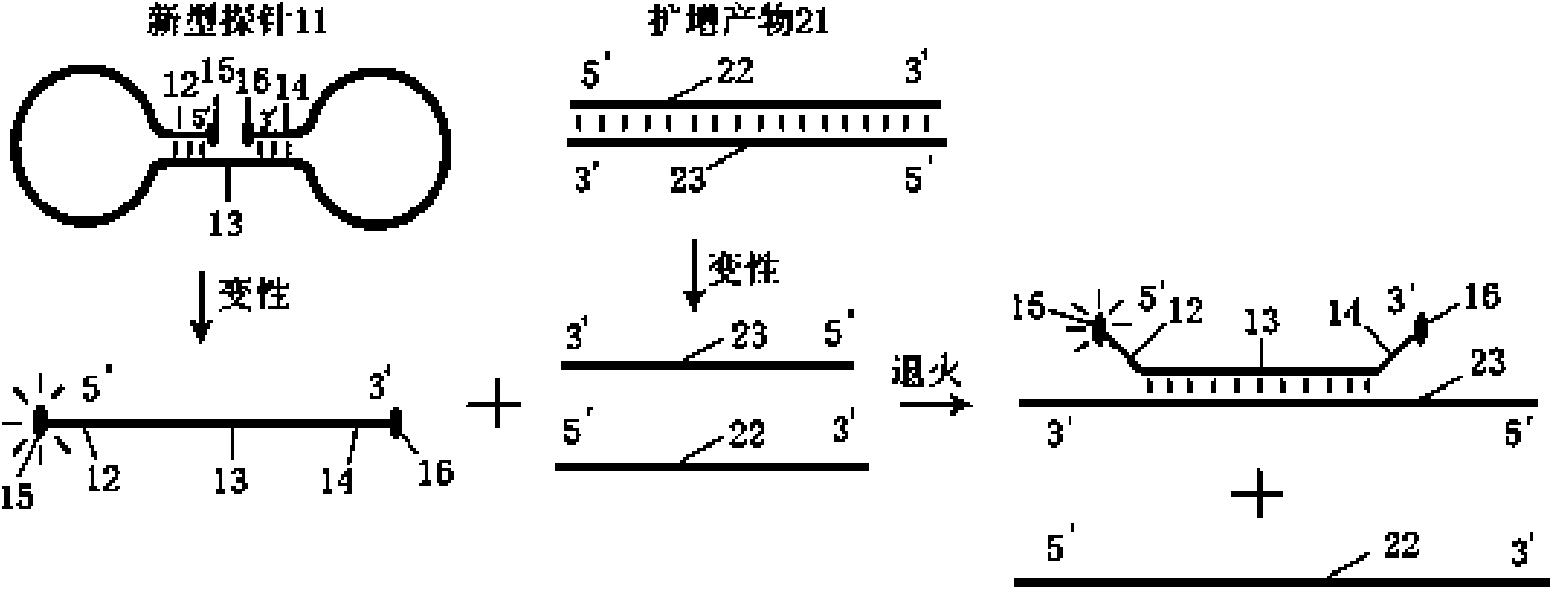
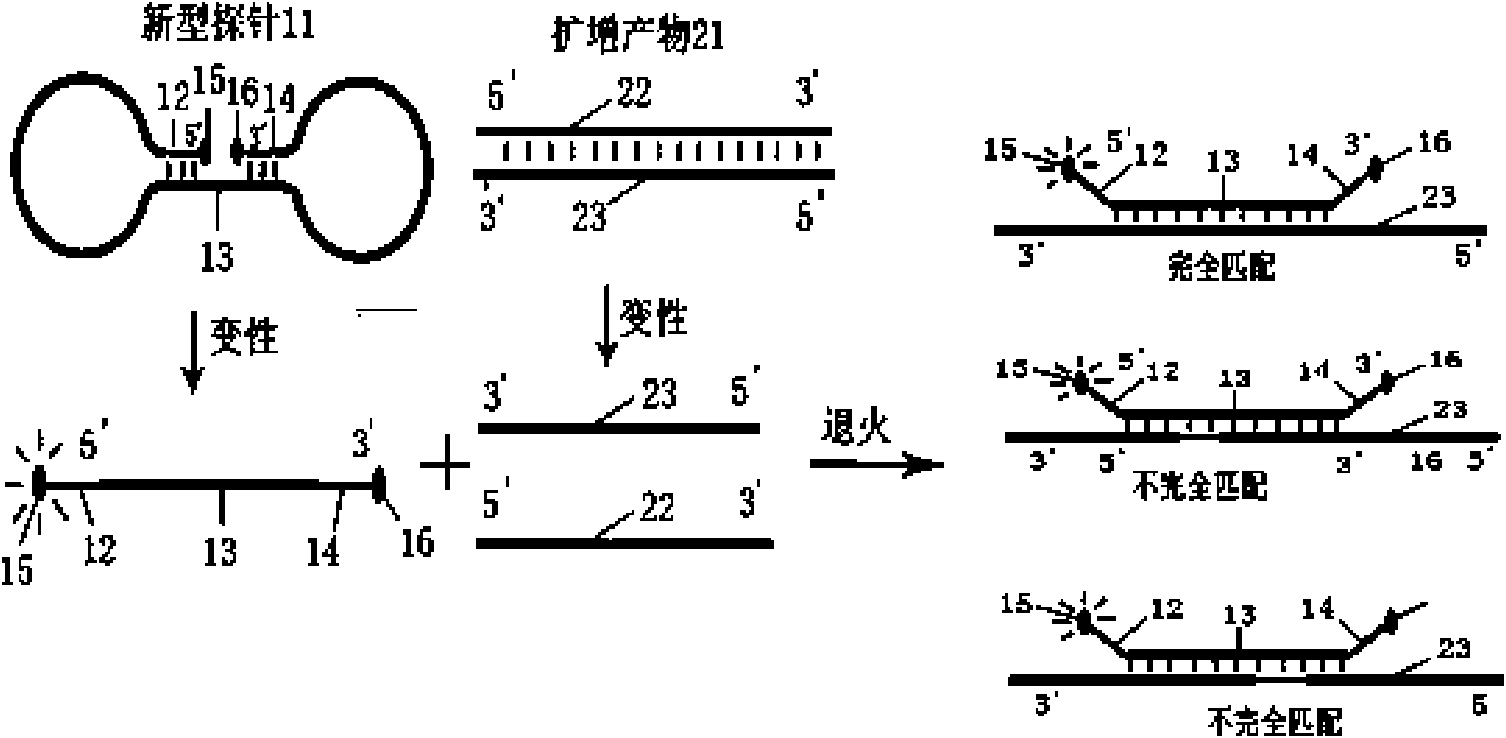
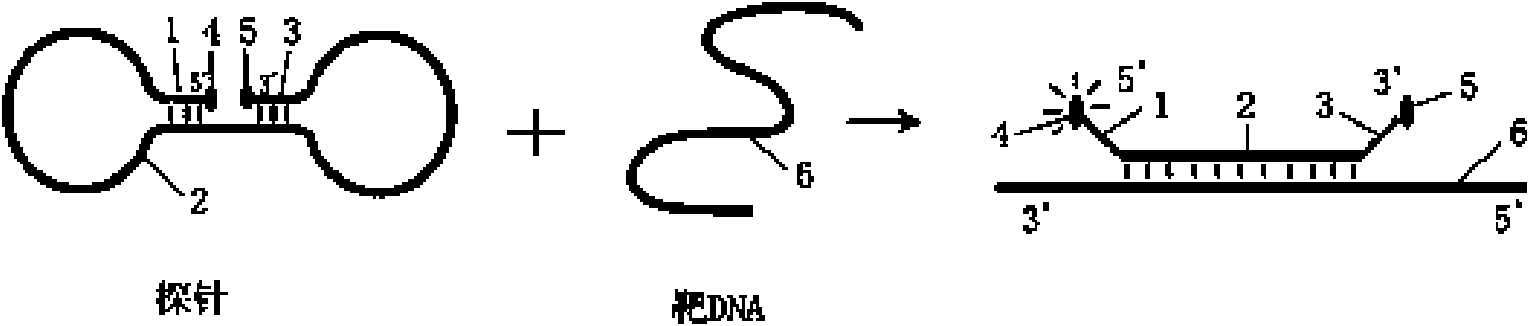Probe for real-time detection of nucleic acid
A real-time detection and probe technology, which is applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, DNA/RNA fragments, fluorescence/phosphorescence, etc., can solve the problems of limited single-base mutation recognition ability, high fluorescence background, complex design, etc., to achieve Wide application range, simple synthesis, and good applicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Embodiment 1: real-time PCR detection of hepatitis B virus bicyclic probe
[0038] In order to investigate the effectiveness of the double-loop probe application in real-time PCR detection, the PCR template is a series of diluted standard DNA samples. The total volume of the reaction system is 50 μl, including 5 μl 10×buffer (160 mM [NH 4 ] 2 SO 4 , 670mM Tris-HCl pH8.8, and 0.1% w / v Tween 20), 1.5μl 25mM MgCl 2 , each dNTP 400 μM, upstream and downstream primers 0.4 μM, probe 0.1 μM, 1.0U Taq DNA polymerase, 5 μl template DNA. The real-time PCR reaction was carried out on the RotorGene3000 real-time PCR instrument. The reaction conditions are: pre-denaturation at 96°C for 2min, followed by denaturation at 96°C for 15s, 68°C at 59°C (1°C drop per cycle) for 15s, extension at 72°C for 15s, 10 cycles; 94°C for 3min; 94°C for 15s, 58°C 20s (detection of FAM, fluorescent signal), 15s at 72°C, a total of 35 cycles. Serial 10-fold serial dilution of standard DNA, H 2 O...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2: Bicyclic probes are used to distinguish single-base mutation target sequences
[0042] The HPA 1 gene of human platelet alloantigen (HPA) was selected as the research object. HPA-1 results in two antigens, HPA-1a and HPA-1b, due to a single base mutation, namely T>C mutation. The double loop probe is designed to target the HPA-1a antigen gene, the sequence is: The underlined bases are the bases for mutagenesis, and the bases with an outer frame are the bases of the loop-forming binding region. The synthesized hybridization sequence was 2 bases longer than the probe at both ends. The target sequence of HPA-1a is: 5'-GCCCTGCCTCTGGGCTCACCTCG-3', the underlined bases are the mutation bases; the target sequence of HPA-1b is: 5'-GCCCTGCCTCGGGGCTCACCTCG-3', the underlined bases are the mutations Base generation; 25μl reaction system containing 1×buffer (67mM Tris-HCl, 16.6mM (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 , 85μg / mL BSA, pH 8.0), 2.0mM MgCl 2 , 0.4 μM probe and 1.6 μM hybrid...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Example 3: Detection of SNPs with double loop probes in real-time PCR
[0045] The HPA 4 gene of the human platelet alloantigen (human platelet alloantigen, HPA) is selected, because there is a G>A mutation in the gene, resulting in the production of two platelet antigens, HPA-4a and HPA-4b, and HPA-4a is Wild type, HPA-4b is mutant. Double-circle probes were designed for the gene sequences of the two antigens, and the difference between the two probes was only 1 base, and 3 typical samples with known genotypes were selected for testing. One is a pure and HPA-4a sample, one is a pure and HPA-4b sample, and one is a heterozygous sample containing both HPA-4a and HPA-4b. At the same time as the test, do a no (negative) sample, that is, H 2 O control. The wild-type (HPA-4a) probe sequence is: The mutant (HPA-4b) probe sequence is: The underlined bases are the bases for mutagenesis, and the bases with an outer frame are the bases of the loop-forming binding region. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com