Preparation of modified graphite cathode material of lithium ion secondary battery
A secondary battery and graphite negative electrode technology, applied in battery electrodes, electrode manufacturing, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of poor high-current charge and discharge performance, low initial charge and discharge efficiency, poor electrochemical cycle performance, etc., and achieve good Improvement of cycle performance, reversible capacity, and stable capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
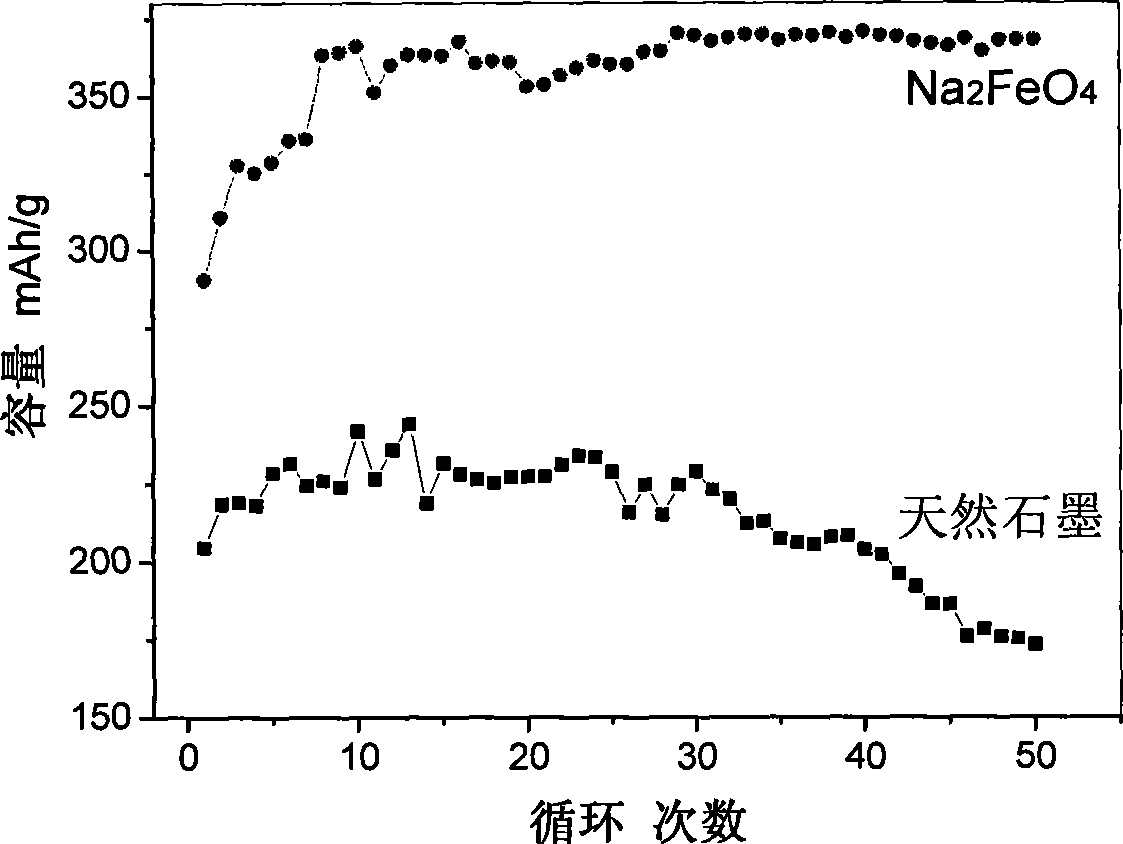
[0020] Add 1 mol / L LiOH solution into an electrolytic cell with a volume of 0.9 liters, use barbed wire as the anode and nickel foam as the cathode, and electrolyze at a constant current of 2A for 1 hour at 0°C under stirring conditions to prepare ferrate Li 2 FeO 4 solution. In the prepared ferrate Li 2 FeO 4 Add 10 g of natural graphite to the solution, and carry out oxidation treatment for 1 h at 0° C. with stirring. Then aged at -10°C for 5 hours. The treated samples were washed with hydrochloric acid solution and deionized water, filtered with suction, and dried at 70° C. to obtain modified graphite. The modified sample obtained in this example has a 0.1C specific capacity of 310 mAh / g, and after 50 cycles, the capacity still maintains 85% of the highest capacity.
Embodiment 2
[0022] Add 20mol / L NaOH solution into a 0.9-liter electrolytic cell, use barbed wire as the anode and foamed nickel as the cathode, and conduct constant current 0.5A electrolysis at 100°C and stirring for 24 hours to prepare ferrate Na 2 FeO 4 solution. In the prepared ferrate Na 2 FeO 4 Add 20g of natural graphite into the solution, and carry out oxidation treatment at 100°C for 24h under stirring conditions. Then aged at 40°C for 72h. The treated samples were washed with phosphoric acid solution and deionized water, filtered with suction, and dried at 150° C. to obtain modified graphite. The modified sample obtained in this example has a 0.1C specific capacity of 345 mAh / g, and after 50 cycles, the capacity still increases steadily.
Embodiment 3
[0024] Add 5 mol / L LiOH solution and 1 g of natural graphite into an electrolytic cell with a volume of 0.9 liters, use barbed wire as the anode and nickel foam as the cathode, and conduct constant current 1A electrolysis at 70 ° C and stirring conditions for 10 h, using the prepared ferrate Li 2 FeO 4 In situ modification of graphite. Then aged at 20°C for 24 hours. The treated samples were washed with hydrochloric acid solution and deionized water, filtered with suction, and dried at 120° C. to obtain modified graphite. The modified sample obtained in this example has a 0.1C specific capacity of 330 mAh / g, and after 50 cycles, the capacity still maintains 90% of the highest capacity.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com