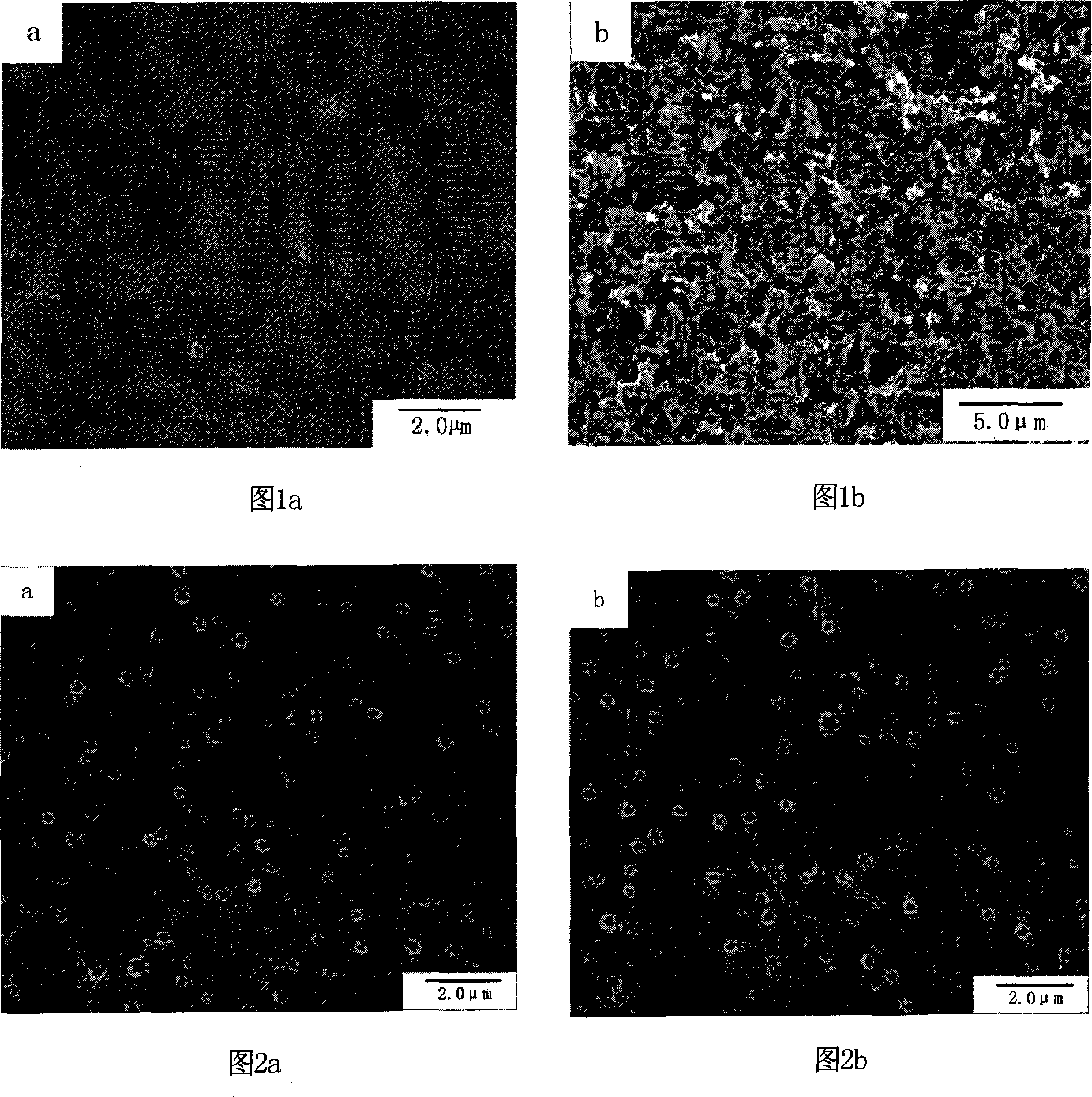
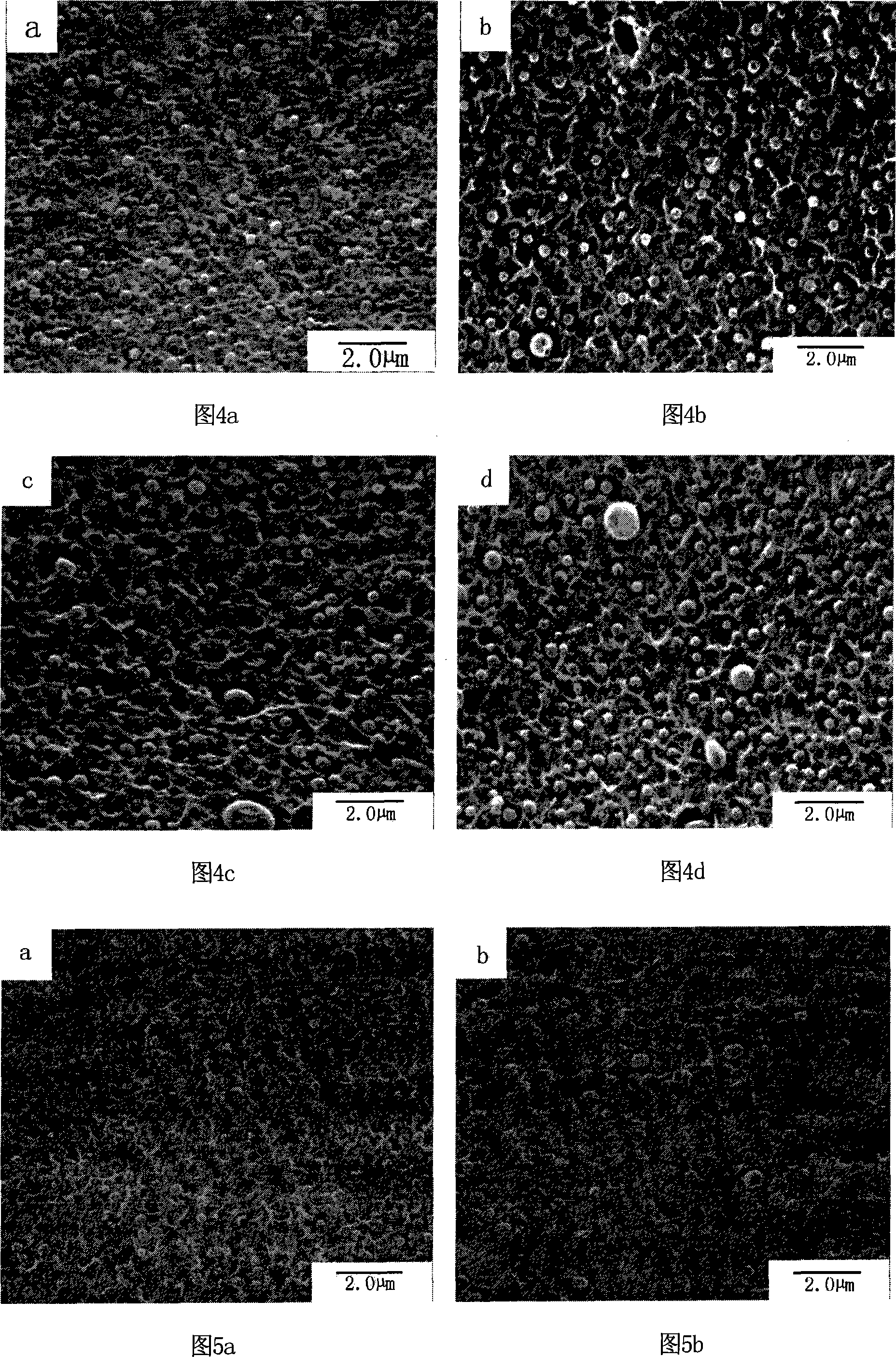
Microetching method on ABS engineering plastic element surface without chromium pollution
A technology for engineering plastics and parts, which is applied in the field of micro-etching treatment on the surface of ABS engineering plastics parts, can solve problems such as environmental pollution and achieve good results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
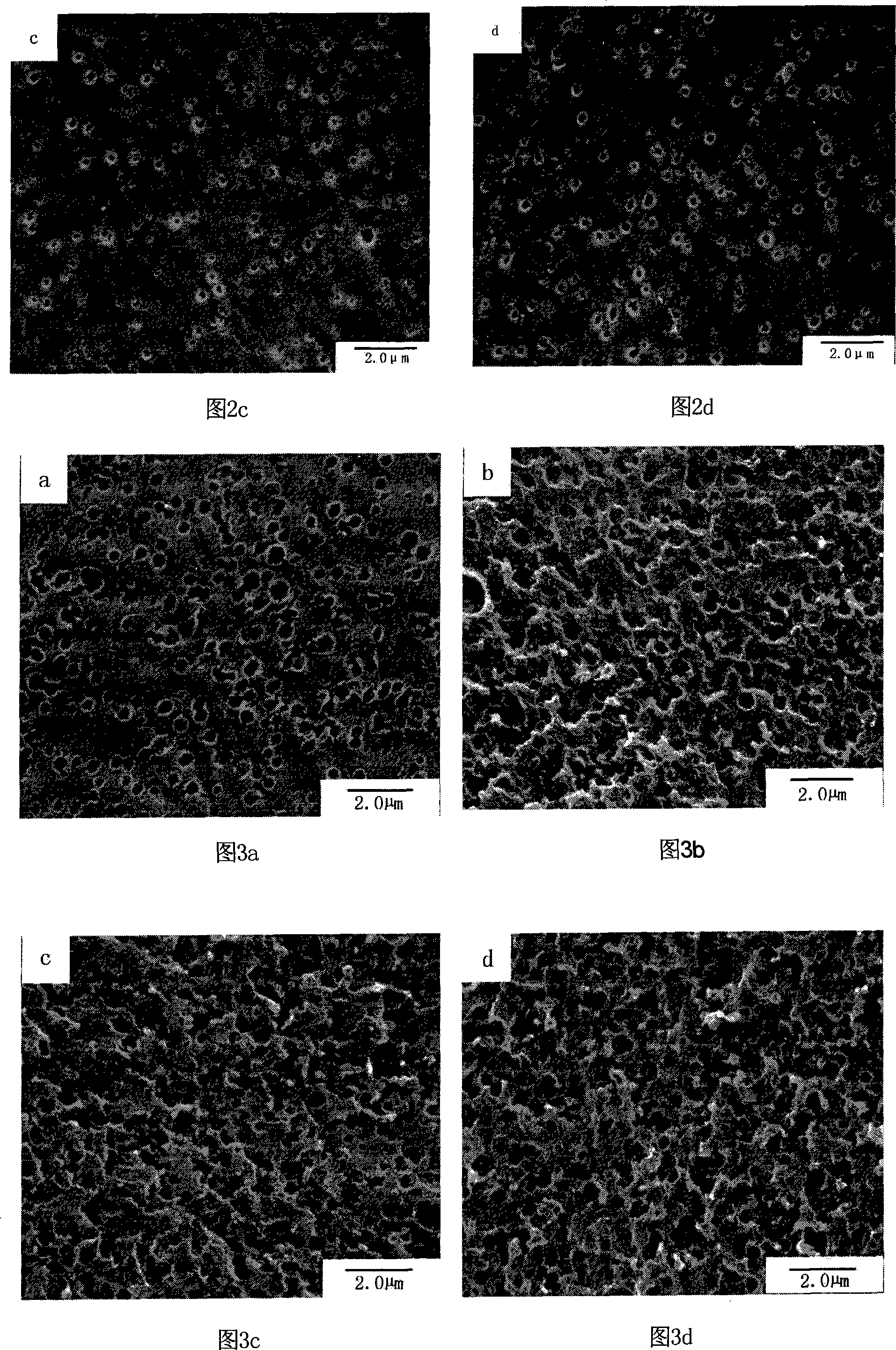
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Taking the micro-etching treatment on the surface of ABS engineering plastic board as an example, the process steps are as follows:
[0030] 1. Degreasing
[0031] Preparation of degreasing solution: Take 500mL of chemical degreasing liquid concentrate of model SYT8010 and distilled water at a volume ratio of 1:1 to prepare 1L of degreasing liquid. The chemical degreasing liquid concentrate is provided by Shanghai Xinyang Semiconductor Materials Co., Ltd. The degreasing fluid can also be prepared with other types of degreasing fluid or according to the existing formula.
