Non-contact phase-difference type torque sensor
A torque sensor, non-contact technology, applied in the field of sensors, can solve the problems of reduced sensor accuracy, shortened service life, high installation requirements, etc., and achieve the effects of long service life, simple structure and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0030] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the embodiments shown in the accompanying drawings.
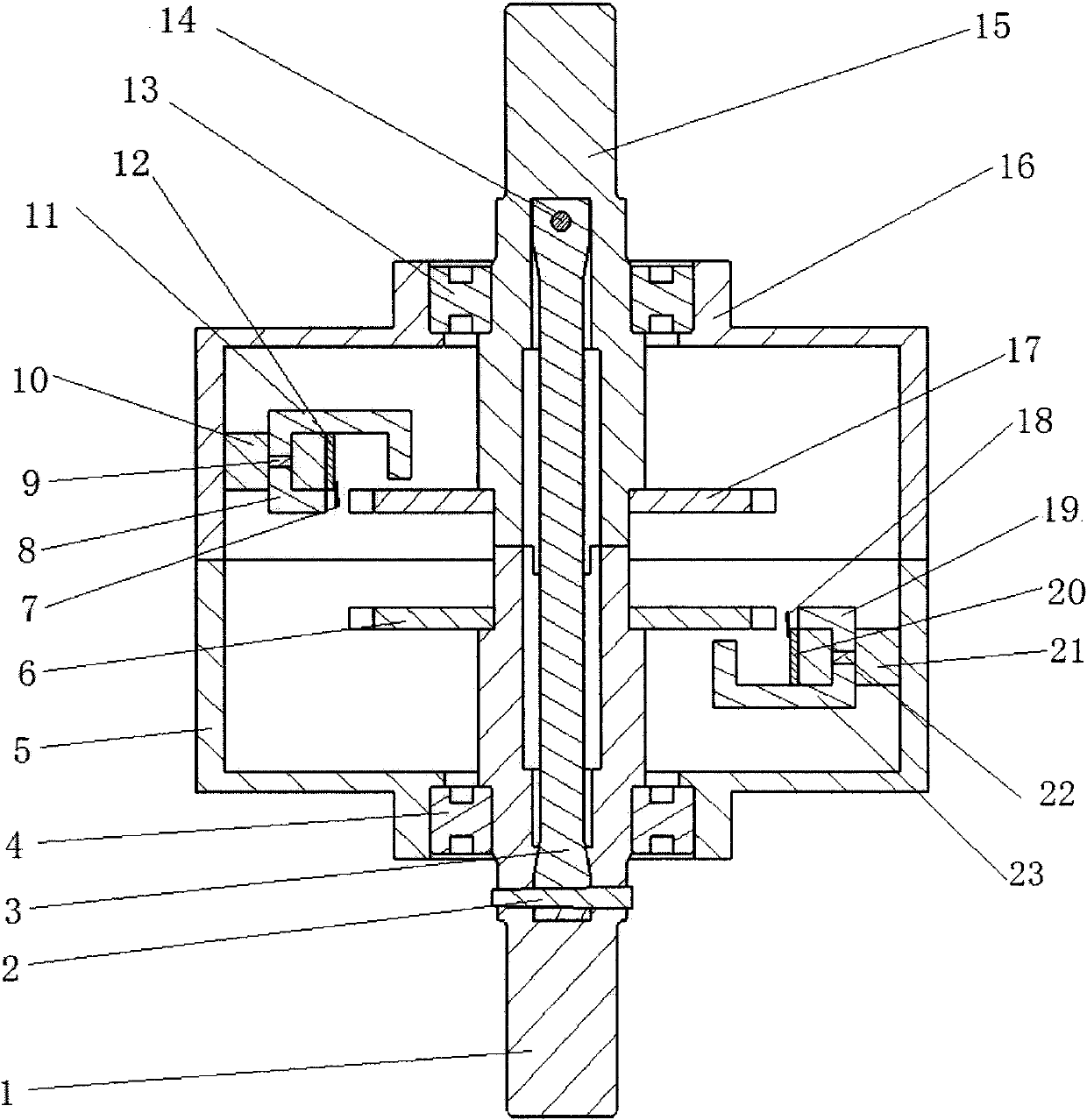
