Method for treating waste liquid containing magnesium
A treatment method and technology of waste liquid, applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve the problems of difficult treatment and high moisture content, and achieve the effect of simple process, low cost and easy control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
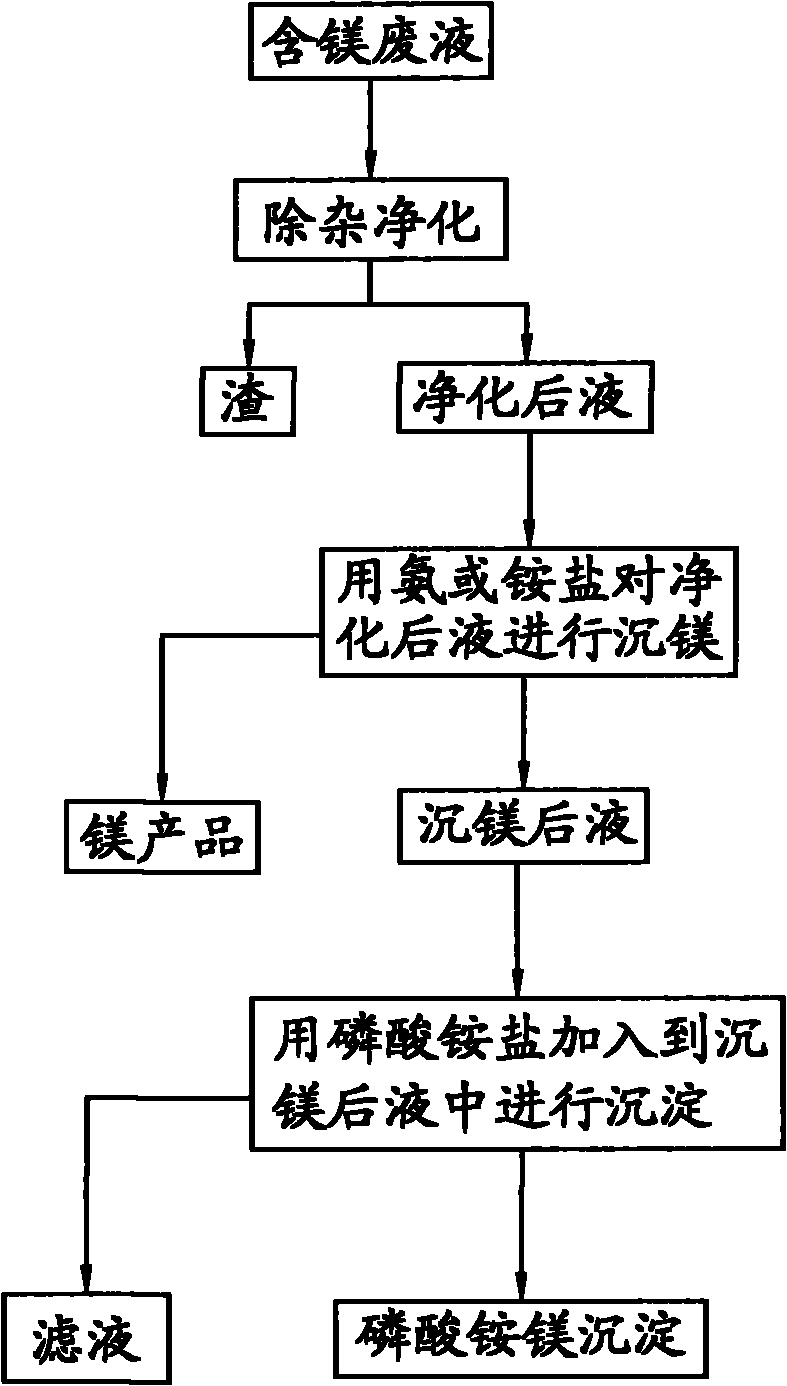
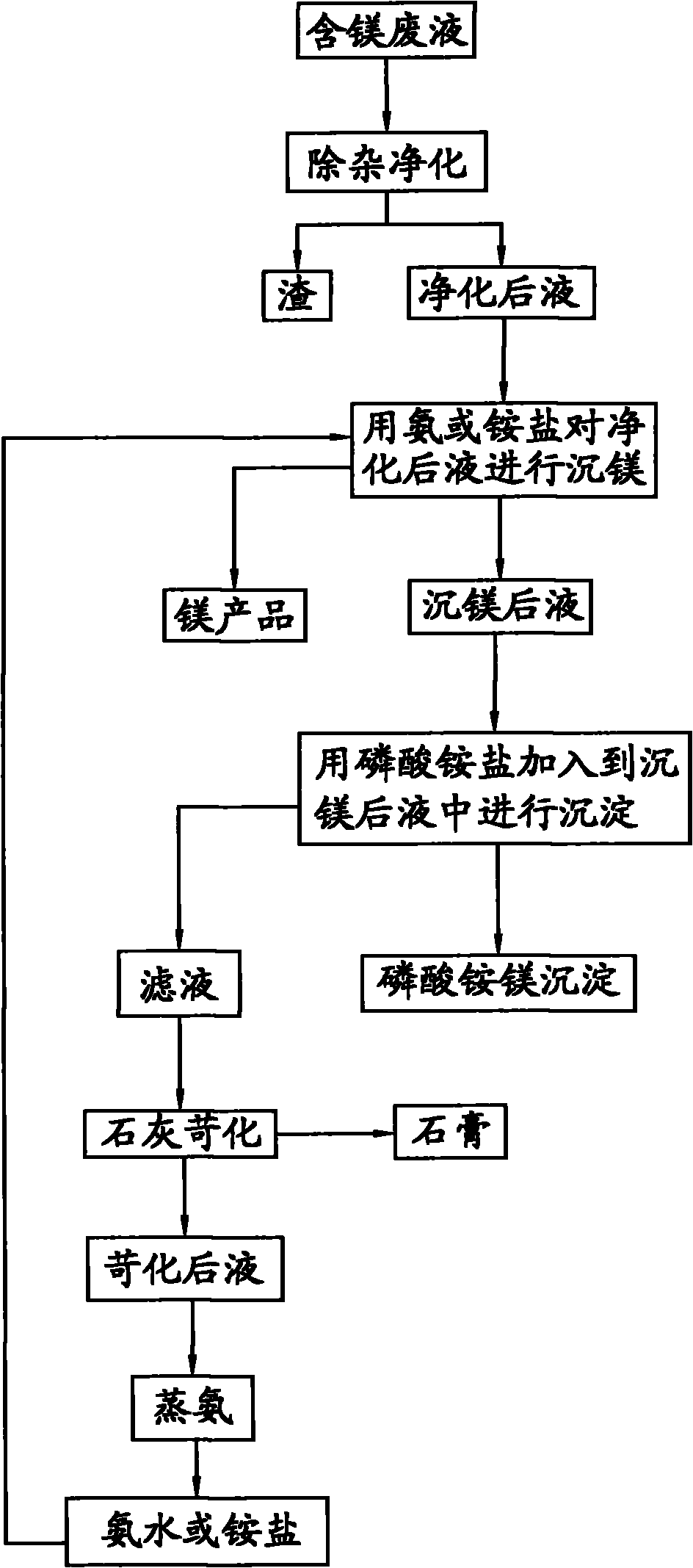
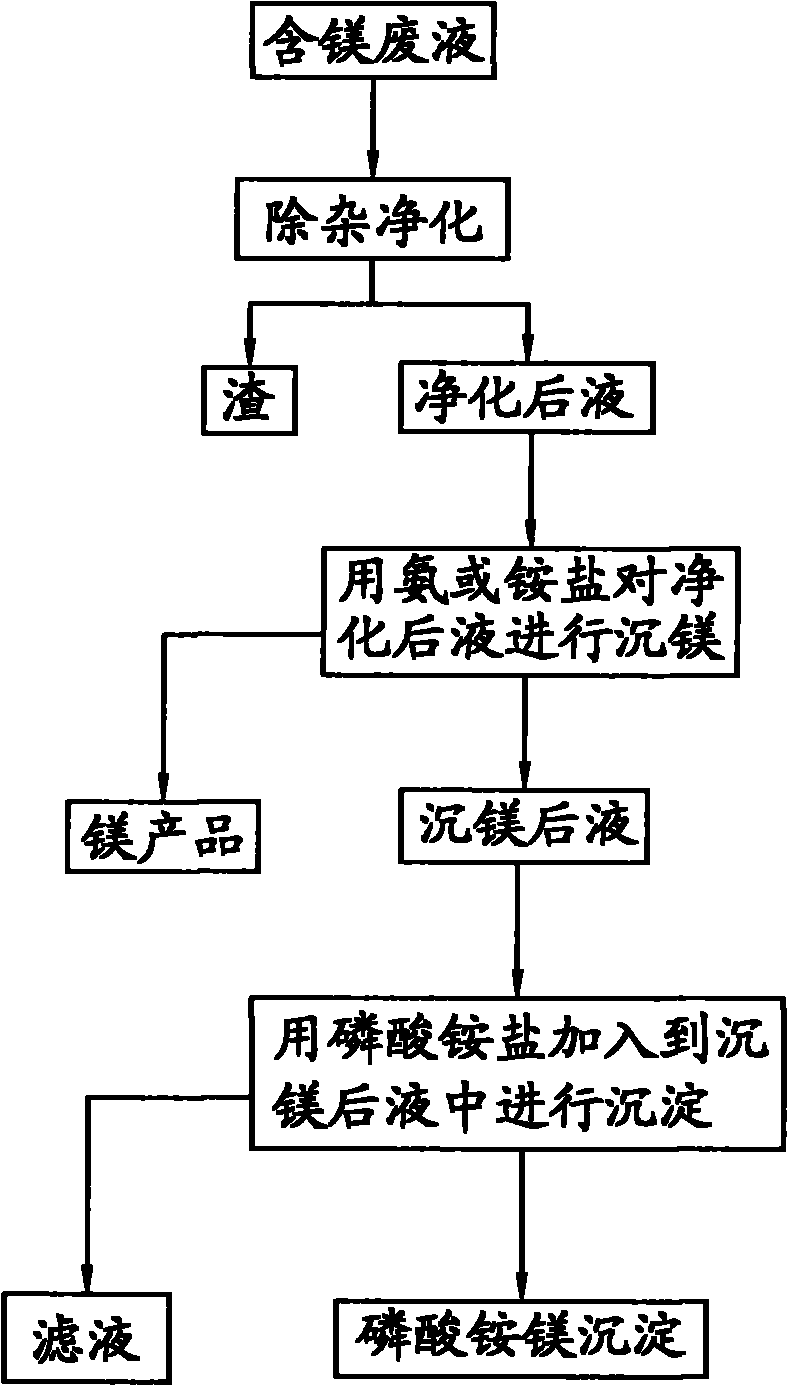
[0033] Take 1L of magnesium-containing waste liquid, and use the ammonia method to precipitate magnesium to precipitate magnesium ions, and finally obtain a magnesium-precipitated liquid with a magnesium content of 10g / L. Add ammonium dihydrogen phosphate to the solution after magnesium precipitation, and react for 30 minutes at a temperature of 35°C and pH=9.1, filter out the magnesium ammonium phosphate precipitate, wash with water and dry at 50°C. Analyzing by a conventional method, the magnesium content in the filtrate obtained after filtering out the magnesium ammonium phosphate is 10 mg / L, and the magnesium precipitation rate is greater than 99%; the purity of the magnesium ammonium phosphate is greater than 99%.
