Push cam type internal combustion engine without side pressure
An internal combustion engine, cam-type technology, applied in mechanical equipment, engine components, machines/engines, etc., can solve problems such as aggravating cylinder wall, piston wear, large pressure axial force, vibration and noise, complex mechanism, etc., to eliminate friction and wear and The effect of friction power consumption, improving work efficiency and simplifying the valve train
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Embodiment 1: Four-phase cam four-cylinder internal combustion engine
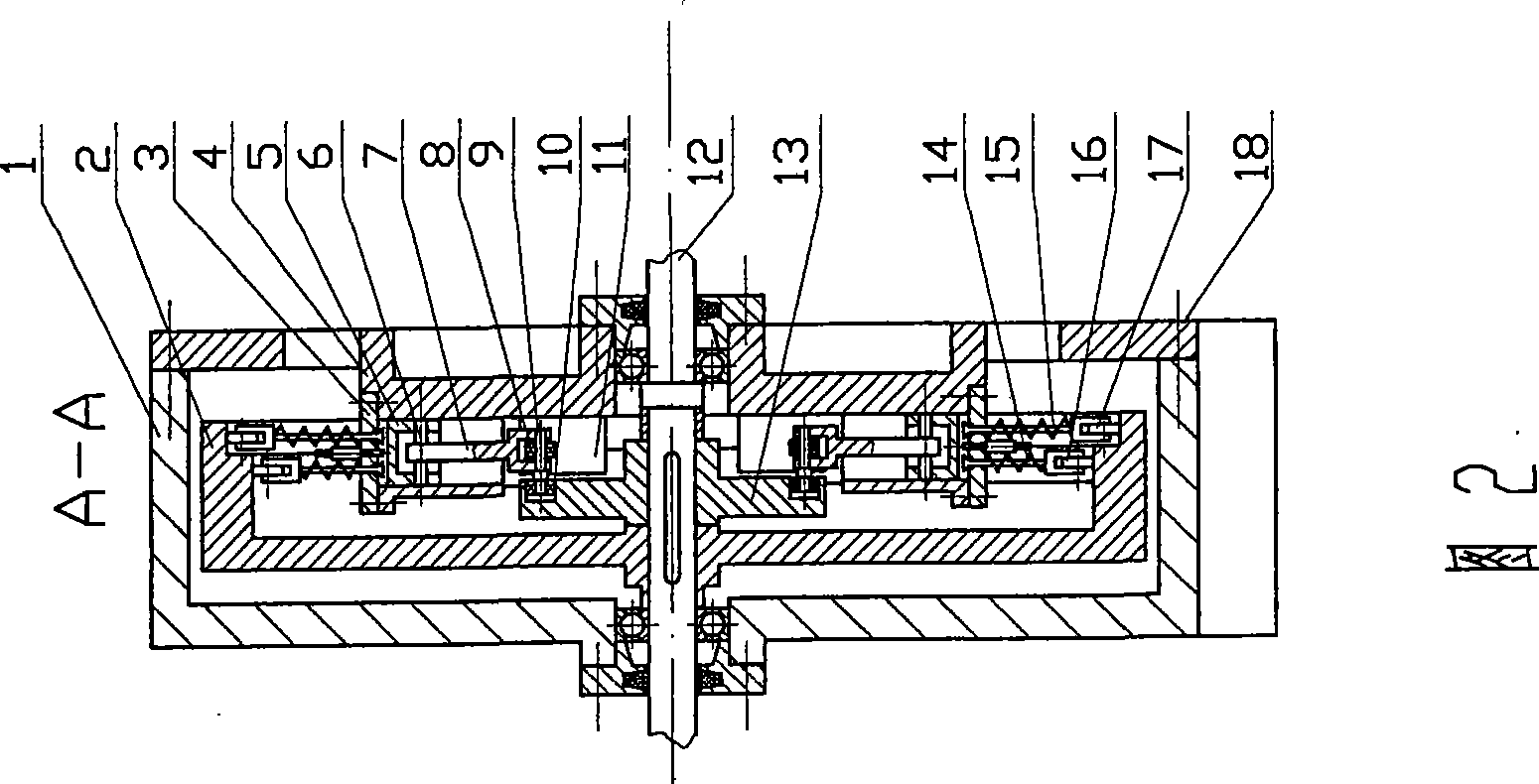
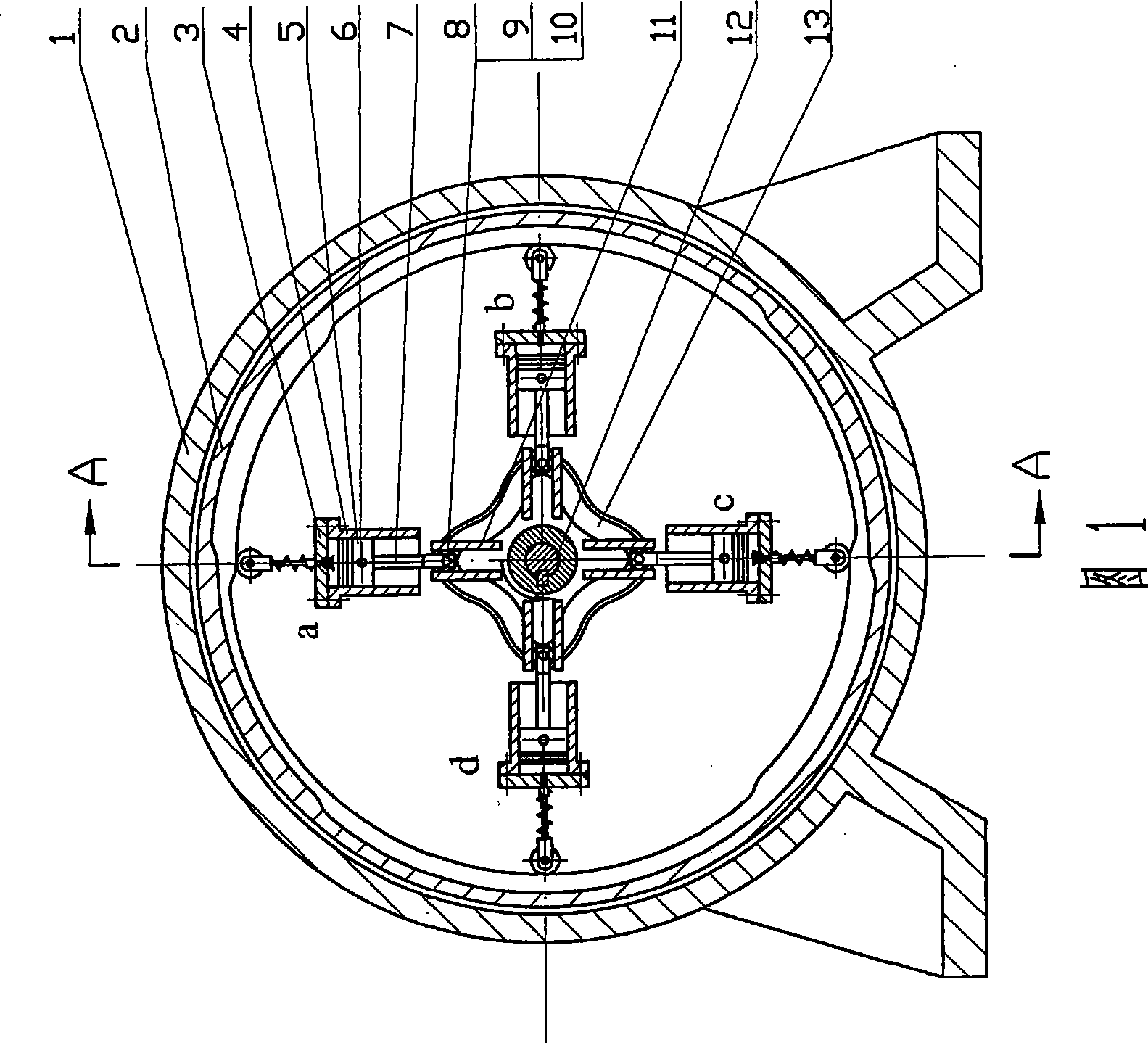
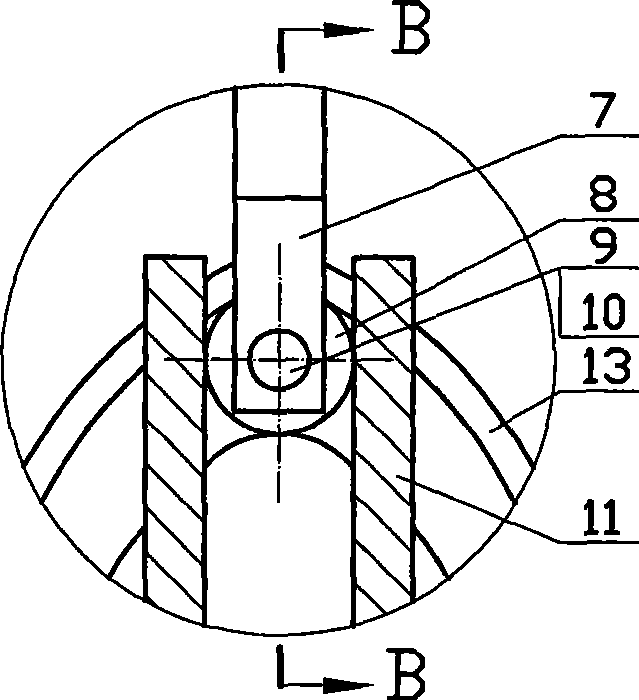
[0036] Refer to attached picture 1~ Image 6 : In Figure 1~ Figure 4 In the shown four-phase cam four-cylinder internal combustion engine, the main shaft (12) is supported by two left and right bearings, and the four cylinders (4) are symmetrically distributed around the main shaft (12), and the angle between two adjacent cylinders is 90 °, and each cylinder is integrated with the frame (18) (the cylinder can also be manufactured separately, and then it is fixed on the frame with pins and bolts). Air vents are arranged on the