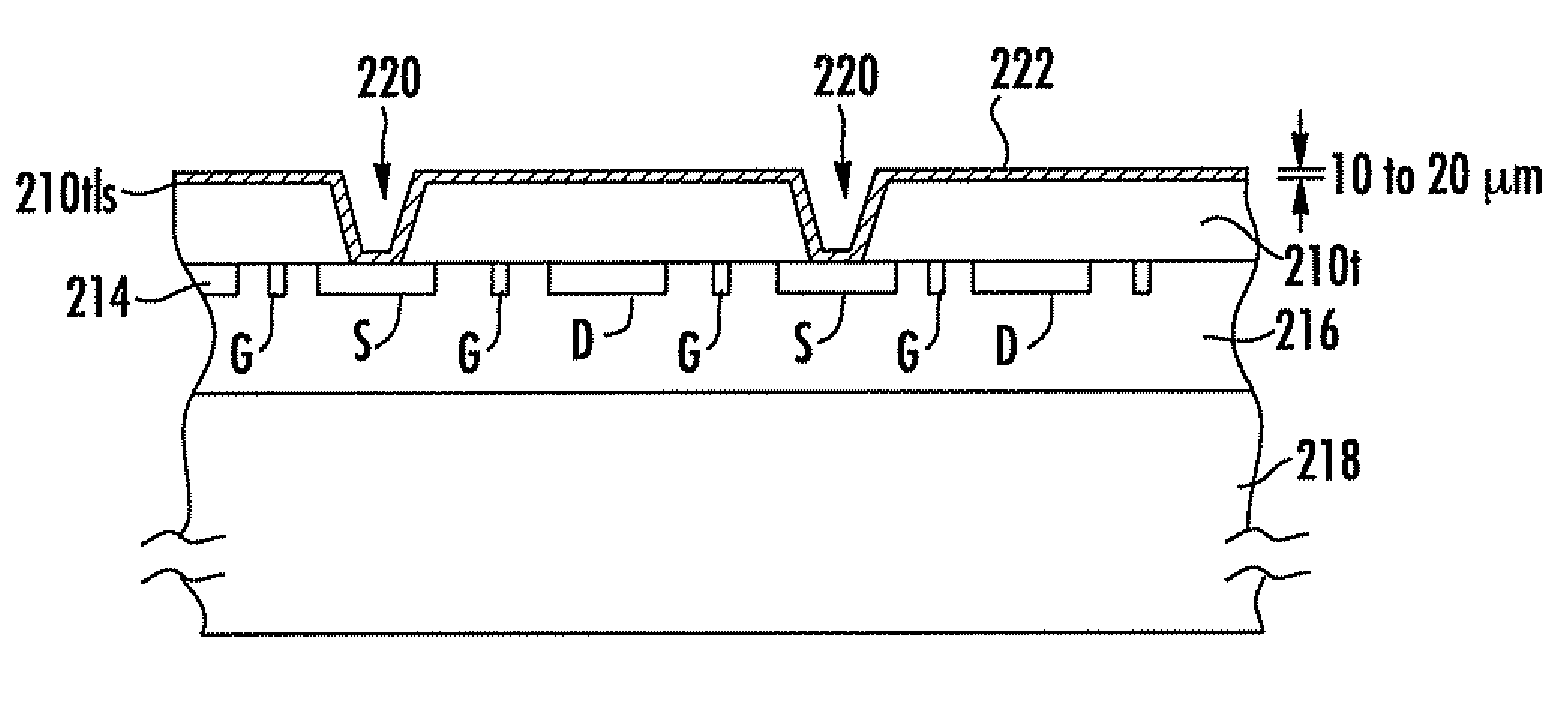
The invention discloses a microwave transistor of a patterned grid structure. The transistor is provided with a patterned region between the source electrode and the drain electrode of a barrier layer. Within the patterned region, the surface of the barrier layer partially concaves downwards along the thickness direction to form a plurality of grooves. A grid is arranged to cover the patterned region. The length of the grid is larger than the lengths of the grooves along the length direction of the grid, so that the grid can completely cover the grooves. On one hand, by means of the grooves, the grid control capability of a device is improved and the short-channel effect is suppressed. On the other hand, an original heterostructure below the grid is preserved. In this way, the reduction of the conductive capacity due to the density reduction of two-dimensional electron gas can be avoided. Therefore, the current output capability of the device is ensured while the short-channel effect is suppressed at the same time. The invention also discloses a manufacturing method of the above microwave transistor.
Owner:XIAMEN SANAN INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
Setup and method for noise parameter measurement
ActiveUS10429426B1Noise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceMicrowaveEngineering
A noise parameter test setup allows accurately measuring the four noise parameters (Fmin, Rn, ┌opt) of microwave transistors over a wide frequency range using two distinct wideband measurement paths, based on differential wafer probes, instead of SPDT switches, to commute between s-parameter (signal) measurement and noise measurement path, avoiding thus the uncertainty of the accuracy as well limited availability of SPDT switches. Calibration of the system is the same as when using switches, when hopping the DUT chip from one set or subset of probes to the next. Additional power control precautions of the VNA sources are necessary to avoid injecting signal power into the sensitive noise receiver during s-parameter measurements and jamming the weak noise power during noise measurement.
Owner:TSIRONIS CHRISTOS
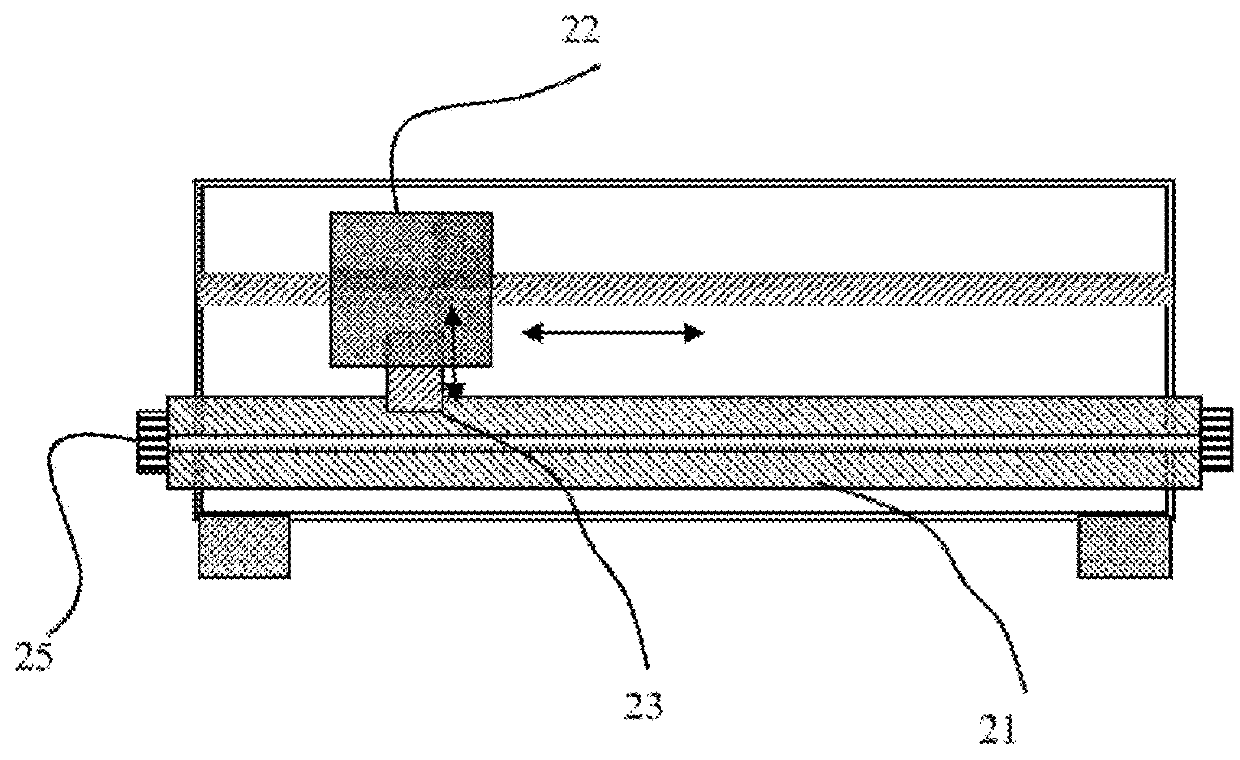
Pre-matched coaxial transistor test fixture
ActiveUS10725092B1Electrical measurement instrument detailsRadiofrequency circuit testingTransformerEngineering
Coaxial microwave transistor test fixtures provide lowest insertion loss possible and include, as part of the input and output sections, transformer networks either in form of single stage λ / 4 segments, or, for larger bandwidth, multiple step segments or ramped transitions from 50Ω to the impedance closer to the internal impedance of the power transistor. The transforming networks are flat or cylindrical and can be made exchangeable in order to accommodate various transforming ratios using the same fixture body and coaxial adapters. The fixtures can be calibrated using standard TRL method.
