Method for synthesizing rod-like and echinoid molybdena-based nano-material
A sea urchin-shaped, molybdenum oxide technology, applied in the directions of molybdenum oxide/molybdenum hydroxide, nanotechnology, nanotechnology, etc., can solve the problems of long synthesis time, difficult preservation, etc., and achieve controllable reaction conditions, short hydrothermal time, and cost. low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] The preparation of α-molybdenum trioxide nanorod, its specific steps are:
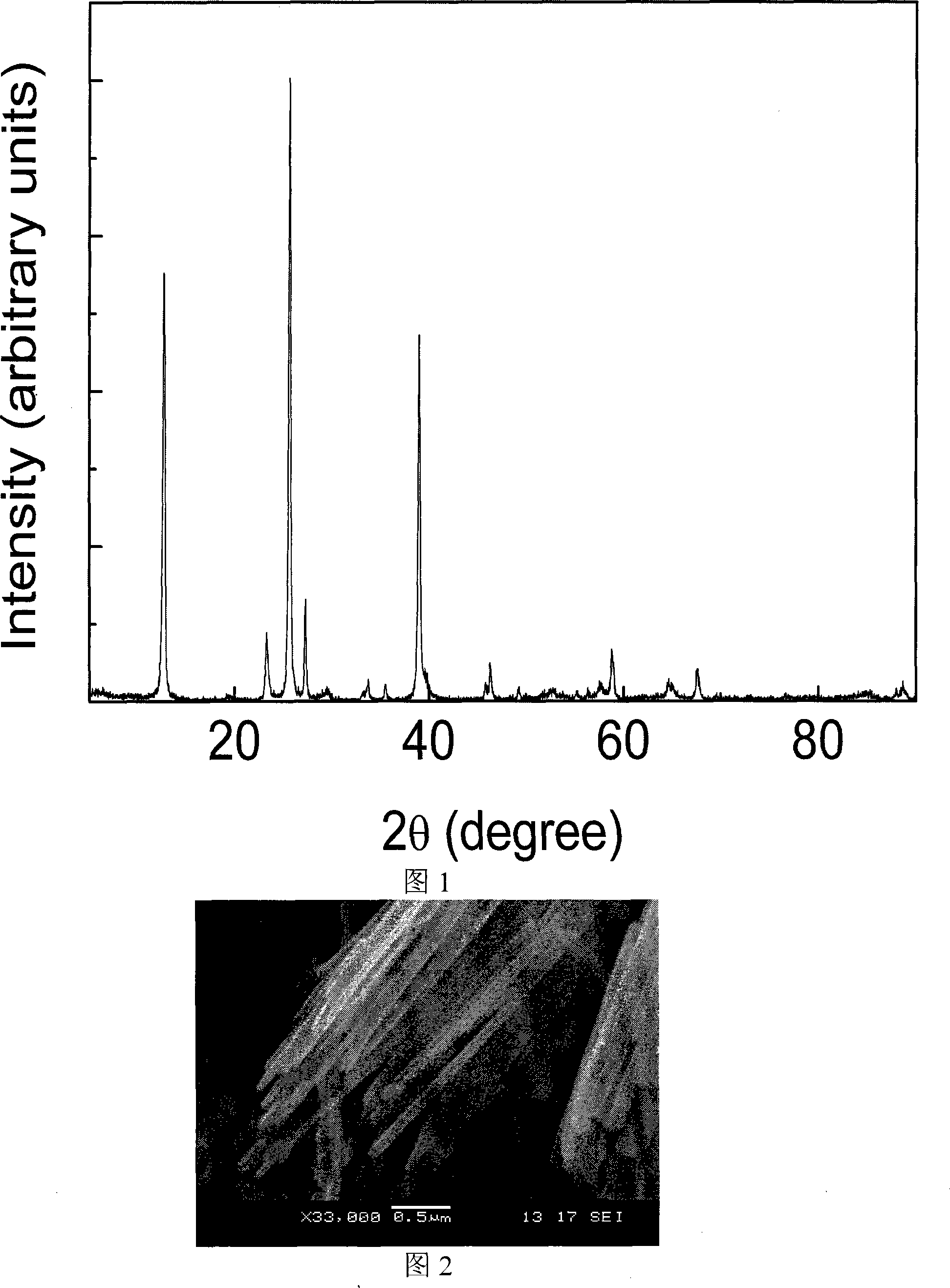
[0042] A) Add 1.44 g of molybdenum trioxide (10 mmol) into 10 ml of 30% hydrogen peroxide aqueous solution, keep the external temperature at 30° C., and stir. After reacting for 6 hours, the molybdenum trioxide was completely dissolved to obtain a clear yellow-green aqueous solution of molybdic acid peroxide (wherein the concentration of molybdenum was 1.0 mol / L).
[0043] B) Using aqueous molybdic acid peroxide as a precursor solution. The solution was transferred into a Teflon-lined stainless steel hydrothermal synthesis kettle. Seal the hydrothermal synthesis kettle, place it at 180°C, and heat it in an electric furnace for 48 hours. After the heating, the hydrothermal synthesis kettle was taken out, and the kettle body was placed in the laboratory, and cooled naturally at room temperature. The solid product was separated by centrifugation, washed repeatedly and thoroughly with deionized w...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The preparation of α-molybdenum trioxide nanorod, its specific steps are:
[0047] A) with embodiment 1A)
[0048] B) Dilute the molybdenum peroxide aqueous solution with deionized water to a molybdenum concentration of 0.2 mol / L, as a precursor solution. The solution was transferred into a Teflon-lined stainless steel hydrothermal synthesis kettle. Seal the hydrothermal synthesis kettle, place it at 180°C, and heat it in an electric furnace for 48 hours. After the heating, the hydrothermal synthesis kettle was taken out, and the kettle body was placed in the laboratory, and cooled naturally at room temperature. The solid product was separated by centrifugation, washed repeatedly and thoroughly with deionized water, and the solid product was dried at room temperature to obtain α-molybdenum trioxide nanorods.
