Distributed media access control protocol for increasing capacity of wireless local area network
A media access control and wireless local area network technology, applied in the field of distributed access, can solve the problems that the polling algorithm cannot accurately predict the queue status of polled nodes, reduce service QoS performance, and cannot use distributed environments, etc., to achieve Increase system throughput, improve fairness, and increase system throughput
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0044] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and example the present invention is described in further detail.
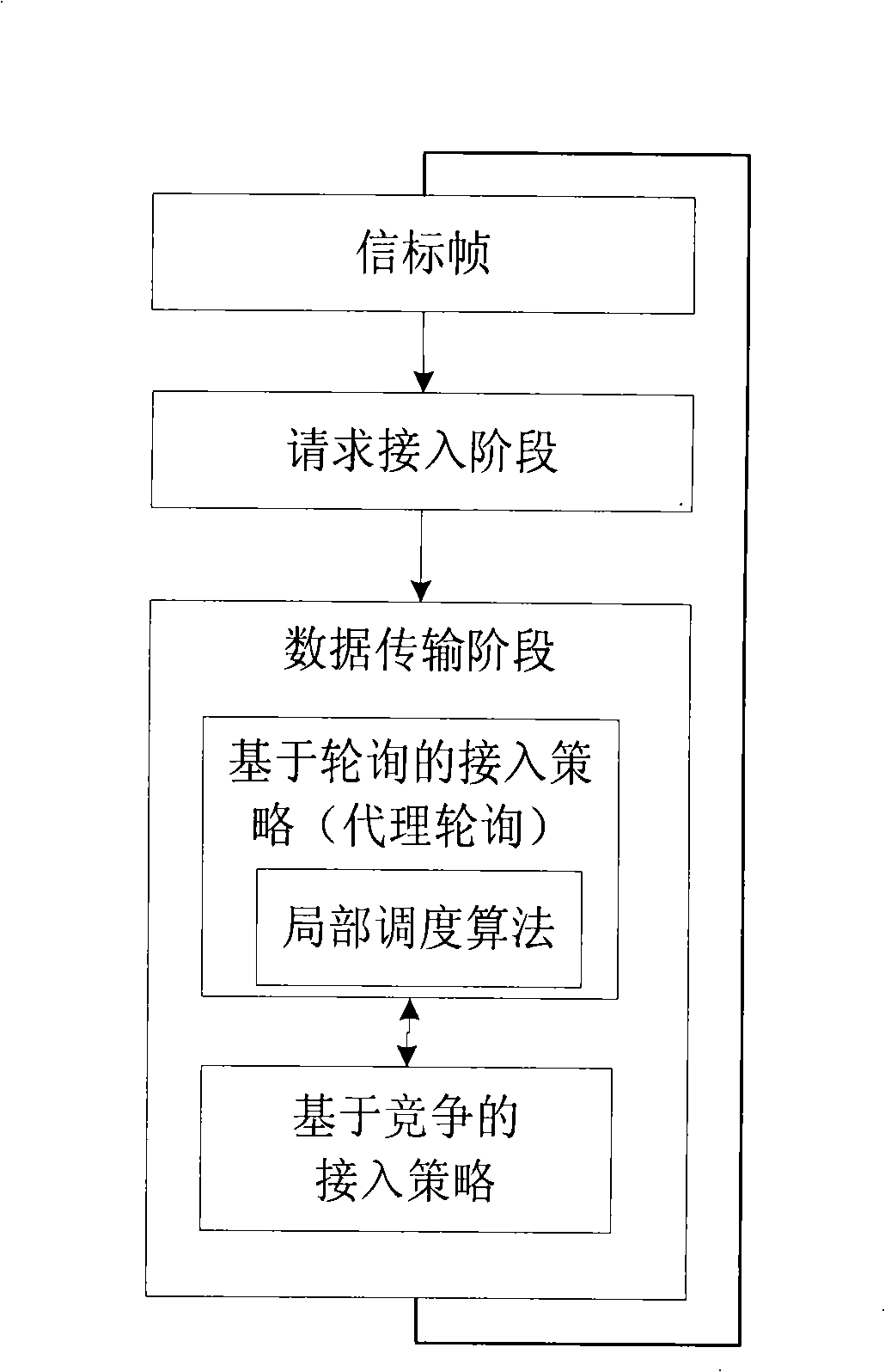
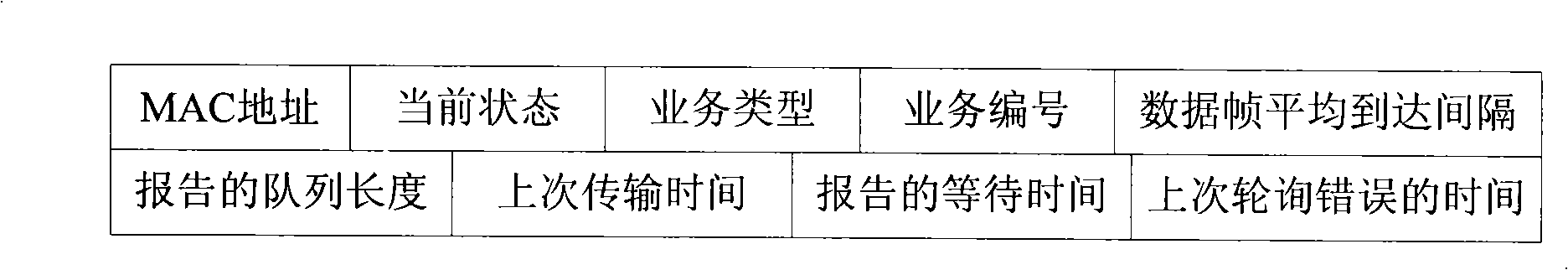
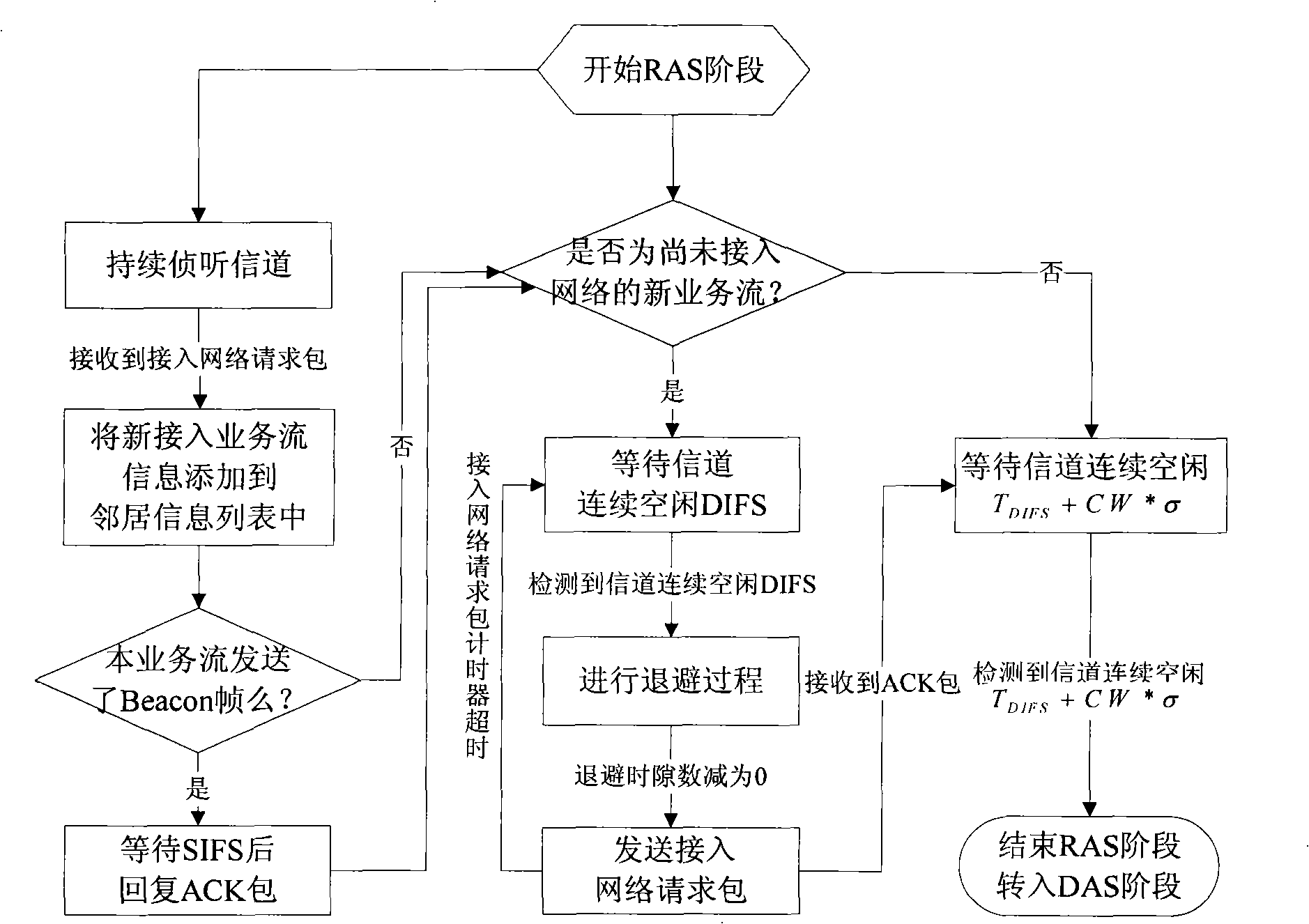
[0045] figure 1 It is a system structure diagram of the DPHA protocol. Time is divided into superframes, and each superframe consists of a beacon frame (Beacon), a request for access phase (RAS) and data transmission phase (DAS) and is repeated periodically. The next transport service flow selected at the end of the previous superframe will transmit the beacon frame in the current round of superframe. The RAS stage is used for newly arriving service flows to compete for sending access network request frames. The DAS stage is the stage of data frame transmission. In this stage, the transmission of data frames mainly adopts the access strategy based on polling to avoid channel conflicts, and at the same time adopts the access strategy based on contention as a supplement to solve the problem when the polling decision is wrong. The competition-based access ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com