Circuitry and method for reducing second and third-order nonlinearities
A technology of third-order nonlinearity and circuits, which is applied in the direction of improving amplifiers to reduce nonlinear distortion, electrical components, components of amplifiers, etc., and can solve problems such as no discussion of second-order nonlinearity elimination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
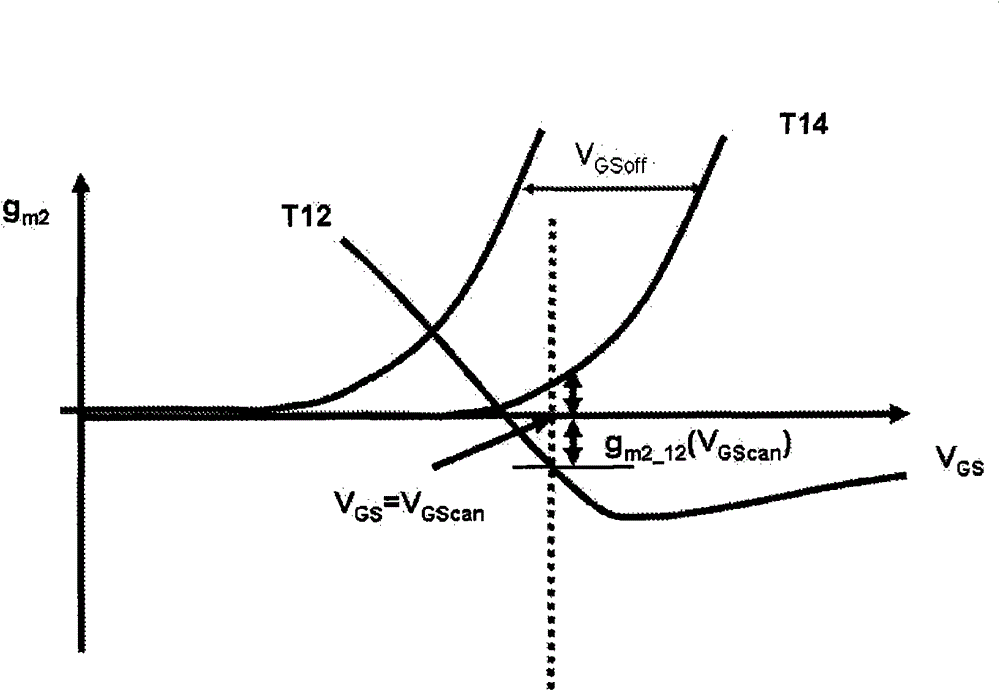
[0027] In operation, the transconductance of a transistor depends not only on the gate-source voltage but also on the drain-source voltage, as do the second- and third-order nonlinearities. In addition, transistor size and threshold voltage are also two important parameters to consider when dealing with transistor nonlinearity. With these conditions in mind, a circuit and method for eliminating second and third order nonlinearities is described below.