Owner:TSIRONIS CHRISTOS
Frequency adjustable pre-matching coaxial transistor test fixture
ActiveUS10591511B1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisMicrowaveTransformer
Coaxial microwave transistor test fixtures provide lowest insertion loss possible and include, as part of the input and output sections, transformer networks in form of single stage λ / 4 segments bringing (pre-matching) the system 50Ω load closer to the conjugate internal impedance of power transistors. The transforming networks are flat, cylindrical or have oval or elliptical cross sections and have adjustable length, thus operating optimally for transistors with varying optimum frequency and internal impedance and / or capacitive or inductive impedance part. The change in length is done without affecting the overall fixture geometry and structure. The fixtures can be calibrated using standard TRL method.
Owner:TSIRONIS CHRISTOS
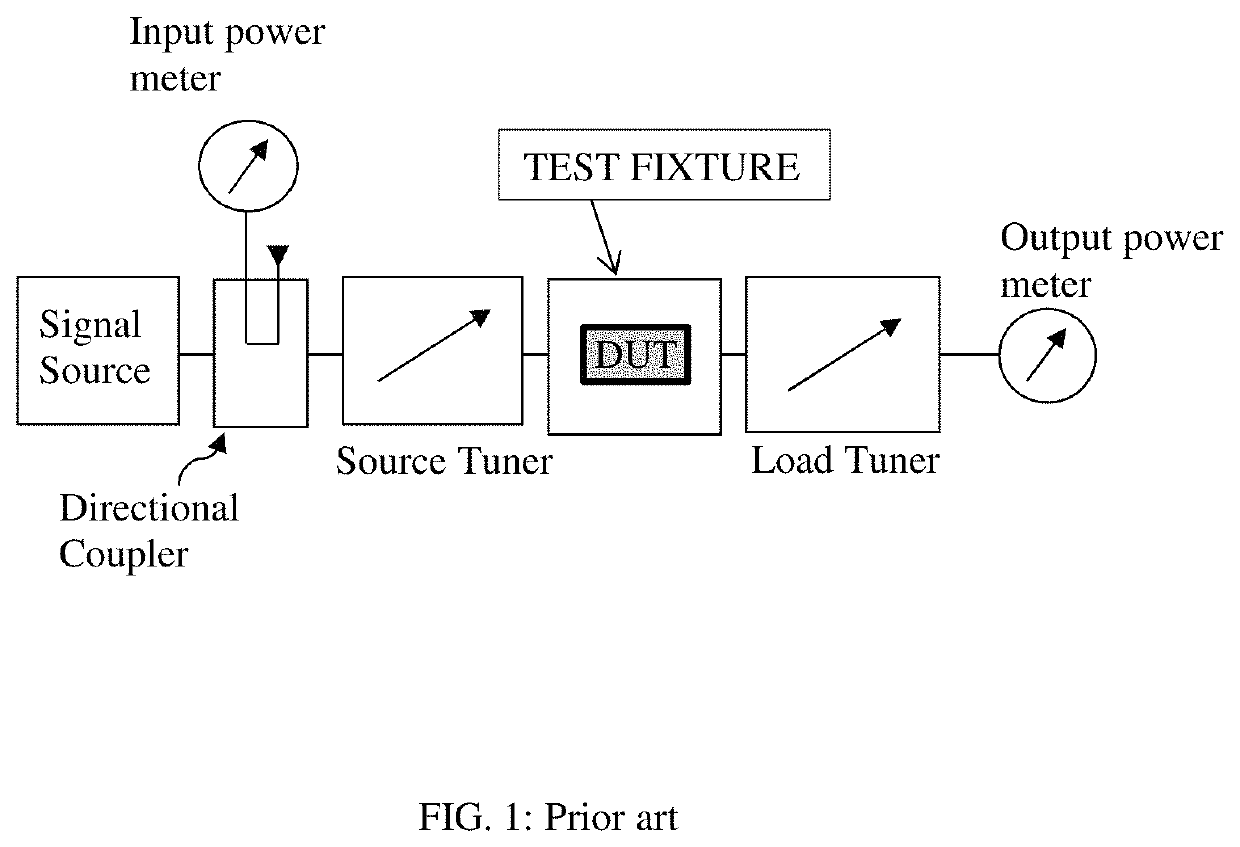
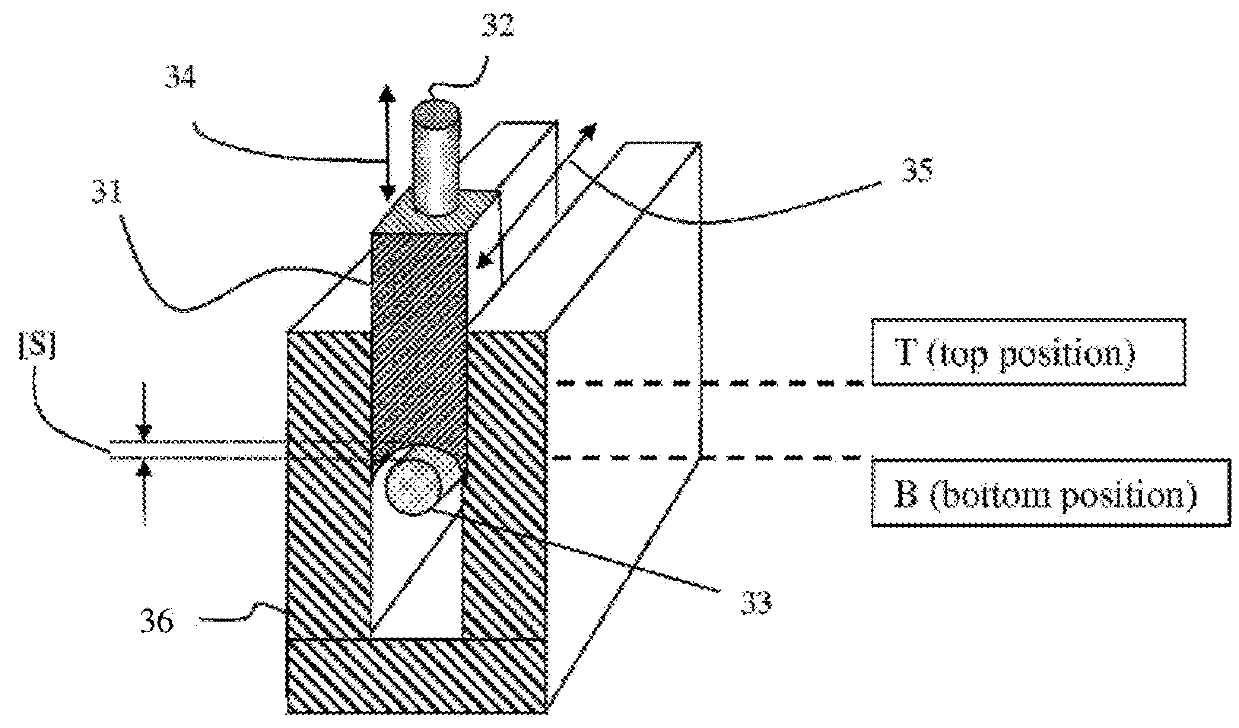
Stable load pull operation using tuners
Load Pull tuning pattern and probe movement algorithms allow creating a test pattern allowing to avoid instability regions and spurious oscillations of microwave transistors during testing using slide screw load and source tuners. The impedances are selected based on the stability circle and instability area on the Smith chart and the probe movement trajectory allows both avoiding the static and circumventing the transient crossing through the instability area. All tuning commands are saved in a pattern file.
Owner:TSIRONIS CHRISTOS
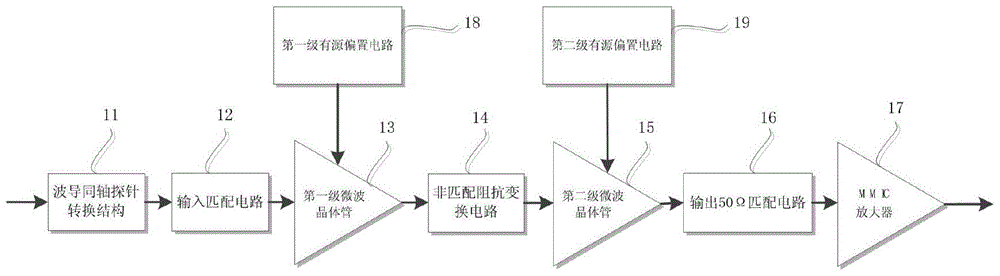
K band inter-stage mismatch type low noise amplifier
ActiveCN105680804AImprove noise figureReduce volumeAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influencePower amplifiersElectricityAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a K band inter-stage mismatch type low noise amplifier. The low noise amplifier can be applied to a Ka band satellite communication system. The K band inter-stage mismatch type low noise amplifier disclosed by the invention comprises: a waveguide probe containing an air transition cavity, a preceding stage of the low noise amplifier is composed of two inter-stage mismatch microwave transistors, an active bias provides a static bias voltage for the microwave