Radiator of electronic device
A technology of electronic devices and radiators, applied in the field of radiators, can solve problems such as liquid leakage, electronic equipment not allowed, and air cooling technology that cannot meet the cooling requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
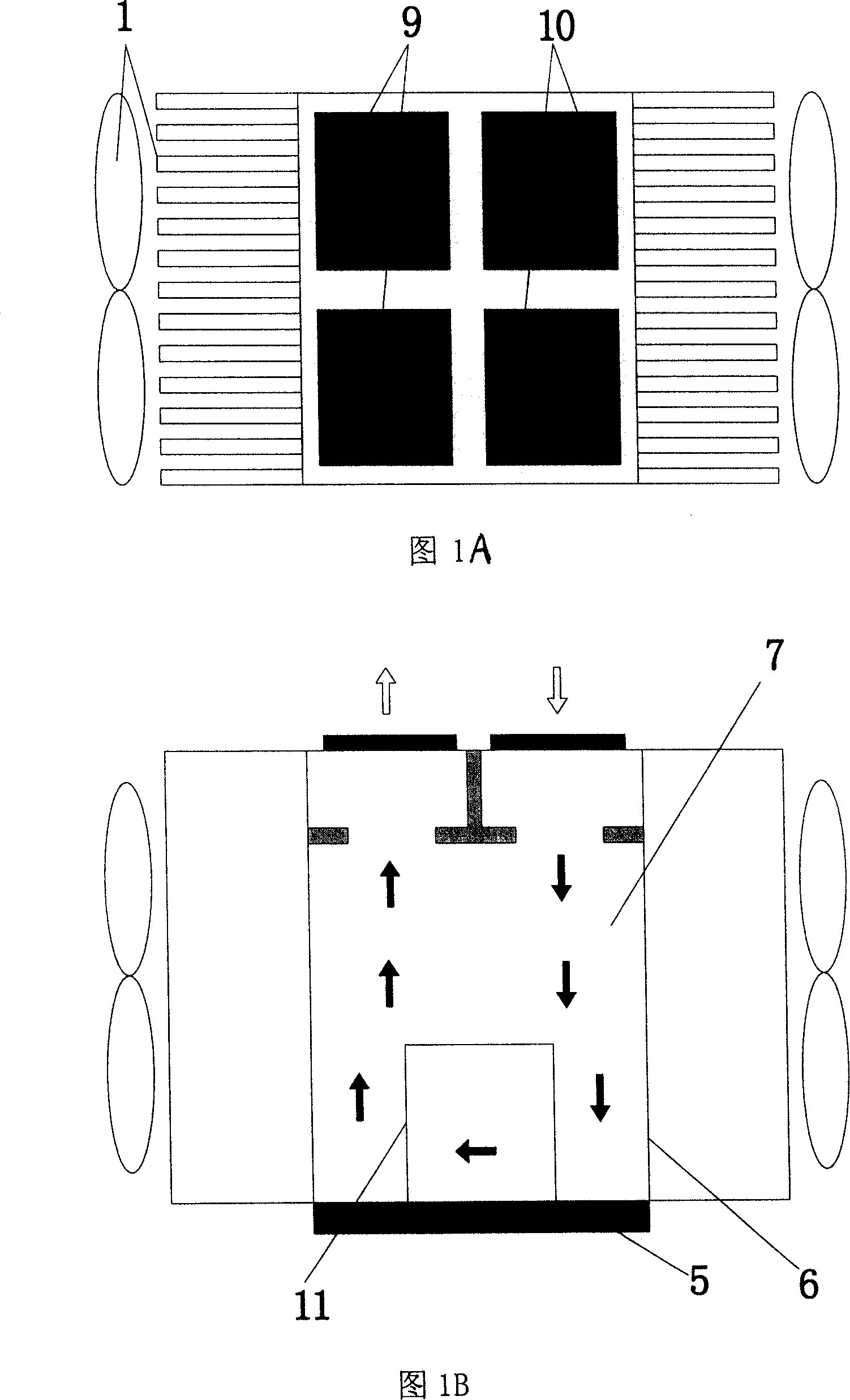
[0015] See Figure 1A, Figure 1B, the working principle of the radiator: when the piezoelectric diaphragm group 9 is energized and deformed downward, at the same time, the piezoelectric diaphragm group 10 is energized and deformed upward, and the deformation of the two piezoelectric diaphragm groups will cause the radiator The cooling liquid 7 in the shell 6 moves, and the cooling liquid 7 in contact with the heat source 5 flows quickly to other parts of the radiator after absorbing heat, and the heat carried by the heat fluid is carried out by the radiator fins 14 on the four walls and the fan 1. Heat exchange, transfer heat to the surrounding environment, the temperature of the fluid drops rapidly, when the cooled fluid returns to the bottom of the radiator shell 6, the heat sink 11 in the radiator shell 6 absorbs the heat from the heat source 5 Conducted heat, the cooled fluid reabsorbs heat and begins a new cycle.
