Method for producing glucosamine by microorganism
A glucosamine and microorganism technology, applied in the field of glucosamine production, can solve the problems such as the inability to reduce the cost of the culture medium, the inability to greatly increase the output of glucosamine, and achieve the effects of few steps, low cost, and simple analysis method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Embodiment 1 test culture medium
[0028] 1. Test strain
[0029] The present invention is a method for fermenting by using microorganisms that have not undergone genetic transformation to change the medium to produce glucosamine. The microorganisms used are as follows: Monascus pilosus BCRC31527 and Aspergillus sp.BCRC31742 ); the above two strains were purchased from the Institute of Food Industry Development (Taiwan, Hsinchu).
[0030] 2. Medium
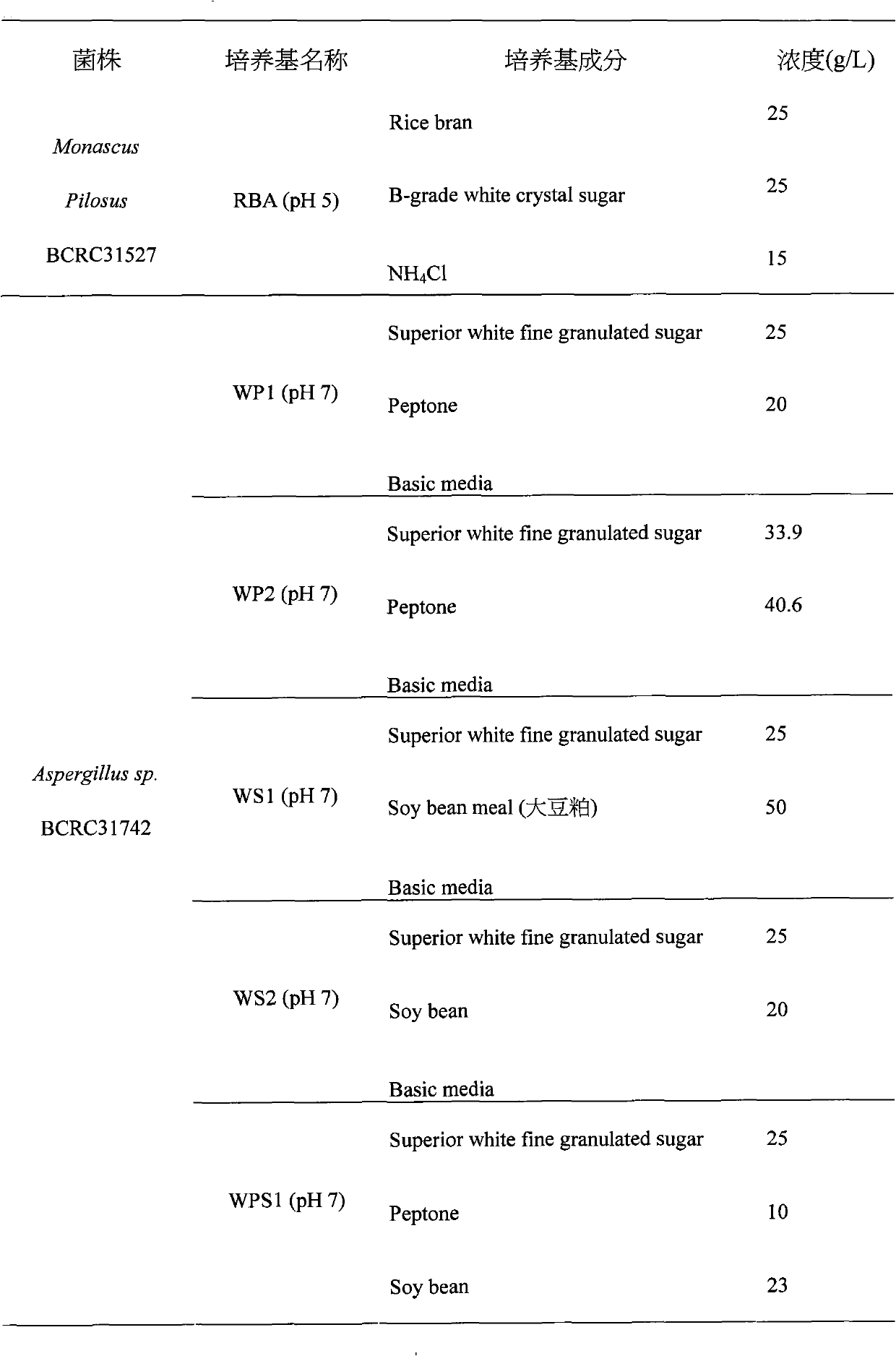
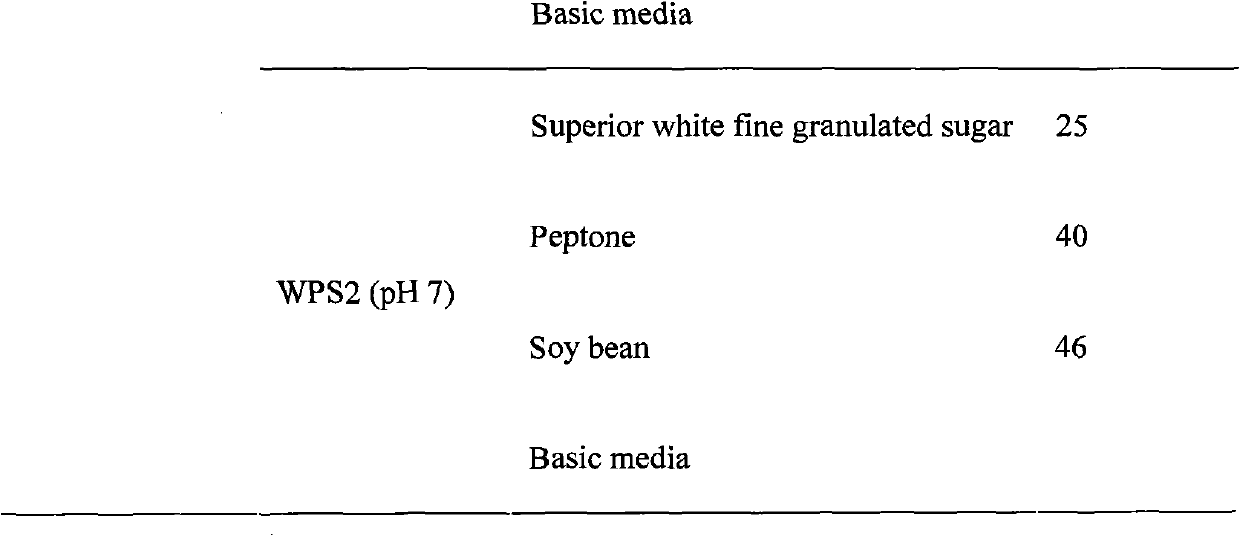
[0031] According to the different characteristics of the above two strains, select the appropriate medium for the production of glucosamine; the medium selected for each strain is shown in Table 1.
[0032] Table 1 The medium used for the production of glucosamine by each bacterial strain
