Sintered R-Fe-B permanent magnet and its production method
一种制造方法、永磁体的技术,应用在电感/变压器/磁铁制造、磁性物体、永久磁铁等方向,能够解决环状磁体磁特性偏差大、制造成本高、端部易引入裂纹等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
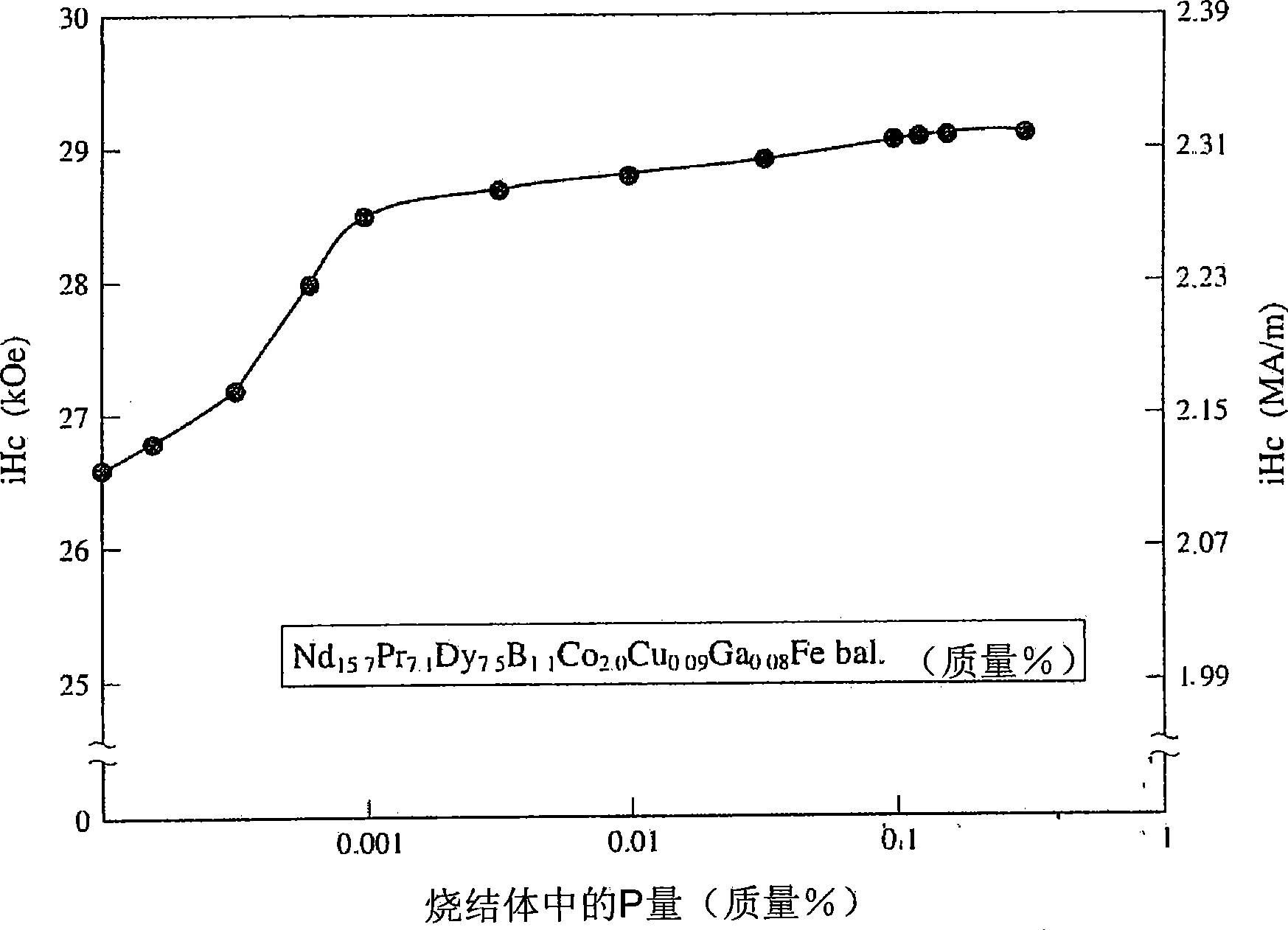
[0093] Based on mass, it is made of 17.6% Nd, 7.9% Pr, 5% Dy, 1.1% B, 0.08% Al, 1.5% Co, 0.1% Cu, 0.01% P, 0.01% 0. An ingot composed of 0.004% C, 0.006% N, and the rest being Fe. This ingot is pulverized to form a coarse powder with a particle diameter of 20 to 500 μm. The composition of the coarse powder was analyzed, and the results were as follows: 17.5% Nd, 7.7% Pr, 5% Dy, 1.1% B, 0.08% Al, 1.5% Co, 0.1% Cu, 0.01% P , 0.15% of 0, 0.015% of C, 0.006% of N, and the rest is Fe.
