Microwave/millimeter wave sensor apparatus
一种传感器装置、毫米波的技术,应用在测量装置、无线电波的反射/再辐射、仪器等方向,能够解决检测灵敏度不利、高RF/IF变换增益、复杂结构等问题,达到实现单纯结构、高效放射特性、高效接收特性的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
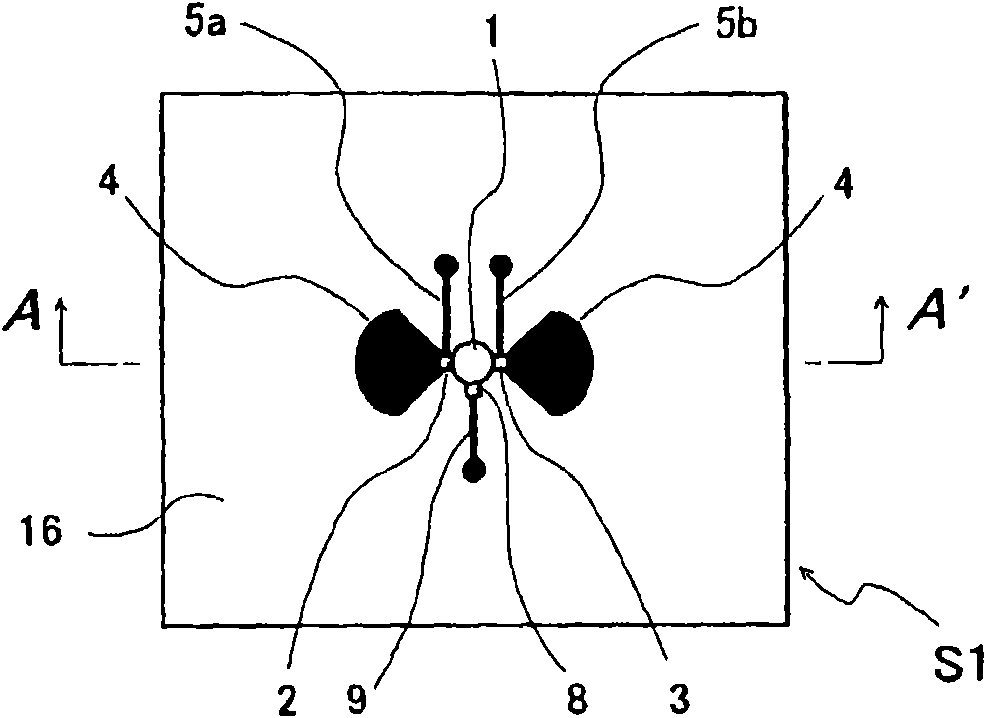
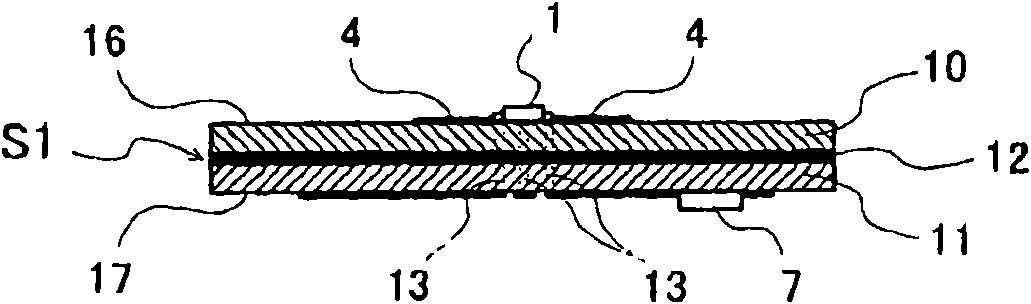
[0096] Figure 1A , Figure 1B , Figure 1C A schematic configuration of the microwave / millimeter wave sensor device according to the first embodiment is shown, Figure 1A is the surface diagram of the radial oscillator substrate S1, Figure 1B yes Figure 1A A cross-sectional view in the arrow direction of line A-A' in FIG. 1C is a rear view of the radial oscillator substrate S1. Radiating oscillator substrate S1 has a three-layer substrate structure in which an inner layer GND 12, which is a ground conductor layer, is interposed between a front-side dielectric substrate 10 and a back-side dielectric substrate 11. The high-frequency transistor 1 of the radiation type oscillator substrate S1 is supplied with DC power, and the detection signal (IF signal) extracted from the radiation type oscillator substrate S1 is processed by the signal analysis processing unit P.