transistors, and a backward stage of the low noise amplifier is composed of an MMIC single amplifier. A coaxial waveguide probe conversion structure in the low noise amplifier comprises an air transition cavity, and the transition cavity can expand the working bandwidth of wave conversion and can assist the assembly and positioning of the probe at the same time; the two microwave transistors adopt a mismatch design, a backward stage tube is used as the load of the preceding stage, and the preceding stage tube works at the minimal noise working point through the allocation of a mismatch impedance inverter circuit; and the active bias can provide constant drain electrode working voltage and current for the microwave transistors in high and low temperature environments to guarantee the stability of the electric properties thereof.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
A ballasting resistor structure of microwave power transistor dynamic emitter electrode
InactiveCN100533761CReduce parasitic capacitanceReduce chip areaTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingJunction temperaturePeak value
The present invention is a dynamic emitter ballast resistor structure of a microwave power transistor. The structure is that the active area is divided into two adjacent areas, the emitter ballast resistor is placed between the two active areas, and the emitter and base electrodes adopt double The layer metal wiring leads out, and the two active areas share a ballast resistor. Advantages: The active area is divided into two adjacent areas, the emitter ballast resistor is placed between the two active areas, and the emitter and base electrodes are drawn out by double-layer metal wiring. Make the two active regions fully thermally coupled to the same ballast resistance, make the ballast resistance value increase with the increase of temperature, increase the additional ballast effect, and realize dynamic ballast. Share a ballast resistor, reduce the parasitic capacitance of the ballast resistor and the chip area. Increase the heat dissipation boundary of the active area and reduce the thermal resistance. For chips with the same power and ballast resistance, the peak junction temperature drops by 15°C-20°C. Meet the requirements of microwave power transistors for microwave performance and reliability.