[0094] After putting 100 kg of this coarse powder into a jet mill, the gas in the jet mill was replaced with Ar gas so that the oxygen concentration was substantially 0%. Next, nitrogen gas was introduced so that the nitrogen concentration in the Ar gas was 0.005%. In this atmosphere, with a pressure of 6.9×10 5 Pa (about 7.0kgf / cm 2 ), and the coarse powder supply per hour is 12kg / h to finely pulverize the coarse powder. A container filled with mineral oil was installed at the fine powder rec...
Embodiment 2
[0099] Based on mass, it is made of 19.8% Nd, 8.9% Pr, 1.3% Dy, 1.1% B, 0.10% Al, 2.5% Co, 0.2% Nb, 0.08% Ga, 0.01% 0. An ingot composed of 0.003% C, 0.005% N, and the rest being Fe. The ingot is pulverized to form a coarse powder with a particle diameter of 20 to 500 μm. The composition of the coarse powder was analyzed, and the results were as follows: 19.7% Nd, 8.8% Pr, 1.3% Dy, 1.1% B, 0.10% Al, 2.5% Co, 0.2% Nb, 0.08% Ga , 0.12% of 0, 0.013% of C, 0.007% of N, and the rest is Fe.
[0100] 454 g of the aqueous solution which melt|dissolved 5 mass % sodium hypophosphite in pure water was mixed with this coarse powder 100k, and it dried in vacuum. Analyze the composition of the coarse powder after drying, the result is 19.7% Nd, 8.8% Pr, 1.3% Dy, 1.1% B, 0.10% Al, 2.5% Co, 0.2% Nb, 0.08% Al Ga, 0.008% of P, 0.16% of O, 0.013% of C, 0.009% of N, and the rest is Fe. The coarse powder was finely pulverized in the same manner as in Example 1. The average particle diameter o...
