Cooling cylinder compression cycle of rotor-type compressor
A compressor and rotor type technology, applied in the field of circulation system, can solve the problems of increasing condensing load, increasing condensing load, cycle deterioration, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing motion resistance, reducing net compression work, and improving oil circuit
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0035] The specific embodiments of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
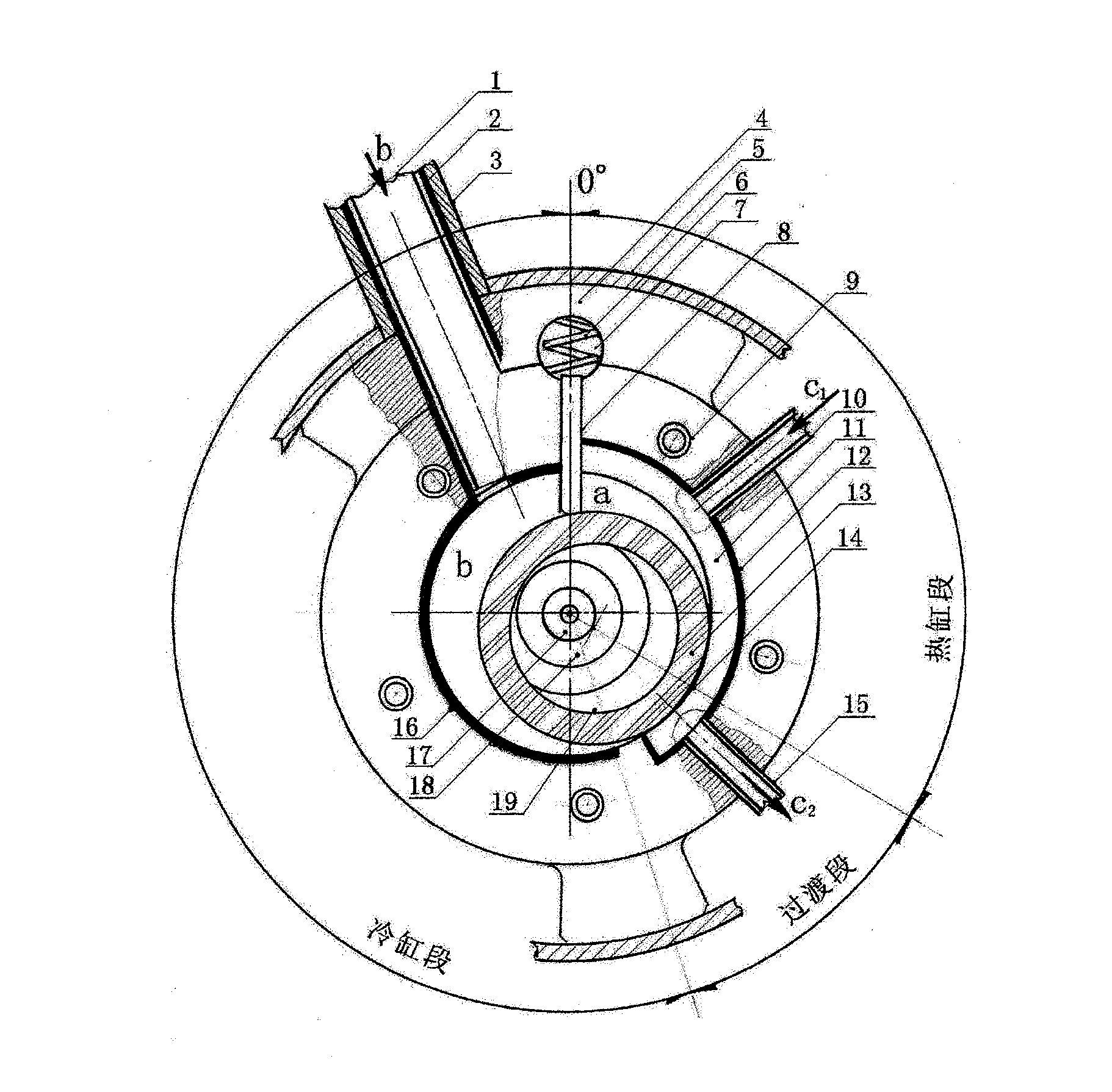
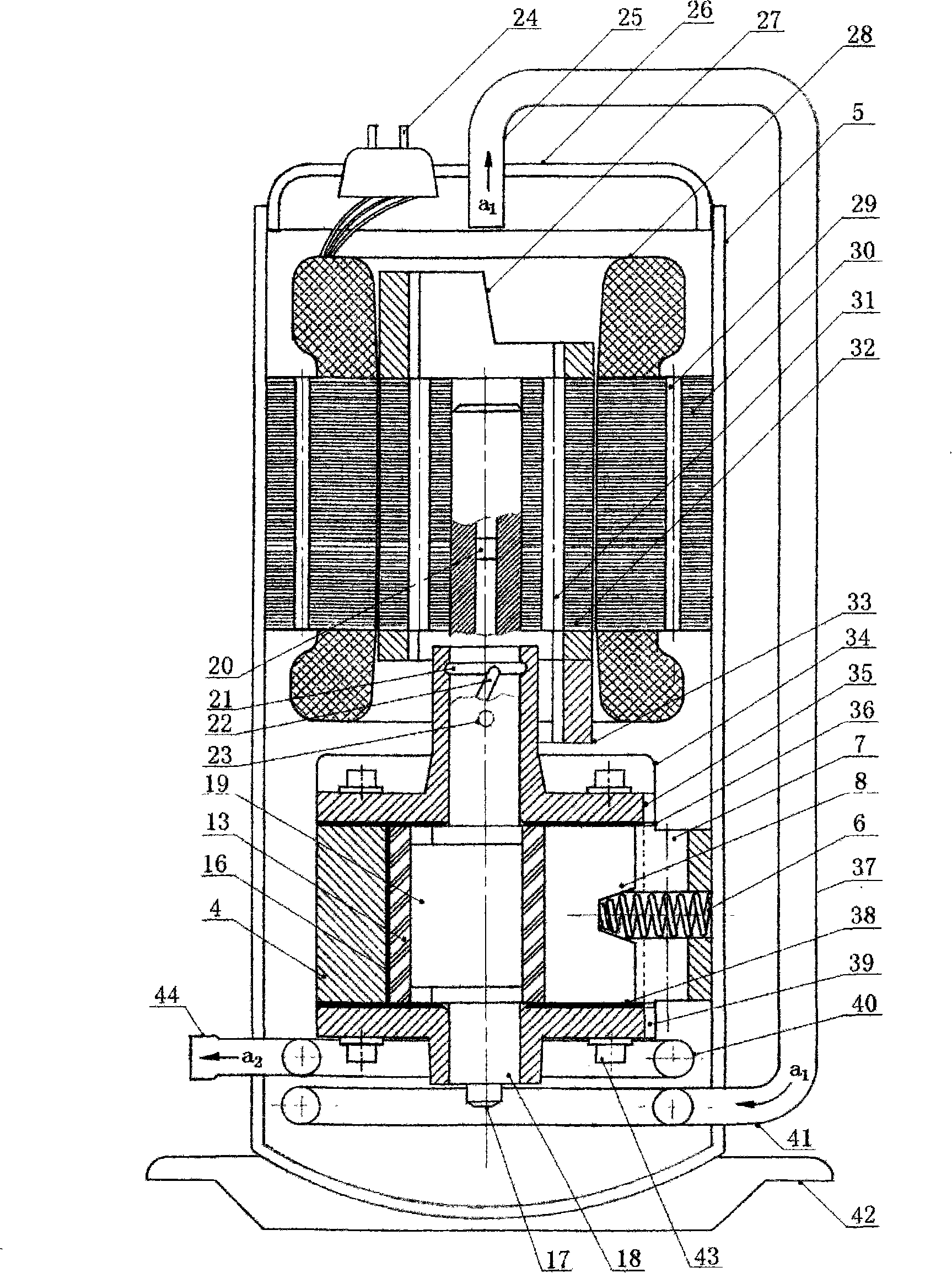
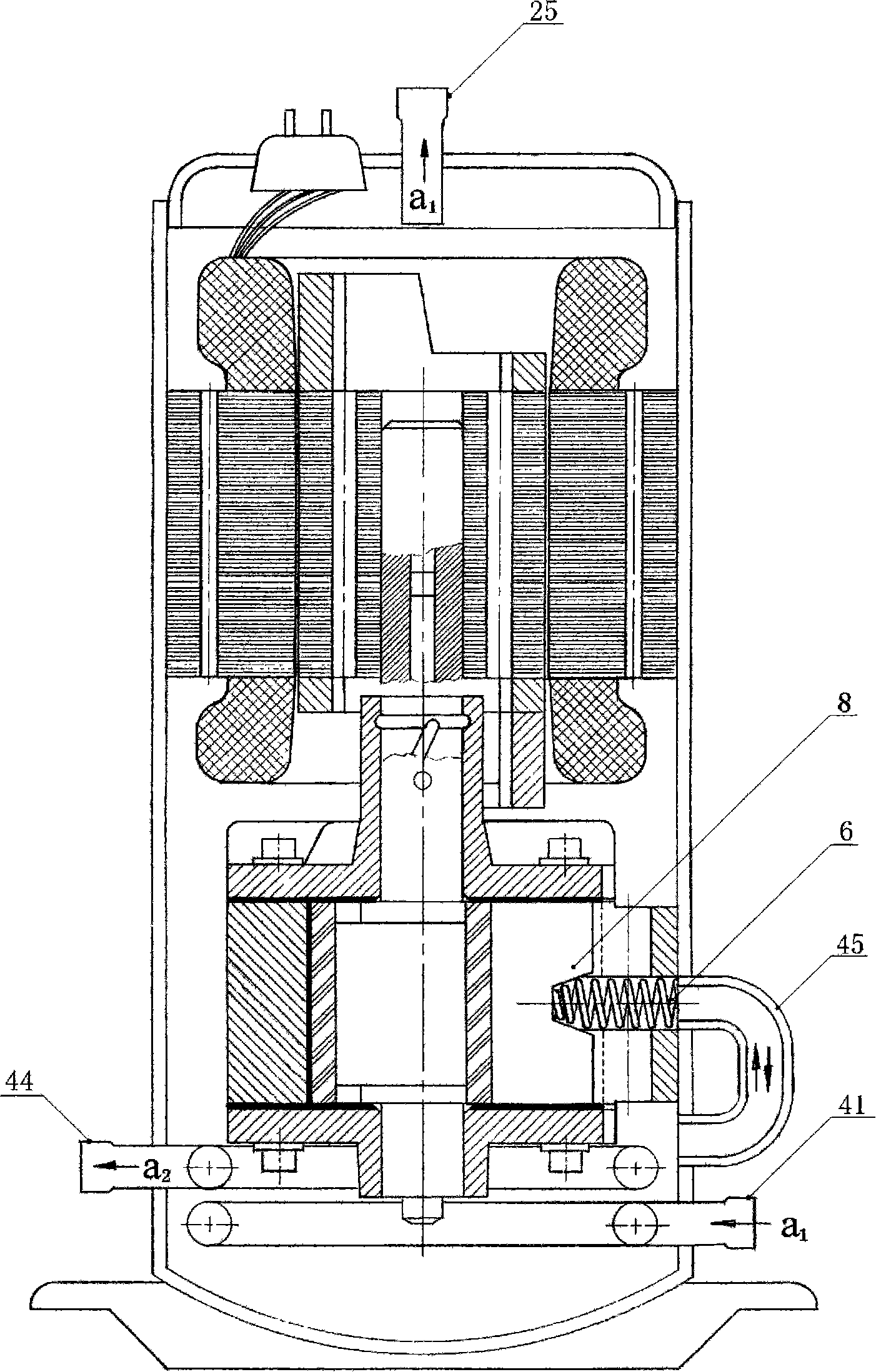
[0036] See attached figure 1 : Suction pipe 1, suction pipe insulation layer 2, suction duct 3, cylinder 4, housing 5, spring 6, tongue oil hole 7, tongue 8, screw hole 9, inlet duct 10, thermal cylinder cooling Block 11, hot cylinder insulation layer 12, rolling rotor 13, tangent point 14, outlet conduit 15, cold cylinder insulation layer 16, oil suction nozzle 17, main shaft 18, eccentric wheel 19.
[0037] The (closest point) tangent point 14 of the rolling rotor 13 and the cylinder 4 is set at the position when the exhaust valve is opened, distributed according to the compression ratio, b is the suction chamber, and a is the condensing pressure P K Isobaric compression chamber; the cylinder wall of the section a from the tangent point 14 to the tongue 8 is the condensing pressure P K The strongly exothermic section of isobar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com