Reactor for treating supercritical water of waste organism
A technology of supercritical water and organic matter, which is applied in the fields of solid waste removal, heating water/sewage treatment, oxidized water/sewage treatment, etc. It can solve problems such as strong corrosion of equipment, blockage of reactors, and stress reduction of reactor walls. , to achieve the effect of delaying the corrosion rate, lowering the temperature and preventing the deposition of salt
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
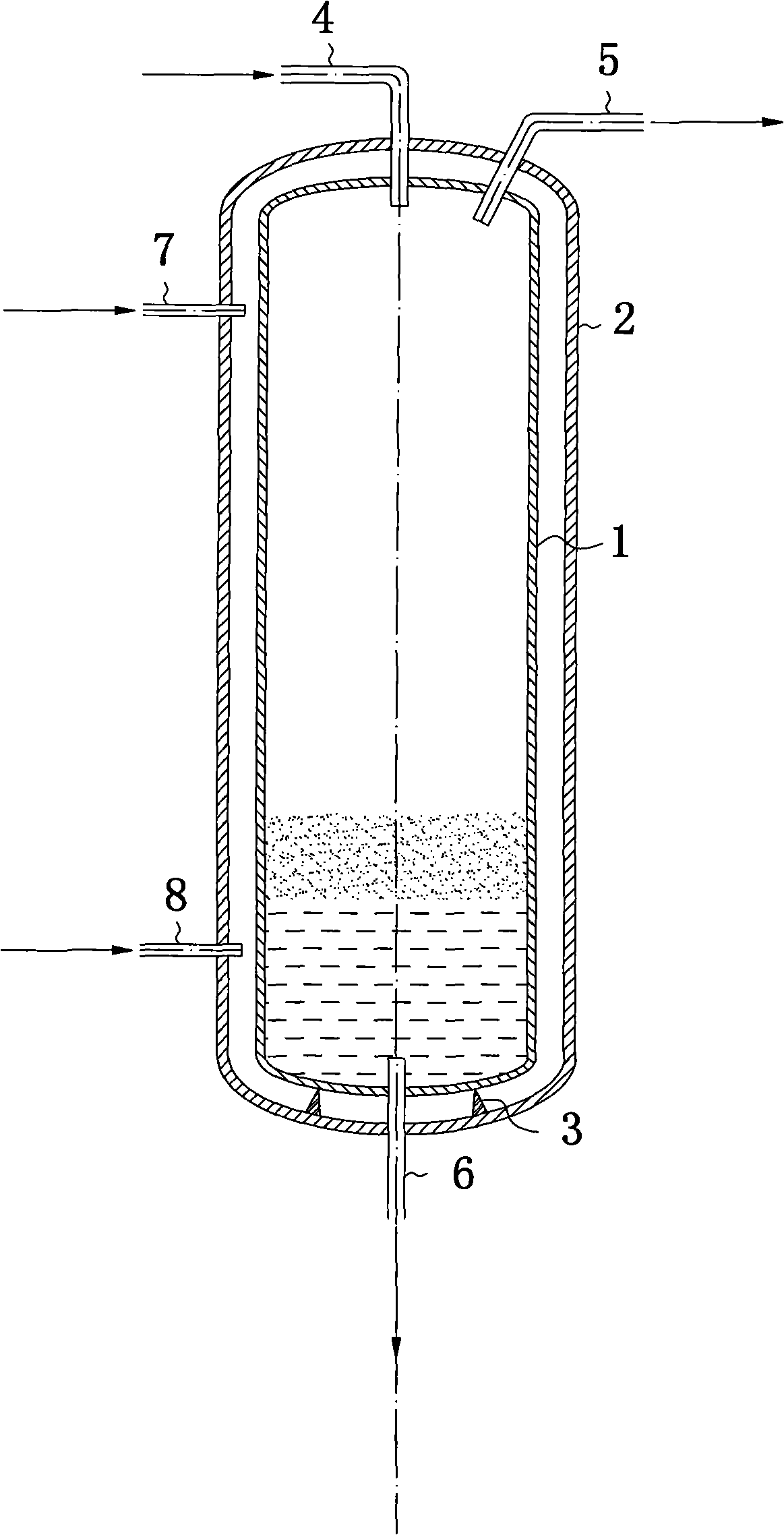
[0021] see figure 1 , The reactor for supercritical water treatment of waste organic matter of the present invention includes: a pressure chamber 2 and an inner chamber 1 composed of an evaporation wall. The inner chamber 1 of the reactor is fixed in the pressure chamber 2 by the bracket 3 , and a space is reserved between the pressure chamber 2 and the inner chamber 1 . The material inlet pipe 4 is located at the uppermost end of the reactor, and extends into the inner chamber 1 after passing through the top of the pressure chamber 2 . The overflow pipe 5 is located at the upper part of the reactor, and passes through the top of the pressure chamber 2 and extends into the interior of the inner chamber 1 for the outflow of the reacted material. The water inlet pipe 7 for evaporating wall water is located on the upper part of the side wall of the pressure chamber 2, extends into the gap between the pressure chamber 2 and the inner chamber 1, and provides evaporating wall water...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com