[0016] In order to prevent the electrical input of the pie...
Embodiment 2
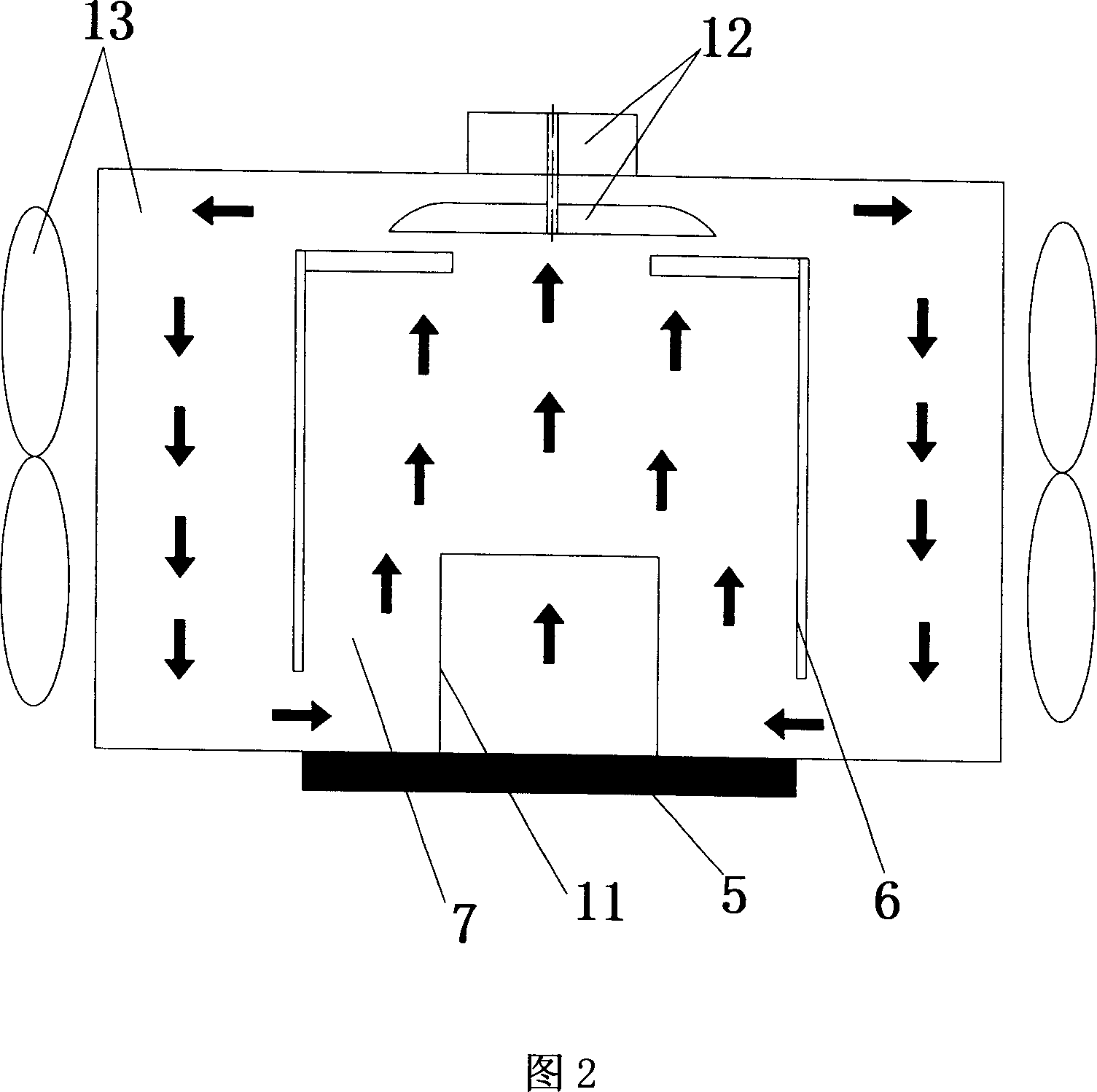
[0019] Referring to FIG. 2 , Embodiment 2 is the same as Embodiment 1, except that the liquid driver is a miniature centrifugal pump 12 . The blades of the micro-centrifugal pump 12 are arranged in the cavity. When the micro-centrifugal pump rotates, the cooling liquid 7 that has absorbed the heat of the heat source flows, and then drives these hot fluids to flow into a plurality of cooling channels provided on the inner wall of the radiator, and the cooling liquid The heat carried by 7 is transmitted to the environment through the outer wall of the heat sink and the fan, and the temperature of the cooling liquid 7 drops. When the cooled cooling liquid 7 returns to the bottom of the radiator housing 6, it will absorb the heat of the heat source again and start a new process. cycle. In order to obtain a large fluid driving force and lower noise, the micro motor should use a high-speed DC motor.