[0033]
[0034]
[0035] Note: The following components are all commercially available.
[0036] RBA: Rice bran (rice bran, commercially available) + B-grade white crystal sugar (Taiwan second grade white granulated sugar, purc...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Embodiment 2 Shake flask fermentation test
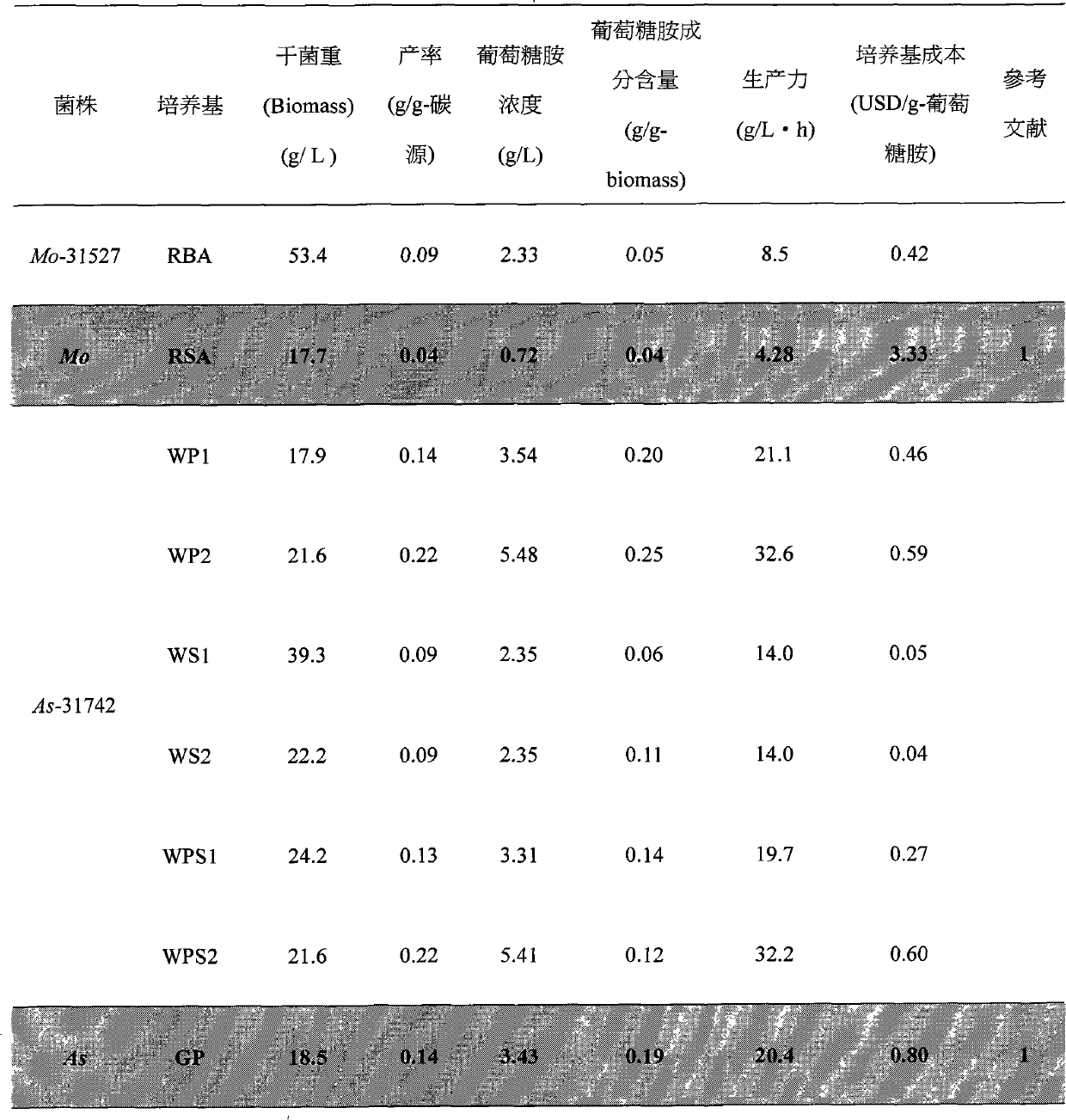
[0045] Each bacterial strain described in Example 1 was first cultured in solid state with PDA (200g / L Diced potatoes (cutting potatoes), 20g / L Glucose (glucose), 15g / L Agar (agar)) based on 30°C, three districts Streak culture was activated for 5 days, and then a single colony was placed into a 250ml shake flask containing 200ml of sterilized PDB (Potato Dextrose Broth: 20g / L Diced potatoes, 4g / L Glucose) liquid medium for secondary activation. Cultivate for 7 days in a constant temperature incubator at 30° C. and 200 rpm.
[0046]Get each activated bacterial strain and inoculate it in its appropriate culture medium (as table 1), control its culture medium pH value respectively: the culture medium pH value of microorganism Monascus pilosus BCRC 31527 is pH5, the culture medium pH value of microorganism Aspergillus sp.BCRC 31742 The pH value of the culture medium is pH 7, at a temperature of 30°C and a rotation speed of 200r...
Embodiment 3
[0067] Embodiment 3 fermenter fermentation test
[0068] Firstly, the Aspergillus sp.BCRC 31742 described in Example 1 was subjected to secondary activation culture in the same manner as described in Example 2. Fermentation tests were carried out in a batch of stirred fermenters. Inoculate 100ml of the activated Aspergillus sp.BCRC 31742 into the fermenter of WP1 medium. The working volume was 2L, and its pH value was pH 7. Under the temperature of 200rpm, the fermentation culture was carried out, and the pure oxygen was fed through the external pipeline, and the dissolved oxygen was controlled at 10%, which was the optimal condition obtained from the shake flask experiment.
[0069] After the fermentation tank was collected, the bacteria block was obtained after suction and filtration, and the bacteria block was sampled and dried at 100°C, and the wet / dry cell weight ratio (ratio of wet cell weight to dry cell weight) was obtained. After the cell disruptor was crushed, 10ml ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com