Owner:NO 55 INST CHINA ELECTRONIC SCI & TECHNOLOGYGROUP CO LTD
Pulse radar device
ActiveUS8922424B2Low costQuality improvementOscillations generatorsAntenna feed intermediatesReflected wavesImpulse radar
A radiation type oscillator including a radiation type oscillator substrate including a microwave transistor for generating negative resistance by short-duration operation and a resonant cavity structure; a high-frequency pulse signal of an oscillation frequency / frequency bandwidth determined by negative resistance produced by the short-duration operation of the microwave transistor and the resonant cavity structure is generated as a transmitted RF signal and simultaneously radiated into space. The radiation type oscillator performs oscillating operation when a received RF signal that is a reflected wave of the transmitted RF signal from an object of detection enters the radiation type oscillator, an IF signal is acquired from an IF signal output terminal owing to homodyne mixing by the radiation type oscillator itself, and this is analyzed and processed to detect the object of detection.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH +1
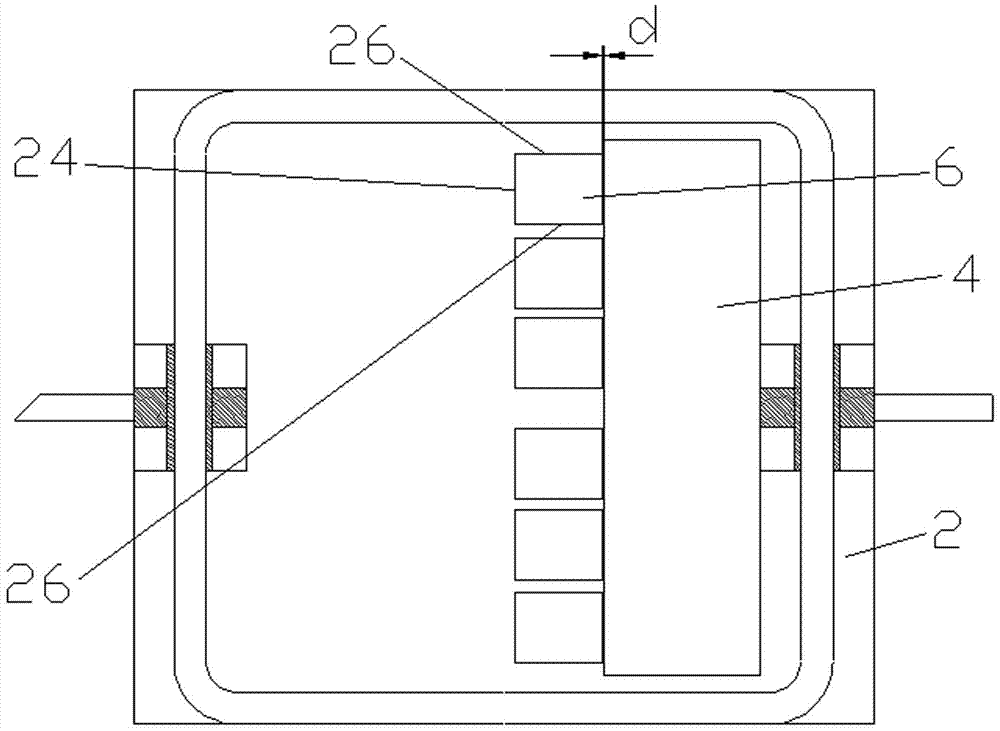
High temperature aging device for microwave transistor
The invention discloses a high temperature aging device for a microwave transistor. The high temperature aging device comprises an aluminum shell, a lower ceramic substrate, two L-shaped copper columns and an upper ceramic substrate, wherein the upper ceramic substrate, the two L-shaped copper columns and the lower ceramic substrate are put into the aluminum shell sequentially from top to bottom;the two L-shaped copper columns are arranged in a groove between the upper ceramic substrate and the lower ceramic substrate; and two long arms of the two L-shaped copper columns extend out of two square holes in the front wall of the aluminum shell respectively