Patents
Literature
321 results about "Radio access point" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
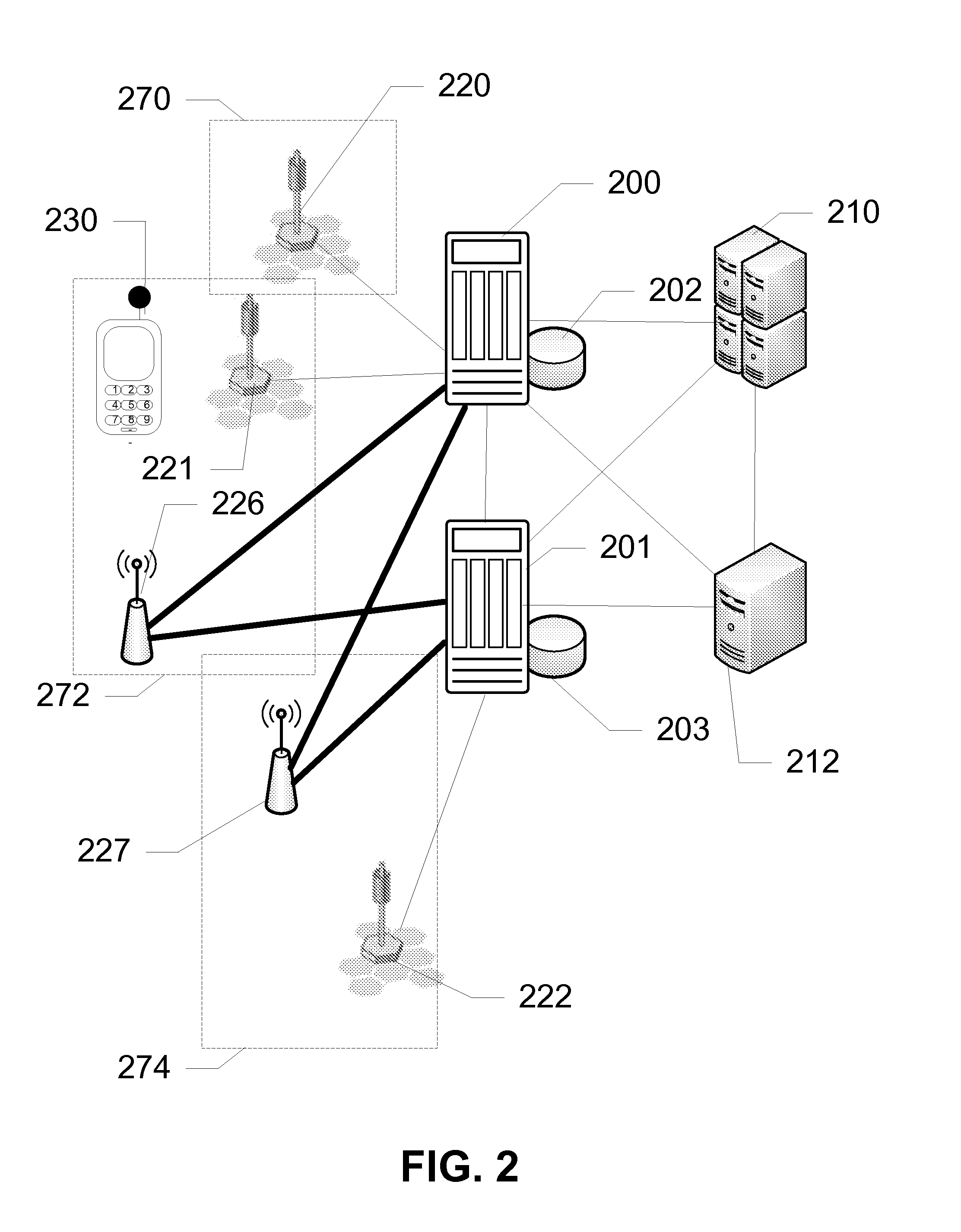
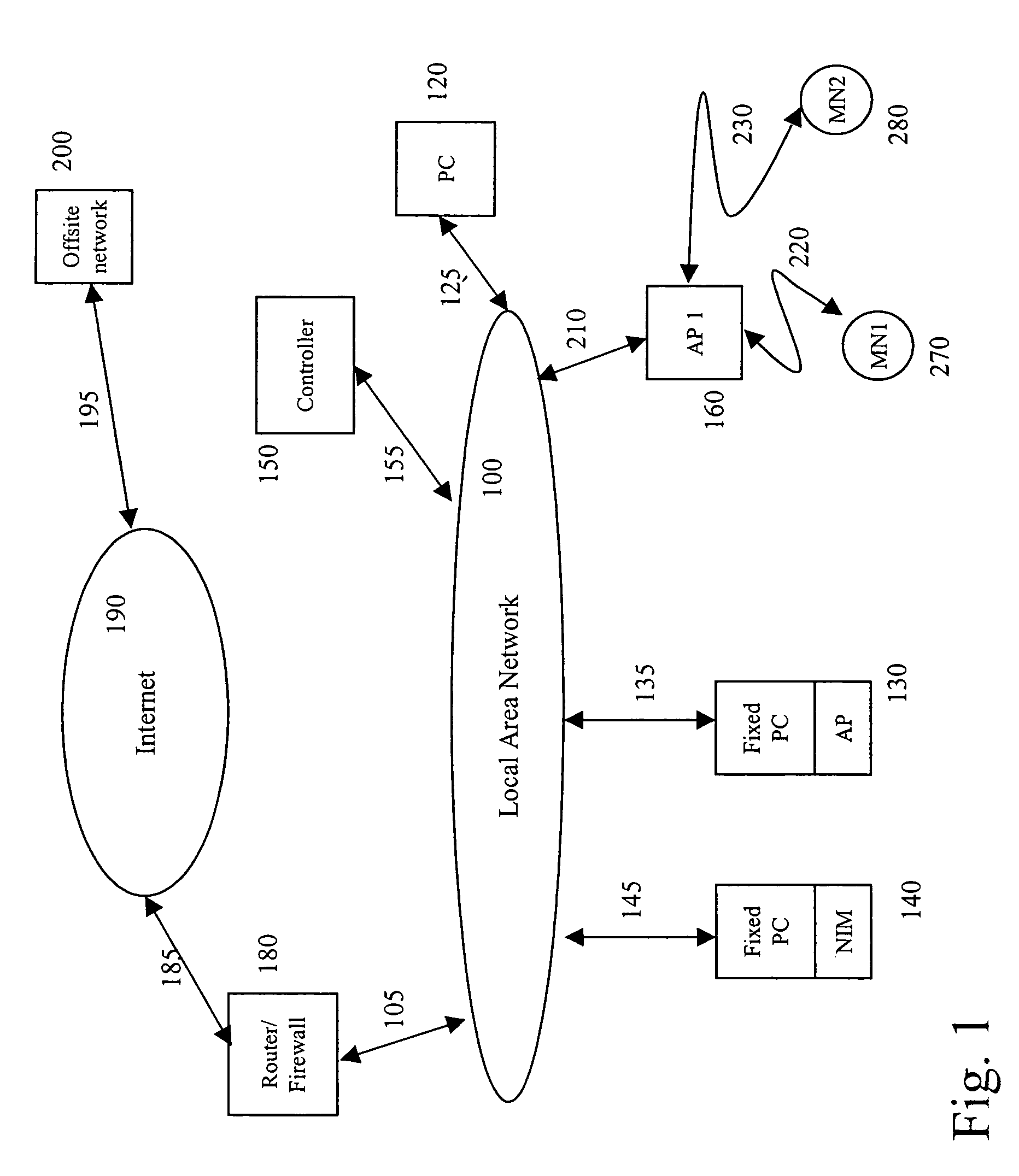
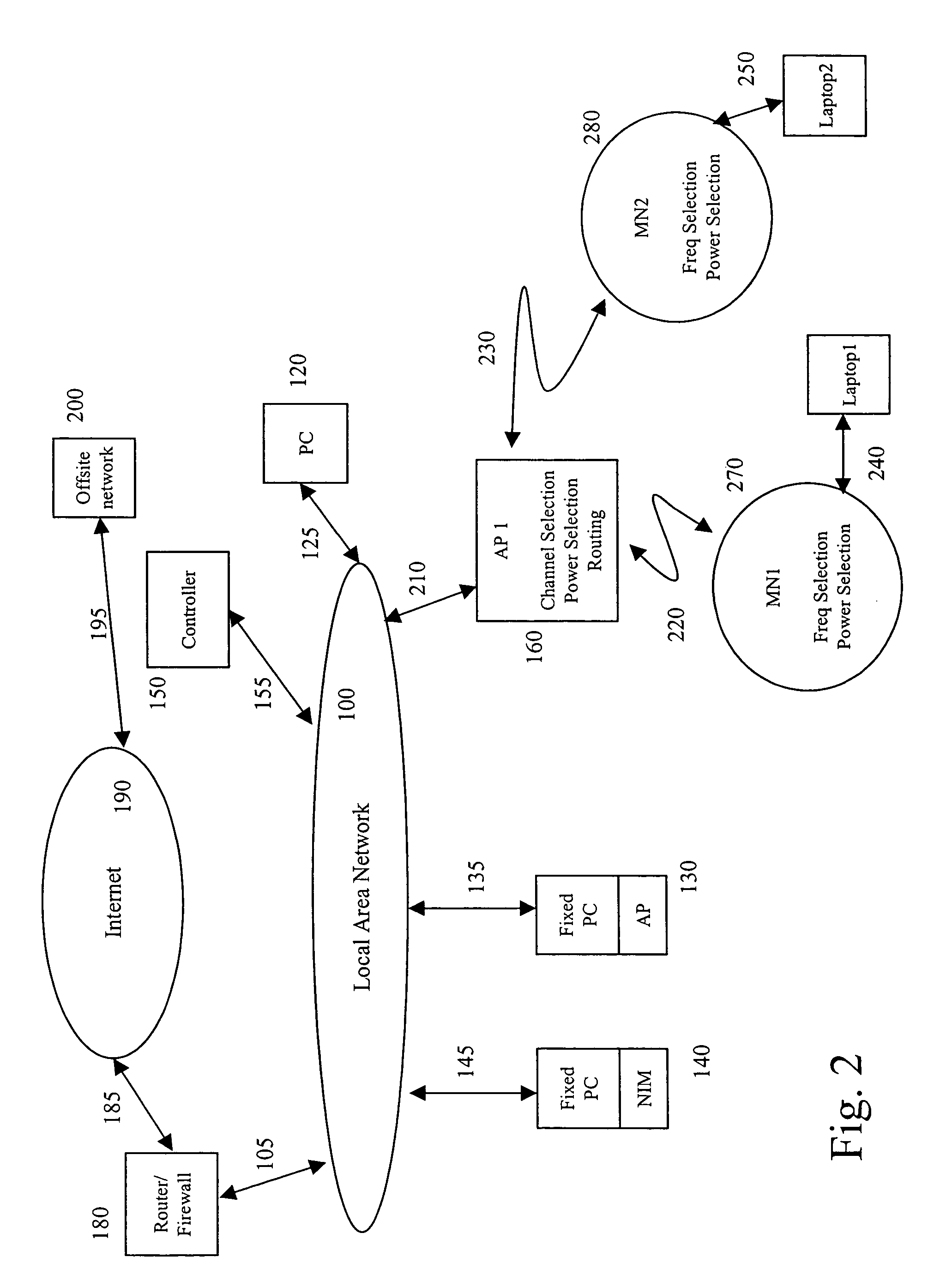
An access point is a pico base station or network access point in a WLAN radio network, consisting of a radio (often more than one) and a network connection, enabling WLAN clients to access network resources connected to a home or enterprise network.
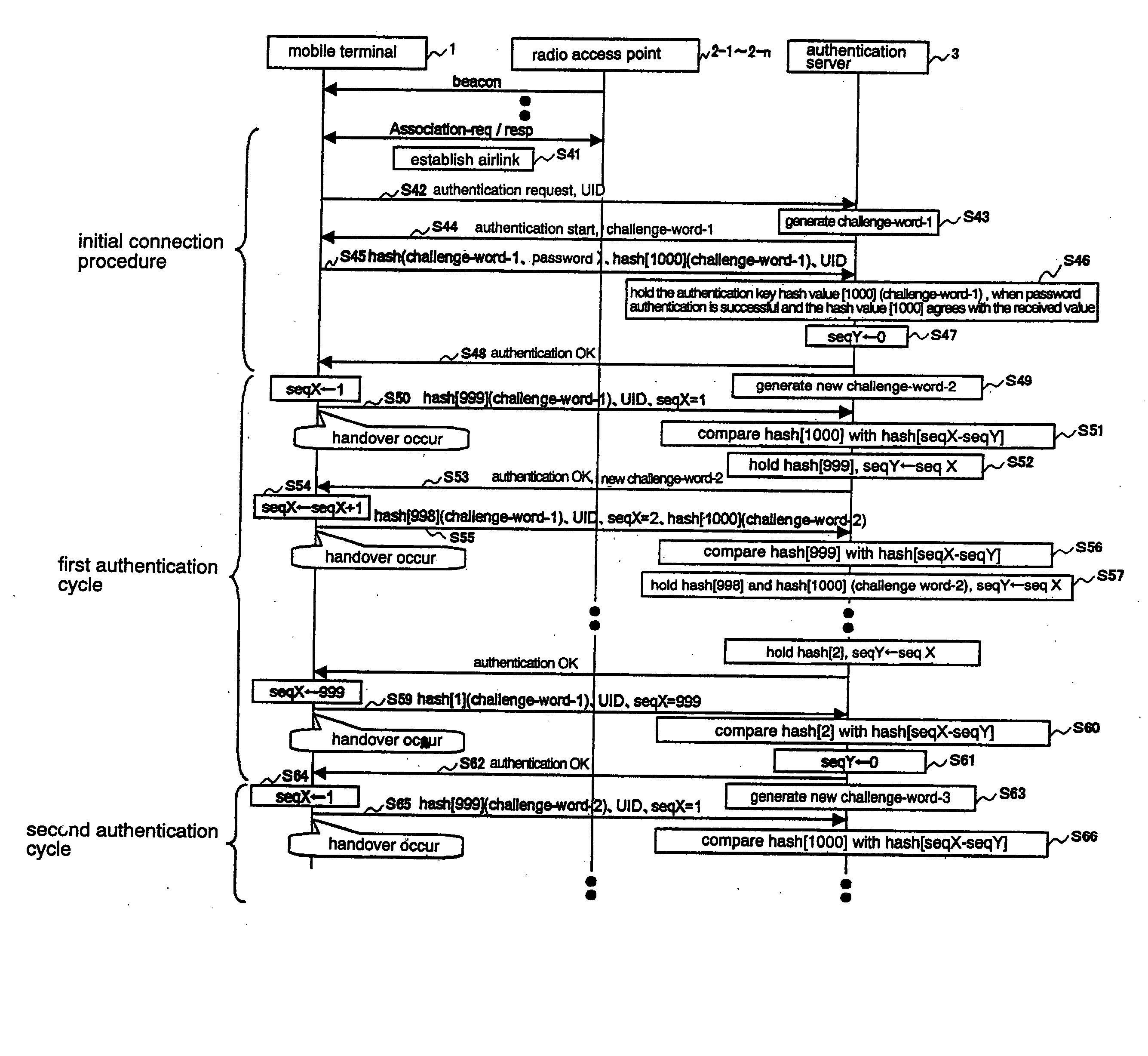
Mobile terminal authentication method capable of reducing authentication processing time and preventing fraudulent transmission/reception of data through spoofing
InactiveUS20050113070A1Shorten the timePreventing fraudulent data transmission/receptionUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsReceiptRadio access point
A mobile terminal transmits an N-th authentication key to an authentication server when the mobile terminal has moved from a coverage area under a certain radio access point to a coverage area under another radio access point. The N-th authentication key is generated by applying a hash function to a random number a number of times one smaller than an (N−1)th authentication key which was transmitted when the mobile terminal moved to the coverage area under the certain radio access point. Upon receipt of the N-th authentication key from the mobile terminal, the authentication server applies the hash function once to the N-th authentication key, and compares the result with the (N−1)th authentication key. Then, the authentication server determines that the authentication is successful when there is a match between both keys.
