Embryonic stem cells of rabbit and constructing method thereof
A technology of embryonic stem cells and embryos, applied in the field of rabbit embryonic stem cell lines and their establishment, can solve problems such as failure to provide, achieve high clone formation rate, and facilitate genetic manipulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0069] Example 1. rbES cell culture
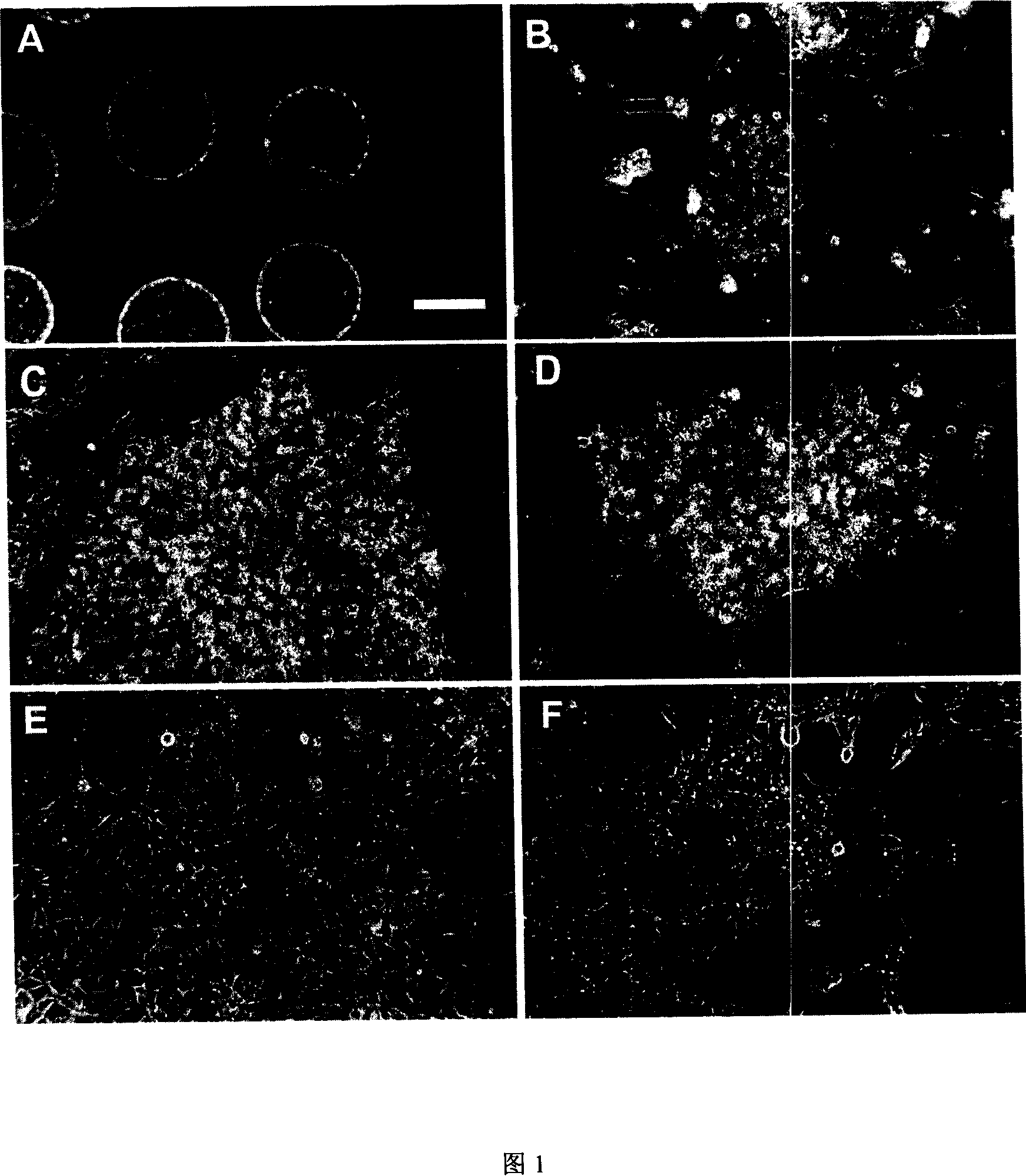
[0070] In this example, we used basically the same isolation and culture methods to isolate embryonic stem cells from rabbit blastocysts of three subspecies (New Zealand, Angola, and Cinnamon). Among them, a cell line was obtained from New Zealand white rabbits, and One cell line was obtained from Angora rabbit, and three cell lines were obtained from Qingzilan rabbit (Figure 1 and Table 1). The successful establishment of rabbit embryonic stem cell lines from three different rabbit subspecies indicates that the method can be equally applied to other rabbit subspecies.
[0071] New Zealand, Angola, and Qingzilan rabbits were purchased from Shanghai Experimental Animal Center, Beijing Institute of Drug Control, and Nanjing Jinling Breeding Rabbit Farm. Four days after natural mating, the blastocysts were flushed out of the uterus with PBS, and the inner cell mass was isolated by mechanical or immunosurgical methods (Davor et al., 1975), a...
Embodiment 2
[0077] Example 2. Molecular markers expressed by rbES cells
[0078] RT-PCR
[0079] Total RNA was extracted with Trizol(R) (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) and treated with DNase I at 37°C for 20 minutes to remove contaminating genomic DNA. First-strand synthesis was performed using Moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase (Promega, Madison, WI) and random primers (Promega) according to the protocol provided by the manufacturer. Primer sequences are shown in Table 4. PCR reactions were performed using the following parameters: denaturation at 94°C for 4 minutes, followed by 35 cycles of amplification consisting of denaturation at 94°C for 30 seconds, annealing for 30 seconds, extension at 72°C for 40 seconds, followed by a final extension at 72°C for 5 minutes. The annealing temperature is shown in Table 4. Samples without reverse transcriptase added during the reverse transcription step were used as controls for genomic DNA contamination. β-actin was used as an ...
Embodiment 3
[0088] Example 3. Calculation of cell cloning and population doubling time
[0089] We investigated the clonogenic rate of three rbES cell lines. Cell colonies were digested into single cells with 0.05% trypsin. 1000 cells per cell line were seeded into culture dishes. After 5 days, the number of colonies was counted, and the colony formation rate was calculated by the following formula: colony formation rate (%)=(clones / 1,000)×100%. As shown in Table 2, the colony formation rates of the three rbES cell lines rbES1, Qzl2 and LHR1 were 0.15±0.01%, 0.18±0.04% and 0.13+0.03%, respectively. The clonal growth of rbES cells will facilitate the selection of rbES cells in the process of genetic manipulation.
[0090] Table 2. Clonogenicity of rbES cells
[0091] cell line
Colony formation rate (%)
rbES1
0.15±0.01
Qz2
0.18±0.04
LHR1
0.13±0.03
[0092] Mark small (about 10 cells) cell colonies at the bottom of the culture...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com