[0097] That is, the radiation oscillator board S1 functions as a "radiation oscillator that integrates three-...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
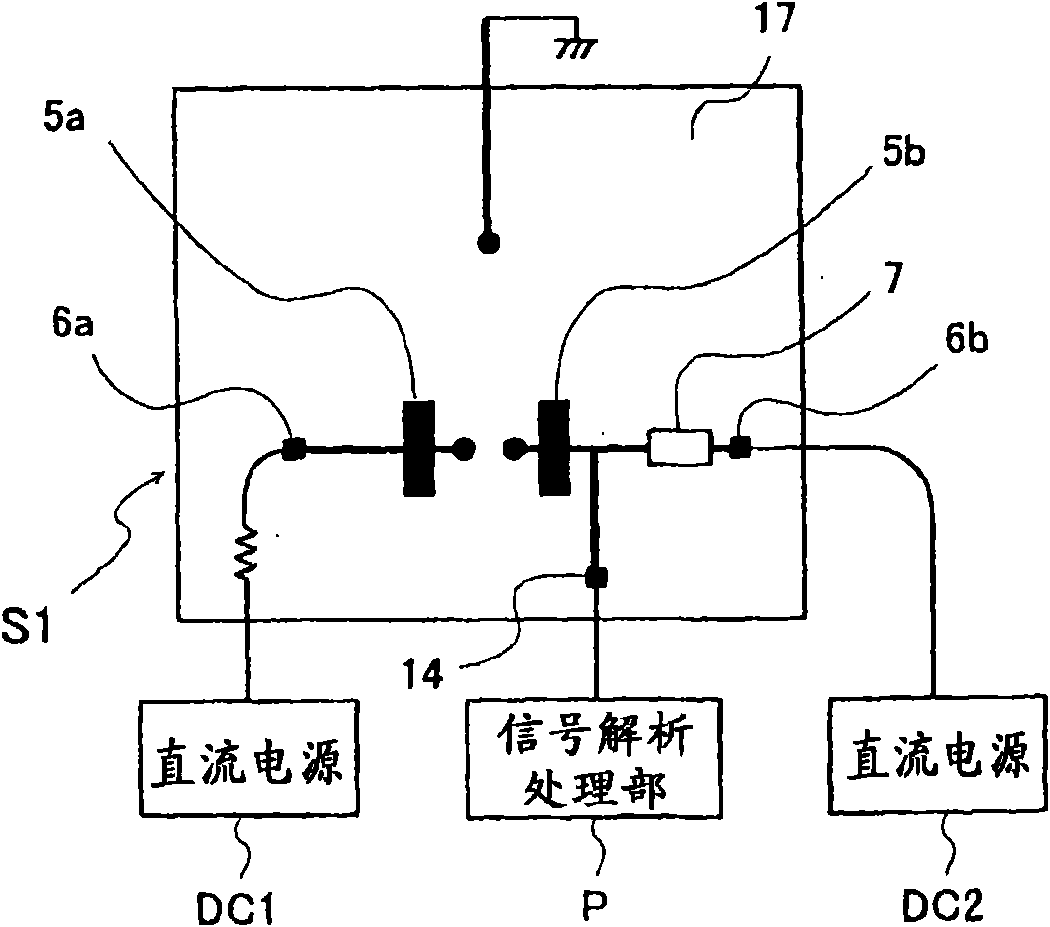
[0118] Figure 5 A circuit configuration diagram of the microwave / millimeter wave sensor device according to the second embodiment is shown. The radiation oscillator substrate S2 is supplied with DC power from the DC power sources DC1 and DC2, and the radiation oscillator substrate S2 is connected to the radiation oscillator substrate S2 through the signal analysis processing unit P. The extracted detection signal (IF signal) is analyzed and processed. The microwave / millimeter wave sensor device of the present embodiment is obtained by changing the extraction position of the IF signal in the microwave / millimeter wave sensor device of the first embodiment. In addition, the same reference numerals are assigned to the same configurations as those of the microwave / millimeter wave sensor device shown in the first embodiment, and description thereof will be omitted.
[0119] In the radial oscillator substrate S2, the source 8 of the high-frequency transistor 1 is connected to the m...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0121] Figure 6 A circuit configuration diagram of the microwave / millimeter wave sensor device according to the third embodiment is shown. Direct current power is supplied to the radiation oscillator substrate S3 from the DC power sources DC1 and DC2, and the radiation oscillator substrate S3 is supplied to the radiation oscillator substrate S3 through the signal analysis processing unit P. The extracted detection signal (IF signal) is analyzed and processed. The microwave / millimeter wave sensor device of the present embodiment is obtained by changing the mounting position of the conductor patch 4 in the microwave / millimeter wave sensor device of the first embodiment described above. In addition, the same reference numerals are assigned to the same configurations as those of the microwave / millimeter wave sensor device shown in the first embodiment, and description thereof will be omitted.
[0122] On the radiation oscillator substrate S3, conductor patches 4, 4 are attached ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com