Owner:NEC CORP
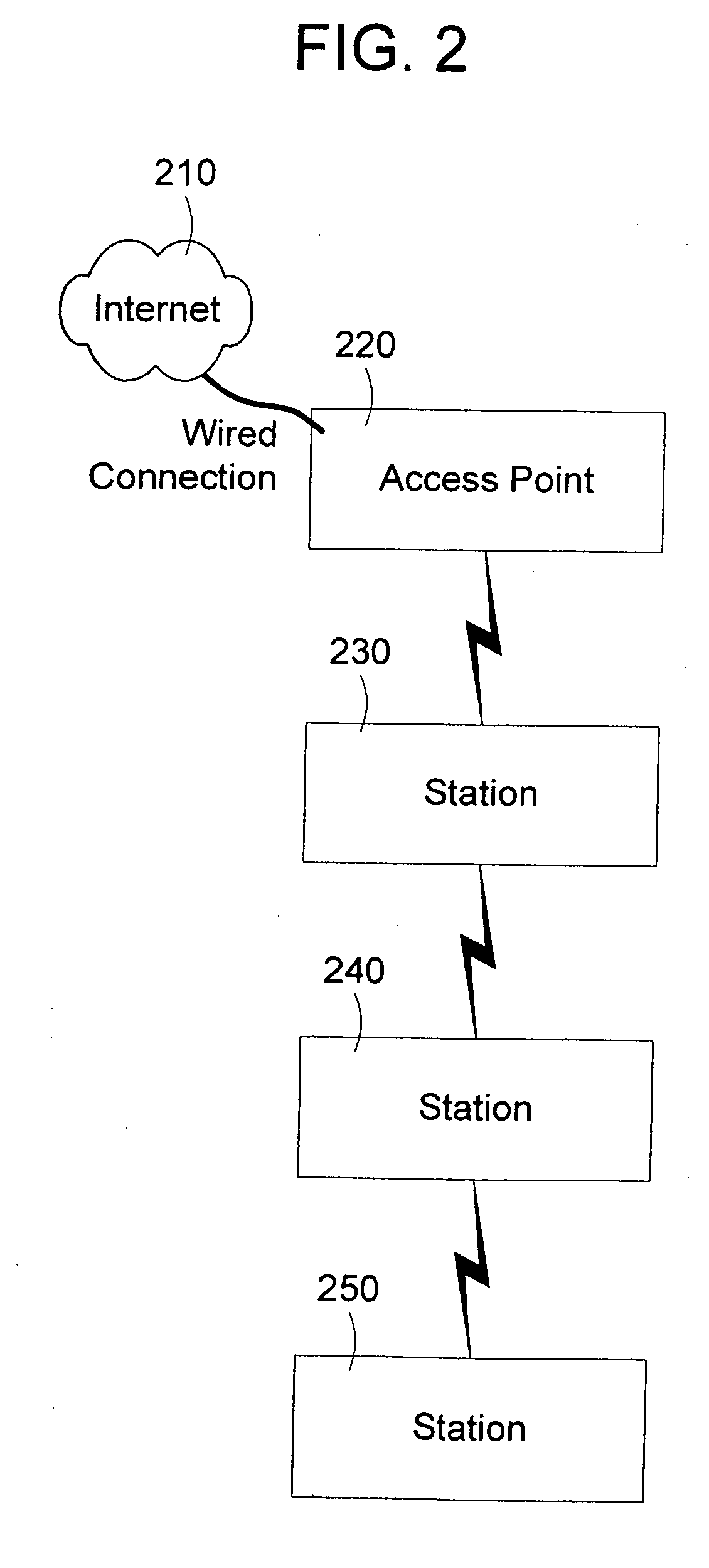
Providing easy access to radio networks
ActiveUS20080186882A1Effective serviceMinimal interventionAssess restrictionRadio transmissionRadio networksRadio access point
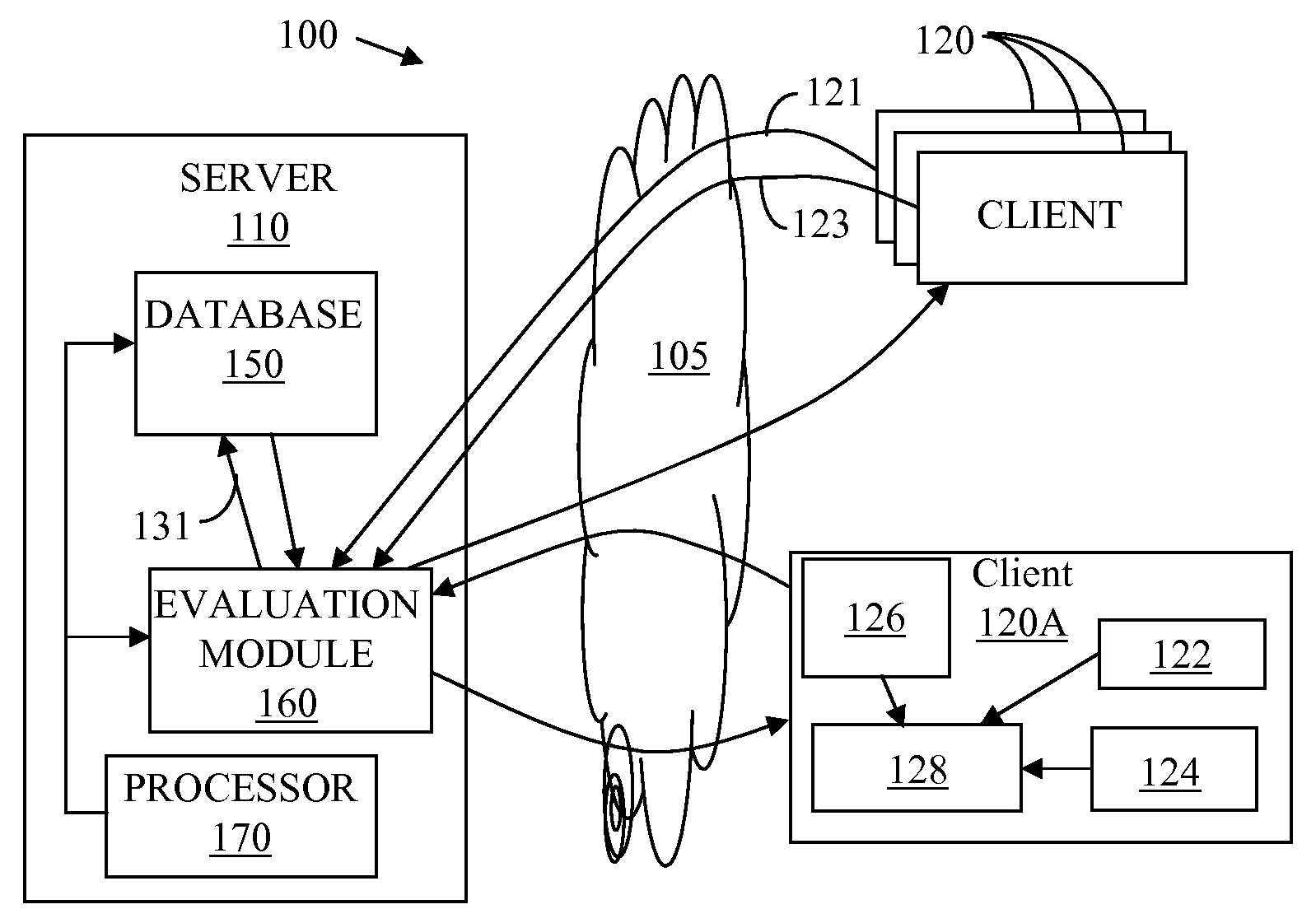
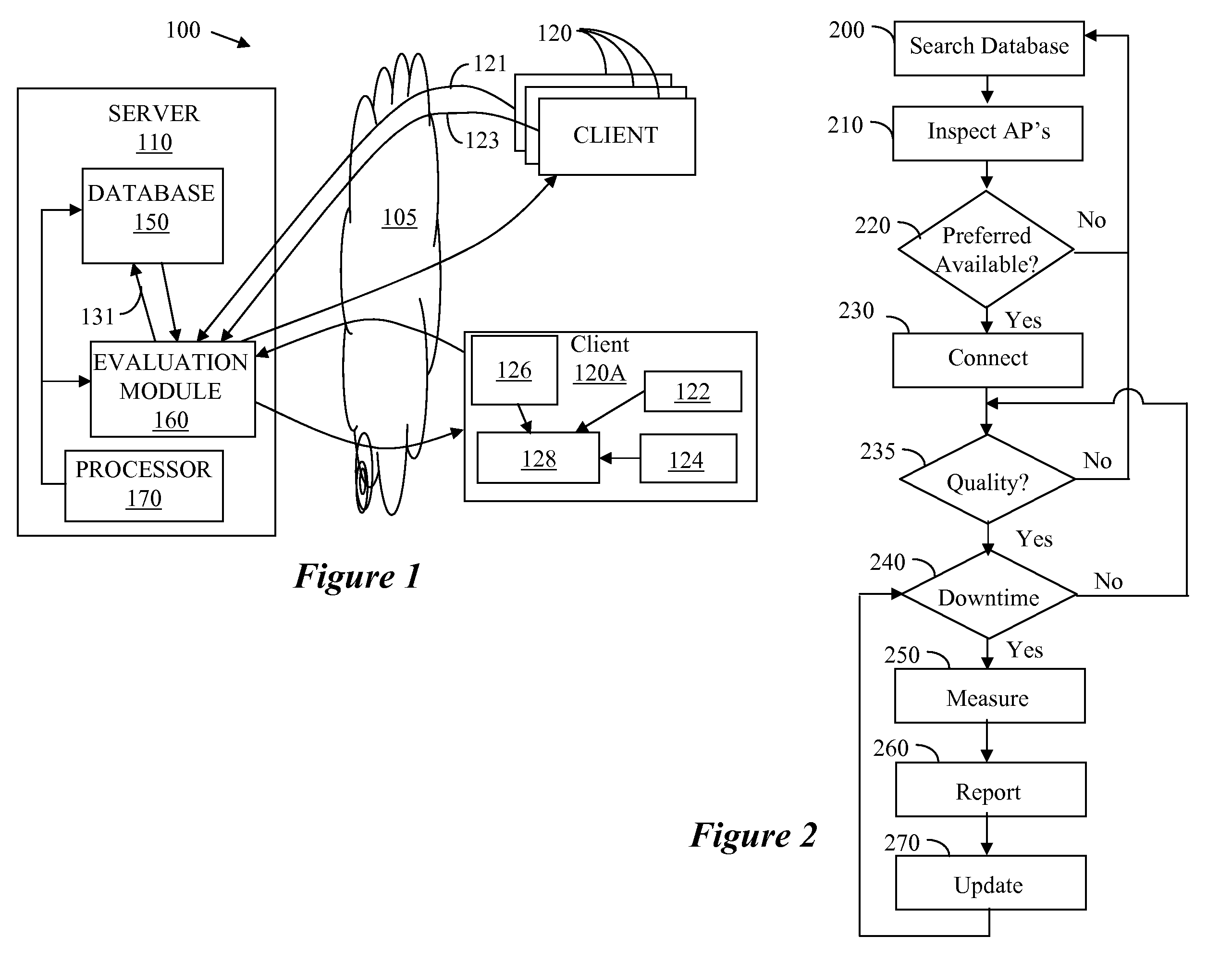
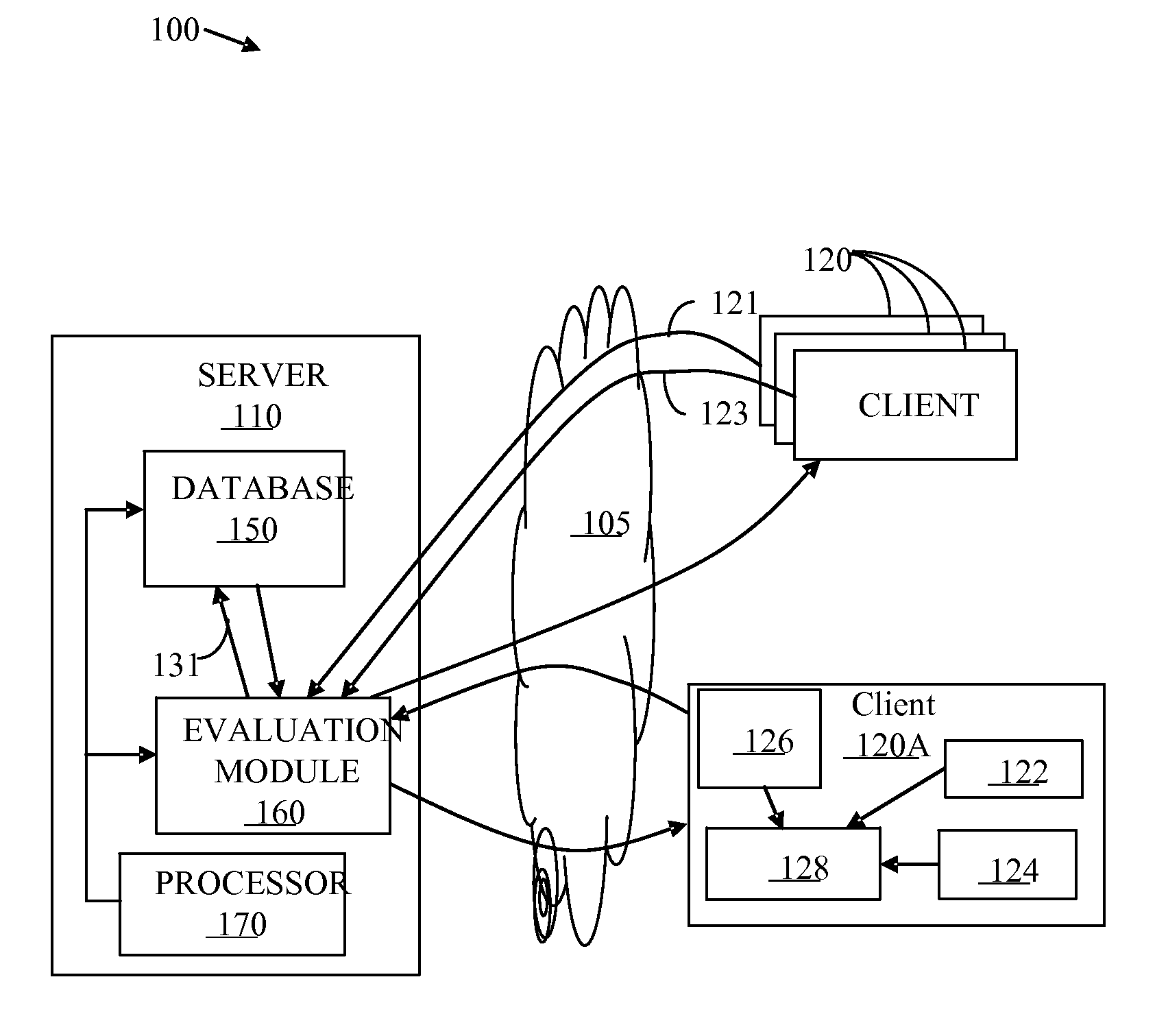
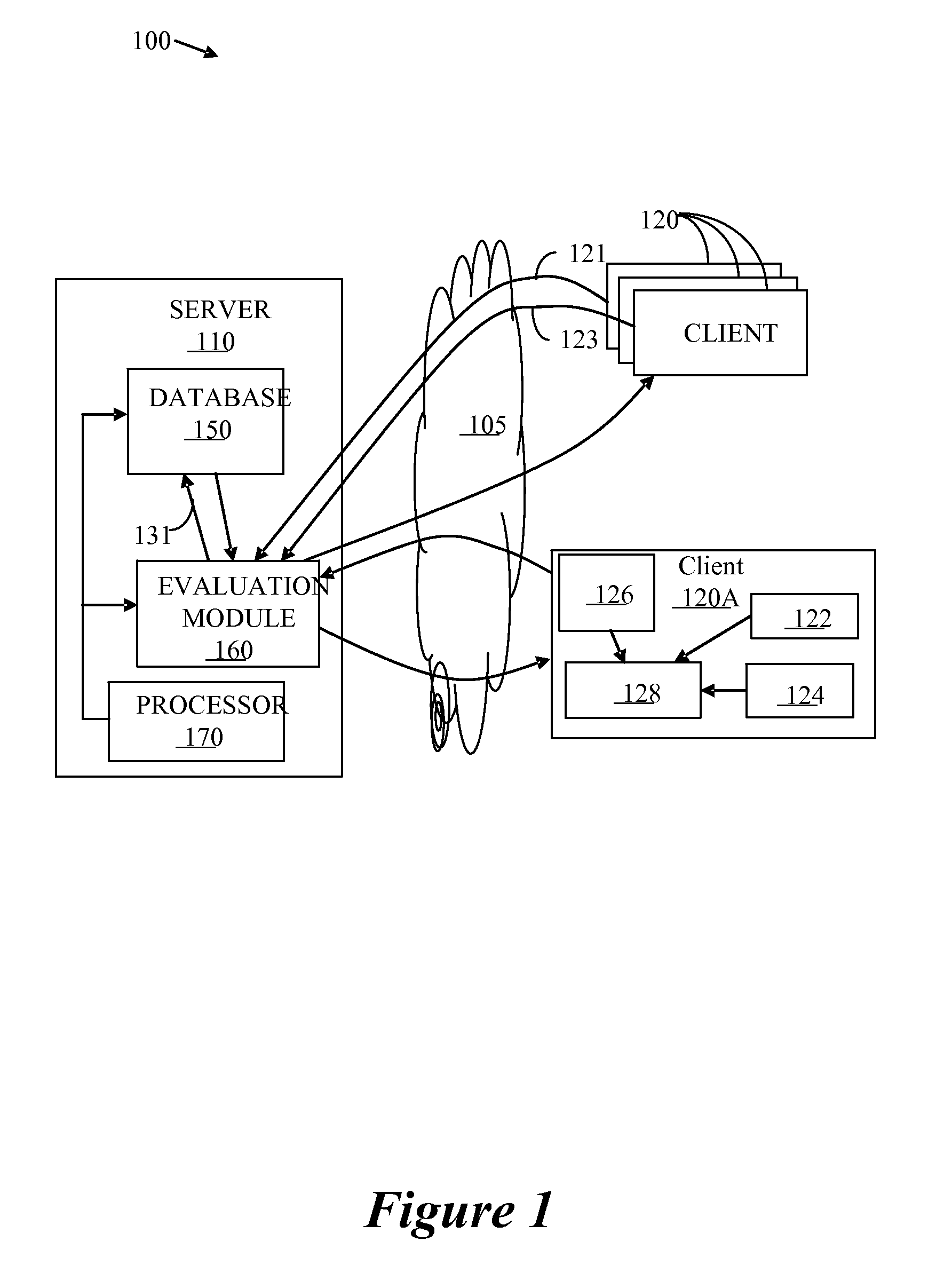
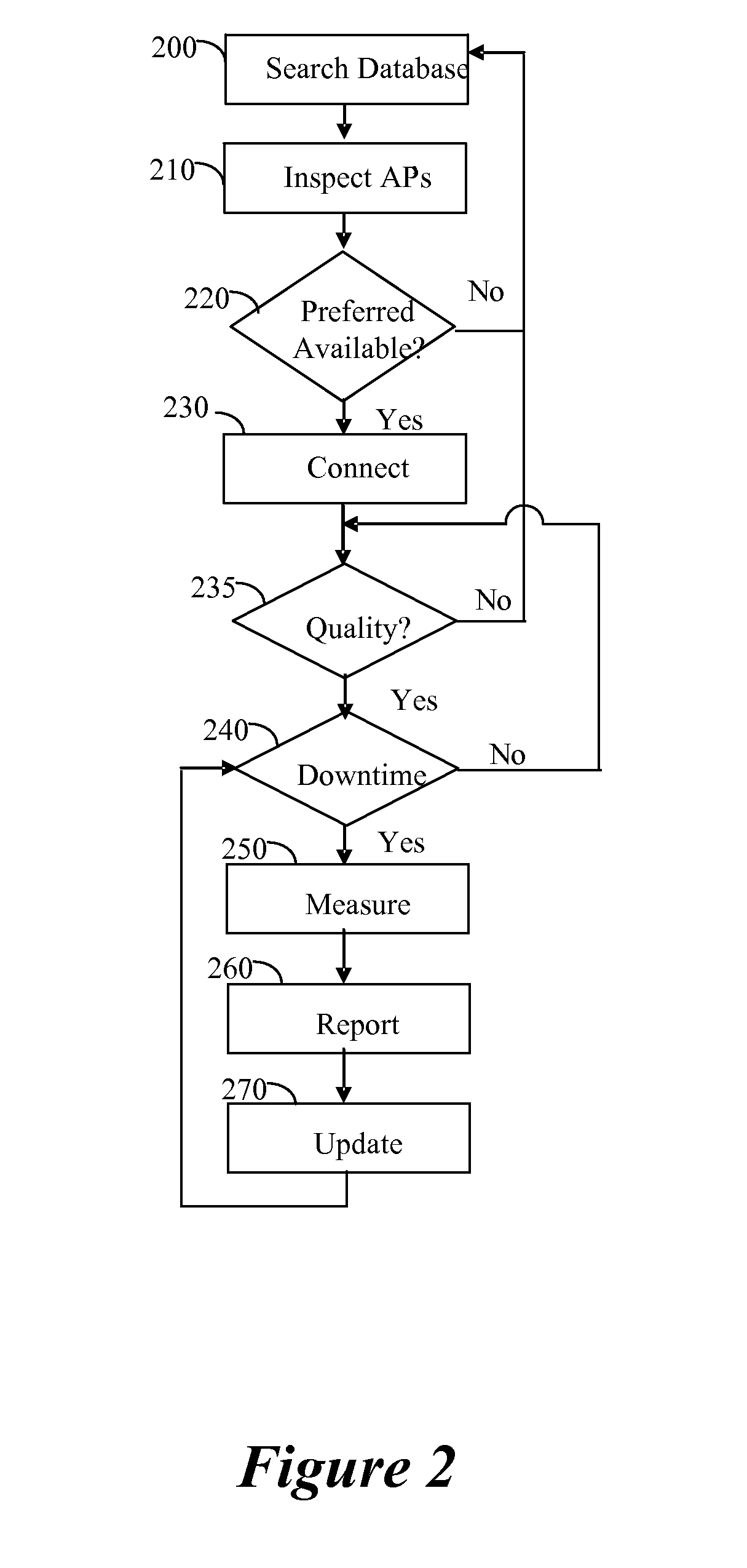
An improved connectivity to radio access point is enabled by a server that includes a database storing data about various radio access points, and an evaluation module evaluating the quality of connection to each of the access points. Clients receive updates about relevant access points from the server and use the information to connect to the preferred access point. The clients also check connectivity to other access points in the vicinity, and report the findings to the server. The server uses the reports to update its database, and send corresponding updates to the clients.