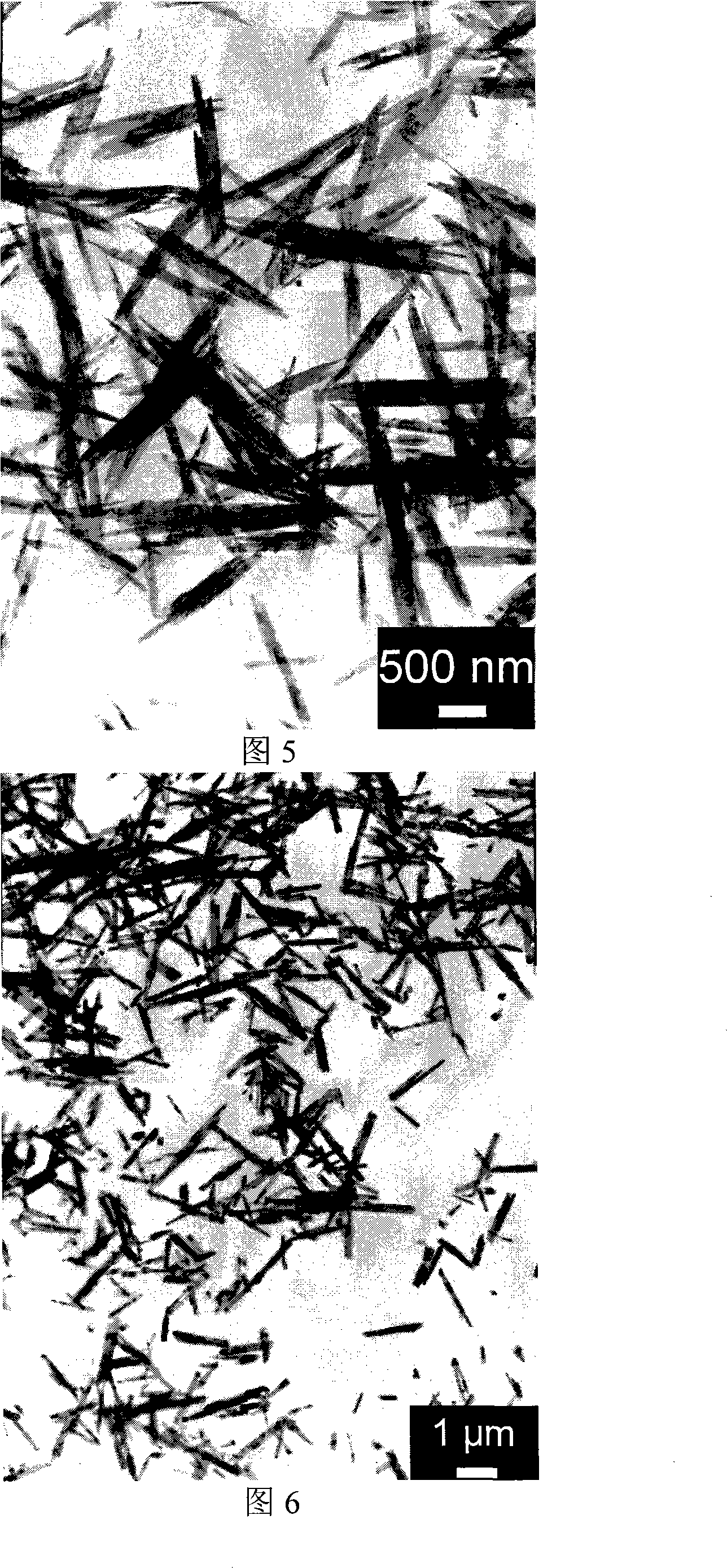
[0049] Depend on Figure 4 It can be seen that the length of α-molybdenum trioxide nanorods is 5.5-7.5 μm, the width is 200-330 nm, most of them are about 250...
Embodiment 3
[0051] The preparation of α-molybdenum trioxide nanorod, its specific steps are:
[0052] A) with embodiment 1A)
[0053] B) Using aqueous molybdic acid peroxide as a precursor solution. The solution was transferred into a Teflon-lined stainless steel hydrothermal synthesis kettle. Seal the hydrothermal synthesis kettle, place it at 80° C., and heat it in an electric furnace for 48 hours. After the heating, the hydrothermal synthesis kettle was taken out, and the kettle body was placed in the laboratory, and cooled naturally at room temperature. The solid product was separated by centrifugation, washed repeatedly and thoroughly with deionized water, and the solid product was dried at room temperature to obtain α-molybdenum trioxide nanorods.
[0054] Depend on Figure 5 It can be seen that the length of α-molybdenum trioxide nanorods is 1-3 μm, the width is 200-300 nm, most of them are about 250 nm. The generated nanorods have small thickness and relatively uniform scale....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com