Mass spectrum kit for detecting squamous-cell carcinoma antigen feminine cervical carcinoma serum protein and preparation method thereof
A technology for squamous cell carcinoma and cervical cancer, applied in the field of protein detection, can solve the problems of high false negative rate and lack of early monitoring methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0068] Example 1 Distinguishing between normal and squamous cell carcinoma antigen-negative cervical cancer patients and preparation of a mass spectrometry kit
[0069] (1) Experimental method
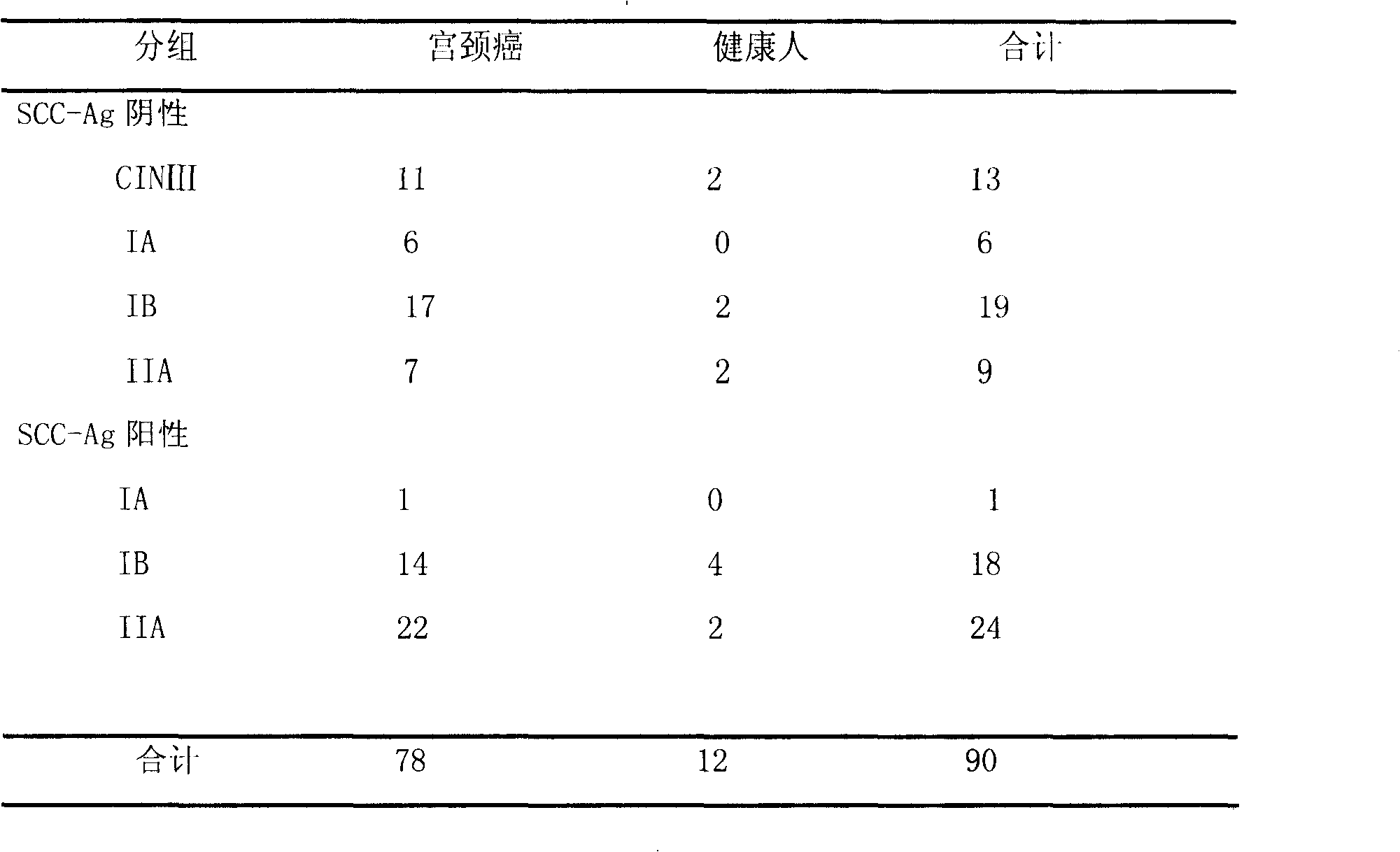
[0070] The preoperative serum of 77 patients with cervical squamous cell carcinoma (including 44 cases of stage I and 33 cases of stage II, with an average age of 44 years) and 13 patients with CINIII (average age of 41 years). There were 52 healthy subjects, with an average age of 42 years, from a population with normal liver function and renal function tests. Collect 1mL of venous blood from the subject on an empty stomach, immediately after collection, let it stand in a refrigerator at 4°C for 2 hours, centrifuge at 4,000r / min at 4°C for 10 minutes to separate the serum, and centrifuge the serum again at 12,000r / min at 4°C for 5 minutes to remove all residual cell debris and insoluble matter, the serum was divided into 100 μL / tubes on ice, a total of 5 tubes, and stored in a -80°C ...
