Application of thinopyron elongatum in formulating low-celiac syndrome antigen encoding DNA wheat
A technology of Etpyrum elongatum and celiac disease, applied in the field of application of Etpyronium elongatum to the creation of DNA wheat with low celiac disease antigen coding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1 Using the Homologous Sequence Method to Screen the Wheat Distant Grass with Low Celiac Antigen Coding DNA
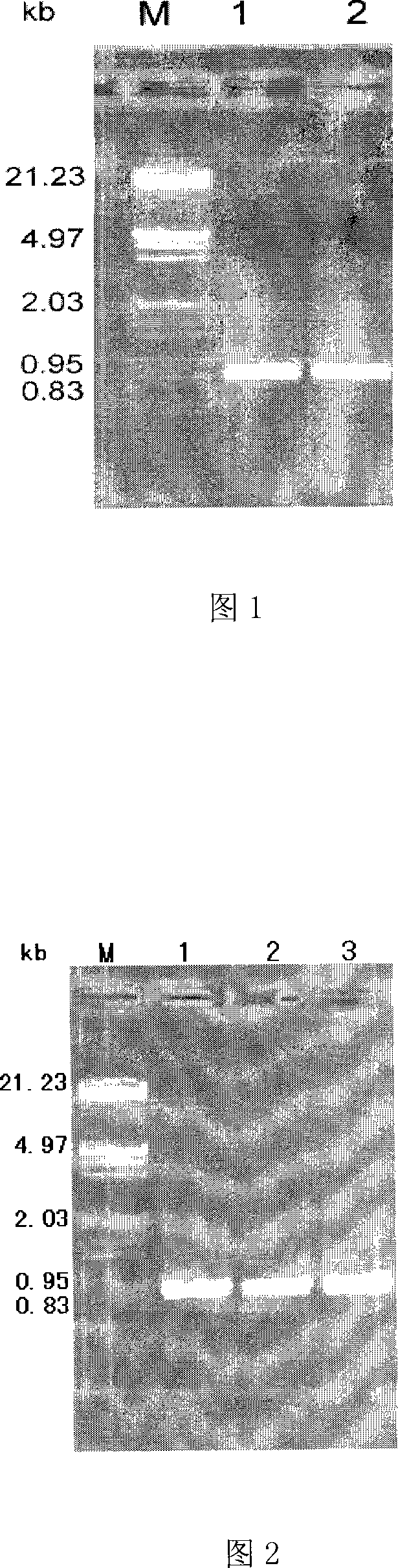
[0028] Take the young leaves of Echinopsis elongatum, and use the CTAB method to extract DNA. The primers are P1: 5'-ATG AAG ACC TTTCTC ATC CT-3', P2: 5'-TCA GTT AGT ACC GAA GAT GCC-3', PCR The enzyme used in the reaction is LA Taq (TaKaRa); cycle conditions: initial denaturation at 94°C / 3min, followed by 30 cycles (denaturation at 94°C / 40s, annealing at 55°C / 1min, extension at 72°C / 2min), and final extension at 72°C / 10min, the PCR results are shown in Figure 1.
[0029] PCR products were electrophoresed on 2.0% agarose gel and recovered (TIANGEN DNA recovery kit). The PCR recovered product was connected to the pMD18-T vector, and then transformed into E.coli DH10B competent cells. The method of cloning and transformation refers to the molecular cloning experiment guideline (Sambrook et al, 1989). The identified positive clones are sequenced bidirecti...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2 Obtaining Wheat Somatic Hybrids Using Asymmetric Somatic Hybridization
[0033] 1) Acquisition of amphipathic embryogenic cells: the recipient material is wheat, and the donor material is distantly related grasses containing low celiac antigens, such as diploid and decaploid Henoptera elongatum. The immature embryos of the recipient and donor are in MS The callus was induced on the medium, and after subculture, the embryogenic callus was selected as the recipient.
[0034] 2) Collection of recipient and donor protoplasts: Take the materials that have been subcultured for 2-5 days, chop them up, use enzymatic hydrolysis technology, that is, at 25°C, free for 3-5 hours, filter with 300-500 mesh stainless steel mesh, Centrifuge at 500rpm for 5min to collect protoplasts.
[0035] 3) UV treatment of donor protoplasts: after washing the collected donor protoplasts with washing solution, adjust the density to 1×10 5-6 / mL, spread on the lower part of a petri dish w...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Example 3 Screening of low-celiac antigen-encoding DNA wheat somatic hybrids
[0049] The method of implementation is the same as the steps and methods in Example 1.
[0050] DNAs encoding four celiac antigens in hybrid II-12 (EU018336-EU018362) and parental wheat (Jinan 177) (EU018268-EU018299) and decaploid Echinopsis elongatum α-gliadin gene (EU018300-EU018335) See Table 1 for comparison.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com