Owner:WEFI
Wireless radio access point configuration
Methods and systems for configuring an access point (AP) are provided. According to one embodiment, a dual radio AP includes: two radios, a first operating at 2.4 GigaHertz (GHz) or 5 GHz and a second operating at 5 GHz; first and second directional antennas coupled to the first and second radios, respectively; first and second transmit queues buffering packets for transmission by the first and second radios, respectively; a location determination module configured to compute locations of recipient devices of the packets; a direction identification module configured to calculate angles to direct the directional antennas based on the computed locations; an interference detection module configured to determine whether interference would take place if the packets are transmitted based on the calculated angles and estimated timing of transmission; and a transmission module configured to transmit the packets without interference between the directional antennas by rescheduling packets if necessary.
Owner:FORTINET
System and Method For Mapping Wireless Access Points
ActiveUS20090042557A1Effective serviceMinimal interventionAssess restrictionWireless commuication servicesLocation detectionRadio access point
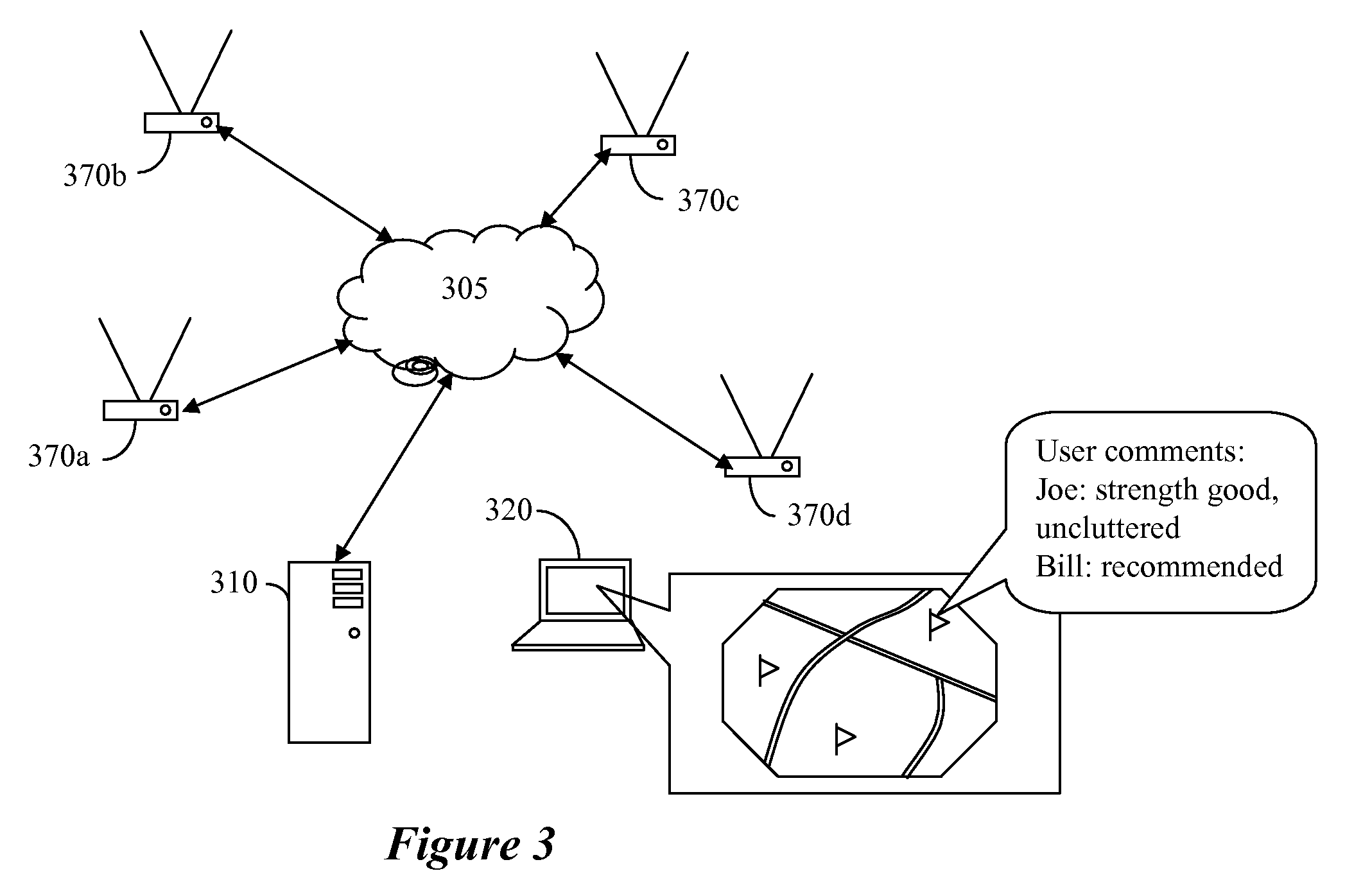
An improved connectivity to radio access point is enabled by a server that includes a database storing data about various radio access points, and an evaluation module evaluating the quality of connection to each of the access points. Clients receive updates about relevant access points from the server and use the information to connect to the preferred access point. The clients also check connectivity to other access points in the vicinity, and report the findings to the server. The server uses the reports to update its database, and send corresponding updates to the clients. The database can include information about the location of the access points. The information about the location of the access points can be manually input or determined using GPS information. The location of an access points can be determined as a function of available information about other access points detected at the same location. An access point can be presumed to be located in approximately the same location as another access point detected in the same location by the same user terminal. Where more than one access point having a known location is detected in the same location as an unmapped access point (having an unknown location), the location of the unmapped access point can be determined as function of a weighted average of the known locations of the other access points and signal strength of the signal received from each access point.
Owner:WEFI
Method for changing route in wireless communication
InactiveUS20100099415A1Improve accuracyAvoid failureNetwork topologiesRadio transmissionRadio access pointUser equipment
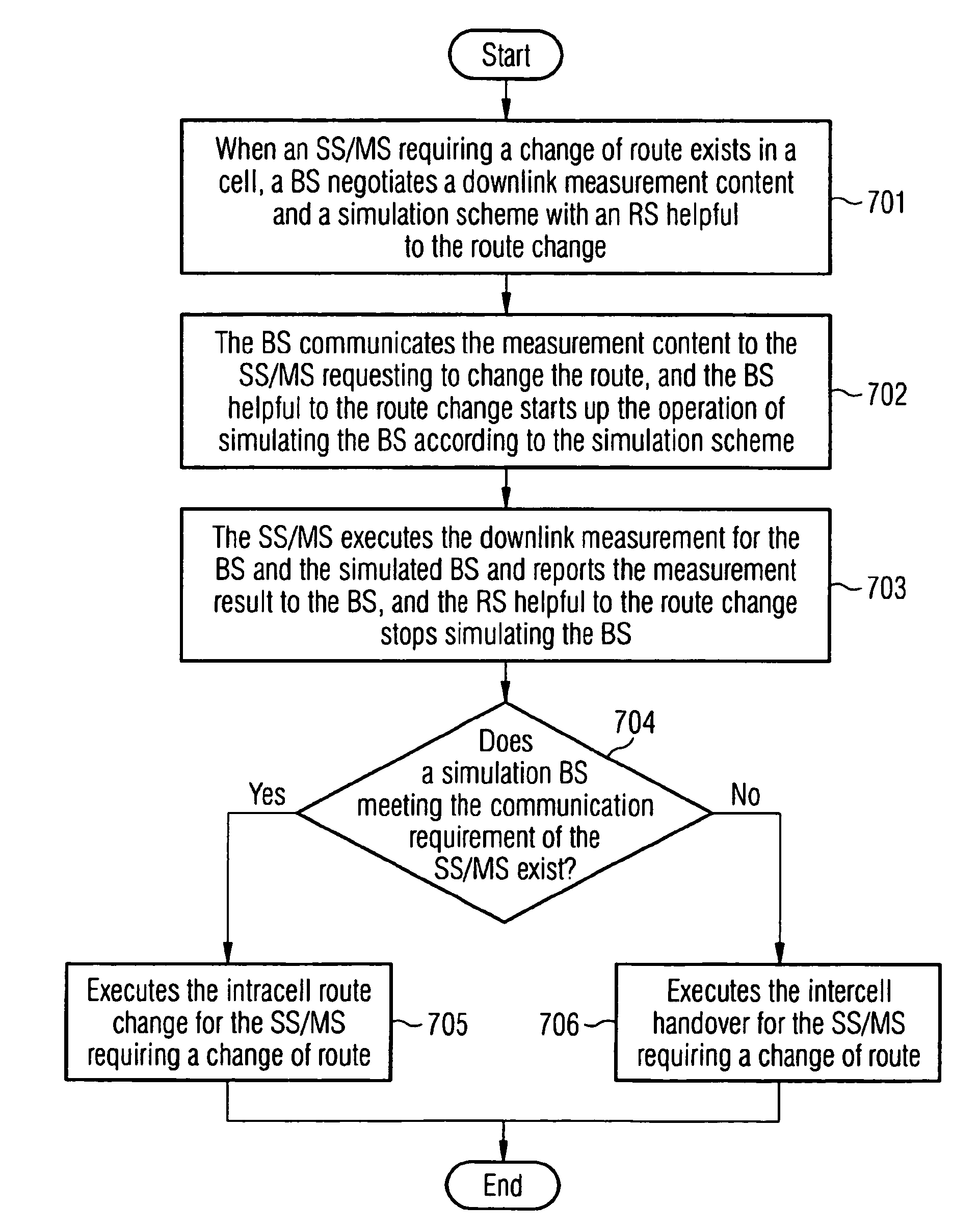
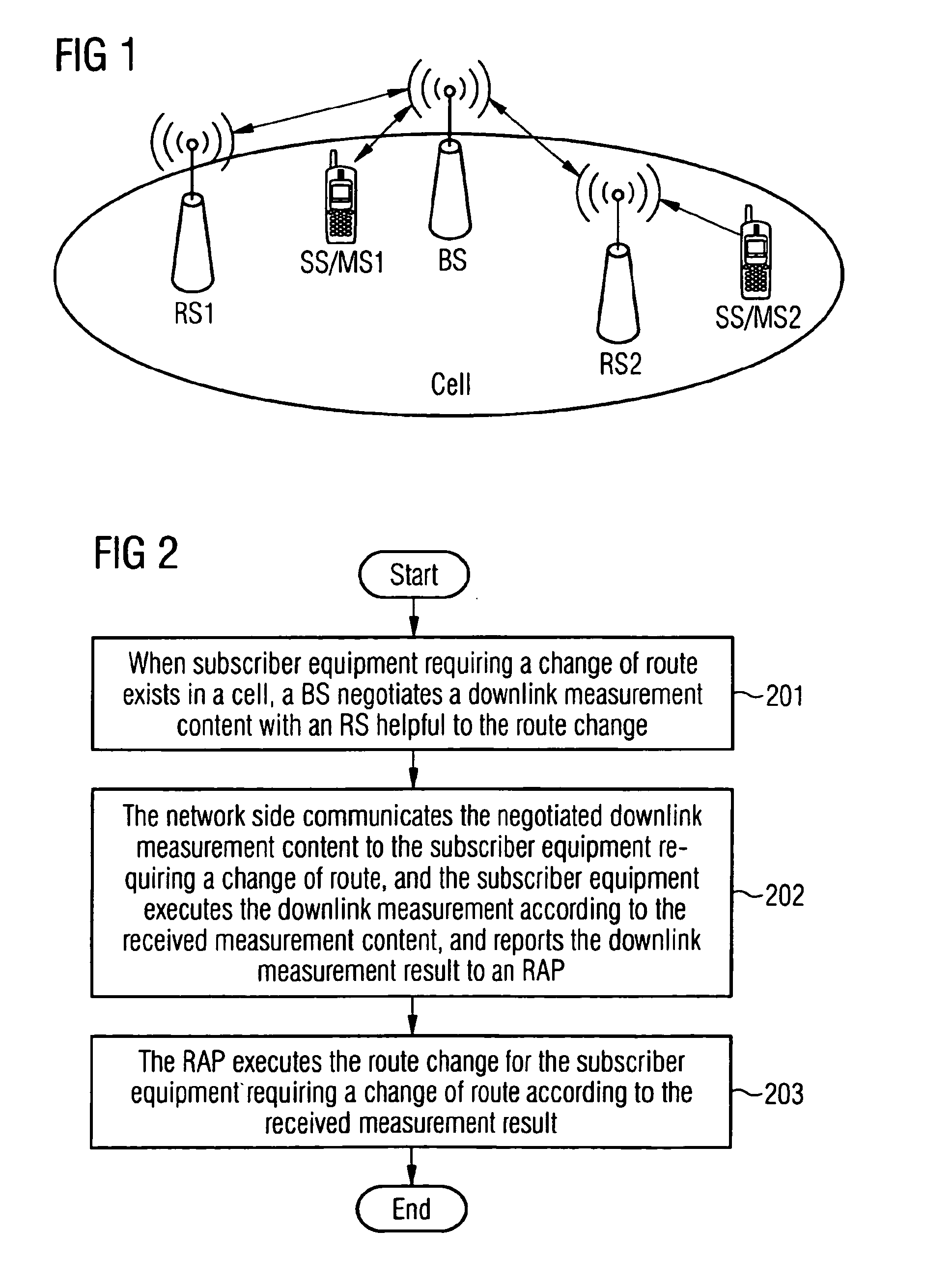
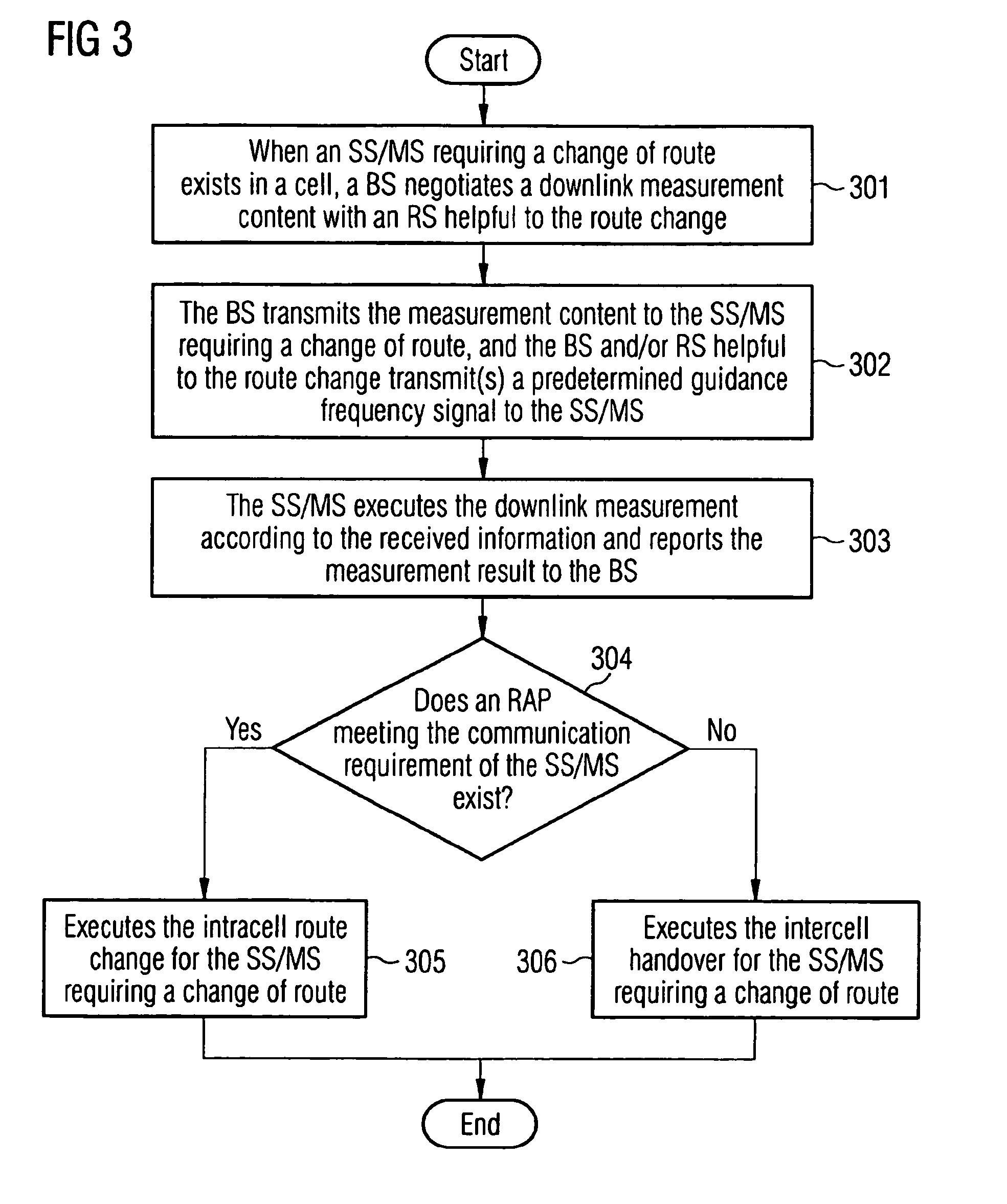