frame, and the frame and the machine base (1) are fixedly connected together with bolts. One end of the push rod (7) is hinged with the piston (5) through the piston pin (6), and the other end is fixed with a push rod pin (9), on which a push rod roller (8) and a cam are mounted. rollers (10). 4 guide grooves (11) produced on the frame (18) are also axisymmetrically evenly...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Embodiment 2: Four-phase cam eight-cylinder internal combustion engine
[0039] refer to Figure 7 and Figure 2~ Image 6 :exist Figure 7 and Figure 2~ Figure 4 In the shown four-phase cam eight-cylinder internal combustion engine, eight cylinders (4) and eight guide grooves (11) are evenly distributed on the periphery of the main shaft (12) in axisymmetric manner, and the angle between two adjacent cylinders is 45° , the symmetry line of the guide groove (11) coincides with the axis line of the cylinder (4), and the shape, structure, connection relationship and working principle of each component are similar to those of a four-phase cam four-cylinder internal combustion engine, so the distance between the piston and the cylinder wall The lateral pressure between them is zero. exist Figure 7 Among them, the pistons in cylinders a, c, e, and g are at the farthest position from the axis, that is, the top dead center position, while the pistons in cylinders b, d, f, a...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Embodiment 3: Six-phase cam six-cylinder internal combustion engine
[0042] Refer to Figure 8~ Figure 11 and Figure 3 ~ Figure 4 : In Figure 8~ Figure 11 and Figure 3 ~ Figure 4 In the shown six-phase cam six-cylinder internal combustion engine, six cylinders (4) and six guide grooves (11) are evenly distributed on the periphery of the main shaft (12) axisymmetrically, and the angle between two adjacent cylinders is 60° , the line of symmetry of the guide groove (11) coincides with the axis line of the cylinder (4), the cylinder (5) and the guide groove (11) are integrated with the frame (18), and can also be fixedly connected to the frame after being manufactured separately superior. The main cam (13) has six axially symmetrical protrusions, and each two protrusions form an angle of 60 °; the main cam also has a cam-shaped groove. The contour curve of the cam-shaped groove on the main cam can select different curves as required. In this embodiment, the conto...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com