Acrylic acid based on renewable raw materials, water-absorbing polymer structures, and method for the production thereof by means of dehydration
A water-absorbing polymer and a technology for the preparation process, which can be used in the preparation of carbon-based compounds, the preparation of organic compounds, the preparation of carboxylate and other directions, and can solve the problems of high cost, difficulty in obtaining crude oil, and large sanitary products.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
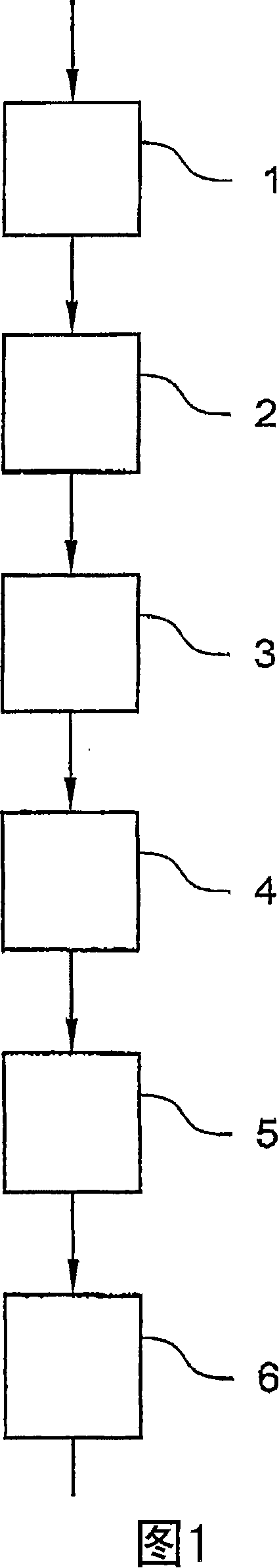
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0132] Embodiment 1: liquid phase dehydration
Embodiment 1a
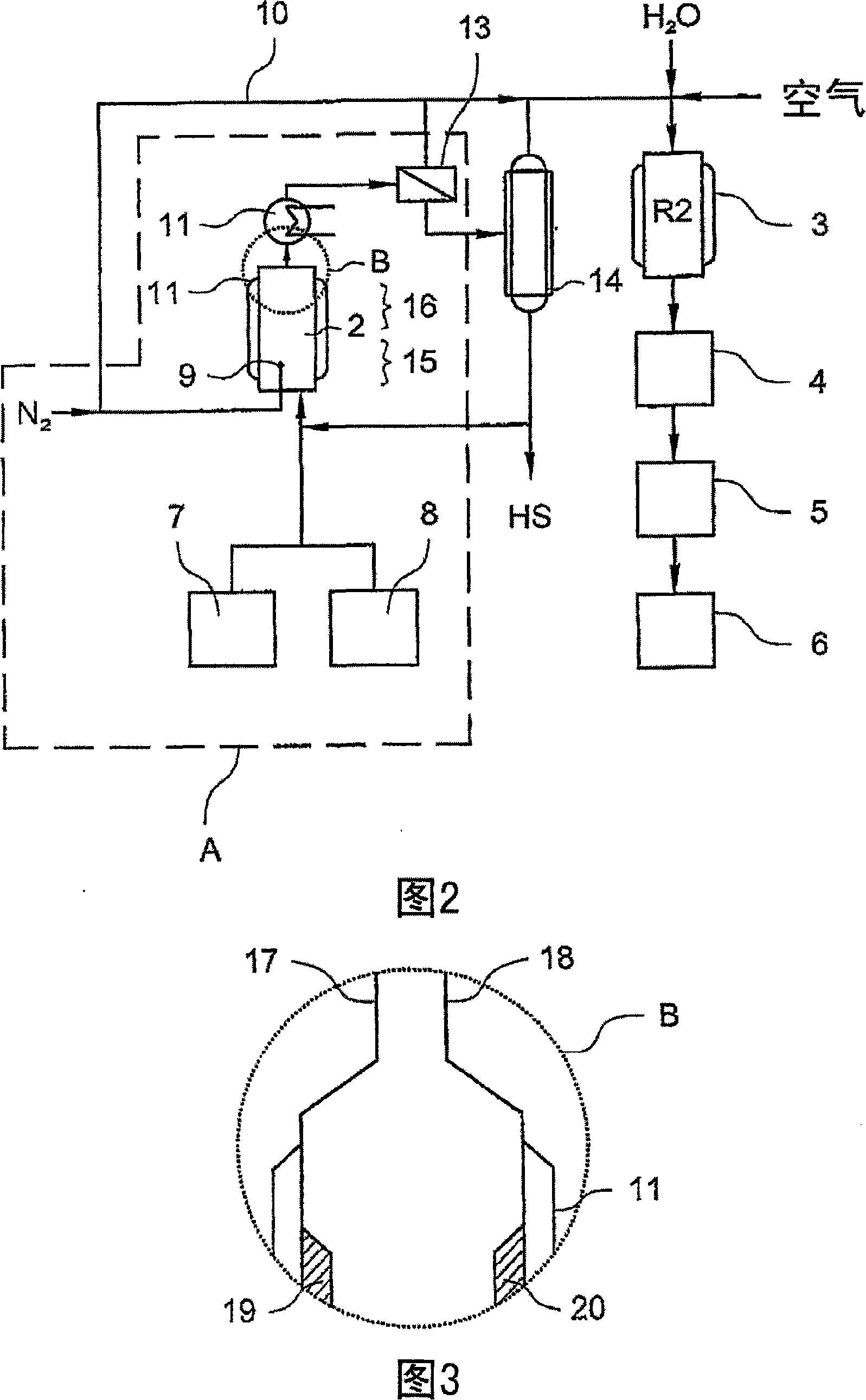
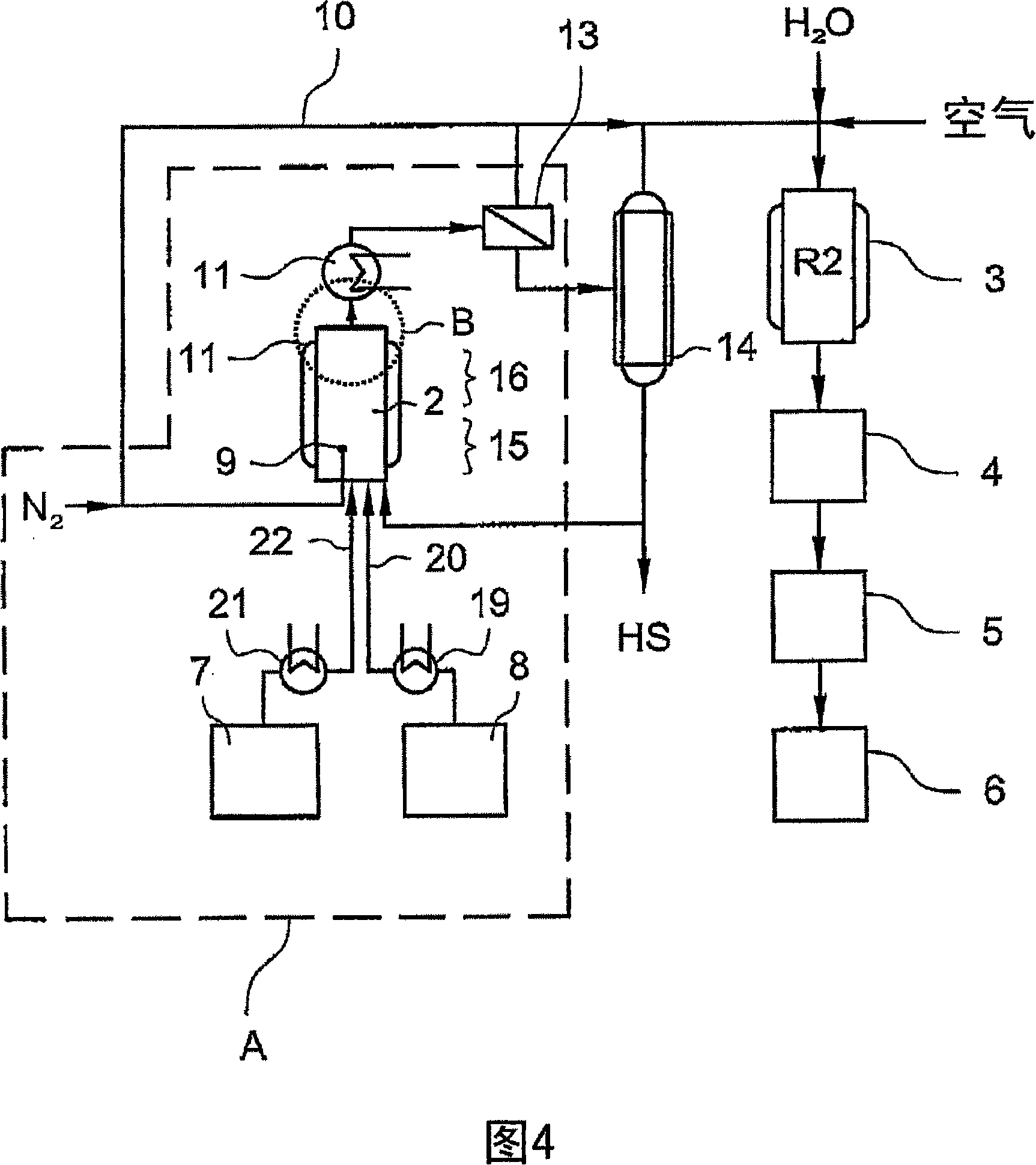
[0134] In the apparatus of Fig. 2A paragraph (in the dotted frame), an aqueous (5%) glycerol solution was injected for liquid phase dehydration, the solution previously adjusted to pH 2.3 with phosphoric acid. The solution was heated in the reactor to 283°C at 58 bar with an average residence time of 9 minutes. Nitrogen bubbles were introduced into the reactor through a metal fritte. The amount of nitrogen charged was 41 Nml based on the volume and hours of the reactor. The conversion rate of glycerin was 61%, and the selectivity rate of acrolein was 85.6%.
Embodiment 1b
[0136] In the apparatus of Fig. 2A, an aqueous (5%) glycerol solution for liquid phase dehydration, which was previously adjusted to pH 2.3 with phosphoric acid, was injected. The solution was heated in the reactor to 285°C at 61 bar with an average residence time of 9 minutes. Nitrogen bubbles were introduced into the reactor through a metal porous device. The amount of nitrogen charged was 41 Nml based on the volume and hours of the reactor. The conversion rate of glycerin was 72.1%, and the selectivity rate of acrolein was 74.8%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com