Embodiment 2
[0095] The double-blind test of embodiment 2 kit
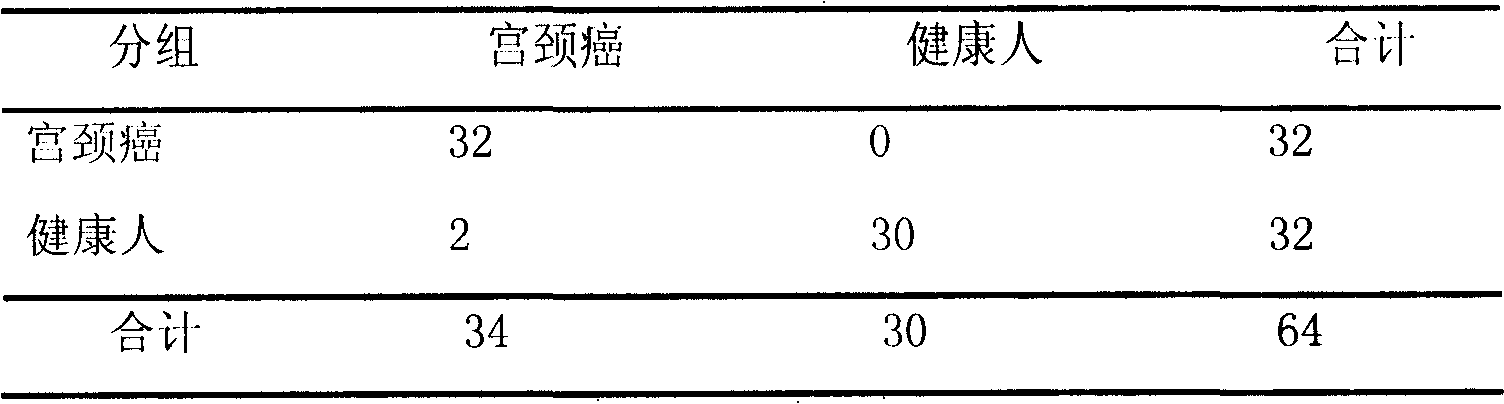
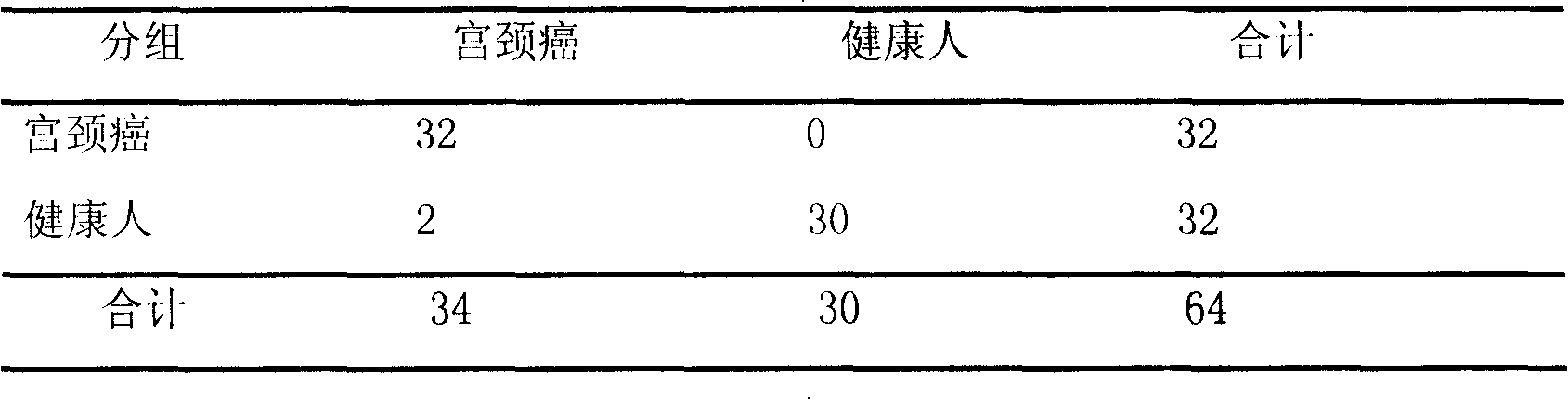
[0096] Screen out several characteristic protein peaks from embodiment 1, 3974,3398, 13761 ± 15Da 3 difference peaks form the test model to SCC-Ag negative expression cervical cancer patient and healthy crowd blind screening test, analyze with this classification method In the mass spectrometry results of 32 cervical cancer samples, 32 of them were correctly differentiated, 0 were wrongly distinguished, and the sensitivity was 100%; 30 of the 32 control samples were correctly distinguished, 2 were wrongly distinguished, and the specificity was 93.75% (see Table 2 ):
[0097] Table 2: Discrimination of test models in biological samples
[0098]
[0099] Note: Sensitivity 100% (32 / 32); Specificity 93.75% (32 / 32)
[0100] The experimental results using C8 and C18 hydrophobic matrix magnetic beads or chips are consistent with the experimental results of the above-mentioned WCX anion matrix magnetic beads or chips.
Embodiment 3CI
[0101] Example 3 CINIII and cervical cancer I, II stage patient polypeptide protein screening
[0102] Comparison of polypeptide proteins between CINIII and patients with cervical cancer stage I and II: After normalization of the protein fingerprints of 13 cervical cancer and 13 CINIII samples, a total of 122 protein peaks were detected in the molecular weight range of 1,500 to 35,000, of which 2 were in There is a significant difference between the cervical cancer group and the control group (P<0.05). The molecular weights, mean values and P values of different peaks are shown in Table 3:
[0103] Table 3: Difference peaks in 13 cases of cervical cancer and 13 cases of cervical CINIII biological samples
[0104] Protein peak Average protein abundance in cervical cancer patients Protein level P value in cervical CINIII patients
[0105] (m / z) x±s mean abundance x±s (P<0.05)
[0106] 9279 15.44±3.97 19.41±4.30 0.0129
[0107] 5944 3.97±1.57 5.28±1.81 0.0257
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com