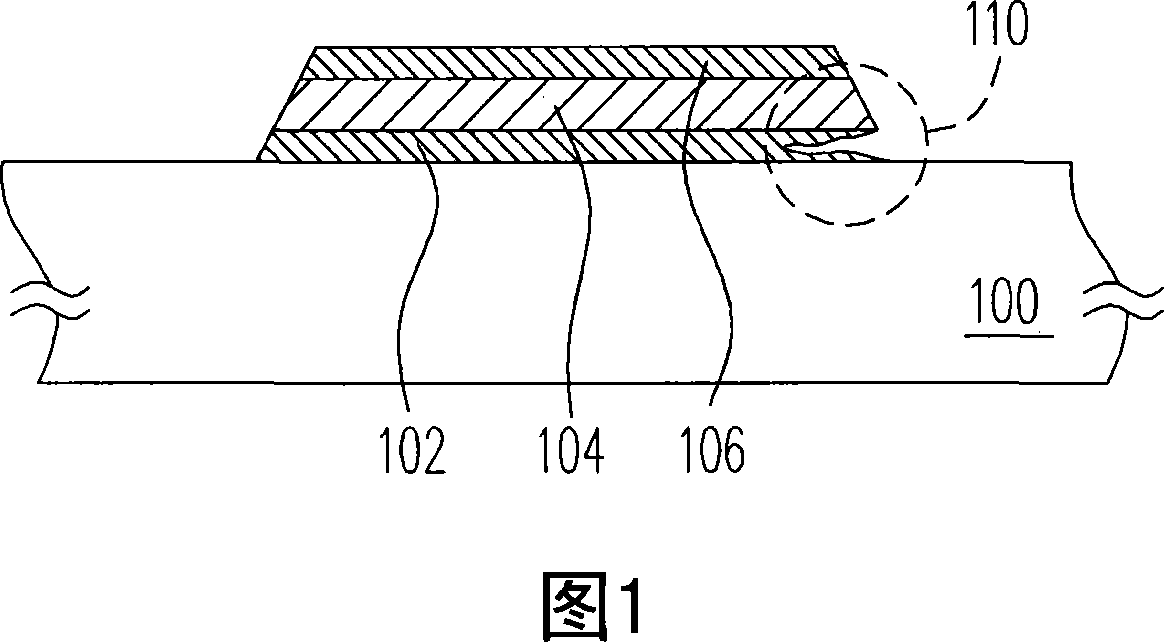
Thin-film transistor, active element array substrate as well as liquid crystal display panel
A technology for liquid crystal display panels and thin film transistors, applied in transistors, electrical components, electrical solid devices, etc., can solve the problems affecting the characteristics of thin film transistor components, disconnection of scanning lines or data lines, and increase in wiring impedance, so as to maintain display quality. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
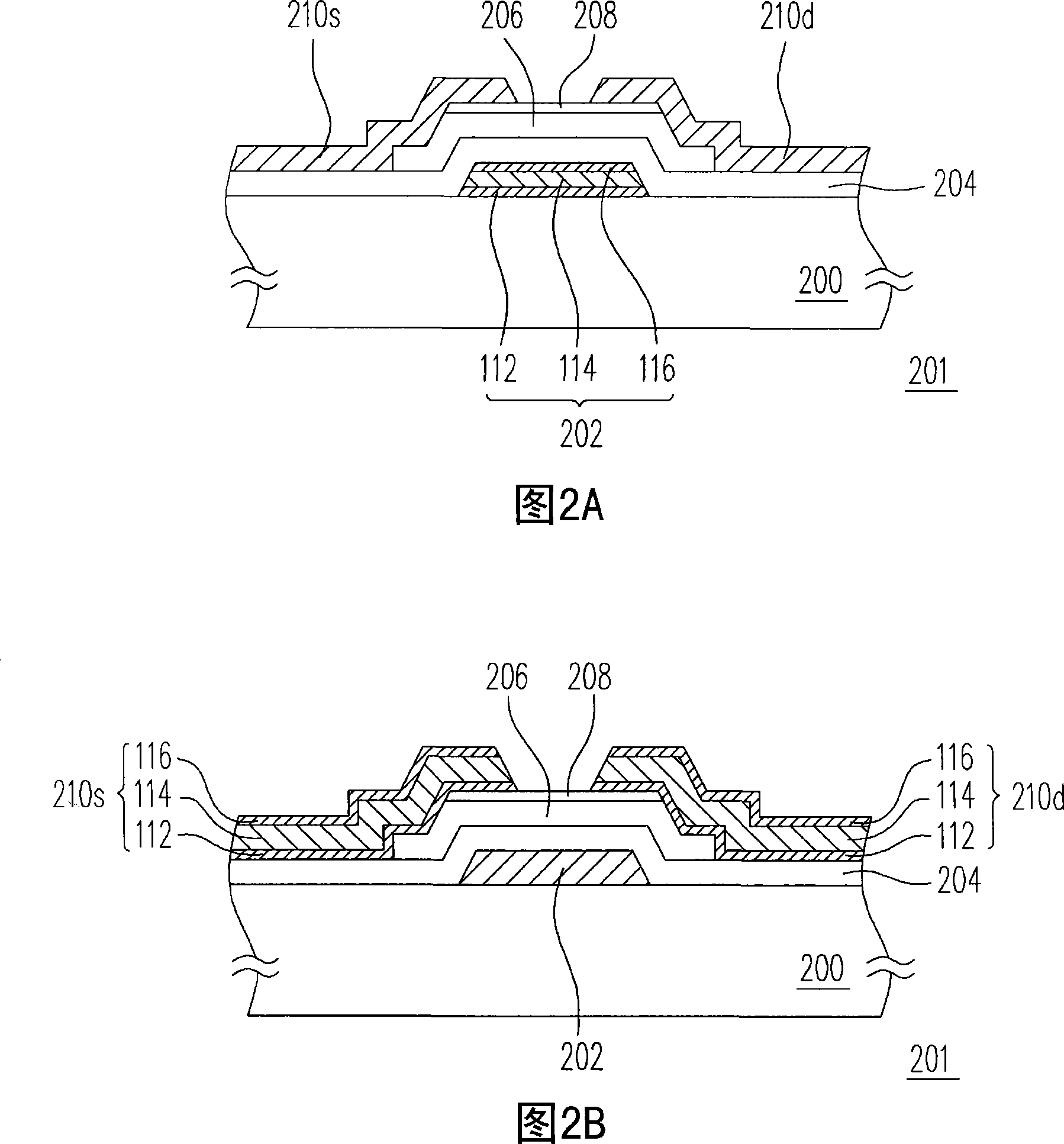
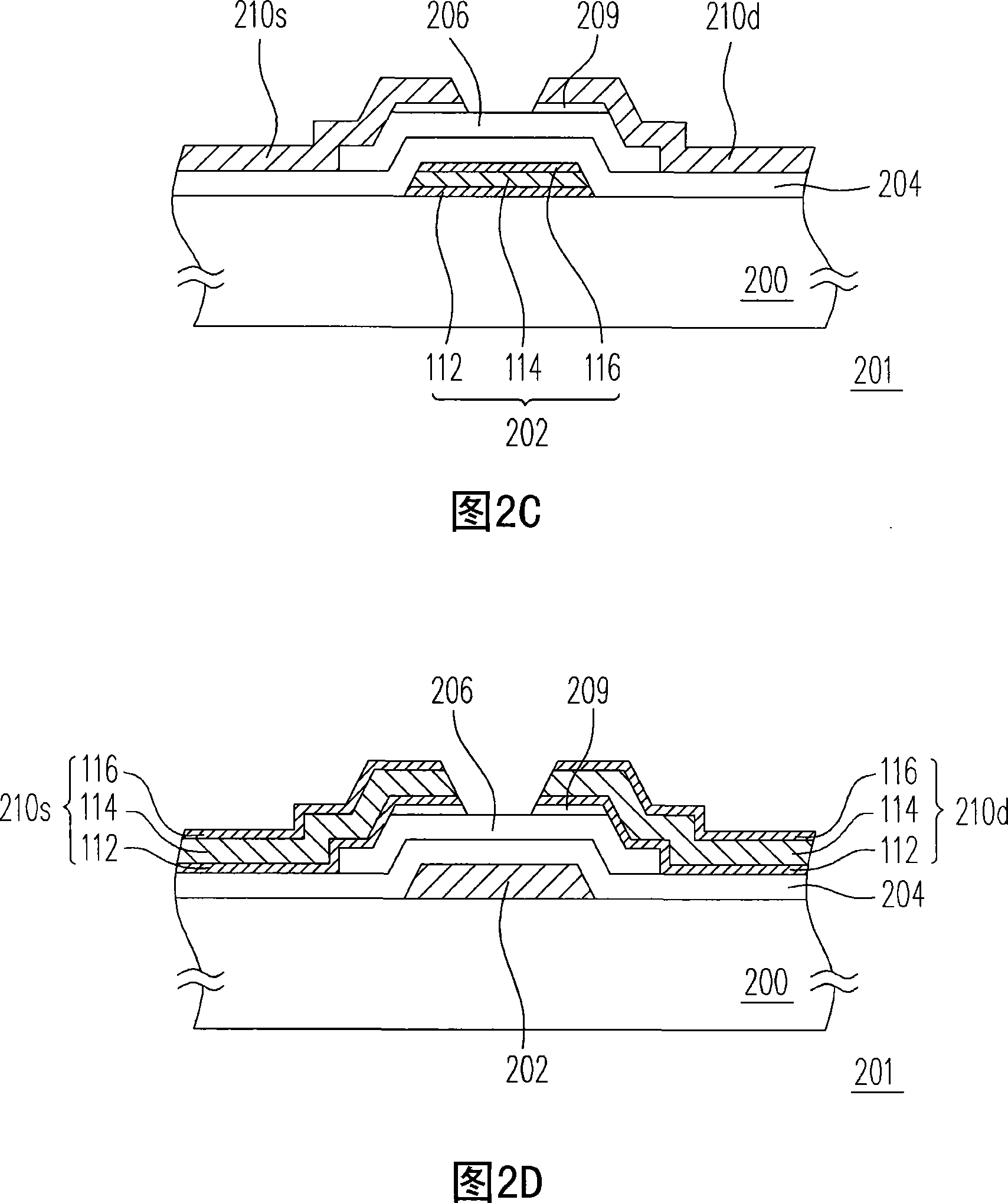
[0070] FIG. 2A is a schematic cross-sectional view of a thin film transistor according to the first embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 2A , a thin film transistor 201 is disposed on a substrate 200 , which includes a gate 202 , a gate insulating layer 204 , a channel layer 206 , and a source 210s and a drain 210d. Wherein, both the gate 202 and the gate insulating layer 204 are disposed on the substrate 200 , and the gate insulating layer 204 covers the gate 202 . The substrate 200 is, for example, a glass substrate, a quartz substrate or other types of substrates. The material