A method for detecting the single nucleotide polymorphism of cattle prdm16 gene
A technique for PRDM16 and single nucleotide polymorphism, applied in the field of detecting the single nucleotide polymorphism at position 212237 of the PRDM16 gene of cattle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
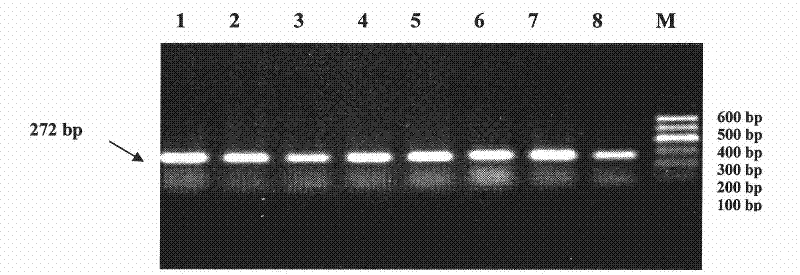
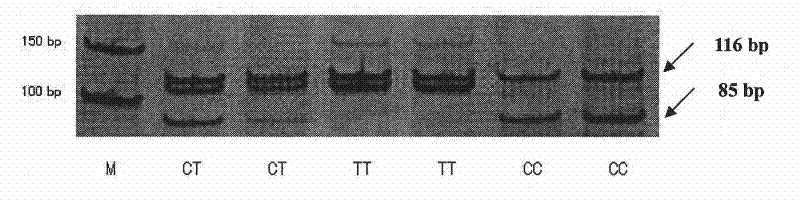
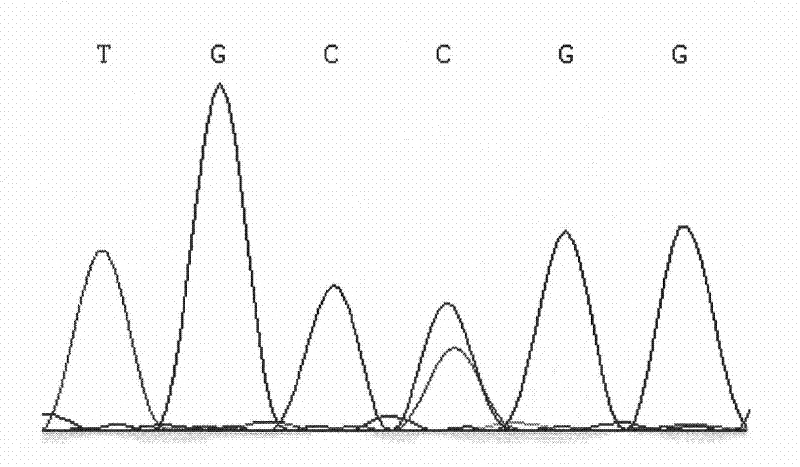
[0024] The present invention uses the PCR-RFLP method to detect the single nucleotide polymorphism that may result in a change in the conformation of the encoded protein due to the mutation of the missense codon at the 212237 site of the cattle PRDM16 gene, and the correlation analysis between the SNP and the traits shows that the site Point polymorphisms can become molecular breeding markers. The following will further describe the present invention in detail, which is an explanation of the present invention rather than a limitation.
[0025] a. Design of PCR primers for the region containing the ninth exon of the cattle PRDM16 gene
[0026] Taking the bovine (NC_007314.3) sequence published by NCBI as a reference, Primer 5.0 was used to design PCR primers capable of amplifying the region of the ninth exon of the cattle PRDM16 gene. The primer sequences are as follows:
[0027] Upstream primer: cctaccactc cgtgttccc 19;
[0028] Downstream primer: tcggctgcca atgctc 16;
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com