Embodiment 3
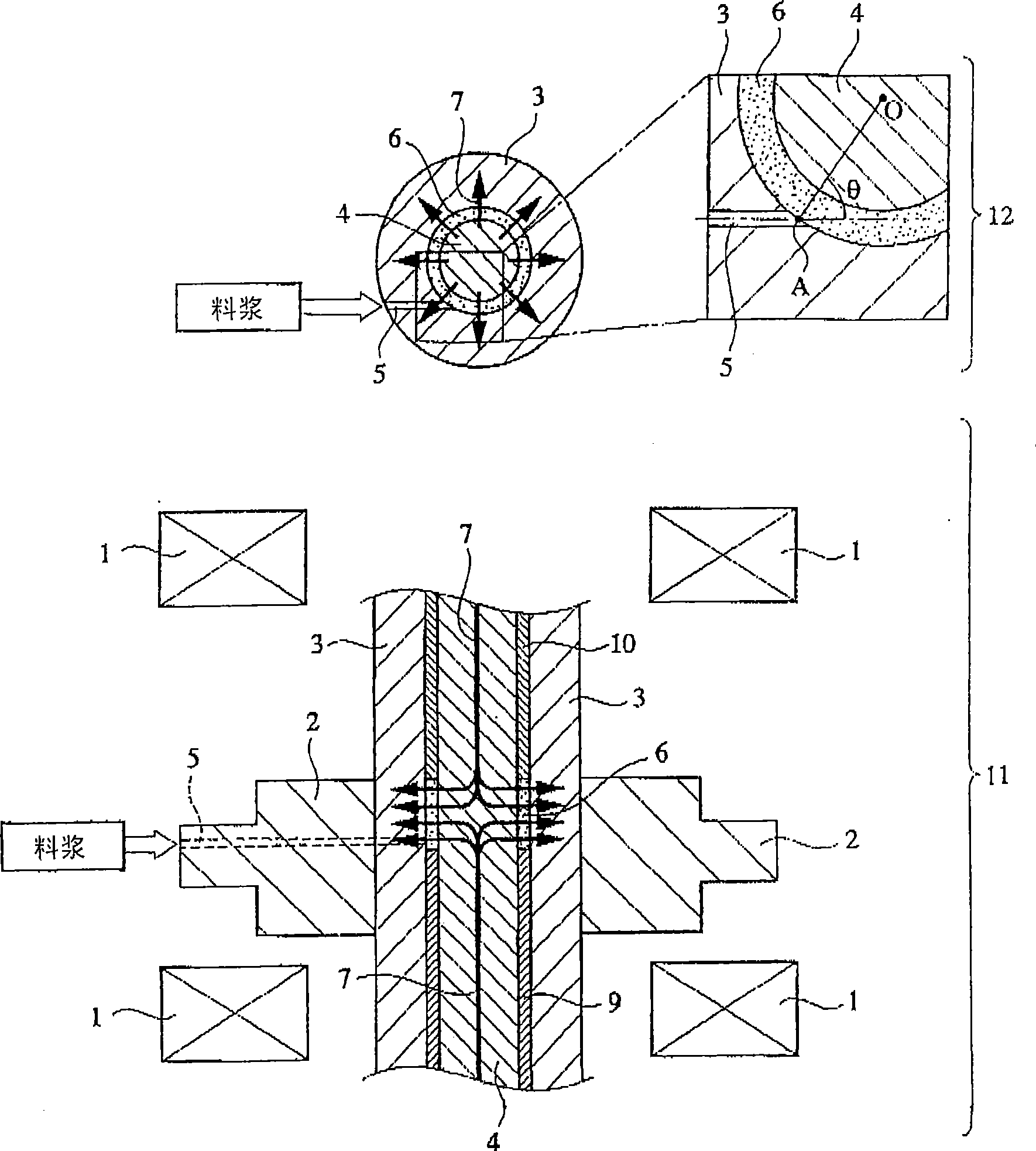
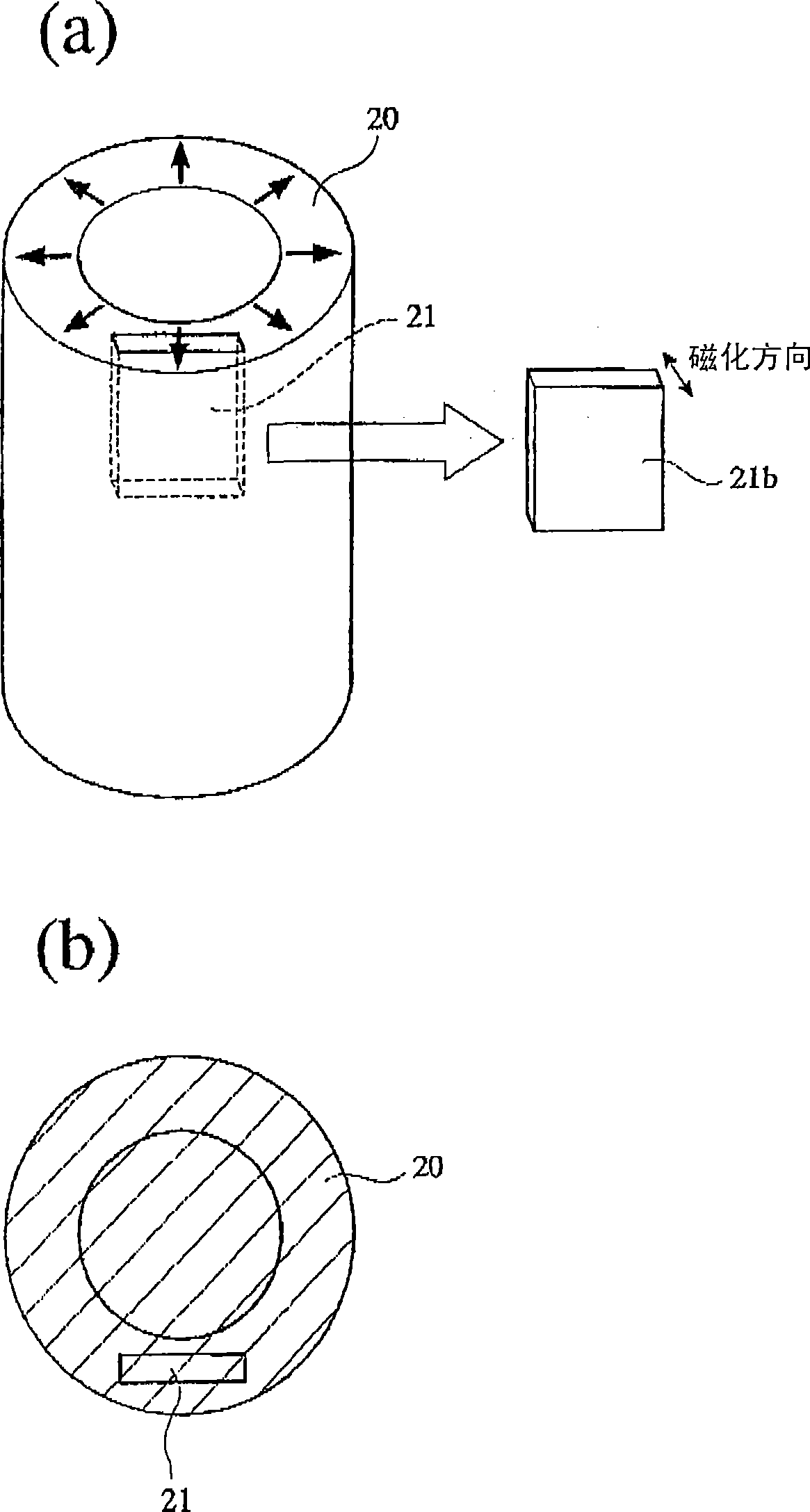
[0108] Based on mass, 19.85% of Nd, 8.95% of Pr, 1.00% of Dy, 1.02% of B, 0.10% of Al, 2.00% of Co, 0.10% of Cu, 0.15% of 0, 0.04% of C , 0.02% N, and the rest are the coarse powder used for the R-Fe-B permanent magnet composed of Fe and put it into the jet mill, replace the gas therein with nitrogen, and press 6.9×10 5 Pa(7.0kgf / cm 2 ), the feed rate of coarse powder is 15kg / h for fine pulverization. The obtained fine powder was directly recovered in mineral oil ("Su-Pa-Zur PA30", manufactured by Idemitsu Kosan Co., Ltd.) installed at the outlet of the jet mill without being exposed to the air to obtain a slurry.
[0109] A 5% by mass sodium hypophosphite glycerol solution was previously mixed with this mineral oil so that the ratio of sodium hypophosphite to the mineral oil would be 0.1% by mass. The mass ratio of mineral oil and coarse powder in the slurry is 1:3. The average particle diameter of the obtained fine powder was 4.5 μm. The slurry made in this way is inject...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| coercivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com