A method for changing a route in wireless communication involves: when there is subscriber equipment requesting a change of route in a cell, a base station negotiates downlink measurement contents with a relay station facilitating the route change in the cell; a network side informs the subscriber equipment requesting a change of route of the negotiated downlink measurement contents, and the subscriber equipment executes a downlink measurement according to the received measurement contents and reports the downlink measurement results to a radio access point; and the radio access point executes the route change for said subscriber equipment according to the received measurement results. The method can effectively improve the accuracy of the route change and alleviate the delay due to the route change.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Handover Optimisation in a Wlan Radio Access Network
ActiveUS20080192696A1Improve switching characteristicsMinimize data lossRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesAccess networkRadio access network
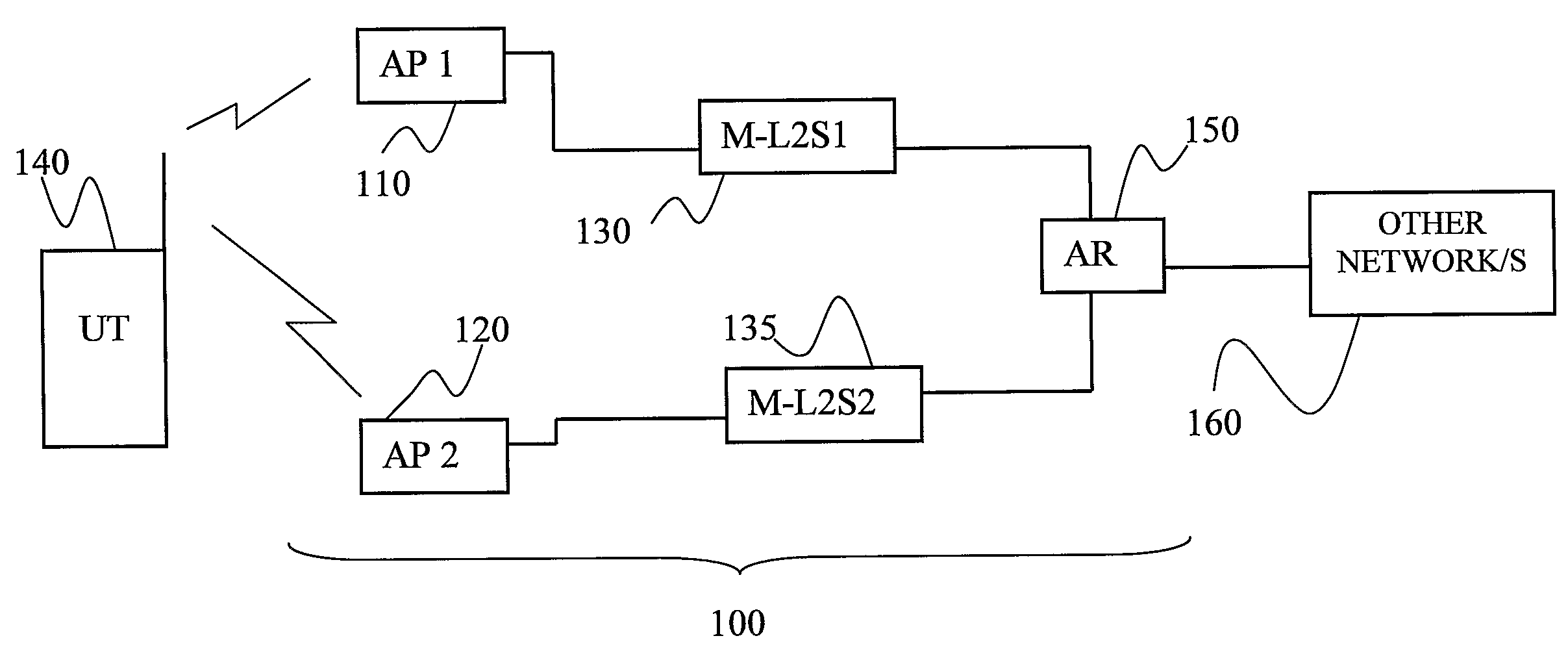
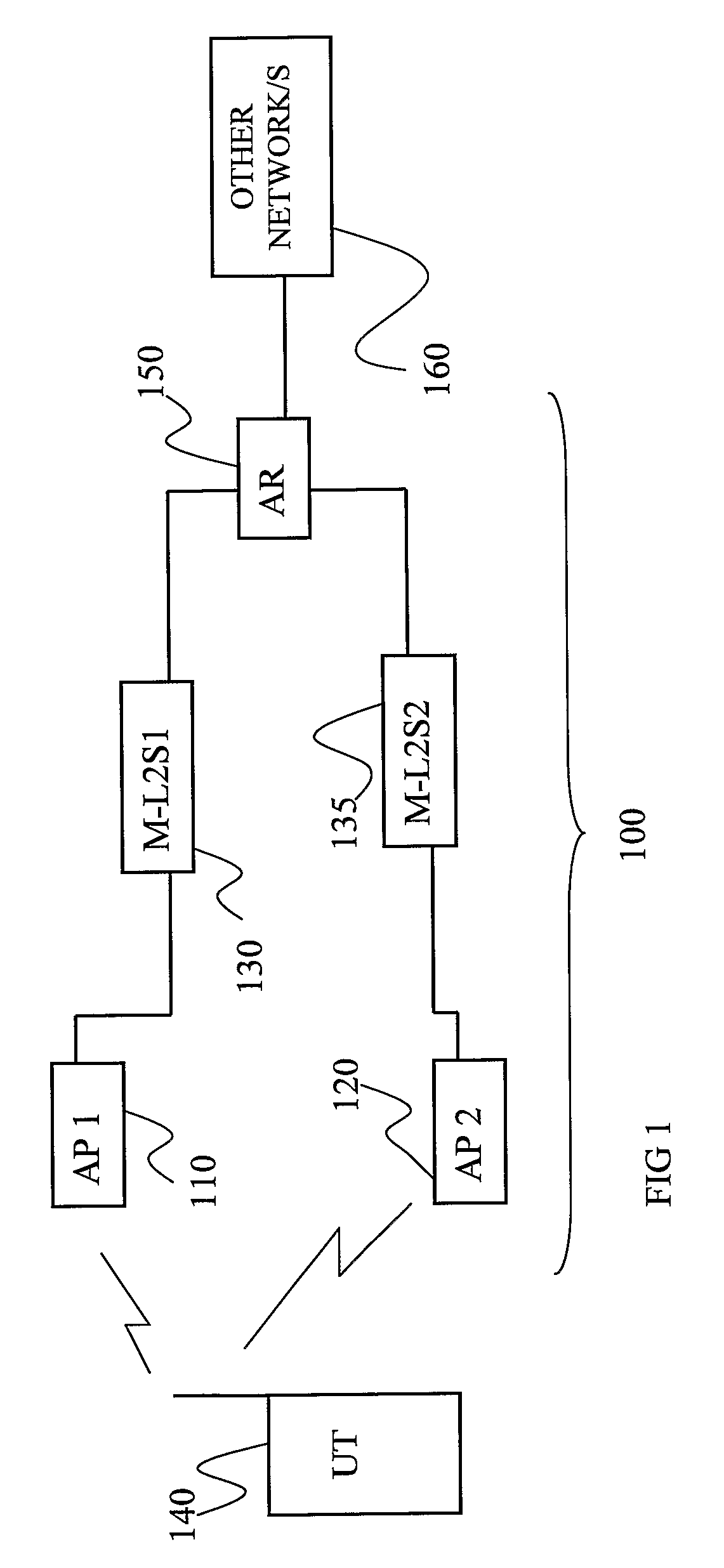
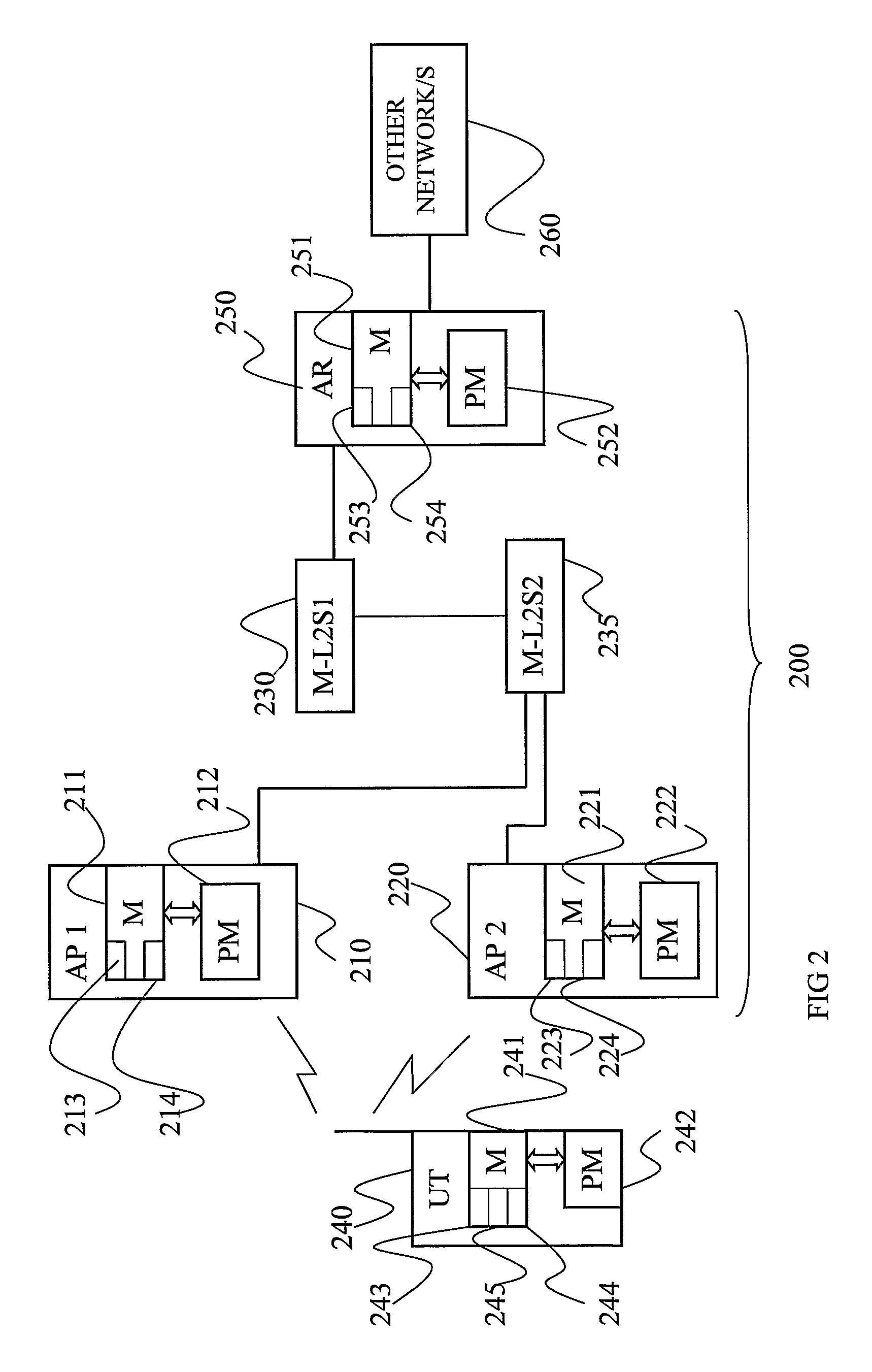
The invention provides a method for assisting handover of a communication session associated with a UT from a first radio access point, AP1, to a second radio access point, AP2, in a radio access network, said method to be carried out by said AP1 and comprising the steps of:—receiving a handover intention notify message comprising a session identifier identifying said session and indicating that said UT intends to perform a session handover,—assigning said session a buffer memory space in a memory of said AP1,—buffering downlink data packets addressed to said UT in said buffer memory as a response on receiving said handover intention notify message. The invention further provides a UT, an AP1, AP2, an AR, and software program / s co-operating and / or realizing the method according to the invention. The invention provides a smoother handover.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
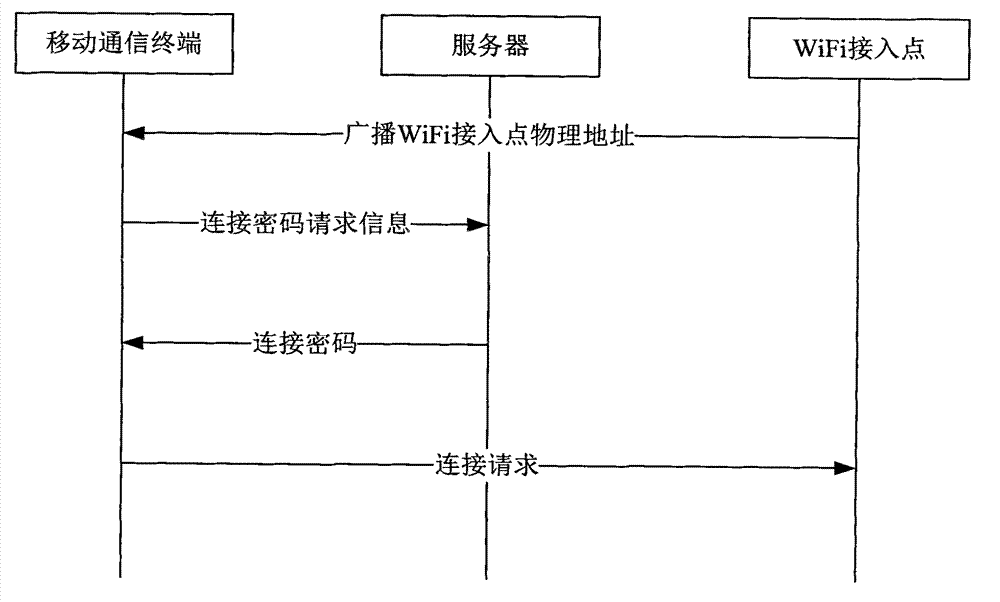
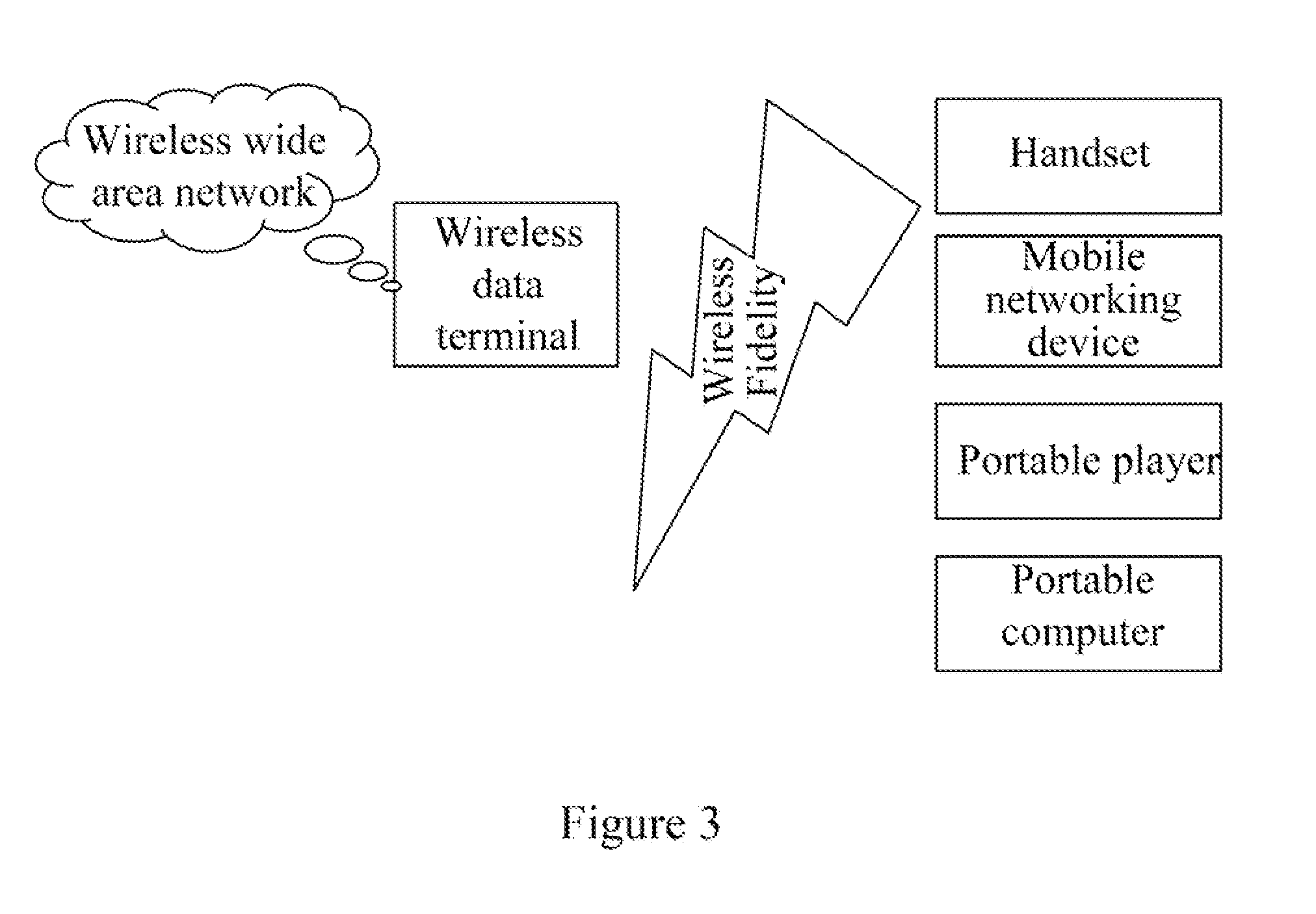
Method and system for automatically connecting to WiFi (wireless fidelity) access points and mobile communication terminal
InactiveCN103298072AEasy to useRealize automatic acquisitionAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesRadio access pointComputer terminal
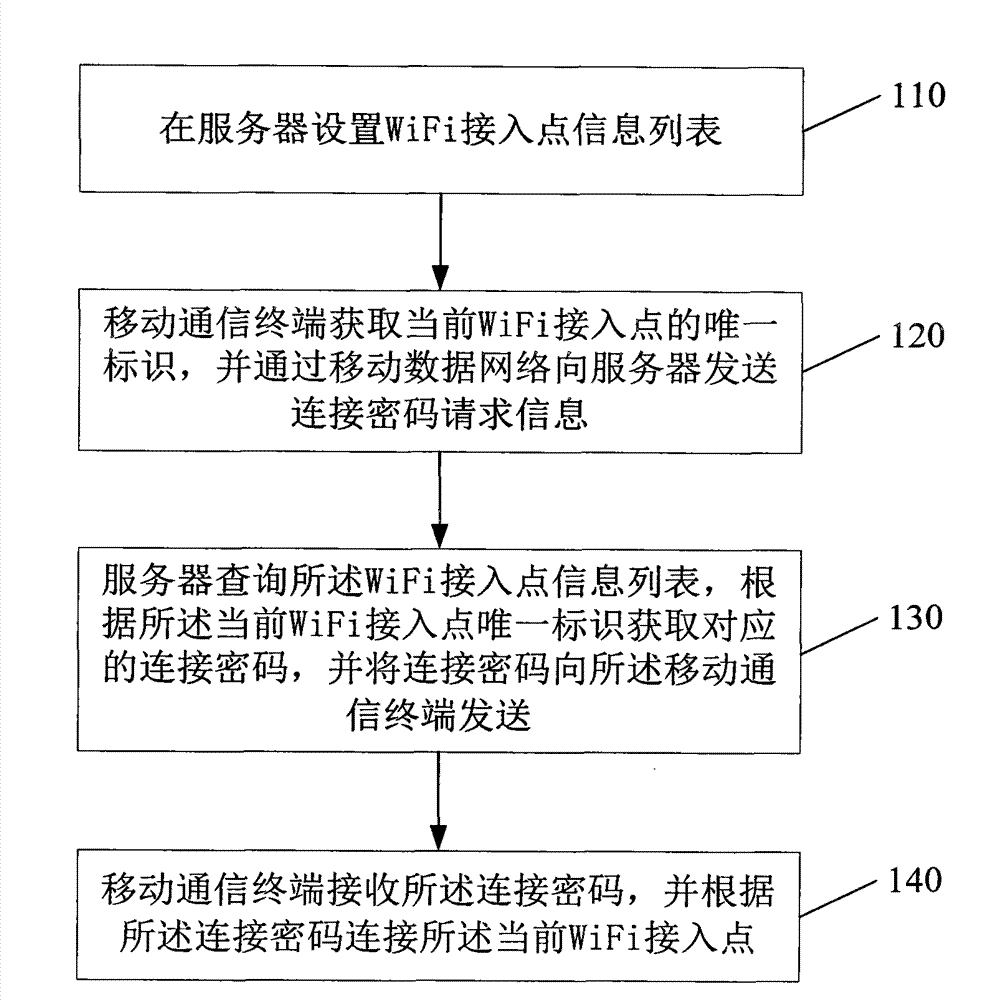
The invention discloses a method and a system for automatically connecting to WiFi (wireless fidelity) access points and a mobile communication terminal. The method includes setting a WiFi access point information list on a server, acquiring unique identification of the current WiFi access point by the mobile communication terminal, sending an access code request message to the server through a mobile data network, querying the WiFi access point information list through the server, acquiring the corresponding access code according to the unique identification of the current WiFi access point, and sending the access code to the mobile communication terminal, and finally receiving the access code by the mobile communication terminal and connecting to the current WiFi access point according to the access code. The WiFi access point information list is used for saving unique identifications and corresponding access codes of the WiFi access points; the access code request message includes the unique identification of the current WiFi access point.