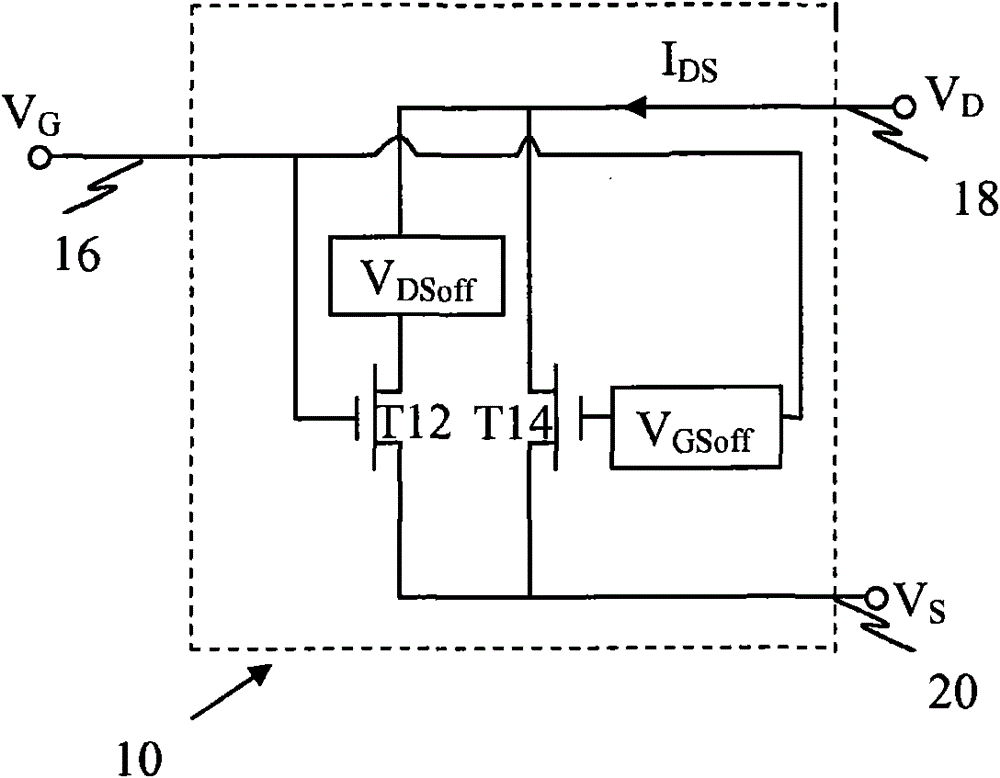
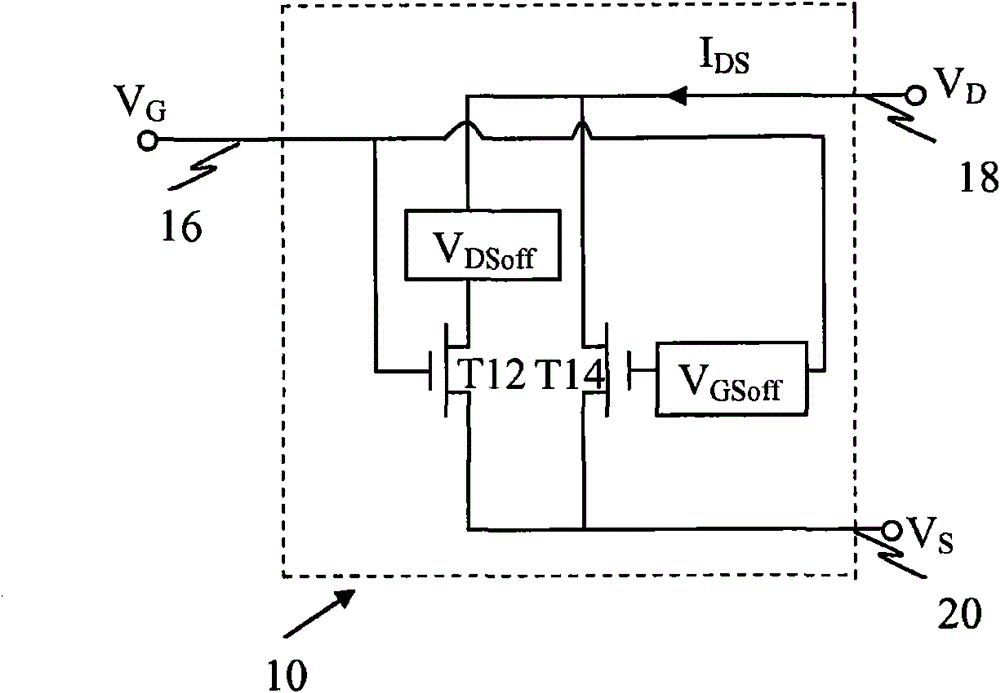
[0028] figure 1 A "composite" transistor circuit 10 is shown, formed by coupling a first transistor T12 in parallel with a second transistor T14 such that the two transistors T12 and T14 share a gate connection 16 , a drain connection 18 and a source connection 20 . (For a bipolar implementation of transistor circuit 10, these connections correspond to base, collector, and emitter connections, respectively.) Offset the gate bias of transistor T14 from the gate bias of transistor T12 by V GSoff . Offset the drain bias of tran...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com