Catalytic thermal cracking method for lignin
A catalytic cracking and lignin technology, applied in the field of lignin catalytic thermal cracking, can solve the problem of difficult liquefaction of fibers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Embodiment 1, pyrolysis sodium lignosulfonate
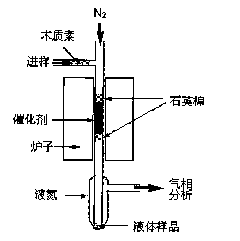
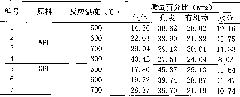
[0026] Take 1 part by mass of sodium lignosulfonate (KL), and place these sodium lignosulfonates in the side pipe of the reactor. Connect the collecting device, and pass nitrogen gas (100ml / min) into the upper end. When the furnace temperature rises to 500°C. The lignin is added slowly so that the lignin is catalytically pyrolyzed through the high temperature zone. The products of catalytic pyrolysis of lignin are separated to obtain liquid, gas and solid products. Use the above method to test the cracking conditions at 600°C, 700°C, and 800°C respectively.
Embodiment 2
[0027] Embodiment 2, catalytic cracking sodium lignosulfonate
[0028] Take 1 part of ZSM-5 molecular sieve catalyst, and place these catalysts in the middle and lower part of the reactor; take 1 part of sodium lignosulfonate, and place the lignin in the side pipe of the reactor; the lower end of the reactor is connected with a liquid condensation device and tail gas Collecting device, feed nitrogen (100ml / min) at the upper end, when the furnace temperature rose to 600°C, slowly add lignin (the amount of feed is related to the reaction device, for the experimental device used in the embodiment, the amount of feed is 0.15 g / min), so that lignin is catalytically pyrolyzed through the high temperature zone. The products of catalytic pyrolysis of lignin are separated to obtain liquid, gas and solid products.
Embodiment 3
[0029] Embodiment 3, catalytic cracking sodium lignosulfonate
[0030] Take 1 part of HZSM-5 molecular sieve catalyst, and place these catalysts in the middle and lower part of the reactor. Take 1 part of sodium lignosulfonate and place the lignin in the side pipe of the reactor. Connect the collecting device, and pass nitrogen gas (100ml / min) into the upper end. When the furnace temperature rises to 600°C. Lignin was slowly added (at a rate of 0.15 g / min) such that the lignin was passed through a high temperature zone to catalyze thermal cracking. The products of catalytic pyrolysis of lignin are separated to obtain liquid, gas and solid products.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com