and are used as transistor lead-out electrodes. In the whole design, all adopted materials have high temperature resistance; a high temperature lead wire is connected with a peripheral circuit, so a circuit board can be prevented from being heated; therefore, a high acceleration life test at temperature of over 400 DEG C can be realized.
Owner:THE 13TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP CORP
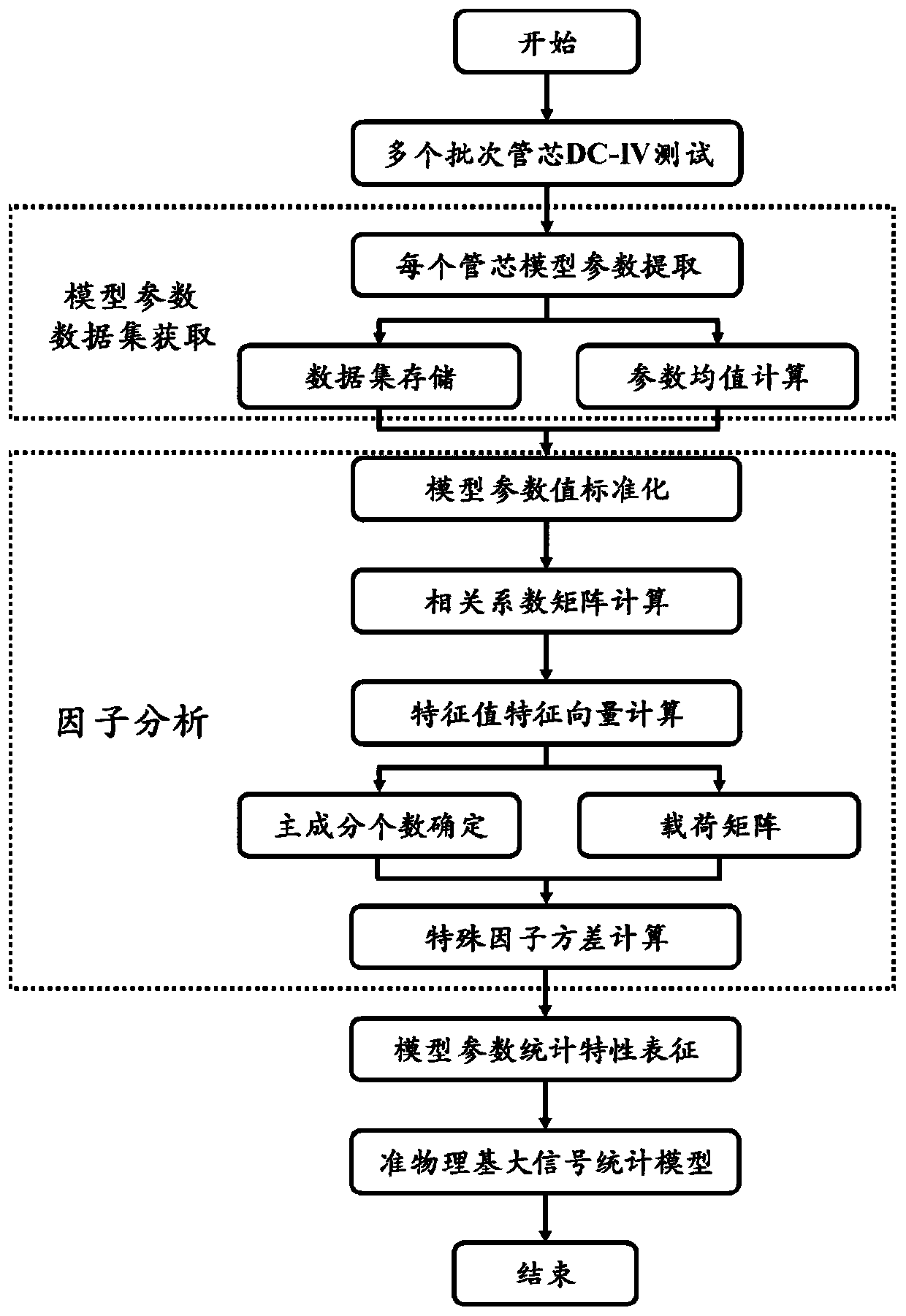
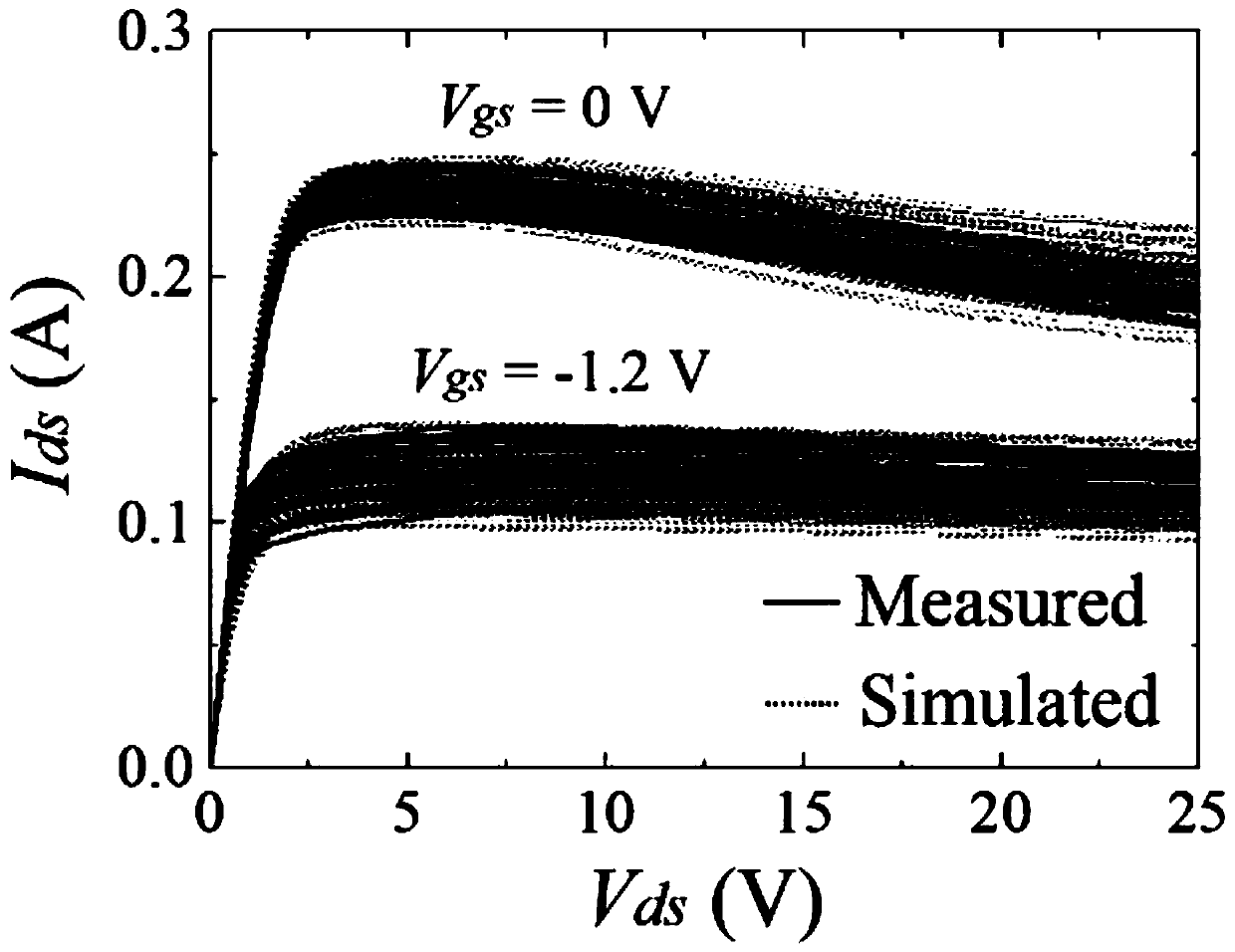
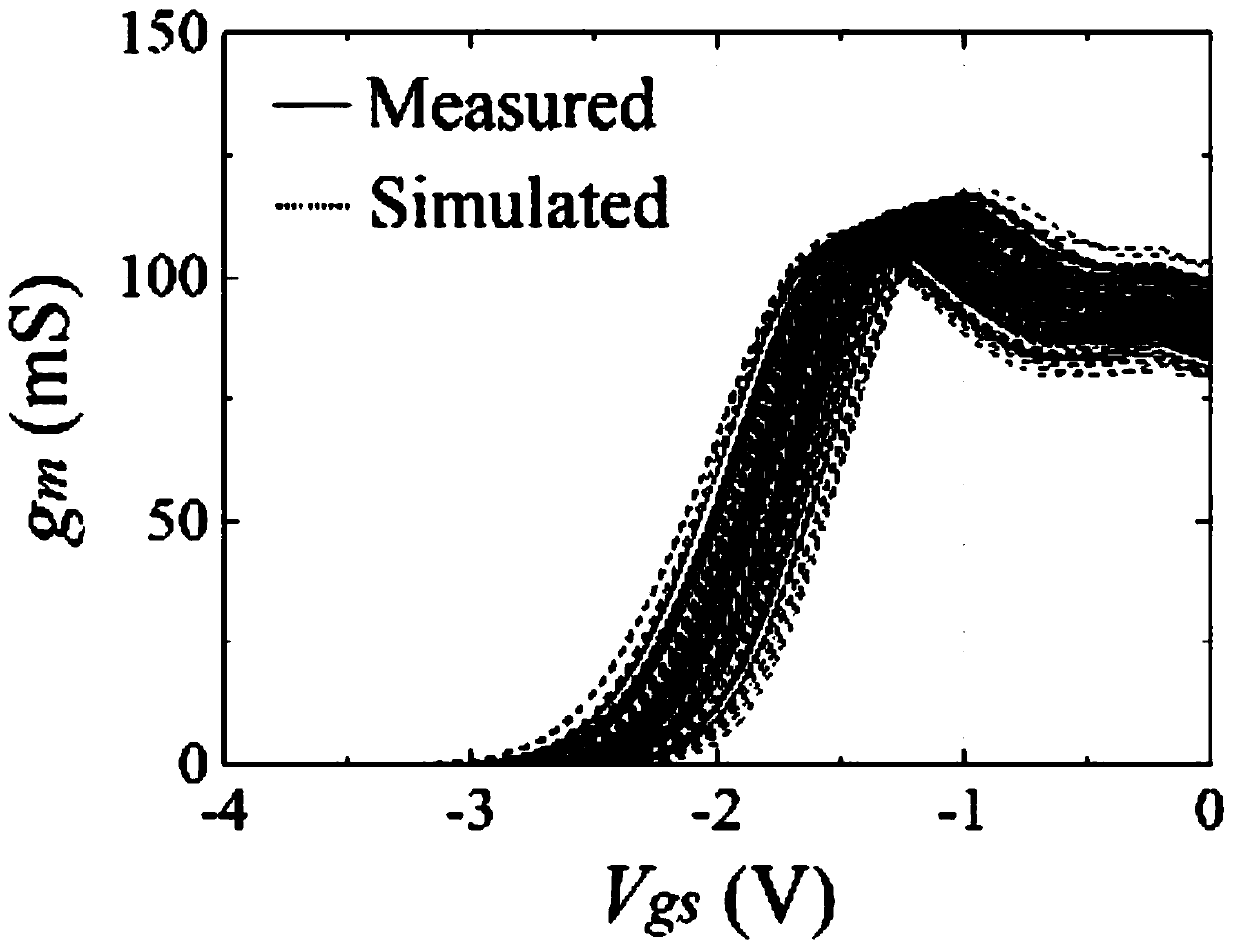
Microwave transistor quasi-physical basis statistical model parameter extraction method
ActiveCN111428437ASolve the problem of efficient parameter extractionSimple designDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingData setStatistical analysis
The invention discloses a microwave transistor quasi-physical basis statistical model parameter extraction method, and relates to the technical field of electronic information-information. In order tosolve the problems in the prior art, the invention provides an implementation method for efficient parameter extraction of a device statistical model of a microwave gallium nitride high-electron-mobility transistor quasi-physical-base large-signal model. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a large signal model parameter data set corresponding to a plurality of different GaN devicedies with the same size; and in the parameter data set, performing statistical analysis on the plurality of physical parameters and the sub-model parameters thereof, accurately characterizing association characteristics among the parameters in combination with a statistical theory of factor analysis, and finally realizing prediction of statistical distribution of device output characteristics.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Pulse wireless communication device
