Method for man-machine cooperation sharing control remote welding
A shared control and human-machine collaboration technology, applied in welding equipment, auxiliary welding equipment, welding/cutting auxiliary equipment, etc., can solve the problem that direct control operations cannot be carried out continuously, independent tracking of weld seam welding cannot be realized, and the welding environment is complex, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of enhancing environmental adaptability, improving autonomy, and improving fault recovery capabilities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
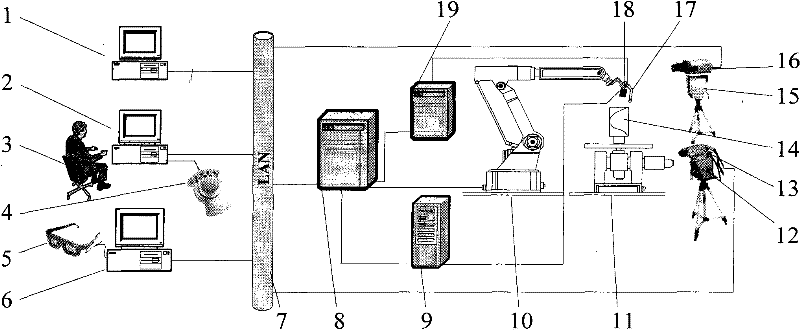
[0016] Specific implementation mode one: combine Figure 1-Figure 3 Describe the present embodiment, the method of the present embodiment is realized by the following steps: Step 1: the macro zoom camera 16 collects two-dimensional video images, and transmits the two-dimensional video images to the macro vision display 1 through the video line, and the operator 3 locally In the central monitoring human-machine interface 2 at the end, the field of view is adjusted through the focus control and the second controllable pan-tilt 15;
[0017] Step 2: The operator 3 operates the space mouse 4 to issue a control command, which is transmitted to the remote robot controller 8 through the industrial Ethernet 7 to control the movement of the remote robot 10, and the robot 10 guides the welding torch 17 to move to 30-40mm above the welding seam At the same time, the robot controller 8 transmits the pose matrix of the welding gun 17 to the central monitoring man-machine interface 2 of the ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
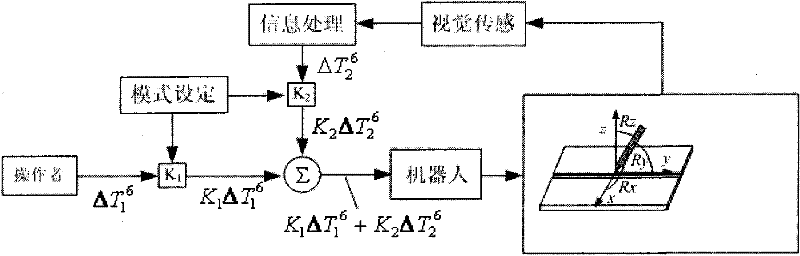
[0025] Specific implementation mode two: combination image 3Describe this embodiment, the degree of freedom weighted fusion algorithm of this embodiment is superimposed by the direct control command of the operator 3 and the visual sensing control command in the robot controller 8 according to the predetermined weight value, and the control commands of the two All degrees of freedom of the robot 10 are affected to jointly change the pose of the welding torch 17, and it is assumed that the driving matrix of the manual control command of the operator 3 is ΔT 1 6 , the weight value is K 1 (01 2 6 , the weight value is K 2 (02 T = K 1 ΔT 1 6 + K 2 ΔT 2 6 ( 0 K 1 1,0 ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
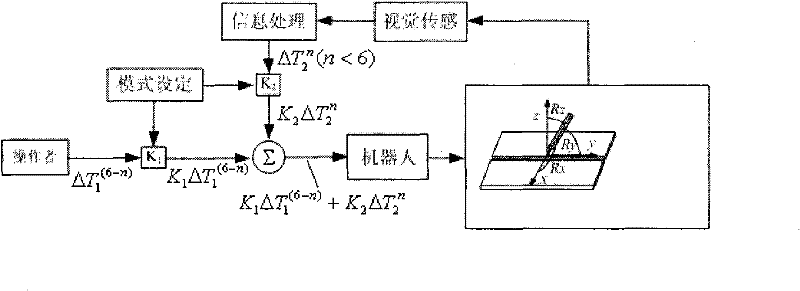
[0026] Specific implementation mode three: combination figure 2 Describe this embodiment, the degree of freedom segmentation algorithm of this embodiment is to divide the six degrees of freedom of the robot, direct control commands and visual sensing control commands respectively control different degrees of freedom, the laser stripes of the laser vision controller 9 hit The surface of the workpiece 14 is reflected on the laser vision sensor working head 18, and the groove information of the weld is extracted through image processing to obtain the position information (X, Y, Z) of the weld feature point, where X is the horizontal direction and Y is the speed , Z is the height, combined with the attitude (Rx, Ry, Rz) of the robot 10 at this time, wherein Rx is the travel angle, Ry is the working angle, and Rz is the spin angle, the drive matrix of the laser vision sensor control command is obtained, set The drive matrix is ΔT 2 n , the weight value is K 2 (02 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com