Composite hydrophillic printing substrate and manufacturing and regenerating methods thereof
A plate-based, hydrophilic technology, applied in the preparation, printing, printing plate and other directions of the printing surface, can solve the problems of increasing process complexity, environmental pollution, loss of raw material thickness, etc., and achieves strong adjustability and flexible selection of process engineering. The effect of convenience and material cost saving
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
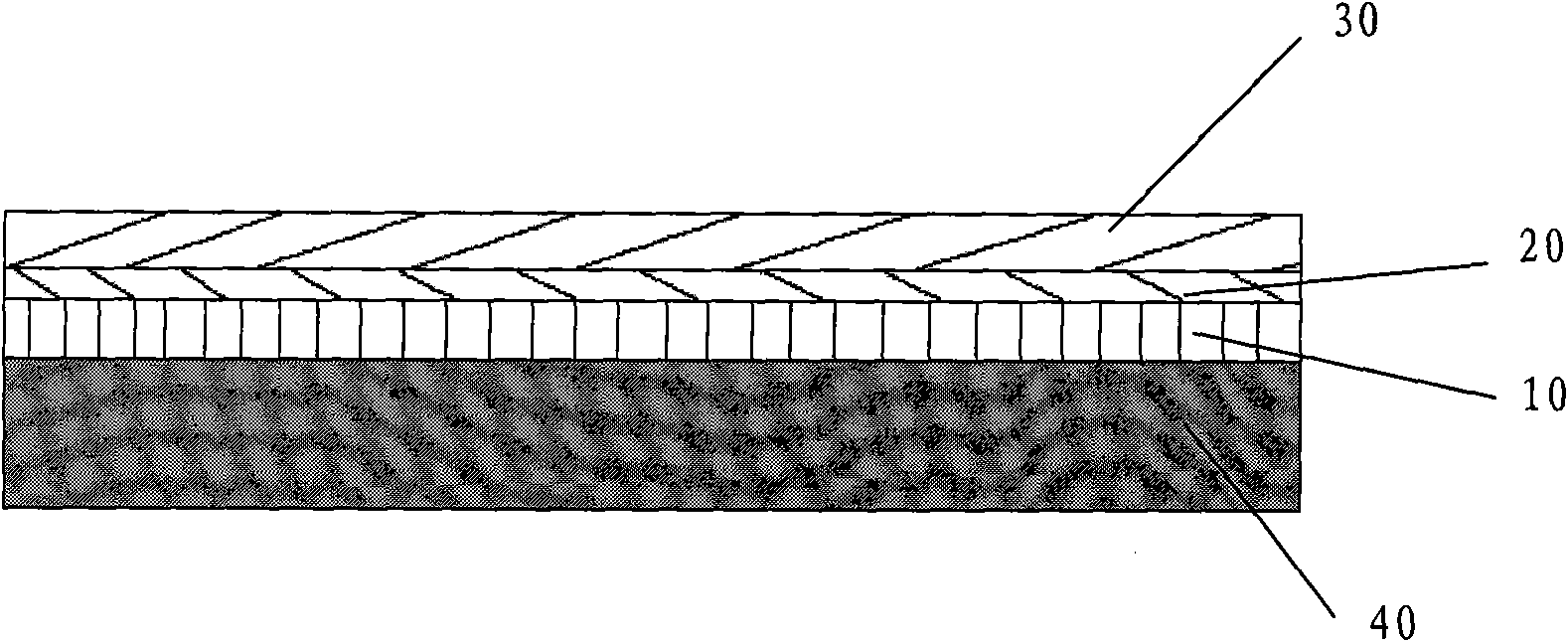
[0025] Please refer to figure 1 , the composite hydrophilic printing plate base of the present invention includes aluminum foil 10, one side surface of the aluminum foil 10 is provided with a substrate layer 20 and a hydrophilic layer 30, and the hydrophilic layer 30 is firmly combined with the aluminum foil 10 through the substrate layer 20 to form a whole . Wherein, the substrate layer 20 is closely attached to and adhered to one side surface of the aluminum foil 10, the hydrophilic layer 30 is closely attached to and adhered to the surface of the substrate layer 20 away from the side surface of the aluminum foil 10, and the other side of the aluminum foil 10 is bonded or coated. method of joining organic sheets 40 or sheets.
Embodiment 2
[0027] The present invention also provides a method for manufacturing the composite hydrophilic printing plate base. exist figure 1 The surface of the shown aluminum foil 10 is first coated with a substrate liquid to form a substrate layer 20, and then coated with a hydrophilic dispersion liquid on the surface of the substrate layer 20 to form a hydrophilic layer 30, and the other side of the aluminum foil 10 is connected to the organic substrate by bonding or coating. Plate 40 or sheet, such as PVC, PE, PP, PET and other materials.
[0028] The specific process is as follows: choose an aluminum foil 10 with a thickness of 0.08mm, go through cleaning and drying procedures, then coat the base layer 20 on the aluminum foil 10, dry it, and then coat the base layer 20 on the surface away from the aluminum foil 10 Coat the hydrophilic layer 30 on the upper surface, then carry out drying treatment, then apply photosensitive glue on the hydrophilic layer 30, carry out drying once ag...
Embodiment 3
[0031] Another optional method for manufacturing a composite hydrophilic printing plate base of the present invention, the specific process is as follows: select an aluminum foil 10 with a thickness of 0.08mm, go through cleaning and drying procedures, and then coat the substrate layer on the aluminum foil 10 20, drying it, and then coating a hydrophilic layer 30 on the surface of the substrate layer 20 away from the aluminum foil 10, followed by drying, and then coating a CTP thermosensitive adhesive on the hydrophilic layer 30, and then Once dried, then apply adhesive liquid on the uncoated side of the aluminum foil 10 (i.e. the side away from the substrate layer 20), and the aluminum foil 10 and the organic plate 40 with a thickness of 0.2mm are bonded to each other to form a thickness of about 0.28mm CTP plate with hydrophilic composite base. The use method of this plate base is the same as that of ordinary thermal CTP plates on the market, that is, through infrared laser ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com