Owner:张洁昕
Enterprise wireless local area network switching system
InactiveUS20080228942A1Overcomes drawbackSolve the quick installationError preventionTransmission systemsWireless mesh networkData stream
A process of controlling a flow of data in a wireless network providing wireless access to the wireless network by wireless devices is disclosed. Data is received from a wireless device by a network device, through one access point of a plurality of access points in communication with the network device, indicating a client identifier for the wireless device. The client identifier is forwarded to an authentication server and the network device mediated authentication of the wireless device with the authentication server. Thereafter, data packets received from portions of the wireless network and from the plurality of access points are evaluated and the received data packets are passed to portions of the wireless network and to the plurality of access points, based on the evaluation of the received data packets. In addition, the network device periodically polls for a status of the wireless device from the access point.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
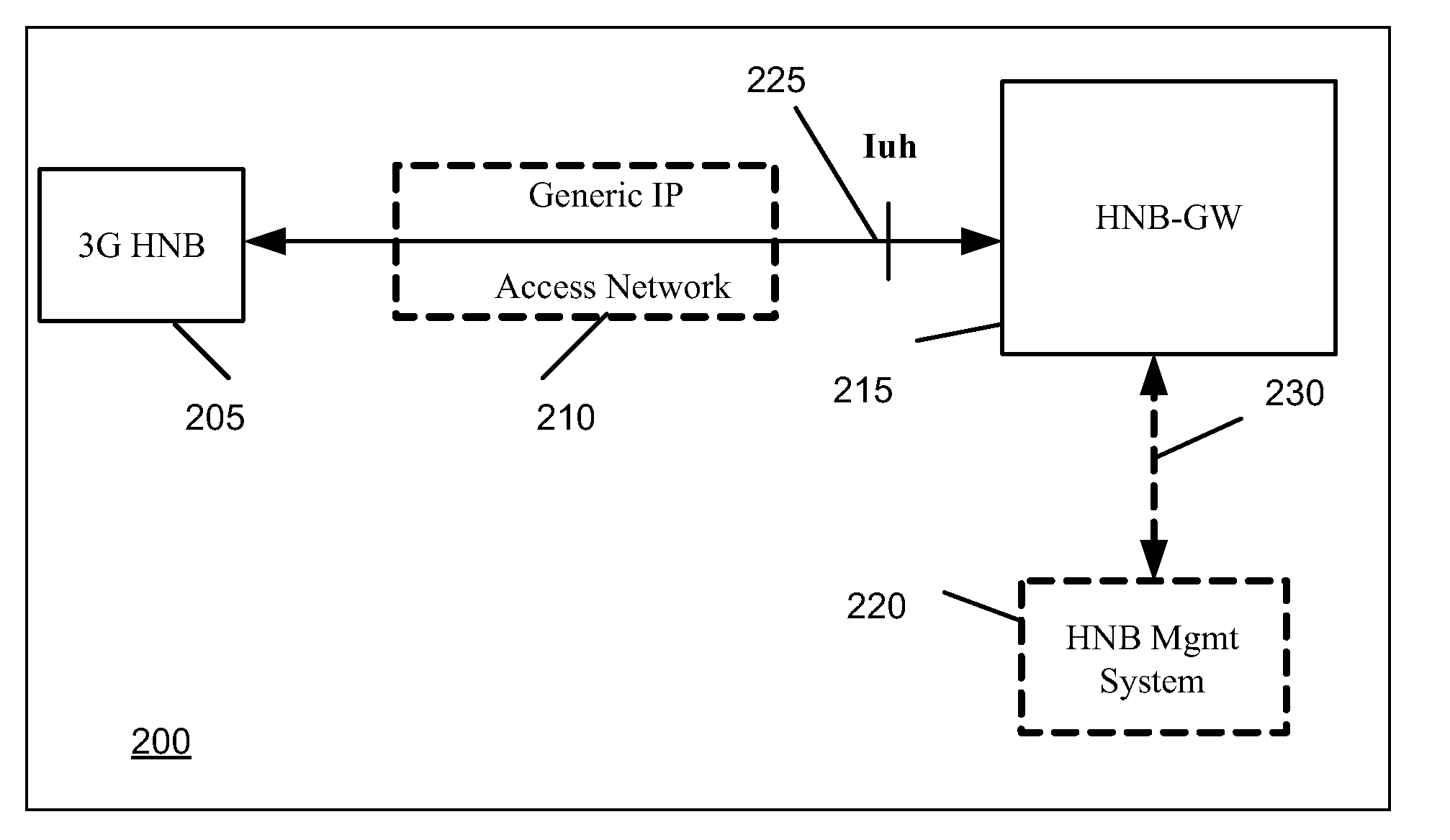
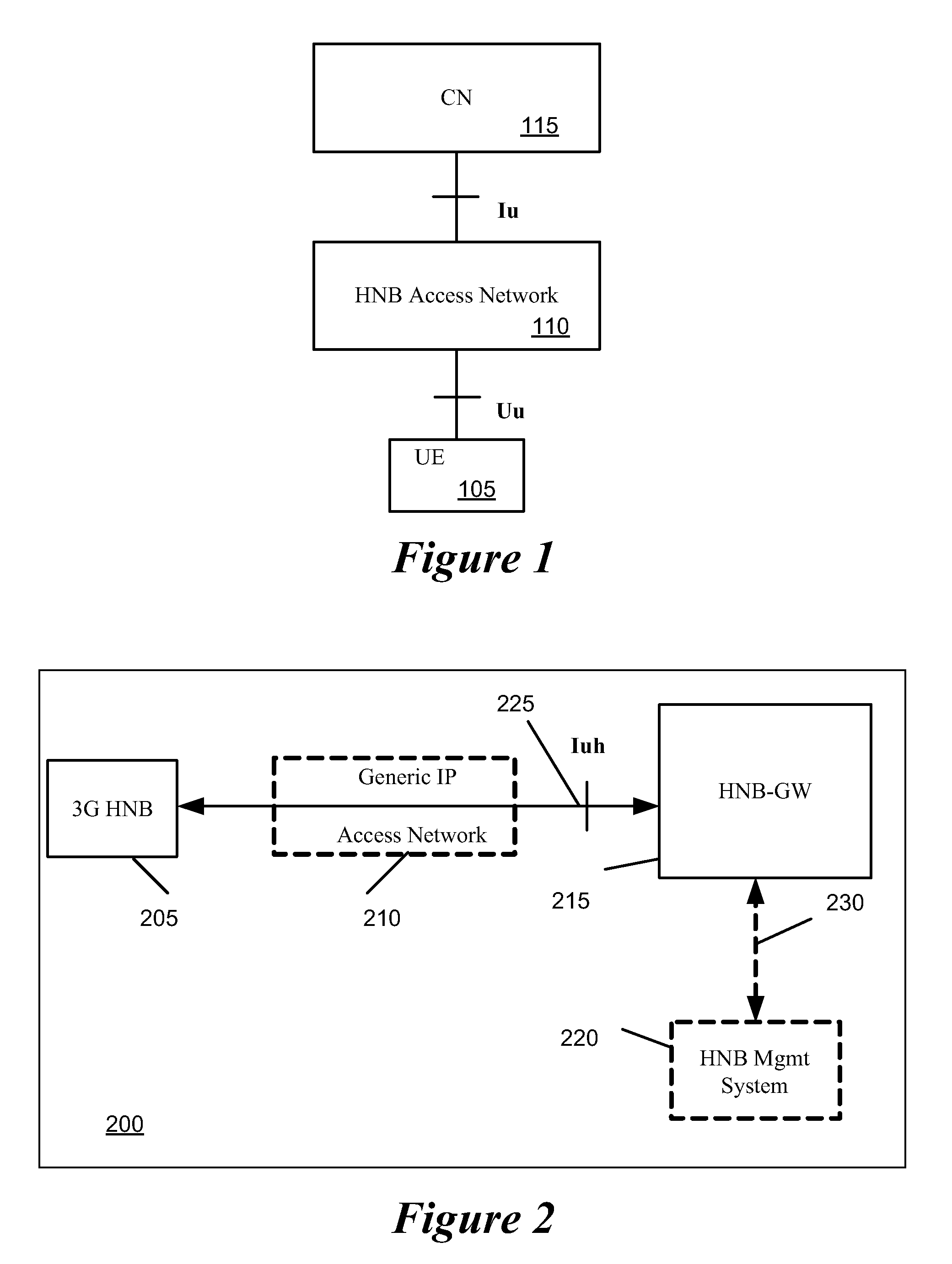
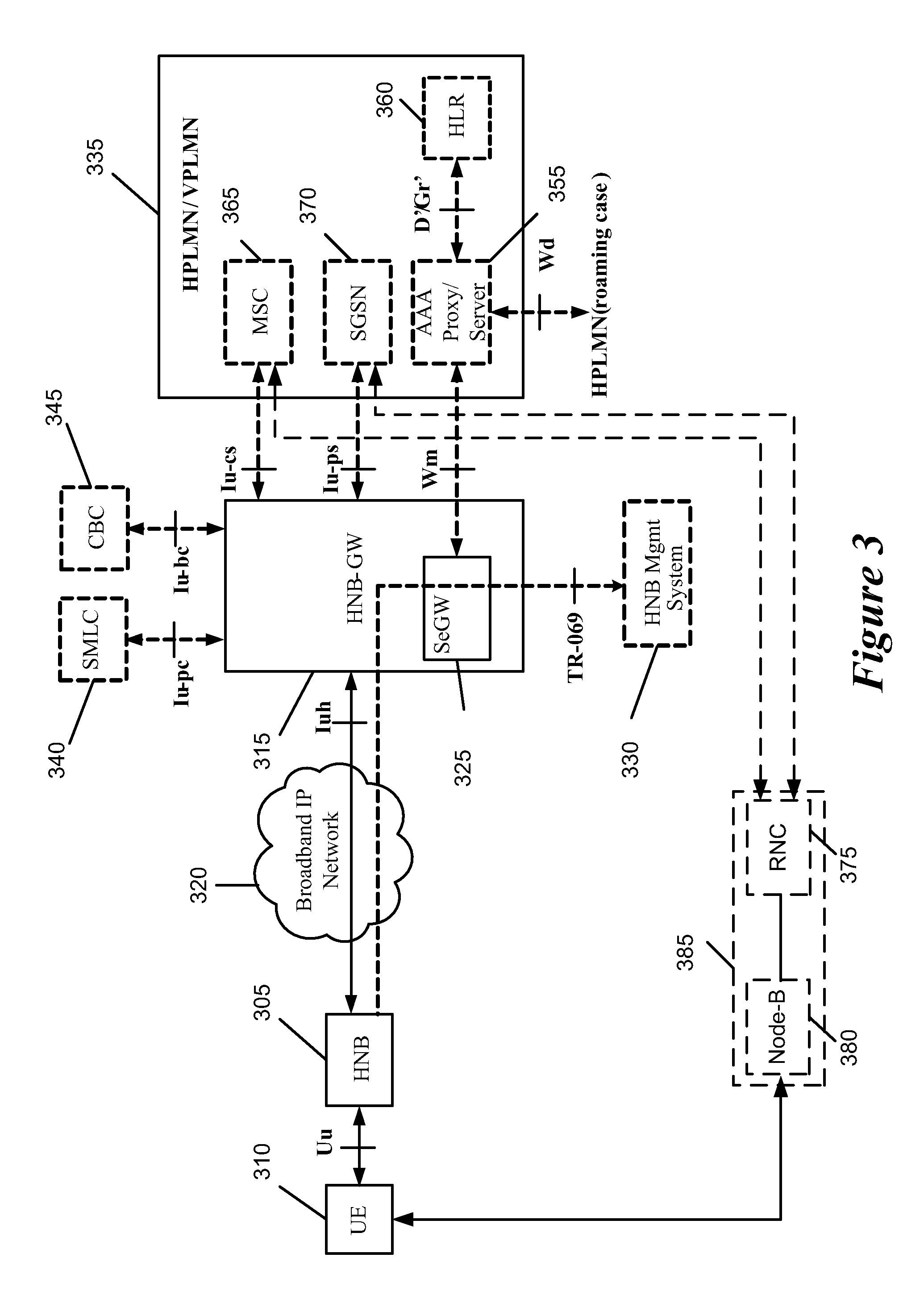
Home Node B System Architecture
InactiveUS20090265542A1Lower deployment costsSpeed andAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesGPRS core networkHome Node B
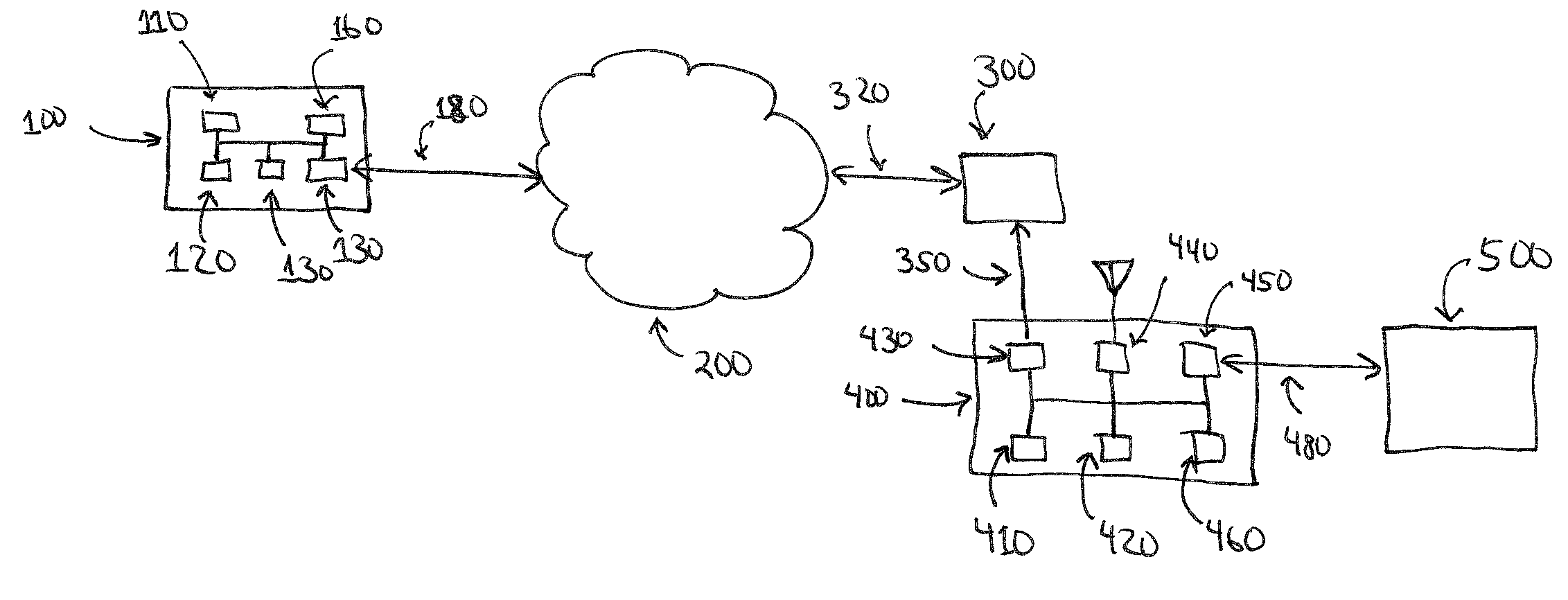
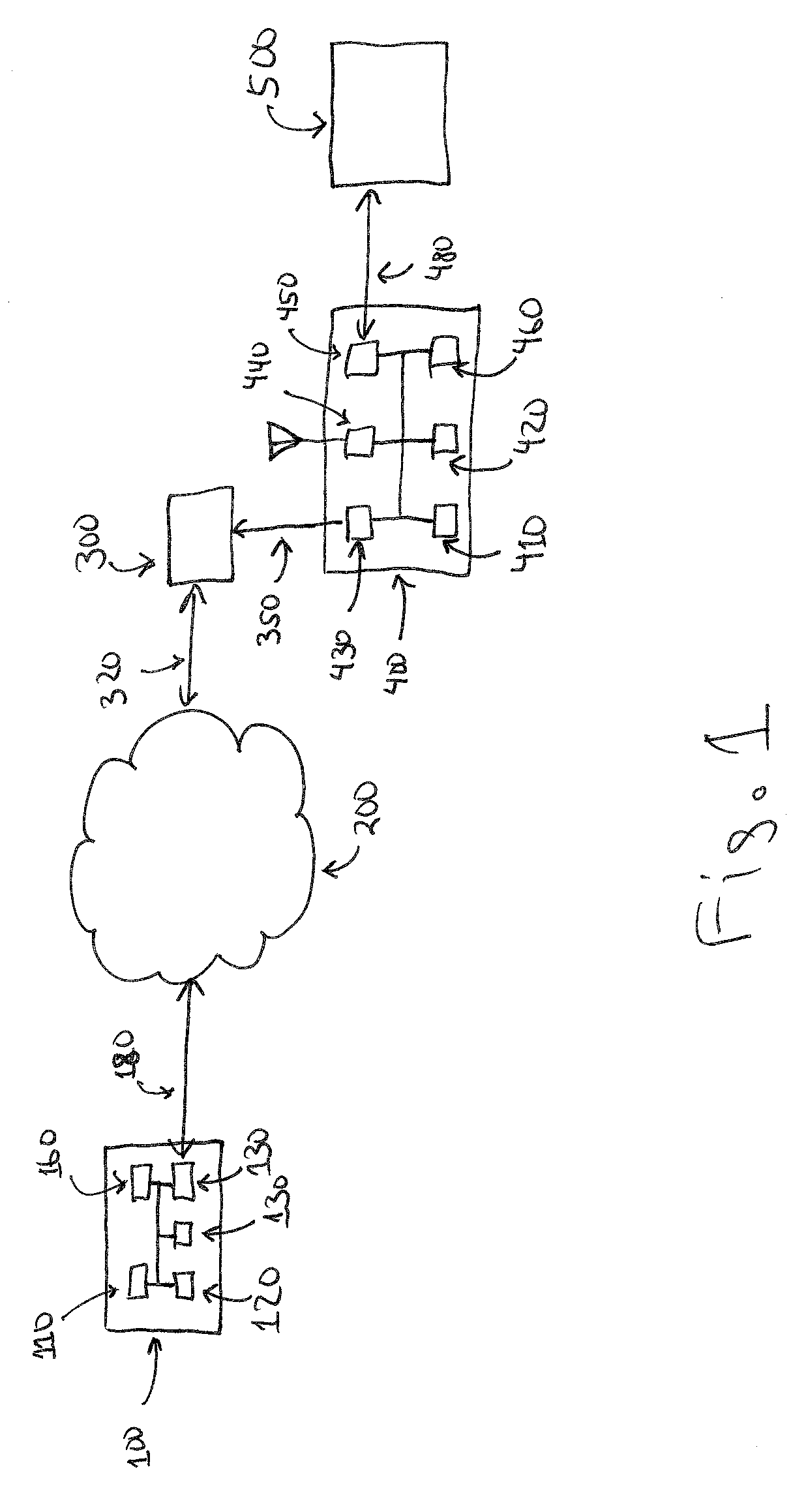
Some embodiments provide methods and systems for integrating a first communication system with a core network of a second communication system that has a licensed wireless radio access network. The first communication system includes one or more user hosted access points that operate using short range licensed wireless frequencies in order to establish service regions of the first communication system and a network controller for communicatively coupling the service regions to the core network. The first communication system includes a Home Node-B (HNB) system where the access points are Home Node-Bs and the network controller is a HNB Gateway (HNB-GW). Some embodiments define multi-layered protocol stacks for implementing management functionality and control plane functionality for the access points and the network controller. The HNB is connected to the HNB-GW via the Iuh interface. The Iuh management functionality is provided via a HNBAP protocol layer and control plane functionality, such as relay of RANAP, is provided via a RUA protocol layer.