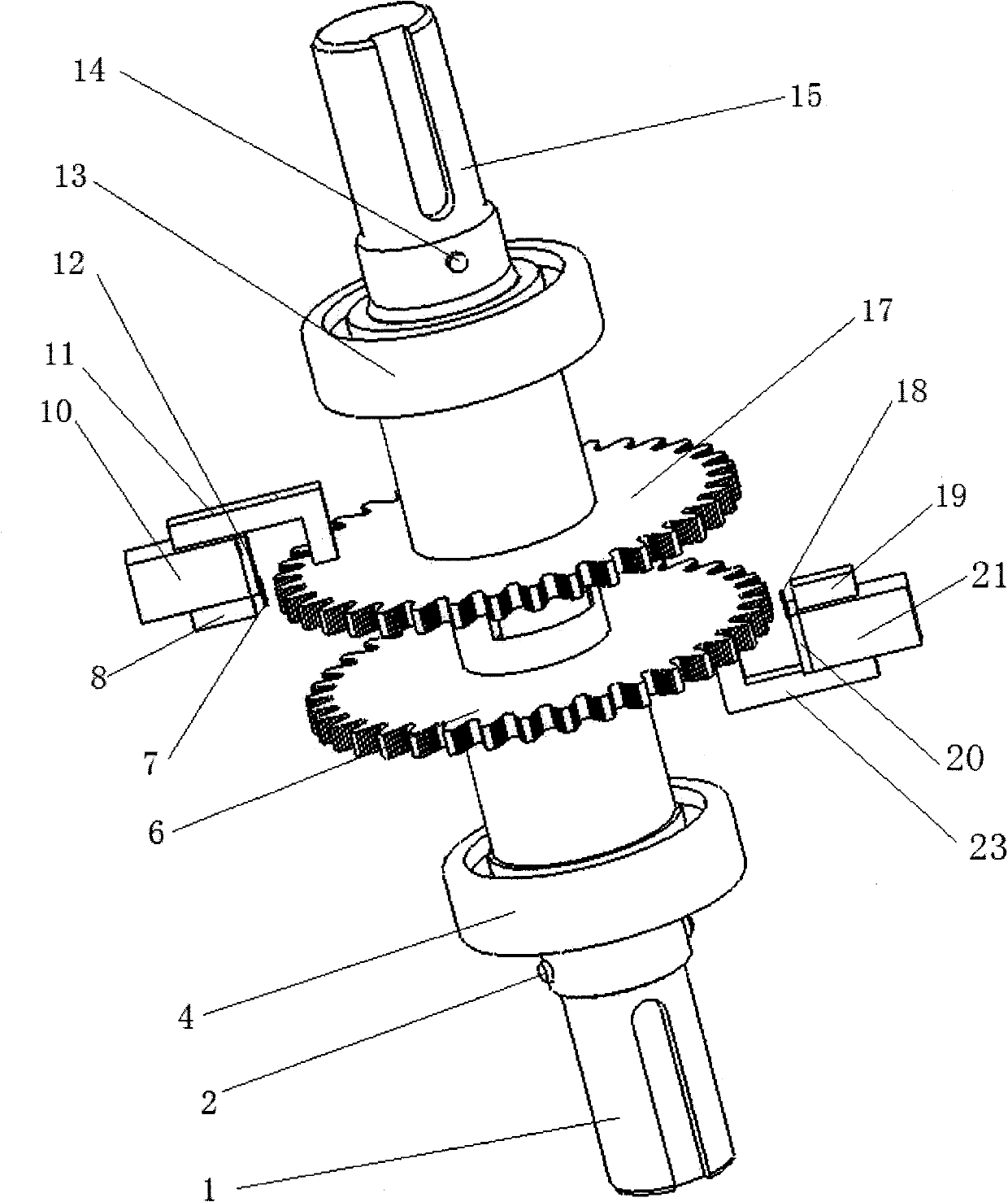
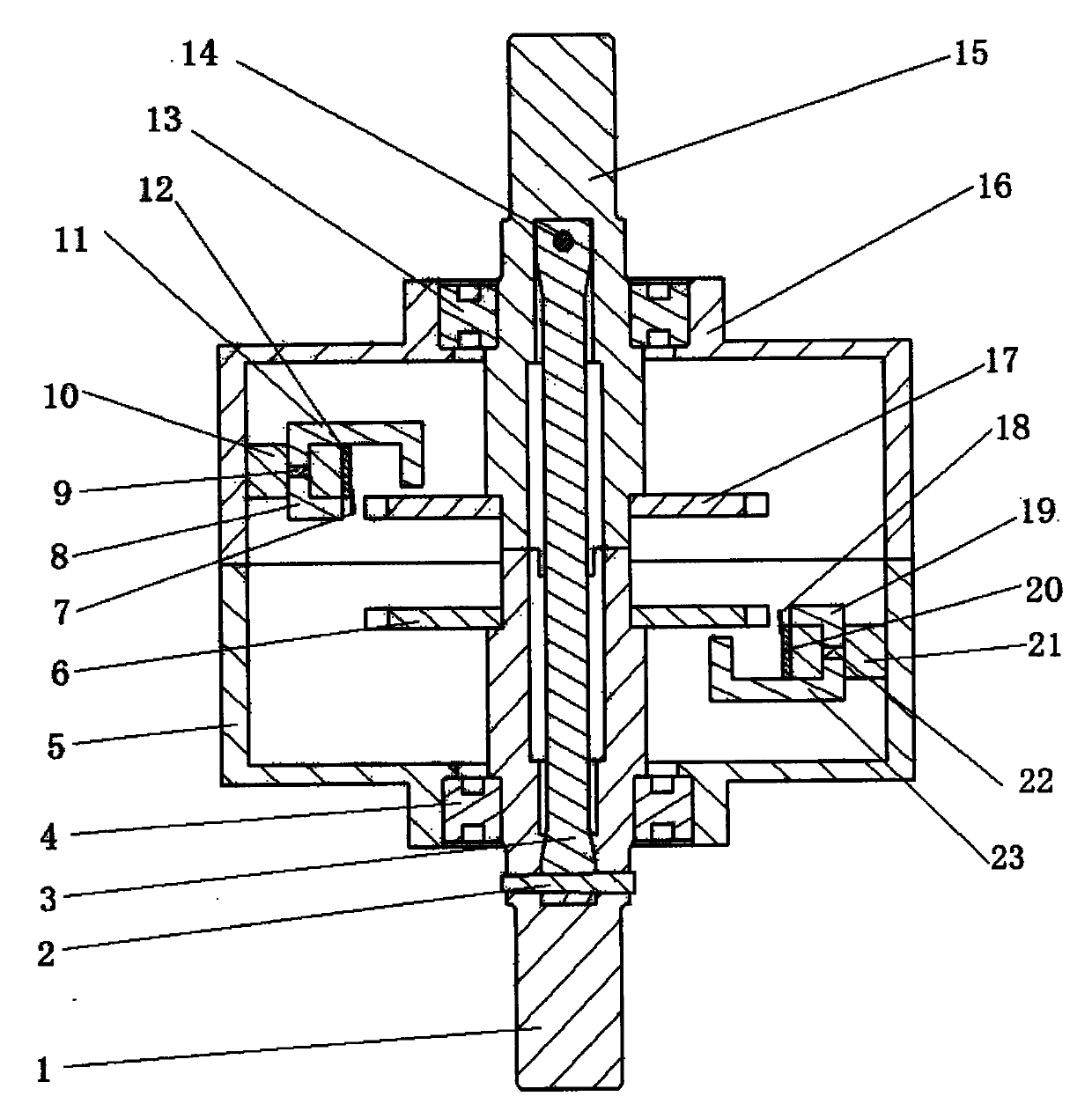
[0031] The present invention is a non-contact phase difference torque sensor, which includes: input sleeve 15, output sleeve 1, torsion bar 3, first pin 2, second pin 14, first bearing 4, second bearing 13, first A sensor housing 5, a second sensor housing 16, a first circuit board 12, a second circuit board 20, a first magnetic circuit support 10, a second magnetic circuit support 21, a first Hall sensor 7, a second Hall sensor Sensor 18, the first involute gear 6, the second involute gear 17, the first magnetic circuit assembly, and the second magnetic circuit assembly, wherein: one end of the input sleeve 15 is connected with the steering wheel through a key, and the input sleeve 15 passes through The spline is connected to one end of the torsion bar 3, and the other end of the torsion bar 3 is connected to the output sleeve 1 through a spli...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com