Method of assaying substance with affinity in sample including step of destroying blood-cell ingredient
A determination method and substance technology, which can be used in biological tests, measuring devices, analytical materials, etc., and can solve the problems of inability to detect particles, the effect of small hole clogging, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0243] [Example 1] Bursting test 1 of whole blood
[0244] (1) Measuring device
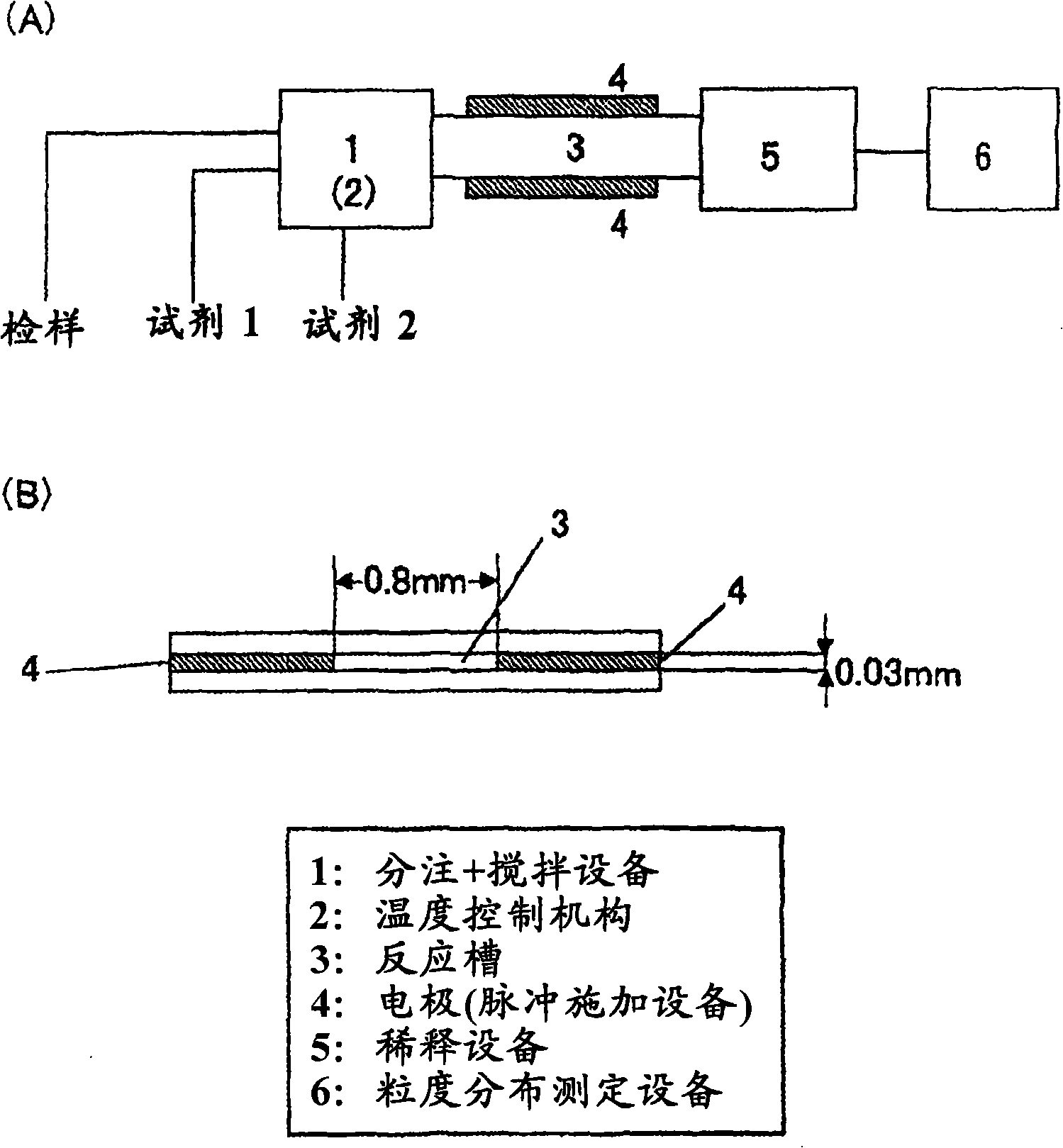
[0245] use figure 1 The apparatus of (A) tests the disruptability of blood cell components contained in whole blood. The whole blood sample and the reagent are injected and mixed in 1 minute, and then the mixed solution is moved into the reaction tank 3 (pulse application tank), and pulse voltage is applied through the electrode 4 for several seconds to several minutes to rupture the blood cell components. Reagent 2 (latex reagent) was not used at this time. Thereafter, the mixed liquid is diluted in the dilution tank 5, and the particle size distribution of the blood cell component is measured with a particle size distribution meter 6. Temperature control mechanisms 1 and 2 are set to off.
[0246] figure 1 (B) shows the cross section of the pulse application groove. The distance between the electrodes was 0.8 mm, the thickness of the electrodes was 0.03 mm, and the length of the electro...