Owner:KINETO WIRELESS
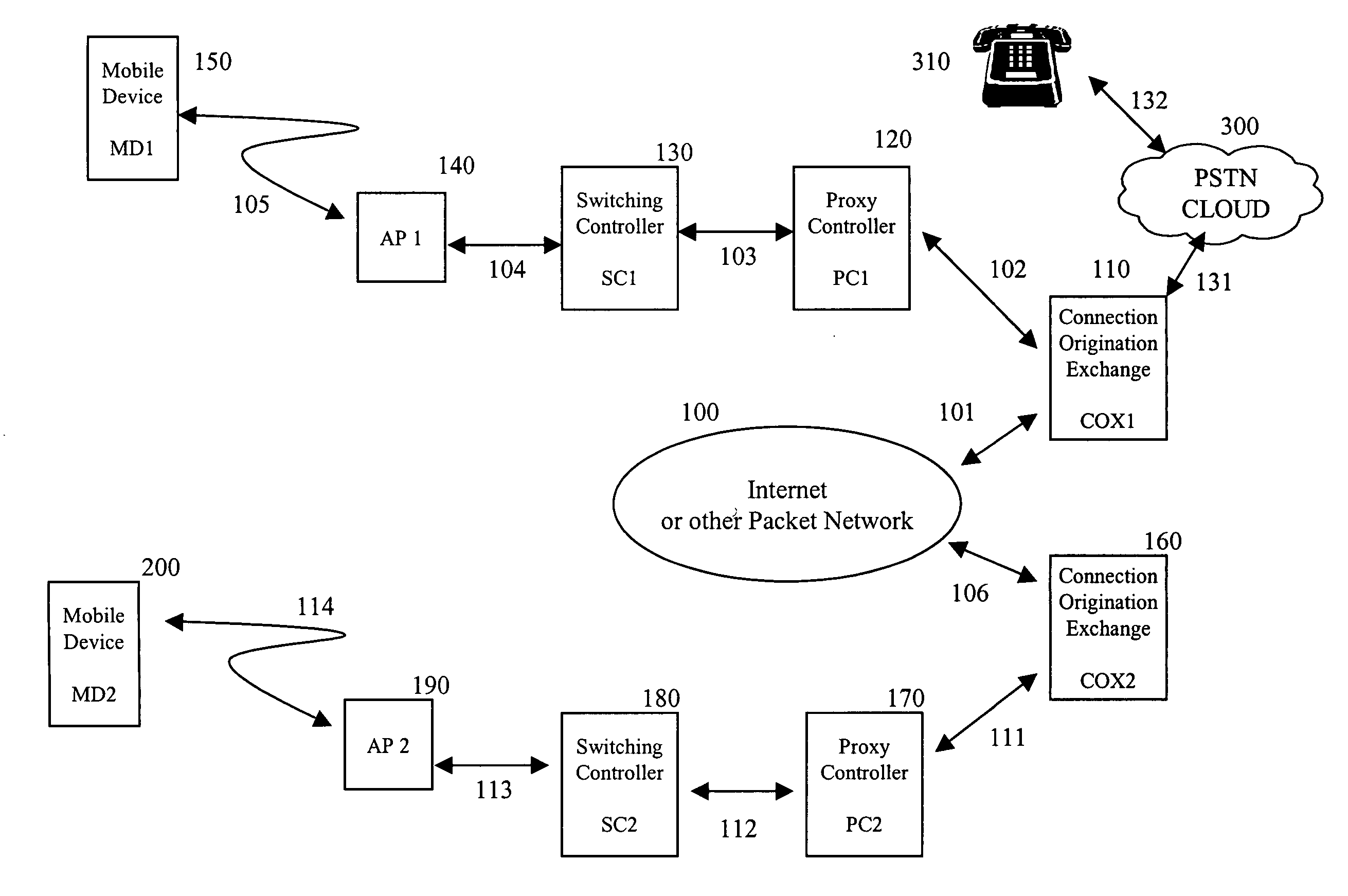
Distributed disparate wireless switching network
ActiveUS20060168111A1Special service for subscribersConnection managementExchange networkNetwork architecture
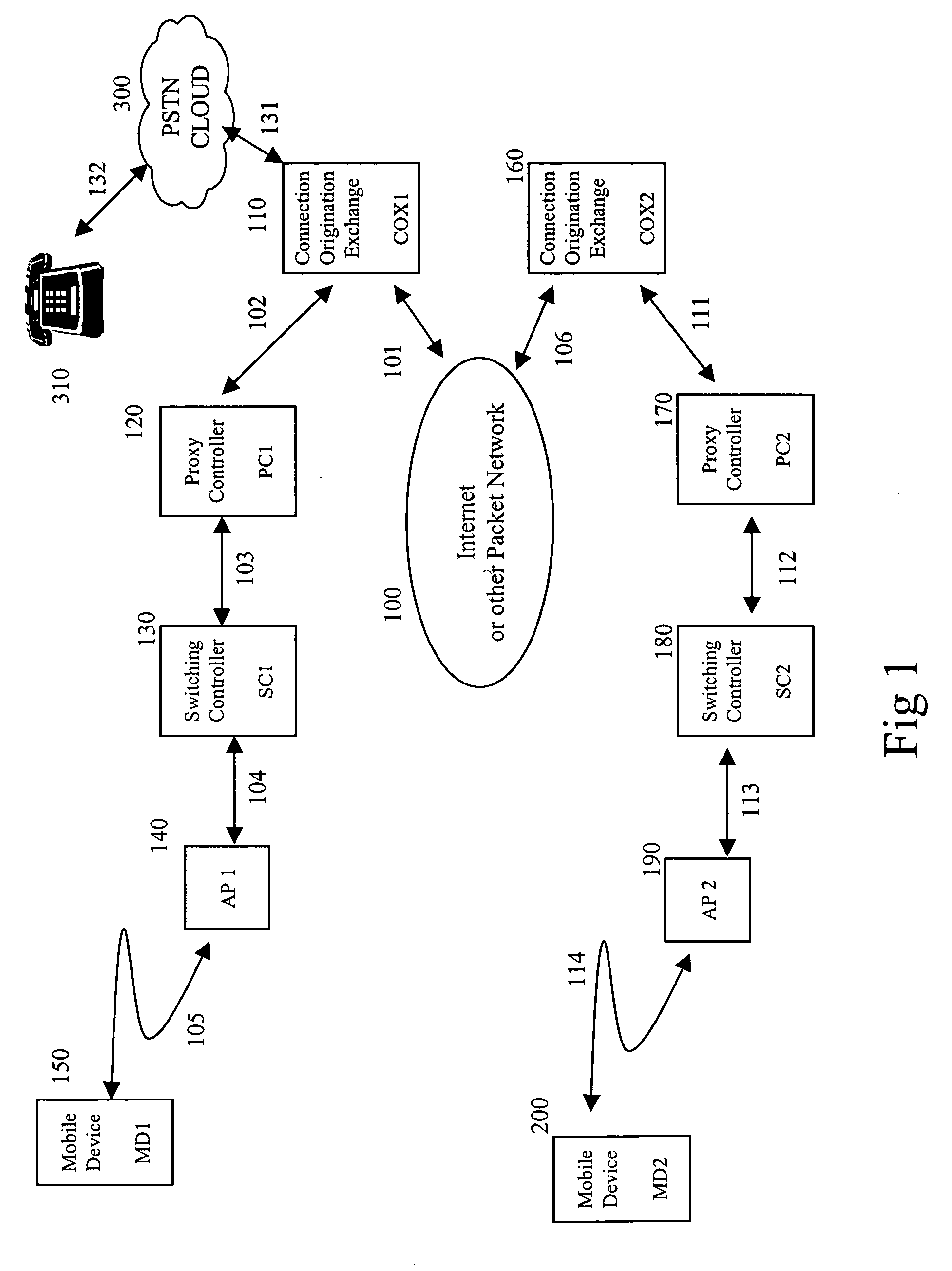
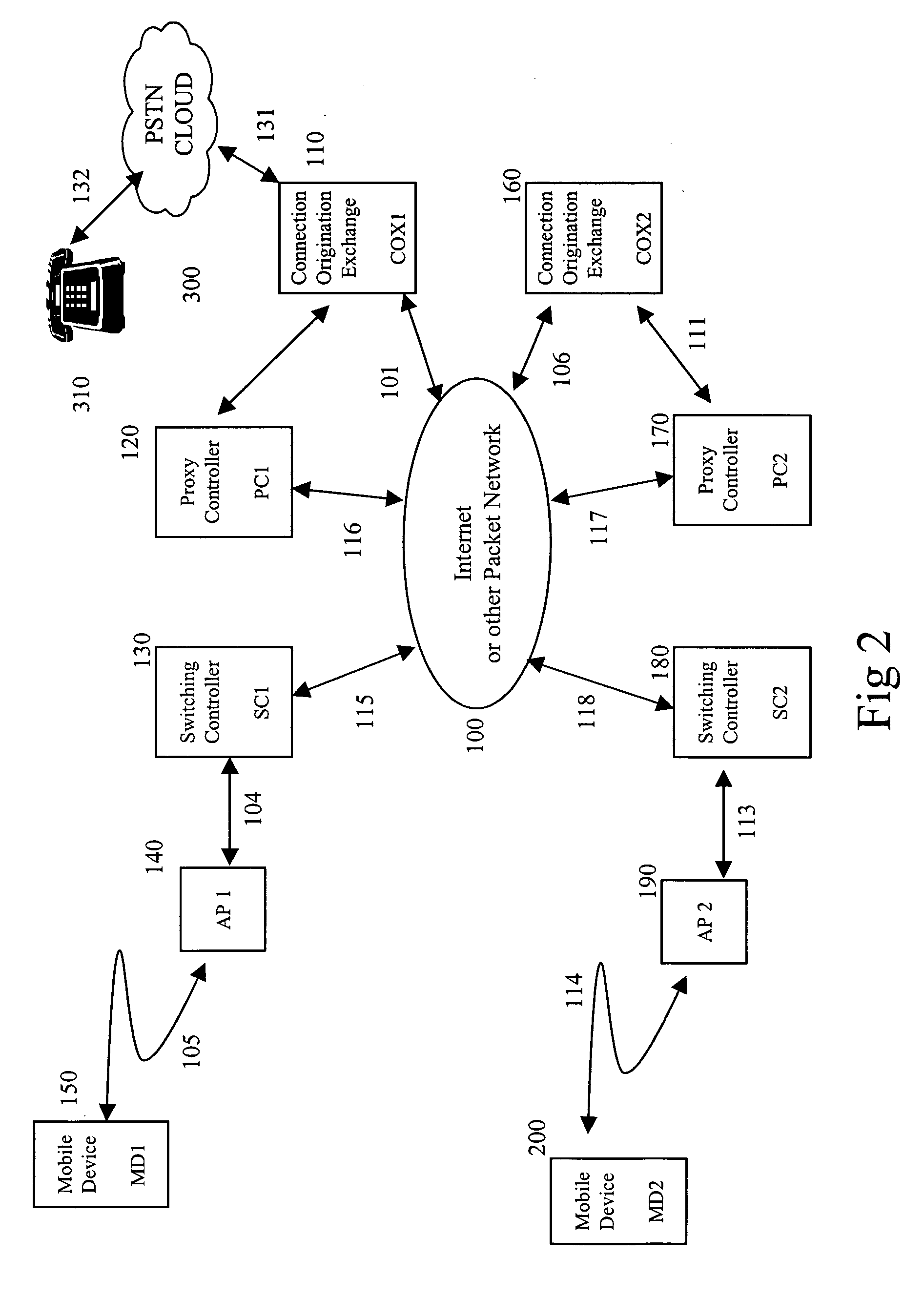
A distributed disparate wireless switching network is described herein. In one embodiment, an exemplary network architecture includes, but is not limited to, a connection origination exchange (COX), a proxy controller coupled to the COX, an access point coupled to the proxy controller, and a mobile node wirelessly coupled to the access point. The mobile node communicates with a terminating node of a network through the access point and the proxy controller using an identification maintained by the proxy controller. The COX originates a connection with the terminating node on behalf of the mobile node using the identification provided by the proxy controller. Other methods and apparatuses are also described.