[0034] Lime is added to the filtrate for causticizing to obtain gypsum and causticizing liquid. The causticized liquid is subjected to ammonia distillation operation, and the obtained ammonia water is returned for ammonia magnesium precipitation.
example 2
[0036] Take 1 L of magnesium-containing waste liquid, and use ammonium carbonate magnesium precipitation to precipitate magnesium ions therein, and finally obtain a magnesium content of 4 g / L after magnesium precipitation. Add ammonium dihydrogen phosphate to the magnesium-precipitated solution, react for 30 minutes at a temperature of 35°C and pH=8.5, filter out the magnesium ammonium phosphate precipitate, wash with water and dry at 50°C. Analyzing by a conventional method, the magnesium content in the filtrate obtained after filtering out the magnesium ammonium phosphate is 15 mg / L, and the magnesium precipitation rate is greater than 99%. The purity of magnesium ammonium phosphate is greater than 99%.
[0037] Lime is added to the filtrate for causticizing to obtain gypsum and causticizing liquid. The ammonia in the causticized liquid is converted into ammonium salt and returned for magnesium precipitation.
example 3
[0039] Take 1 L of magnesium-containing waste liquid, and use ammonium bicarbonate to precipitate magnesium ions to precipitate the magnesium ions therein, and finally obtain a magnesium-precipitated liquid with a magnesium content of 10 g / L. Add ammonium dihydrogen phosphate to the magnesium precipitation solution, react for 60 minutes at a temperature of 45°C and pH=8.2, filter out the magnesium ammonium phosphate precipitate, wash with water and dry at 80°C. Analyzing by a conventional method, the magnesium content in the filtrate obtained after filtering out the magnesium ammonium phosphate is 15 mg / L, and the magnesium precipitation rate is greater than 99%. The purity of magnesium ammonium phosphate is greater than 99%.
[0040] Lime is added to the above filtrate for causticizing to obtain. The ammonia in the causticized liquid is converted into ammonium salt and returned for magnesium precipitation.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com