Embodiment 2
[0253] [Example 2] Bursting test 2 of whole blood
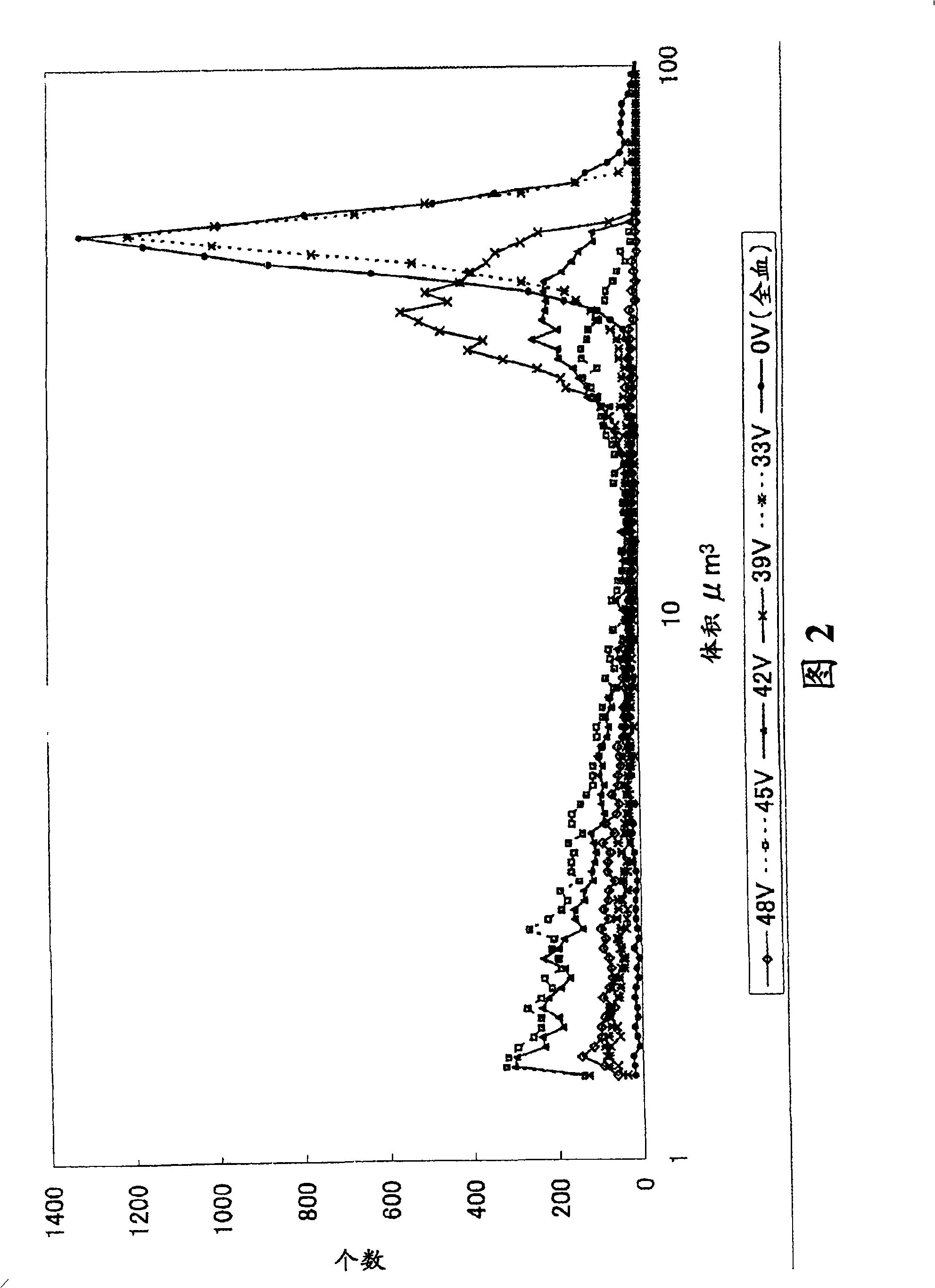
[0254] Using the same whole blood sample and device as in Example 1, blood cell components were destroyed under the following conditions.
