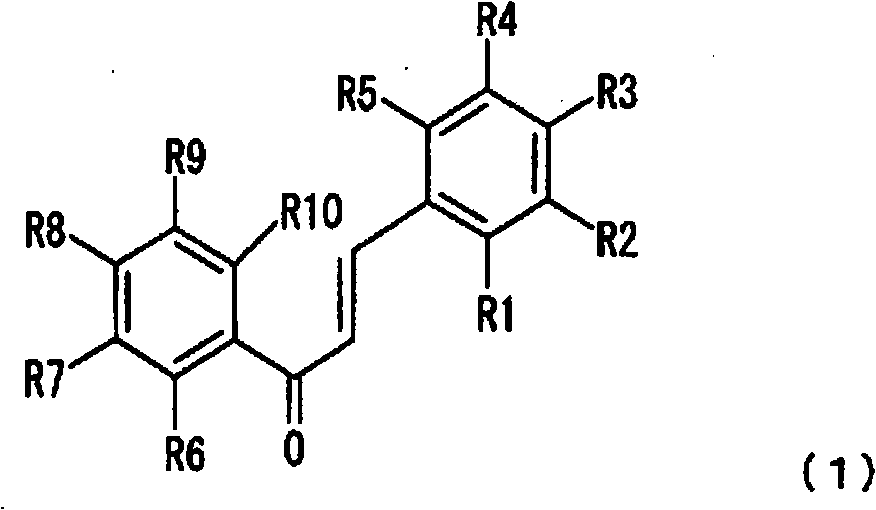
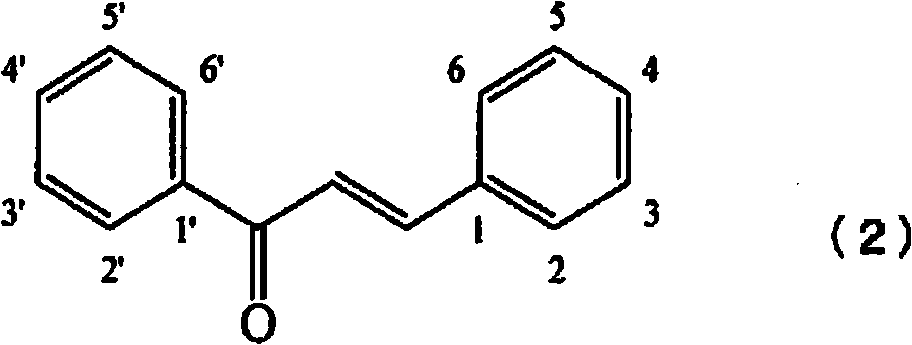
Plant-origin drug for preventing or improving hyperuricemia
A hyperuricemia and improving agent technology, which is applied in the direction of plant raw materials, plant/algae/fungus/moss components, drug combinations, etc., can solve the problem of insufficient xanthine oxidase inhibitory effect and low safety problem, to achieve excellent xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity, high safety, effective prevention and improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0069] Artemisia mugwort (whole plant), snow lotus (whole plant), sage sage (whole plant), Eurasian Huoxuedan (whole plant), peppermint (leaves), Millipede spathifolia (stem) (purchased from Shinwa Products Co., Ltd. chrysanthemum (flower), oregano (leaves and flowers) (purchased from Kaneka Sunspaisu Co., Ltd. above); violet (flower) (purchased from Xiaolingui Co., Ltd.); guava (leaf), peanut (inner bark ) (purchased from a general store above) each 1000g was immersed in 5L ethanol aqueous solution of 99.5% by volume, stirred and extracted at 45°C for 6 hours, and the residue was removed by filtration to obtain an extract. Furthermore, the extract was concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the solvent to obtain the respective extracts. In addition, Pycnogenol was a commercially available product as it was.
Embodiment 2
[0071] When evaluating the xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity of each sample, each extract prepared in Example 1 and Pycnogenol were dissolved in DMSO to make 100 mg / mL. Each DMSO solution was dissolved in 75 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.5) to prepare a 400 µg / mL sample solution.
[0072] 50 μL of the sample solution and 50 μL of an enzyme solution in which buttermilk-derived xanthine oxidase was dissolved in phosphate buffer to a concentration of 0.2 units / mL were added to a 96-well plate, and treated at 25° C. for 15 minutes. Then, 100 μL of a 0.4 mM xanthine solution was added, and the reaction was performed at 25° C. for 15 minutes. At this time, the final concentration of each sample was 100 μg / mL. Then, 20 μL of 1N hydrochloric acid was added to stop the reaction. The absorbance at 295 nm was measured with a microplate reader. In addition, as a solvent control, 50 μL of a solution in which DMSO was dissolved in a phosphate buffer to a concentration of 0.4% was used ins...
Embodiment 3
[0081] When evaluating the xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity of each sample, occanin (from T. chinensis) and allopurinol (manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.) were each dissolved in DMSO at 100 mg / mL. Each DMSO solution was dissolved in 75 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.5) to prepare a 400 µM sample solution.
[0082] 50 μL of the above sample solution and 50 μL of an enzyme solution in which buttermilk-derived xanthine oxidase was dissolved in phosphate buffer to a concentration of 0.2 units / mL were added to a 96-well plate, and treated at 25° C. for 15 minutes. Then, 100 μL of a 0.4 mM xanthine solution was added, and the reaction was performed at 25° C. for 15 minutes. At this time, the final concentration of each sample was 100 μg / mL. Then, 20 μL of 1N hydrochloric acid was added to stop the reaction. The absorbance at 295 nm was measured with a microplate reader. In addition, as a solvent control, 50 μL of a solution in which DMSO was dissolved in a phosp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com