Owner:GIDWANI SANJAY M
Method and apparatus for determining locations of access points
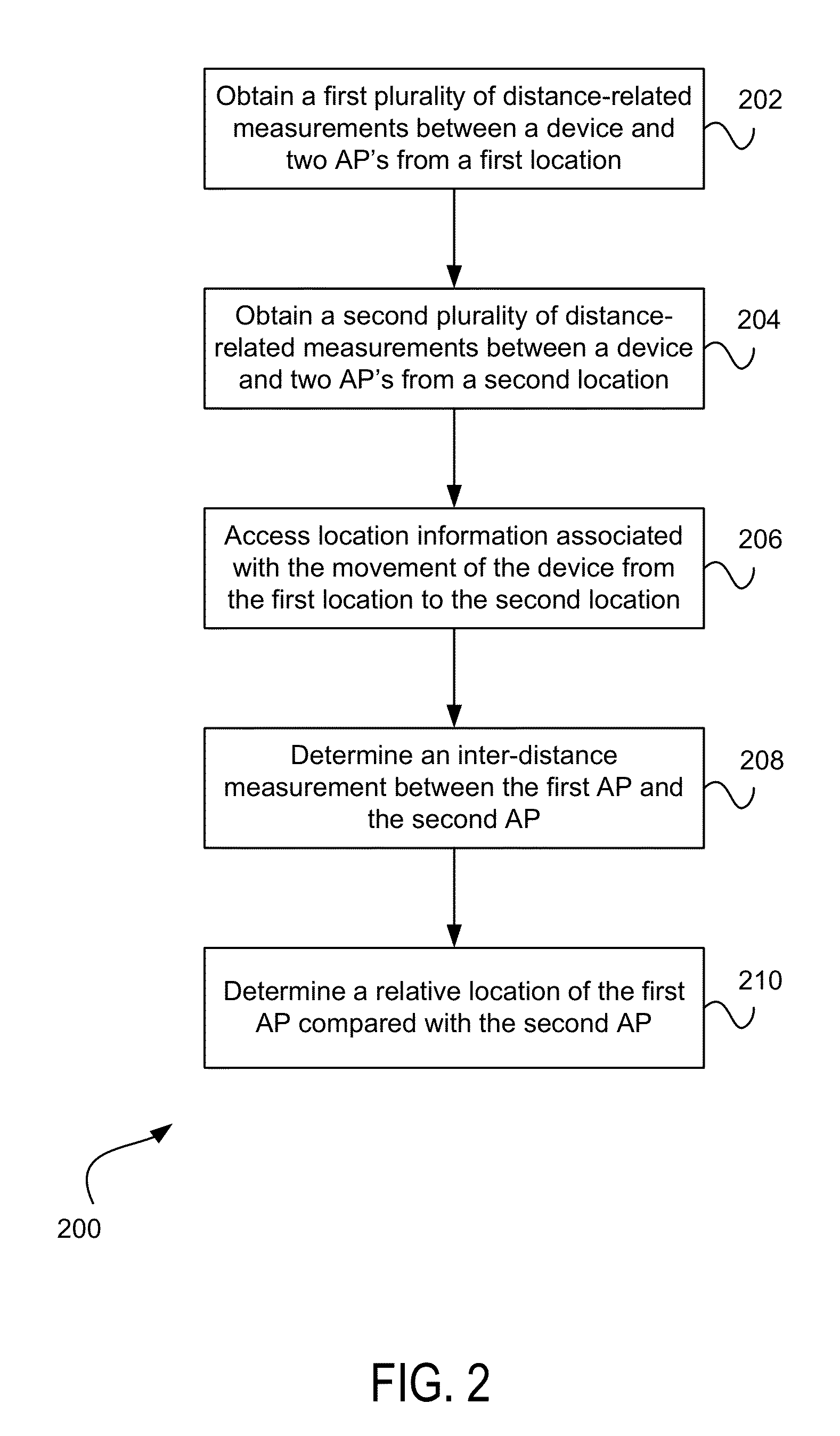
InactiveUS20130307723A1Improve accuracyDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationRadio access pointLocation determination
Methods, systems, computer-readable media, and apparatuses for determining locations of access points (AP) are presented. Techniques are described for determining relative and absolute locations of APs. In one embodiment, a device may send and receive messages to one or more APs for from various locations for determining the distance between the device and the AP. The device may additionally keep track of its own displacement for the purposes of determining the location of the one or more APs. In one embodiment, the device also determines the turnaround calibration factor (TCF) for the AP that compensates for the processing time at the AP may also be used for increasing the accuracy of the determination of the location of the AP.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Measuring communicating and using interference information
Apparatus and methods of performing interference mitigation in a communication network. The interference mitigation can include a controller sending a message to a first access point instructing the first access point to measure at least one signal transmitted by a first wireless terminal communicating a signal having known characteristics; the controller receiving from the first access point signal measurement information; and the controller communicating at least some of the signal measurement information received from the first access point to a second access point.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
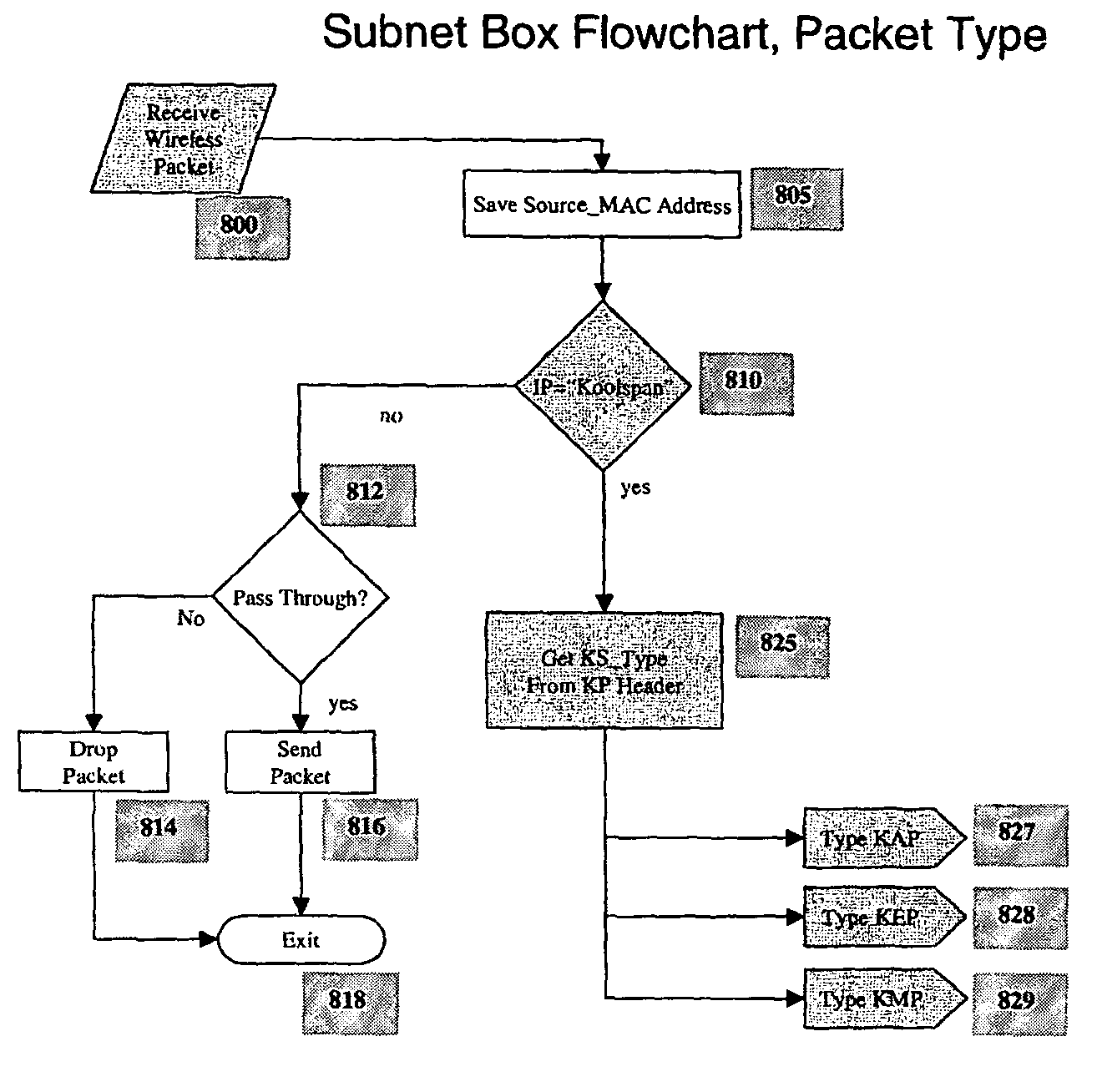
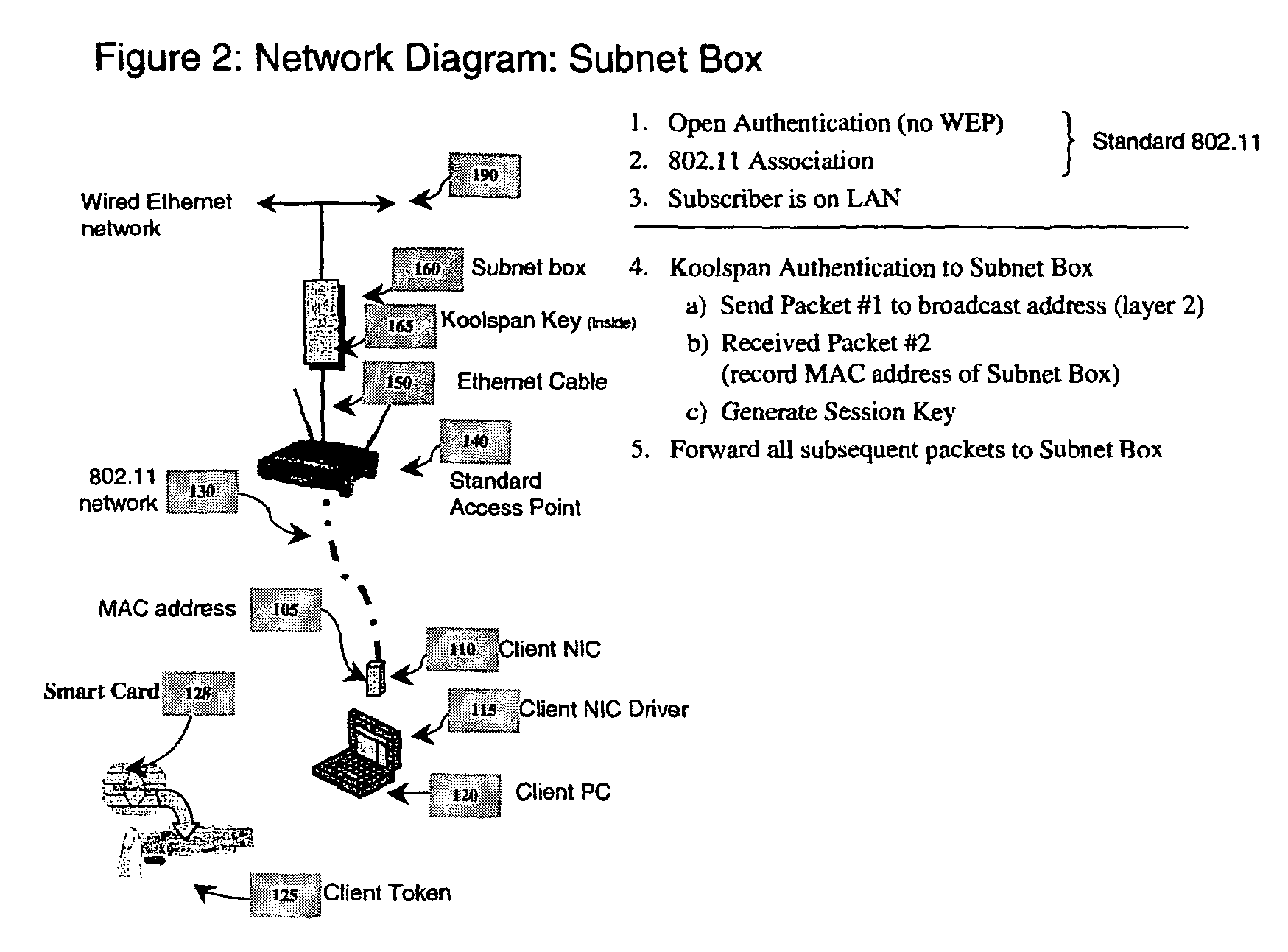
Subnet box
InactiveUS7934005B2Secure transmissionDigital data processing detailsNetwork topologiesWi-FiWired communication
The invention provides an external in-line device (“Subnet Box”) placed between a network and an access point to achieve secure Wi-Fi communications without needing to modify the access point. The Subnet Box comprises an embedded token and will authenticate users based on pre-stored access rights. In at least one embodiment of the invention, the Subnet Box comprises: a first communications port for intercepting data packets communicated to and from a wired communications network; a second communications port for intercepting data packets communicated to and from a wireless access point, wherein the wireless access point is an edge device of the wired communications network; a database comprising a number of serial numbers each associated with a client token and a secret cryptographic key; and a processor for determining whether a computing device having a client token can access the wired communications network via the wireless access point. The processor establishes a secure tunnel between the computing device and the first communications port.
Owner:KOOLSPAN
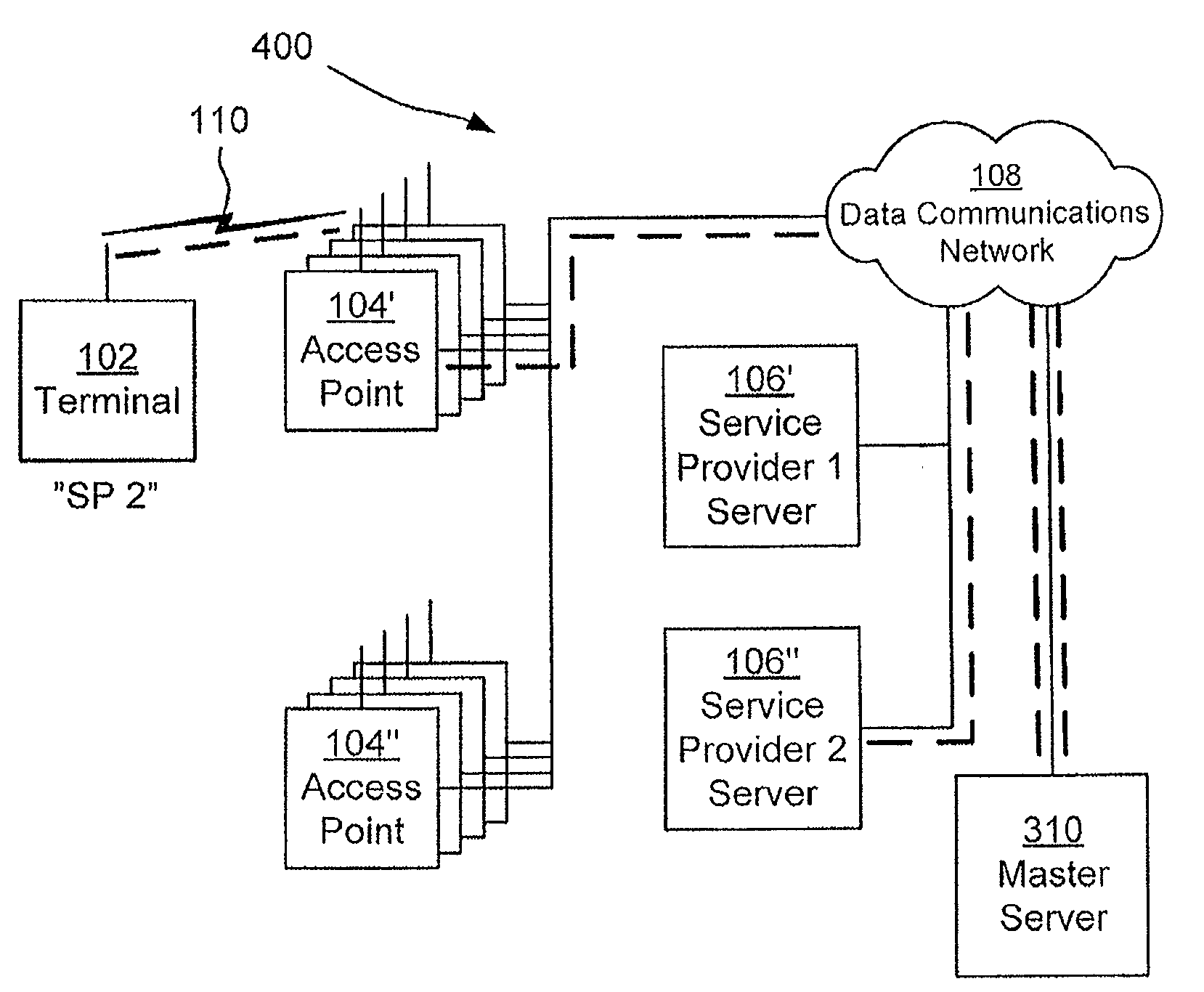
Access point, a server and a system for distributing an unlimited number of virtual IEEE 802.11 wireless networks through a heterogeneous infrastructure
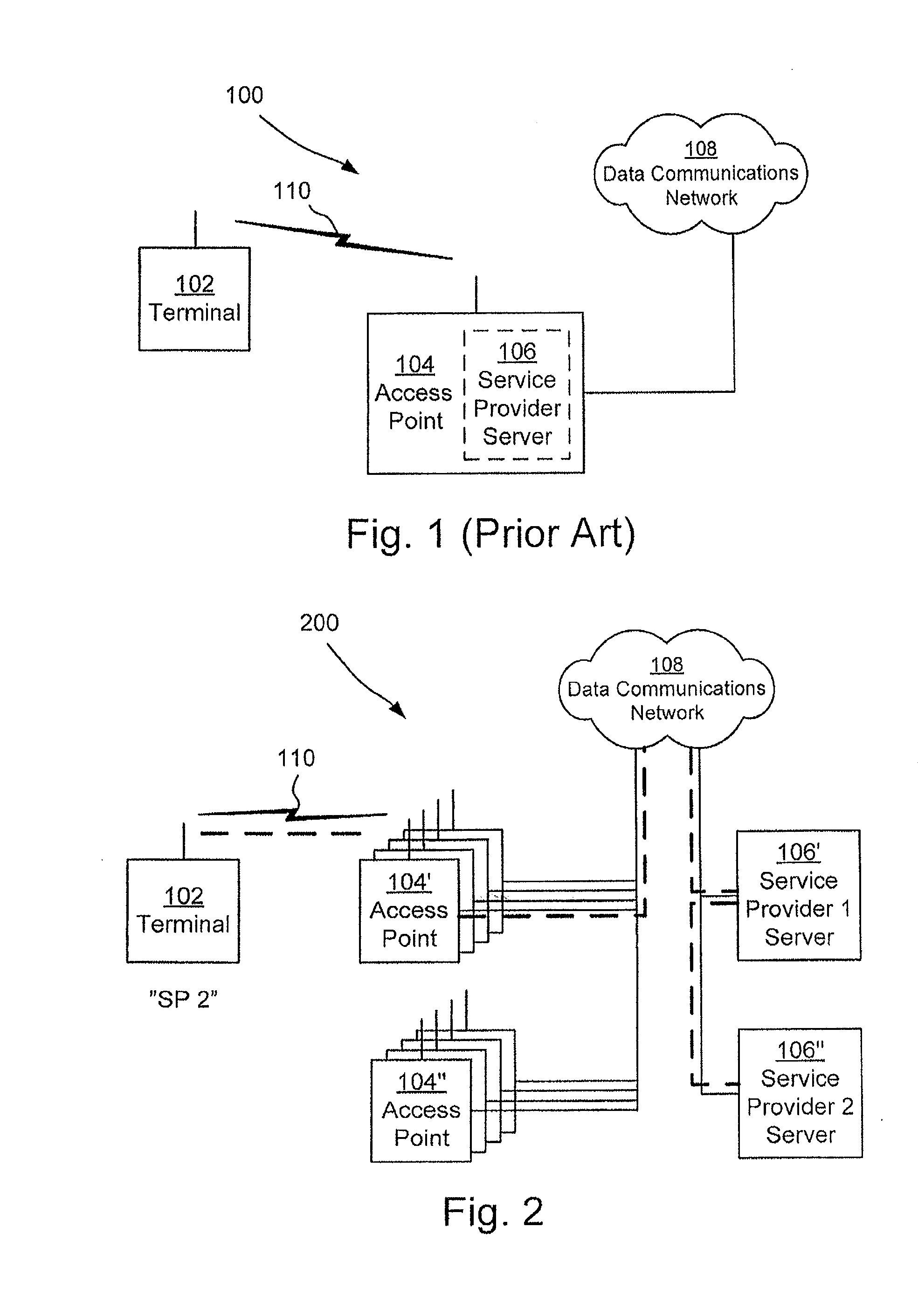
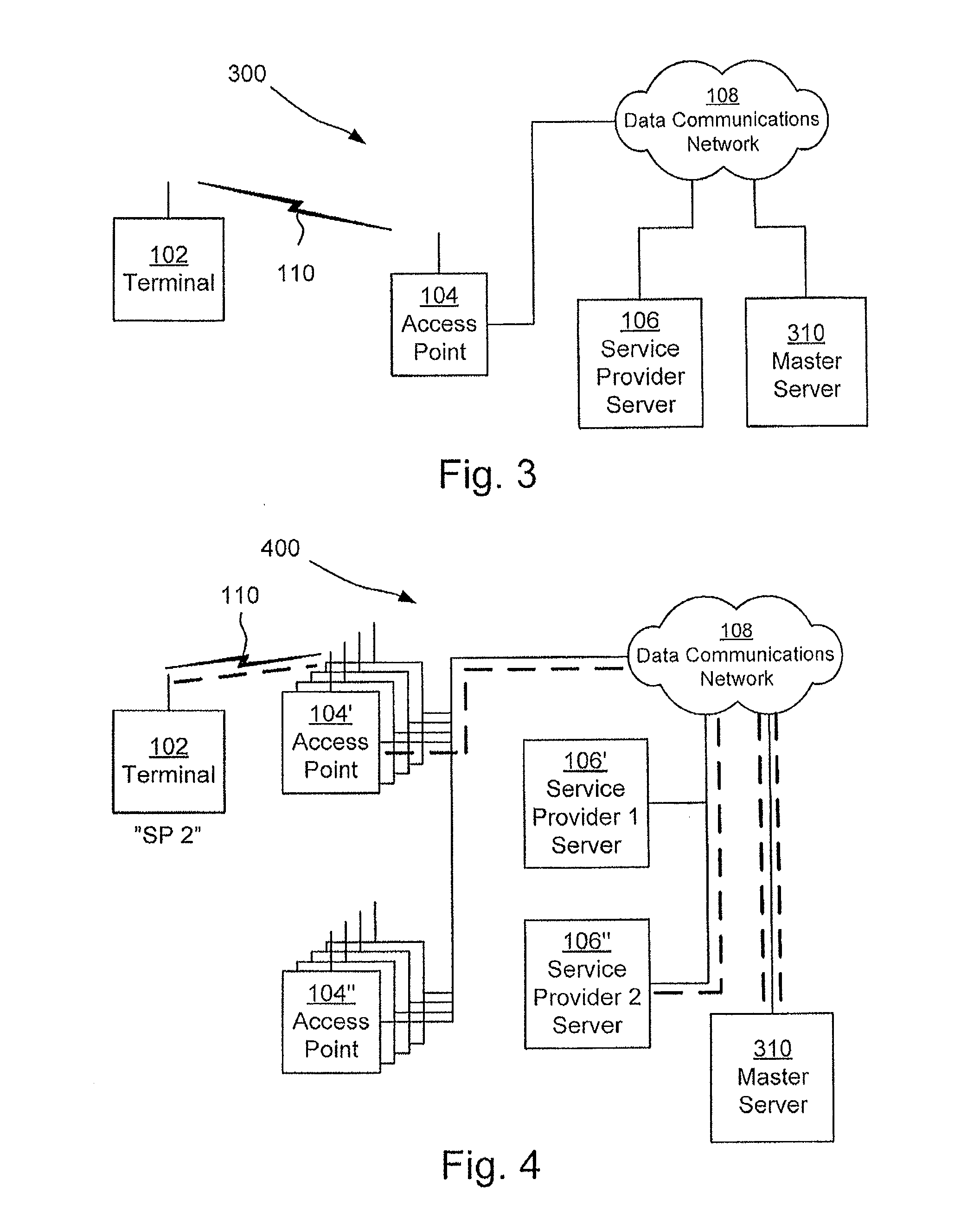
ActiveUS20120209934A1High cost per bitLow network capacityAssess restrictionMultiple digital computer combinationsData connectionWireless mesh network