[0255] Pulse voltage: AC voltage (rectangular wave) with a frequency of 400KHz
[0256] Electric field strength: 48V / 0.8mm
[0257] Application time: 0 to 60 seconds
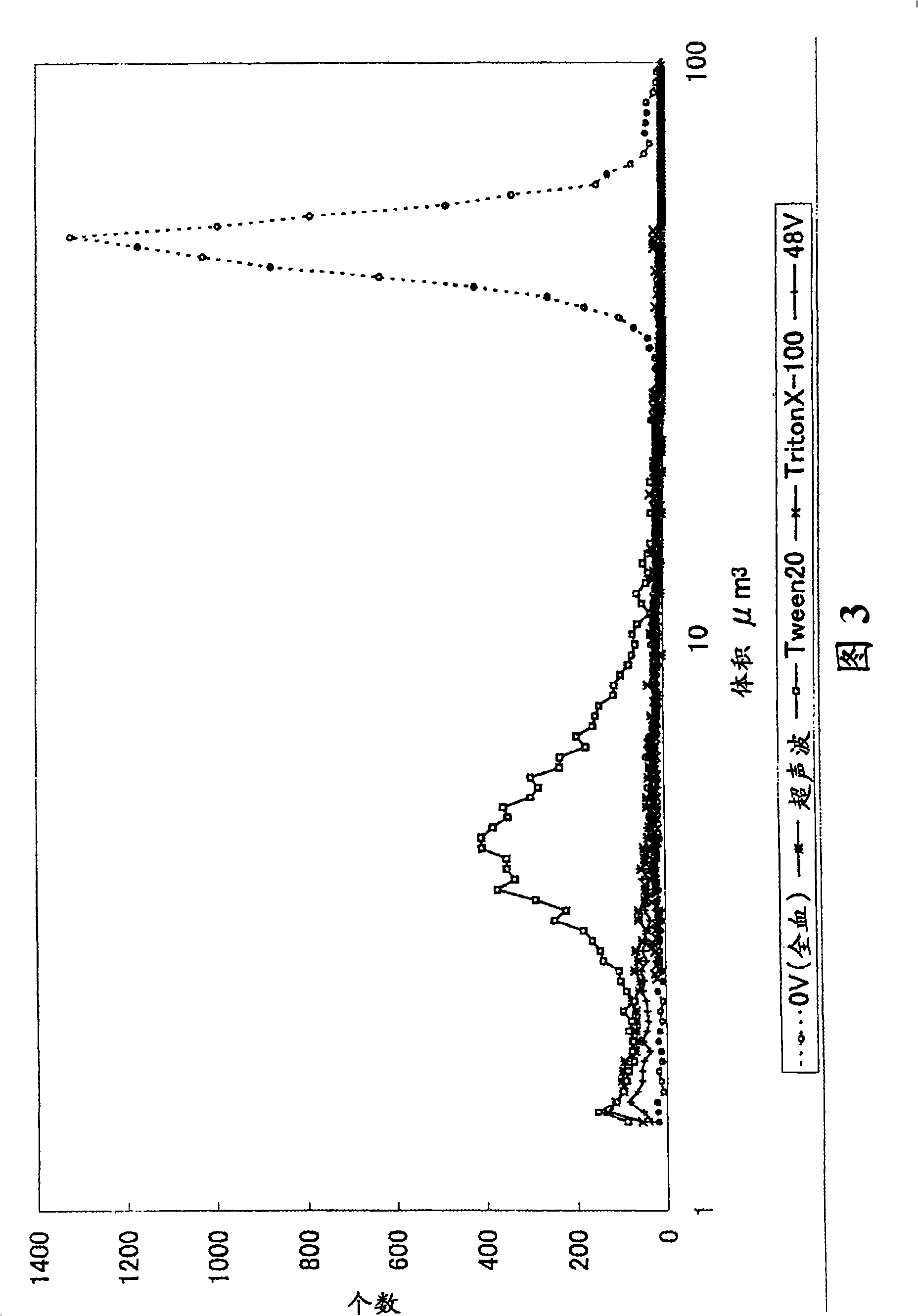
[0258] The results are shown in Table 2. The average volume of the counted particles becomes significantly smaller when the pulse voltage is applied for about 10 seconds. Furthermore, it was also confirmed that the number of particles larger than 3 μm corresponding to blood cell components could hardly be counted by application for 10 to 30 seconds. Therefore, it was confirmed that an application time of about 10 seconds is sufficient for an AC voltage (rectangular wave) with a frequency of 400 KHz and an electrolytic strength of 48 V / 0.8 mm. That is, according to the present invention, blood cell components can be des...
Embodiment 3
[0267] (1) Preparation of anti-CRP antibody sensitized latex reagent
[0268] A latex reagent was prepared as an antibody solution in glycine buffer (containing 50 mM glycine, 50 mM sodium chloride, 0.09% sodium azide, hereinafter abbreviated as GBS) containing 0.15 mg / mL anti-CRP antibody (manufactured by Shibayagi). As for the latex particles, 0.9 mL of GBS was added to 0.1 mL of 1.0 μm latex (manufactured by Sekisui Chemical Co., Ltd., 10% solid content suspension) to prepare a latex suspension.
[0269]1 mL of the antibody solution and the latex suspension were mixed, stirred at 37°C for 2 hours, the sensitized latex was centrifuged, and the supernatant was removed. The precipitate was suspended in 2 mL of glycine buffer (0.5% BSA-GBS) containing 0.5% bovine serum albumin to prepare an anti-CRP antibody sensitized latex reagent.
[0270] (2) Measuring device
[0271] use figure 1 The device in (A) measures biologically specific agglutination reactions (antigen-antibody...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com