[0032] Degreasing: Immerse the ABS engineering plastic board in the degreasing solution, stir, degrease at 60°C for 5 minutes, remove the dirt on the surface of the ABS engineering plastic board, promote uniform roughening, and improve the bonding force of the coating.
[0033] 2. Swelling
[0034] Preparation of swelling liquid: take 90g of sodium hydroxide and put it into a beaker, add distilled wa...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Taking the micro-etching treatment on the surface of ABS engineering plastic board as an example, the process steps are as follows:
[0047] In step 2 of the swelling process, take 70g of sodium hydroxide and add it to the beaker, add distilled water until the sodium hydroxide dissolves, then add 72g of 1-methyl-2-pyrrolidone and 13g of butyl glycol ether, and dilute to 1L with distilled water , be mixed with swelling liquid, swelling step is identical with the swelling step of embodiment 1. In step 3 of the microetching process, take 20g of MnO 2 Add it into 1L of sulfuric acid aqueous solution with a mass concentration of 77.7% to prepare MnO 2 / H 2 SO 4 Microetching solution: The swollen ABS engineering plastic plate is immersed in the microetching solution, stirred, and microetched at 70°C for 20 minutes. In neutralization reaction step 4, take 12.7g of oxalic acid in a beaker, add distilled water until the oxalic acid is completely dissolved, then add 54.4ml of...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Taking the micro-etching treatment on the surface of ABS engineering plastic board as an example, the process steps are as follows:
[0051] In step 2 of the swelling process, take 100g of sodium hydroxide and add it to the beaker, add distilled water until the sodium hydroxide dissolves, then add 124g of 1-methyl-2-pyrrolidone and 22g of butyl glycol ether, and set the temperature with distilled water. Dissolve to 1L, and prepare swelling solution, the swelling step is the same as that of Example 1. In step 3 of the microetching process, take 50g of MnO 2 Add it into 1L of sulfuric acid aqueous solution with a mass concentration of 77.7% to prepare MnO 2 / H 2 SO 4 Microetching solution: The swollen ABS engineering plastic plate is immersed in the microetching solution, stirred, and microetched at 70°C for 20 minutes. In the neutralization reaction step 4, take 63.6g of oxalic acid in a beaker, add distilled water until the oxalic acid is completely dissolved, then ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com