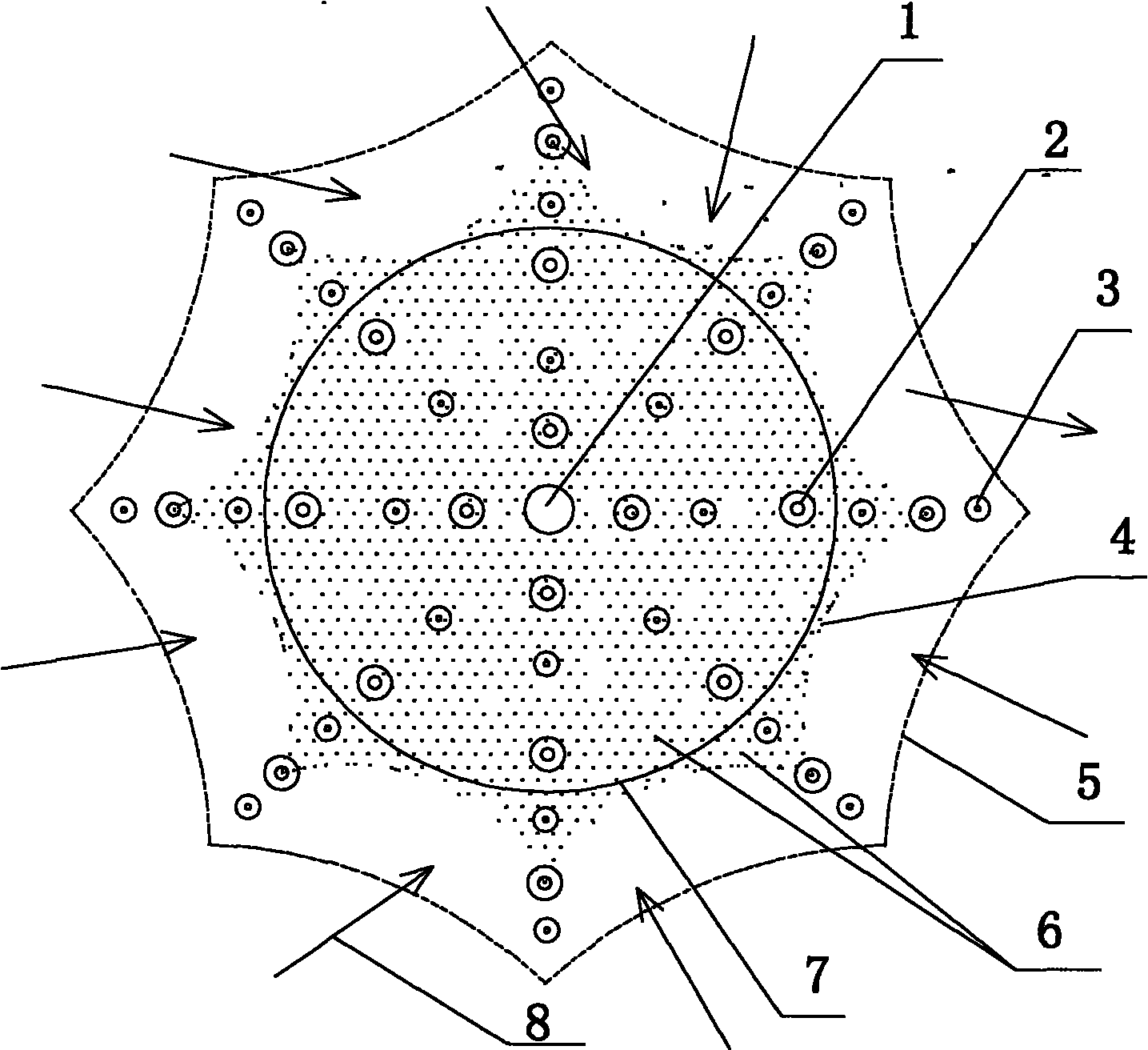
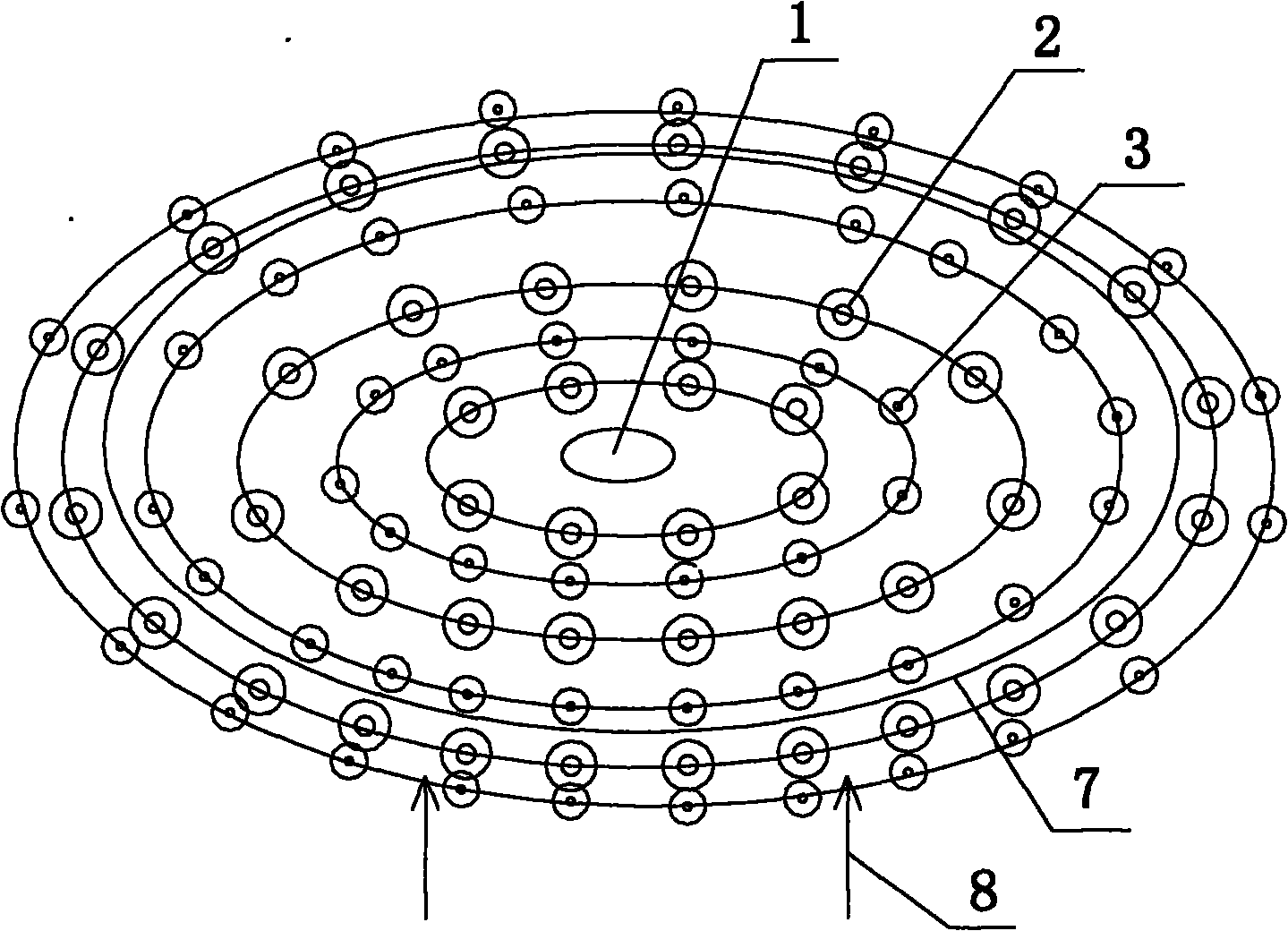
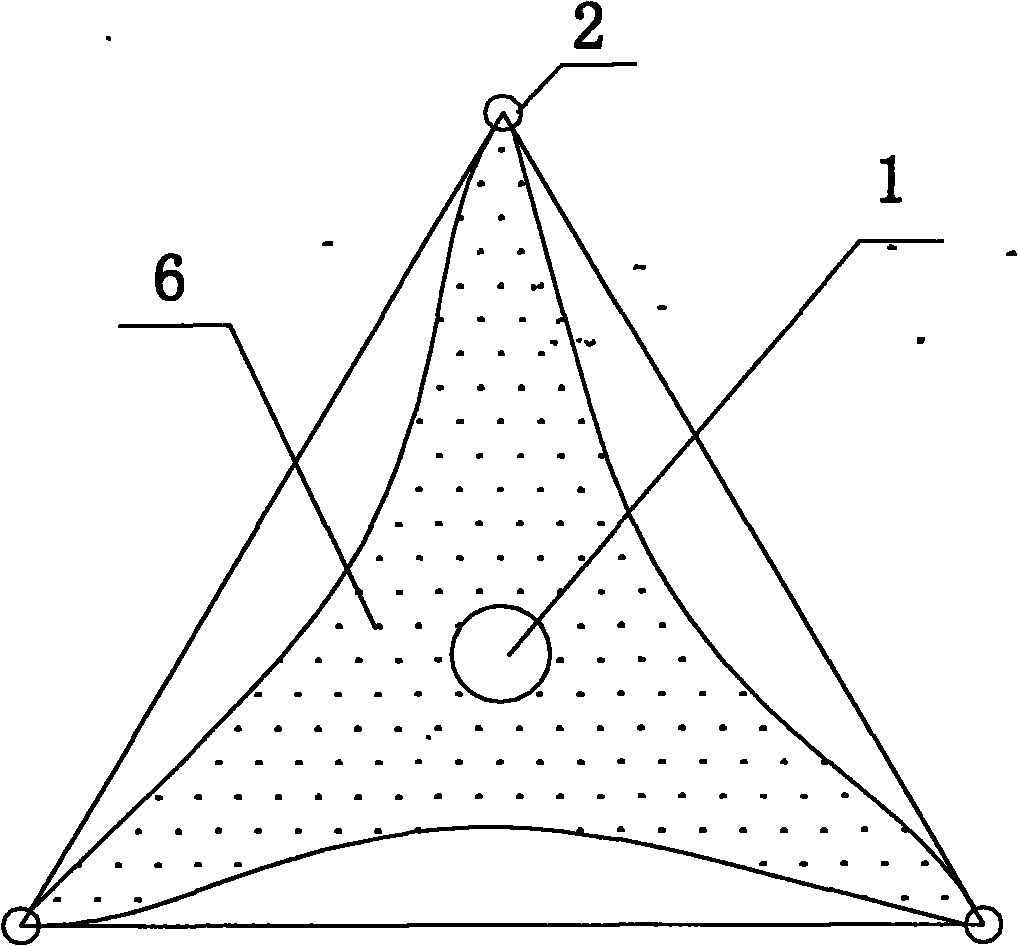
Technique of in-situ remediation of high As groundwater
An in-situ restoration and groundwater technology, which is applied in the field of water treatment, can solve the problems of less application projects, and achieve the effects of low operation and management costs, low investment, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] The results of investigation and research show that the main hydrochemical characteristics of high-arsenic groundwater are high pH (generally greater than 8.0), low redox potential, high concentrations of humic acid, hydrogen sulfide, and methane, and low concentrations of sulfate and nitrate. High arsenic groundwater is in reducing environment. At the same time, areas with high arsenic groundwater are mostly in arid-semi-arid climate conditions. Due to the requirements of groundwater extraction, residents mostly use groundwater in confined aquifers, and groundwater in this layer has high arsenic characteristics. Therefore, in-situ treatment of high-arsenic groundwater is mostly groundwater in