Optical film cutting method and optical film
A cutting method and optical film technology, applied in the field of optical film, can solve the problems of lower productivity of liquid crystal panels, display defects of liquid crystal panels, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
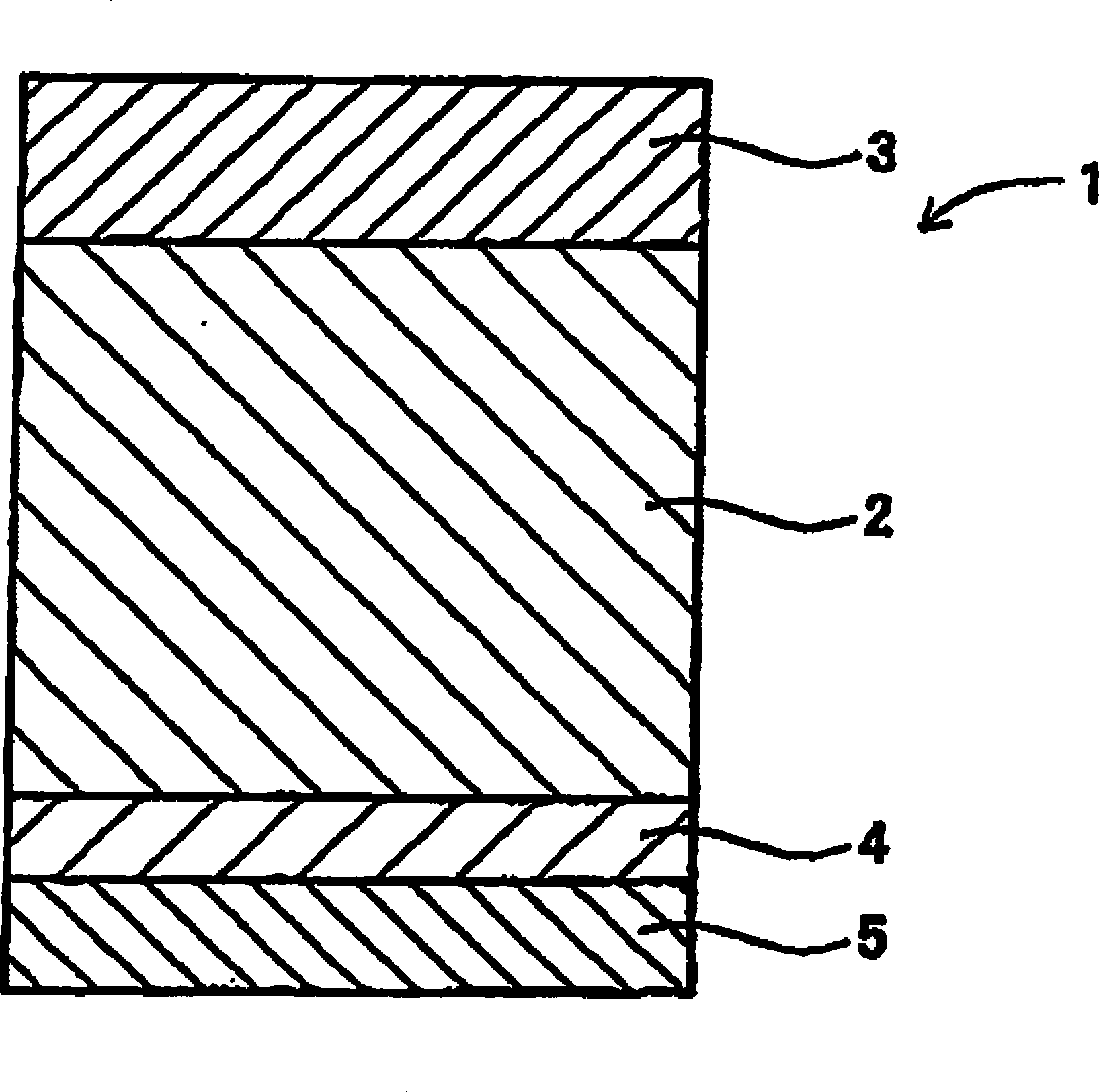
[0051] (production of polarizing plates)
[0052] A polarizer was produced by stretching a polyvinyl alcohol film (thickness: 80 μm) to five times in an iodine aqueous solution, followed by drying. Then, an ultraviolet urethane hard coat layer having a reflectance of 1% or less and a physical optical film (AR layer) were sequentially formed on one surface of a triacetyl cellulose film (TAC film). The treated TAC film was laminated on one surface of the polarizer, and the untreated TAC film was laminated on the other surface of the polarizer via an adhesive to obtain a polarizing plate (thickness: 200 μm, light-transmitting Pass rate: 45%).
[0053] (production of surface protection film)
[0054] In 100 parts by weight of 3,4-epoxycyclohexylmethyl-3,4-epoxycyclohexane formate, add 120 parts by weight of methyltetrahydrophthalic anhydride as curing agent and as 2 parts by weight of tetra-n-butylphosphonium O,O-diethylphosphorodithioate as a vulcanization accelerator, and mix...
Embodiment 2
[0065] In Example 2, as shown in Table 1, the energy per unit length was set to 0.167 J / mm, and the continuous irradiation time was set to 0.033 milliseconds. The beam diameter of the laser beam was adjusted to 100 μm, and the power of the laser beam was adjusted to 500 W. The scanning speed of the laser beam was set to 180 m / min. Other condition parameters are the same as those of Example 1.
[0066] In the case of cutting the optical film according to Example 2, the measurement results of the raised portions generated on the cut surface of the film are shown in Table 2.
Embodiment 3
[0068] In Example 3, as shown in Table 1, the energy per unit length was set to 0.155 J / mm, and the continuous irradiation time was set to 0.025 milliseconds. The beam diameter of the laser beam was adjusted to 100 μm, and the power of the laser beam was adjusted to 620 W. The scanning speed of the laser beam was set to 240 m / min. Other condition parameters are the same as those of Example 1.
[0069] In the case of cutting the optical film according to Example 3, the measurement results of the raised portion generated on the cut surface of the film are shown in Table 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com