ActiveUS8705652B2Low costQuality improvementWaveguide hornsEnergy efficient ICTCommunication deviceVIT signals
To provide a microwave / milliwave UWB pulse wireless communication device that enables realization of structural simplification, high performance, compact integration, easy design, low power consumption, and low cost. A radiation type oscillator is configured by a radiation type oscillator substrate S1 equipped with a microwave transistor 1 for generating negative resistance by short-duration operation and a resonant cavity structure, a high-frequency pulse signal of an oscillation frequency / frequency bandwidth determined based on negative resistance produced by the short-duration operation of the microwave transistor 1 and the resonant cavity structure is generated as a transmitted RF signal and simultaneously radiated into space, and the radiation type oscillator is caused to perform oscillating operation when a received RF signal arriving from an external wireless communication device enters the radiation type oscillator, whereby a received data signal is established based on acquisition of an IF signal owing to mixing by the radiation type oscillator itself.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH +1
High temperature aging device for microwave transistor
The invention discloses a high temperature aging device for a microwave transistor. The high temperature aging device comprises an aluminum shell, a lower ceramic substrate, two L-shaped copper columns and an upper ceramic substrate, wherein the upper ceramic substrate, the two L-shaped copper columns and the lower ceramic substrate are put into the aluminum shell sequentially from top to bottom;the two L-shaped copper columns are arranged in a groove between the upper ceramic substrate and the lower ceramic substrate; and two long arms of the two L-shaped copper columns extend out of two square holes in the front wall of the aluminum shell respectively