of the gate insulating layer 204 is, for example, silicon oxide, silicon nitride or other dielectric materials. The channel layer 206 is disposed on the gate insulating layer 204 above the gate 202 , wherein the material of the channel layer 206 is, for example, amorphous silicon. The source 210s and the drain 210d are respectively disposed on part of the channel layer 206 on both ...
no. 2 example
[0078] 3A is a schematic top view of an active device array substrate according to a second embodiment of the present invention, and FIGS. 3B and 3C are schematic cross-sectional views along section line a-b and section line c-d in FIG. 3A . Please refer to FIG. 3A , FIG. 3B and FIG. 3C at the same time. In this embodiment, only two pixels 220 in the active device array substrate 20 are shown as a representative for illustration. The active element array substrate 20 includes a substrate 200 , a plurality of scan lines 230 , a plurality of data lines 240 and a plurality of pixels 220 . Scanning lines 230, data lines 240, and pixels 220 are all configured on the substrate 200, wherein a plurality of pixels 220 are respectively connected to corresponding scanning lines 230 and data lines 240, and each pixel 220 includes an active element 216 and an active element 216. The element 216 is electrically connected to the pixel electrode 218 . In addition, in this embodiment, the act...
no. 3 example
[0085] FIG. 4 is a schematic top view of a liquid crystal display panel according to a third embodiment of the present invention. Please refer to FIG. 4, the liquid crystal display panel 10 includes the active element array 20, the opposite substrate 30 and the liquid crystal layer 40 in the above-mentioned embodiment, wherein the opposite substrate 30 is arranged on the opposite side of the active element array substrate 20, and The liquid crystal layer 40 is disposed between the opposite substrate 30 and the active element array substrate 20 . In this embodiment, the opposite substrate 30 is, for example, a color filter substrate, and the liquid crystal display panel 10 may be a transmissive display panel, a semi-transmissive display panel, a reflective display panel, or a color filter on an array. (color filter on array) display panel, array on a color filter (array on color filter) display panel, or other types of substrates.
[0086] Due to the plurality of active elemen...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com