Embodiment 3
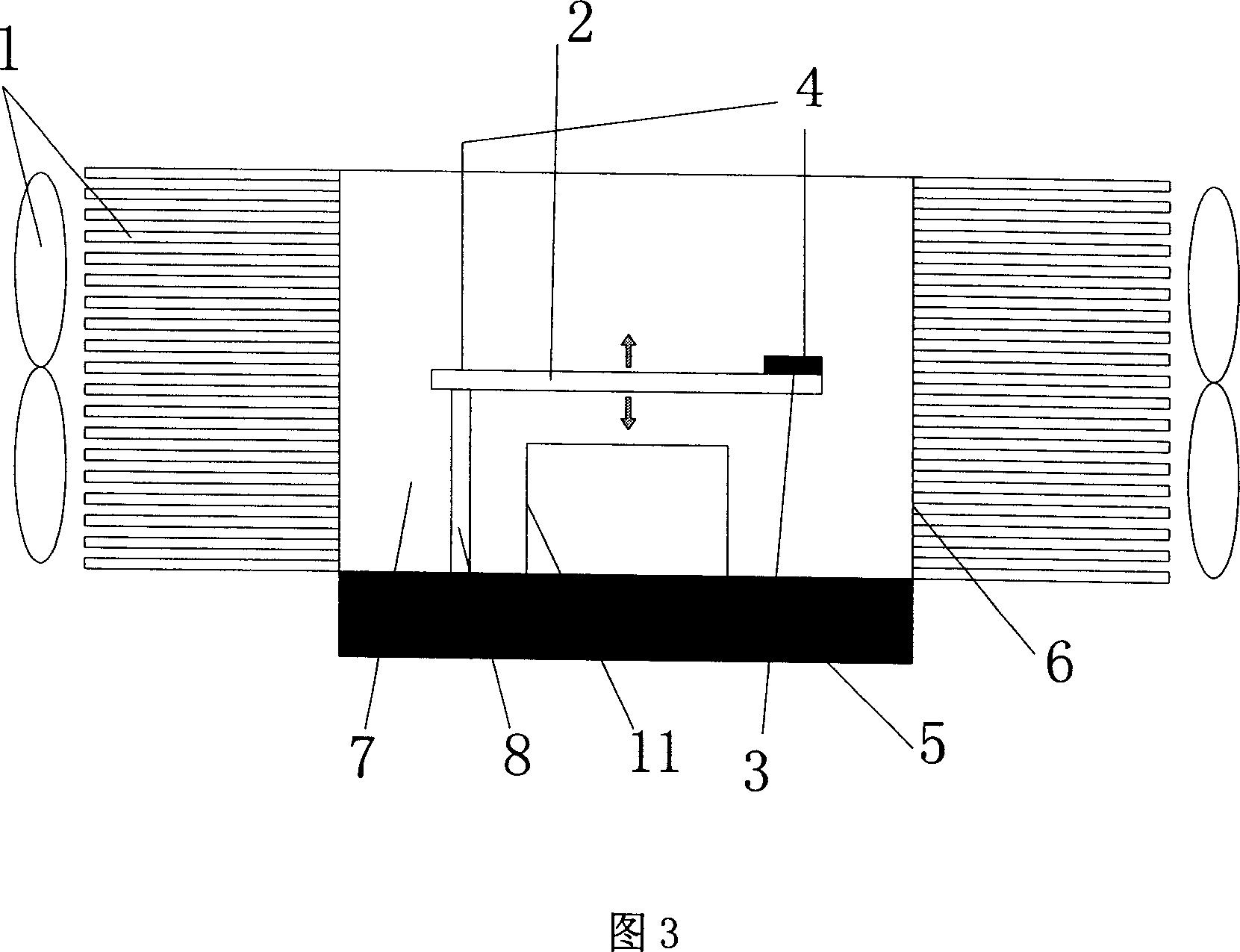
[0021] Referring to Fig. 3, embodiment 3 is the same as embodiment 2, the difference is that the liquid driver is a piezoelectric driver, the piezoelectric driver is composed of a cantilever beam 2 and a support frame 8, and the cantilever beam 2 is a flexible beam, and its working principle is as follows : When the piezoelectric driver 3 is connected to the power supply through the wire 4, the piezoelectric driver 3 starts to vibrate. Due to the characteristics of the cantilever beam, the driving force will cause a large deformation of the cantilever beam, and the deformation of the cantilever beam will drive the radiator shell 6 The cooling liquid 7 inside produces movement, and the cooling liquid 7 in contact with the heat source quickly flows to other positions of the container after absorbing heat, and the heat carried by these hot fluids is transferred to the surrounding environment through the radiator fins 14 and the fan 1 on the four walls In order to lower the tempera...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com