and are used as transistor lead-out electrodes. In the whole design, all adopted materials have high temperature resistance; a high temperature lead wire is connected with a peripheral circuit, so a circuit board can be prevented from being heated; therefore, a high acceleration life test at temperature of over 400 DEG C can be realized.
Owner:THE 13TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP CORP
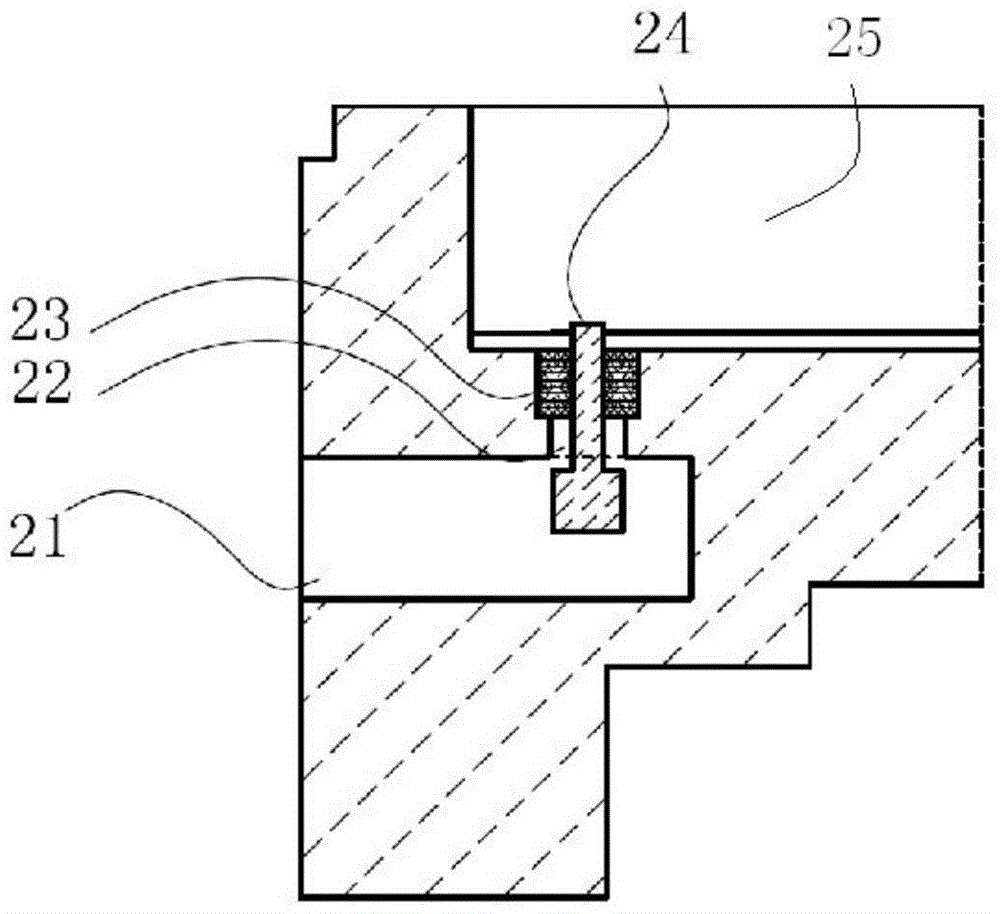
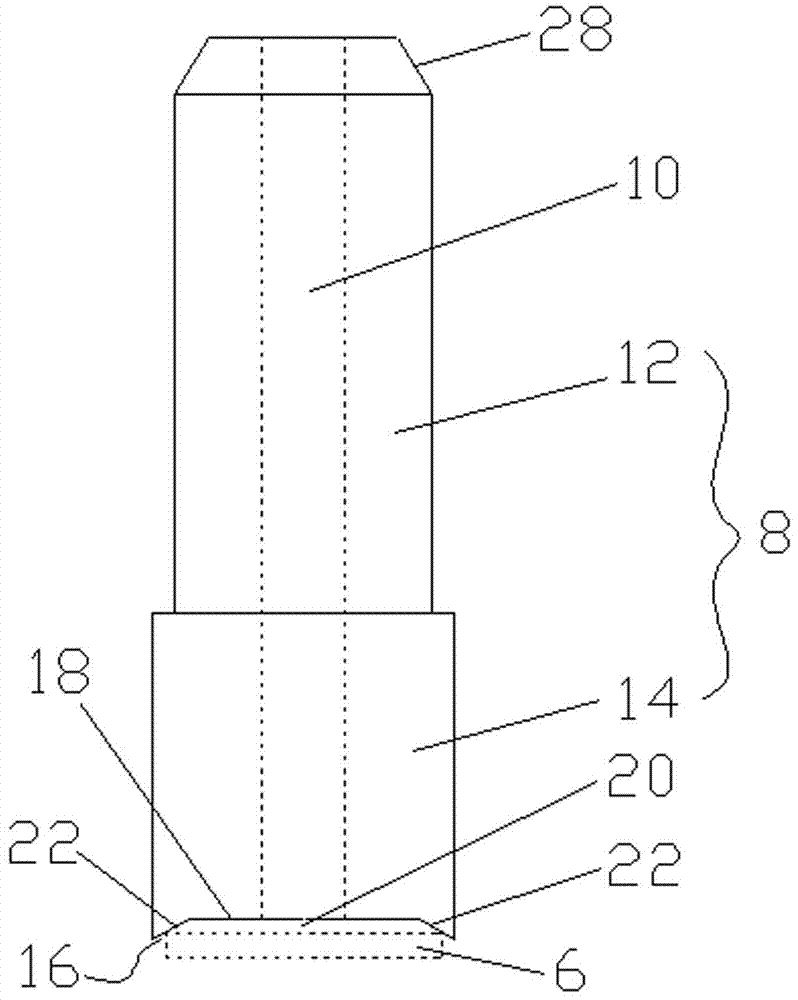
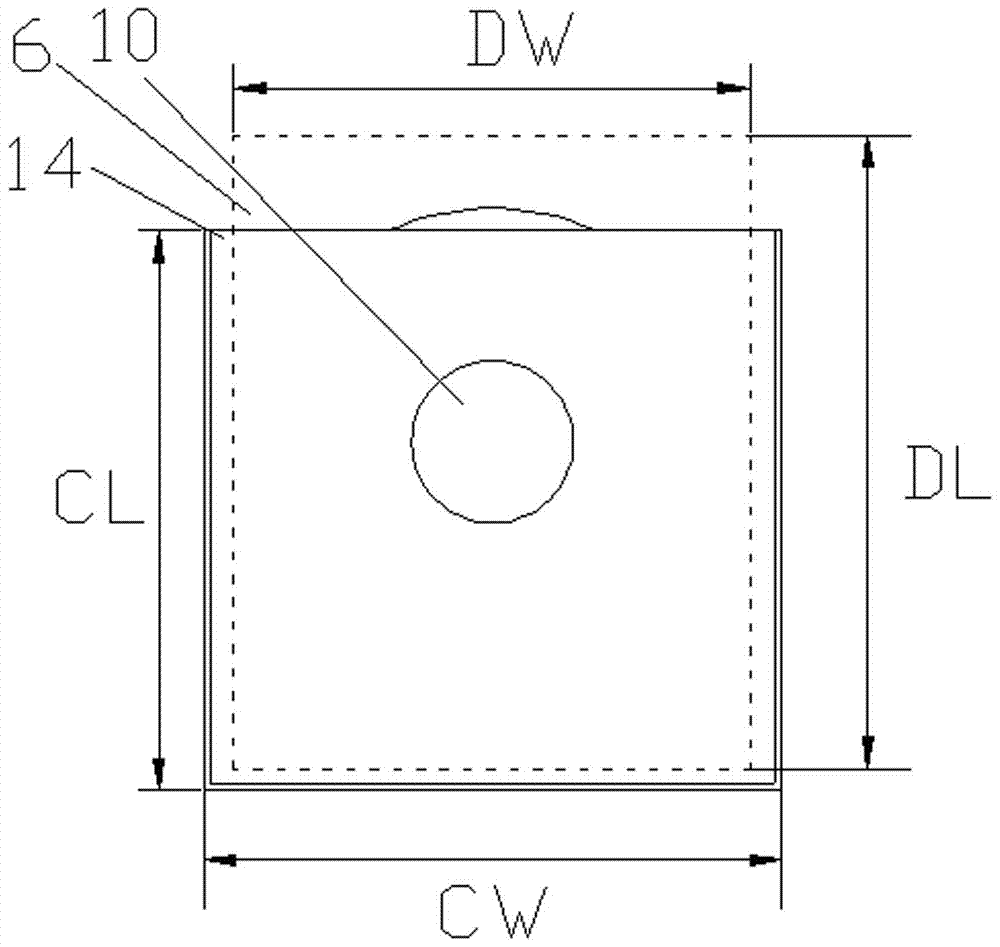
Eutectic soldering nozzle for realizing ultra-fine spacing between SMT devices in microwave tubes
The invention relates to a eutectic welding suction nozzle for achieving ultra fine spacing between patch devices in a microwave transistor case. The eutectic welding suction nozzle comprises a suction nozzle rod and a channel arranged in the suction nozzle rod in the axial direction, the suction nozzle rod comprises a suction nozzle rod body and a suction nozzle head, the bottom of the suction nozzle head is provided with a groove, the channel is communicated with the groove, the groove comprises a top wall, a first side wall and two oppositely arranged second side walls, and the first side wall and the second side walls are arranged in an outwards inclined mode. According to the eutectic welding suction nozzle, the wide side edge and two long side edges of each device are clamped through the first side wall and the two second side walls of the groove respectively, and one device cannot slide in the other three directions in the eutectic scrubbing process but can only slide in the direction close to the adjacent device, so that it is guaranteed that spacing between the adjacent devices is smaller than 20 micrometers all the time, ultra fine spacing is achieved, and a good solution is provided for high integration and miniaturization of microwave power transistors.
