Clock synchronization method and system of master/salve clock equipment
A clock synchronization and master clock technology, applied in time division multiplexing systems, transmission systems, synchronization devices, etc., can solve problems such as time synchronization, network congestion, and increased operation and maintenance costs, so as to realize dynamic notification and improve flexibility sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] In this embodiment, a mobile communication BSS (Base Station System, base station subsystem) is taken as an example to introduce the PTP dynamic deployment solution of the present invention.
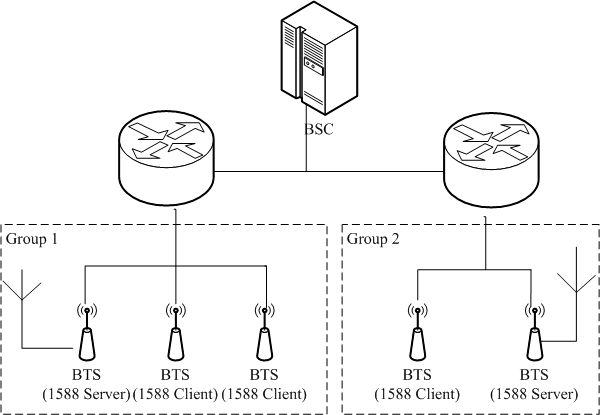
[0064] Such as figure 2 As shown, when the BTS (Base Station Transceiver, Base Station Transceiver) of multiple BSSs is connected to the BSC (Base Station Controller, Base Station Controller), some of the BTSs are connected to GPS as the master clock device, and other BTSs The base station provides time synchronization service.
[0065] The first step is to logically divide all BTSs into groups, and ensure that at least one BTS is connected to GPS as the main clock device in each group.
[0066] Wherein, devices among the divided logical groups do not overlap, that is, a master clock device or a slave clock device can only belong to one logical group, and cannot belong to multiple logical groups at the same time. In this example, if figure 2 Shown is divided into two groups, ...
Embodiment 2
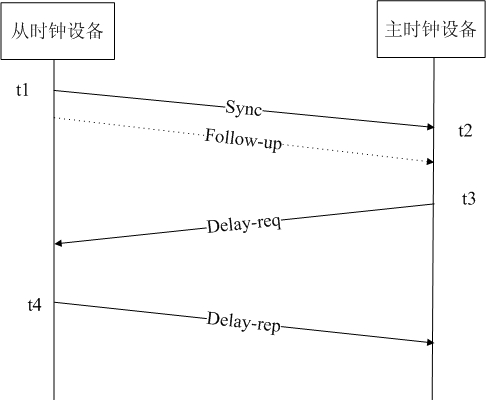
[0078] image 3 It shows the interactive signaling flow of the master-slave clock device implementing clock synchronization in the embodiment of the present invention, as shown in image 3 As shown, the specific description of the process is as follows:
[0079] Step 1, the slave clock device periodically sends a multicast request authorization PTP message, carries its own group number in the PTP message, and uses the reserved field of the PTP message header; at the same time, it also carries synchronization in the PTP message (Sync) Request authorization service information.
[0080] Step 2, after the master clock device receives the multicast request authorization PTP message from the slave clock device, it takes out the group number from the PTP message, and judges whether the slave clock device is in the same group as itself according to the group number, and if so, Then record the IP address of the slave clock device, and respond to the slave clock device with a unicast...
Embodiment 3
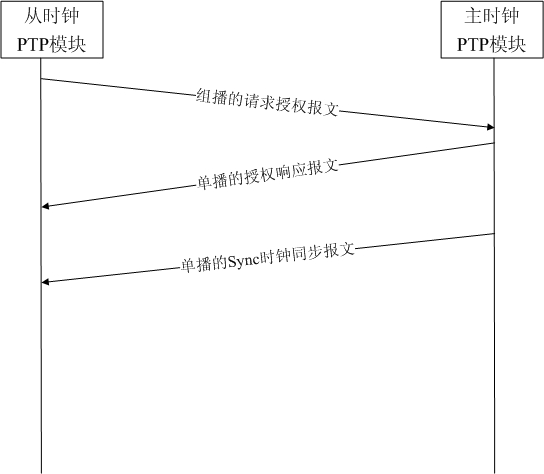
[0084] Figure 4 A schematic diagram of a synchronization process implemented by a slave clock device PTP module according to an embodiment of the present invention, as Figure 4 As shown, the process is described in detail as follows:
[0085] Step 1, the slave clock device regularly sends a multicast request authorization message;
[0086] Step 2, the master clock device judges whether the received authorization message belongs to the same group as itself, if yes, execute the next step 3, otherwise, return to step 1;
[0087] Step 3, recording the IP address of the master clock device;
[0088] Step 4, judge whether the clock synchronization service message is received, if yes, then perform the next step 5, otherwise, return to step 1;
[0089] Step 5, the slave clock device synchronizes the local clock according to the received clock synchronization service message.
[0090] Step 6: After the requested authorization service expires, the slave clock device re-sends a uni...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com