confined aquifers. This example takes the treatment of high-arsenic groundwater in underground confined aquifers in a small area of a village in Shanyin County, Shanxi as an example, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0033] 1) Carry out geological drilling in the work are...
Embodiment 2
[0047] A technique for in-situ remediation of high-arsenic groundwater, comprising the steps of:
[0048] 1) Carry out geological drilling in the work area to be treated, obtain accurate geological data, and determine the location of the water intake aquifer;
[0049] 2) Carry out on-site hydrogeological tests to determine the hydrogeological parameters of the water intake aquifer (such as: the permeability coefficient of the water intake aquifer, the water supply degree of the water intake aquifer, etc.);
[0050] Dispersibility of ferrous chloride in abstracted aquifers:
[0051] In situ treatment of high arsenic groundwater To treat groundwater in confined aquifers, ferrous chloride solution is injected into the confined aquifer. The ferrous chloride solution is a two-dimensional dispersion problem in the confined aquifer, and the concentration c is continuously injected into the aquifer at the rate q0 of ferrous chloride solution, set the concentration c at the injection ...
Embodiment 3
[0062] A technique for in-situ remediation of high-arsenic groundwater, comprising the steps of:
[0063] 1) Carry out geological drilling in the work area to be treated, obtain accurate geological data, and determine the location of the water intake aquifer;
[0064] 2) Carry out on-site hydrogeological tests to determine the hydrogeological parameters of the water intake aquifer (such as: the permeability coefficient of the water intake aquifer, the water supply degree of the water intake aquifer, etc.);
[0065] The dispersibility of ferrous chloride in the abstracted aquifer is the same as calculated in Example 2:
[0066] 3) When the area of the work area to be processed is greater than 1,000,000m 2 When (that is, when the arsenic in the entire high-arsenic area or a certain aquifer in the basin is fixed in situ): along the direction of groundwater flow, with the center of the work area to be treated as the reference point, the liquid injection wells and gas injection ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com