Owner:江苏博普电子科技有限责任公司
Narrow pulse generator circuit based on tunnel diode
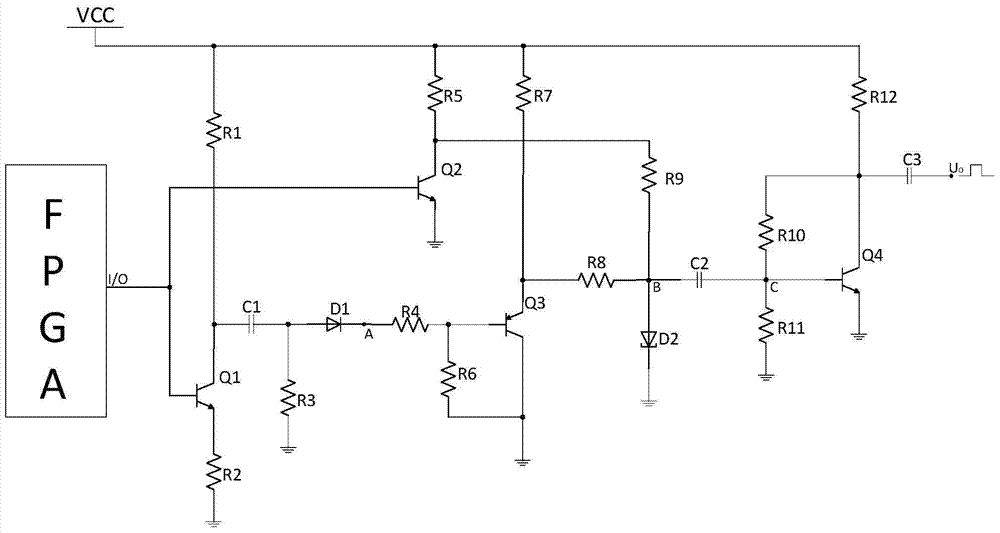
ActiveCN105049009BSimple structureClear structurePulse duration/width modulationDriver circuitTunnel diode
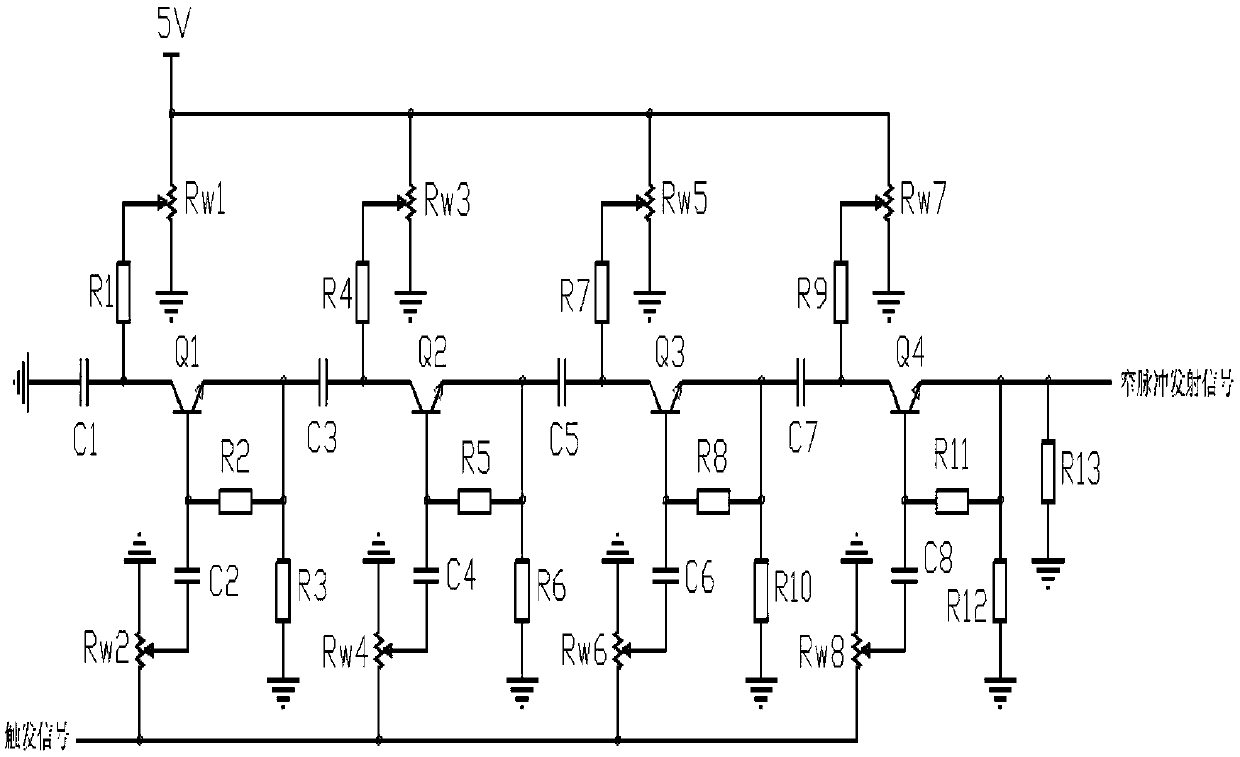
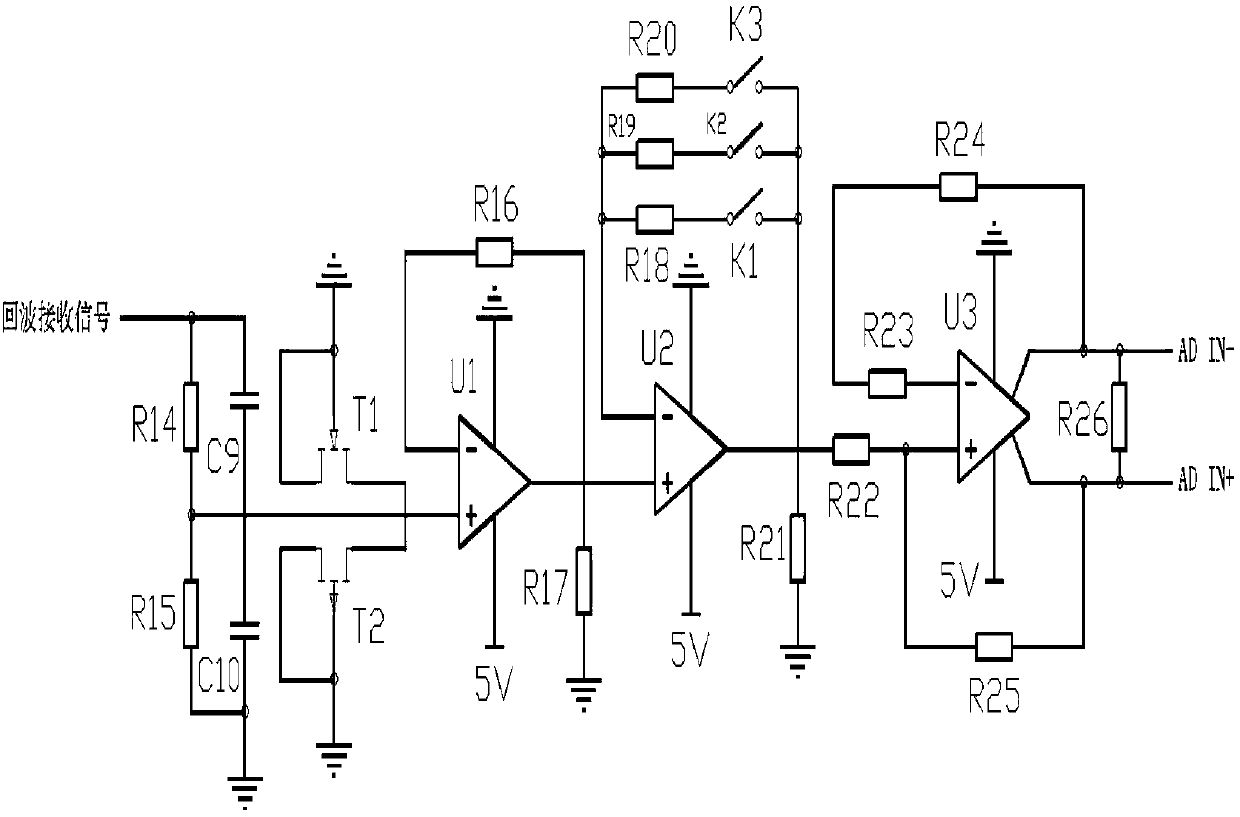
The invention discloses a narrow pulse generating circuit based on a tunnel diode. Including the main circuit and the driving circuit, the main circuit is mainly composed of the upper circuit including the microwave transistor Q2, the lower circuit including the microwave transistor Q1 and the microwave transistor Q3, and the amplification circuit including the microwave transistor Q1; the upper circuit and the lower circuit are connected in parallel, The input terminals of the upper and lower circuits are connected to the drive circuit, and the output terminals of the upper and lower circuits are output narrow pulse signals through the amplifying circuit. The upper, lower and amplifying circuits are all connected to the DC power supply VCC. The invention has simple structure, high emission frequency, can realize narrow pulse signal of nanosecond level or even picosecond level, has large output voltage and high reliability, and can be widely used because of its low cost.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com