There is provided methods, devices and computer program products for distributing a plurality of virtual IEEE 802.11 wireless networks through a heterogeneous infrastructure. A terminal sends a service provider request to an access point. The service provider request is forwarded to a master server which searches for available service providers. Acknowledgement information relating to available service providers capable of operatively connecting the terminal to the data communications network via the access point is sent by the master server to the access point. The access point forwards this information to the terminal. The access point may thus distribute a plurality of virtual IEEE 802.11 wireless networks, their number only constrained by the number of distinct identifiable service providers and the memory of the master server. A data connection may be established in the absence of a direct service agreement between the service provider of the terminal and the operator of the access point.
Owner:ANYFI NETWORKS
Wi-fi access method, access point and wi-fi access system
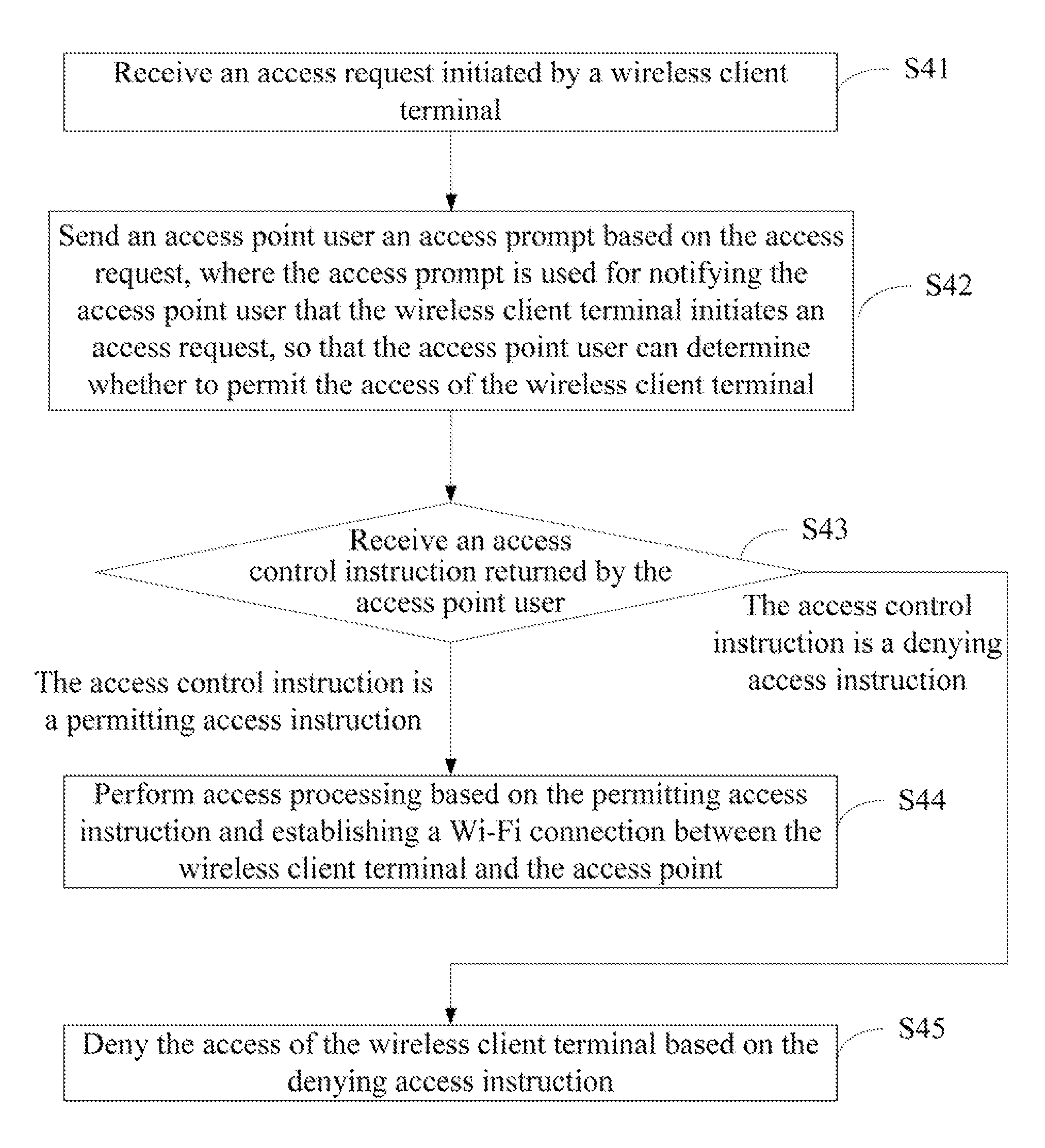
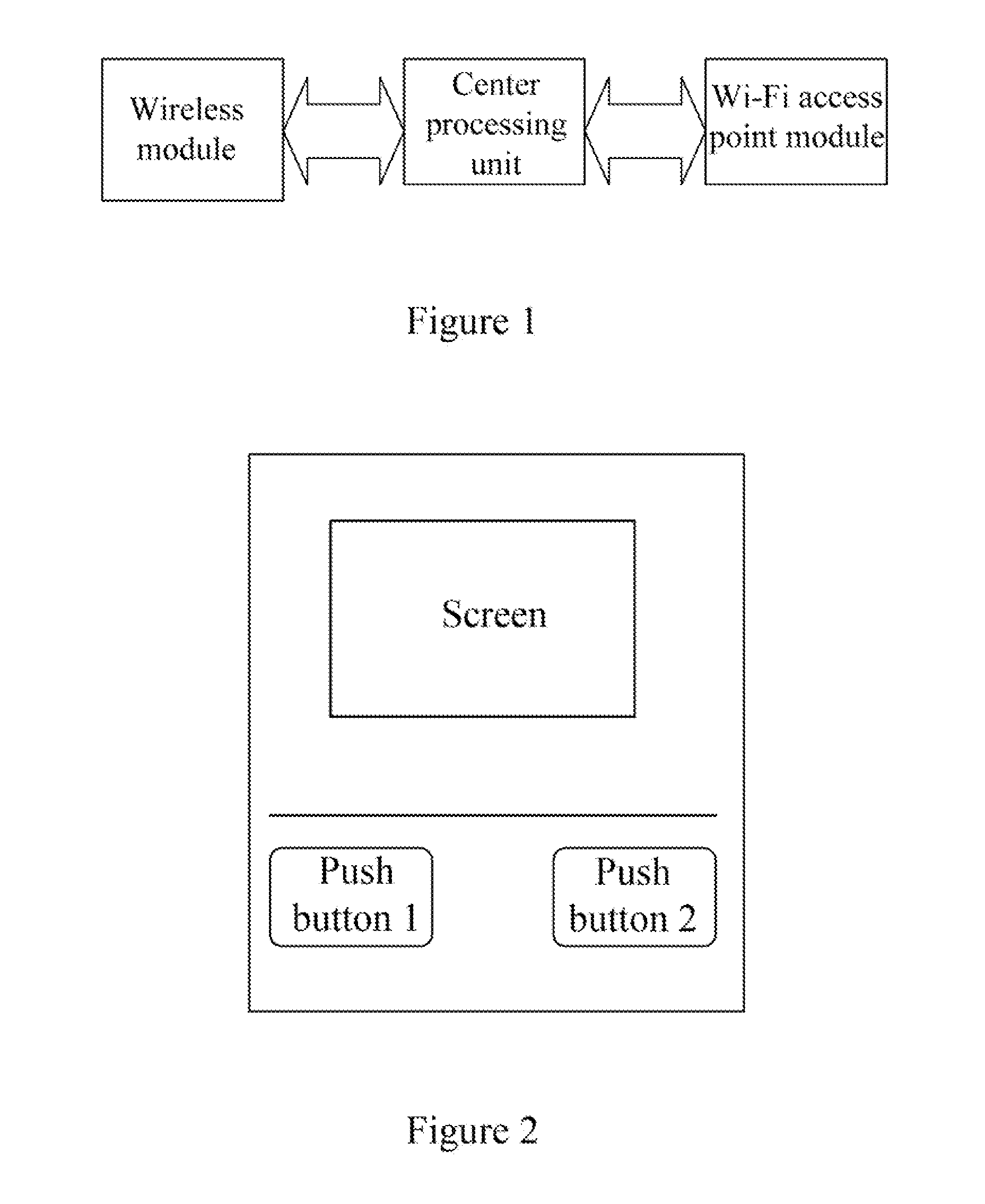
InactiveUS20120036557A1Lower upgradeLow costDigital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsWi-FiAccess method
The present invention discloses a Wi-Fi access method, access point and a Wi-Fi access system. It is related to the field of communication technology and is devised for realizing the security access of a Wi-Fi device with relatively low costs. The Wi-Fi access method comprises: receiving an access request initiated by a wireless client terminal; sending an access prompt to an access point user based on the access request; receiving an access control instruction returned by the access point user; when the received access control instruction is a permitting access instruction sent by the access point user, performing access processing and establishing a Wi-Fi connection between the wireless connection terminal and the access point based on the permitting access instruction; or denying the access of the wireless client terminal based on a denying access control when the received access control instruction is the denying access instruction sent by the access point user. The present invention may cause a Wi-Fi device to access an access point (AP).
Owner:HUAWEI DEVICE CO LTD
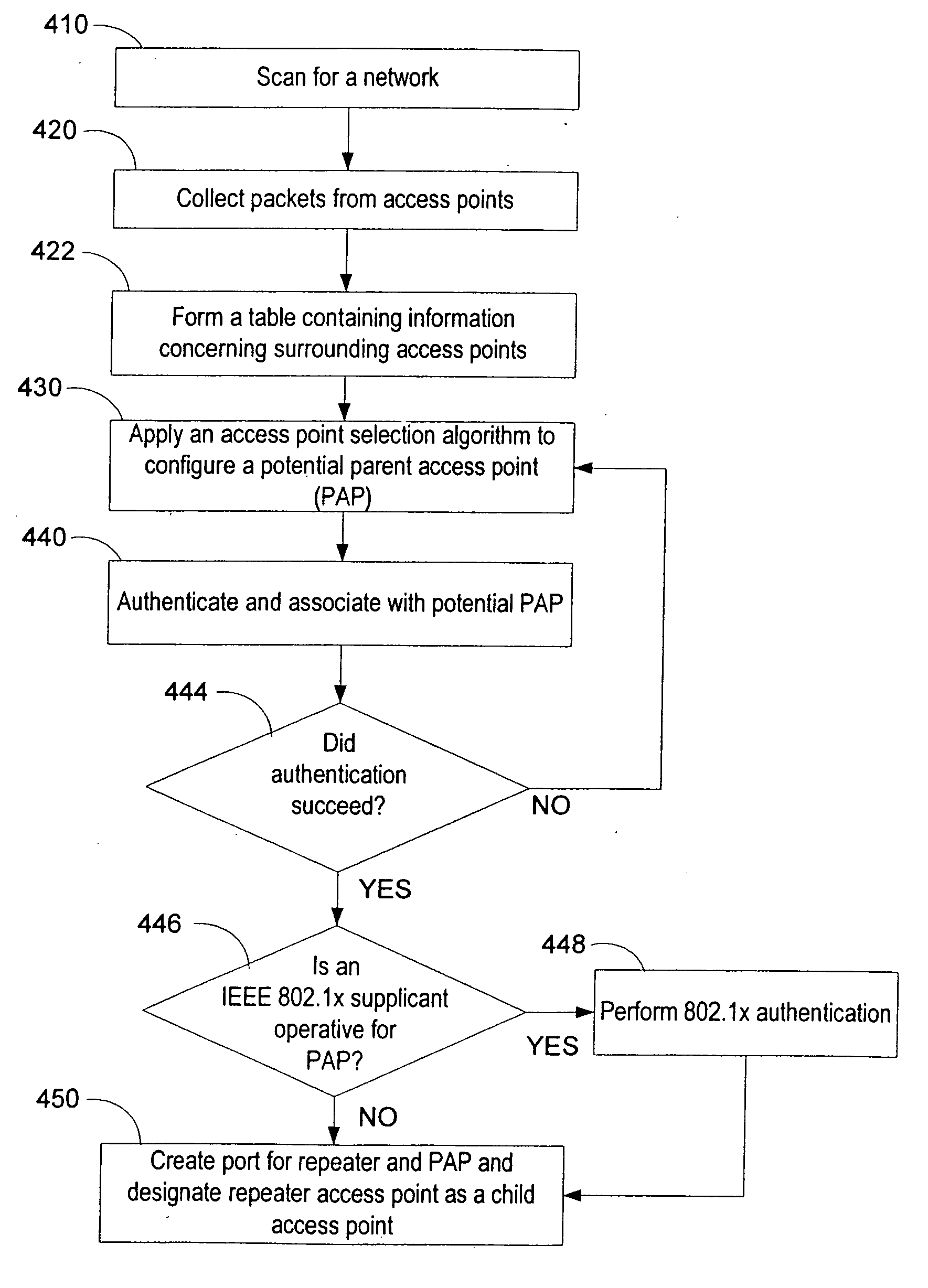
Access point to access point range extension
An architecture and methods for extending the depth of a WLAN to a four-level hierarchal access point structure including wireless access points. The wireless access points in the WLAN can be networked by scanning for a network, collecting one or more packets that identify the network from one or more access points, each packet including an address identifying an ancestry of the access points to an ancestral wired access point; and applying an access point selection algorithm to configure a parent access point. The architecture includes a scanning object configured to issue a scan request to a network interface and collect access point data; a selection object configured to filter and sort the collected access point data; an authentication state machine configured to perform authentication and validate; and an association state machine configured to compose a packet including hierarchical data indicative of access point ancestry to a conventional access point.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
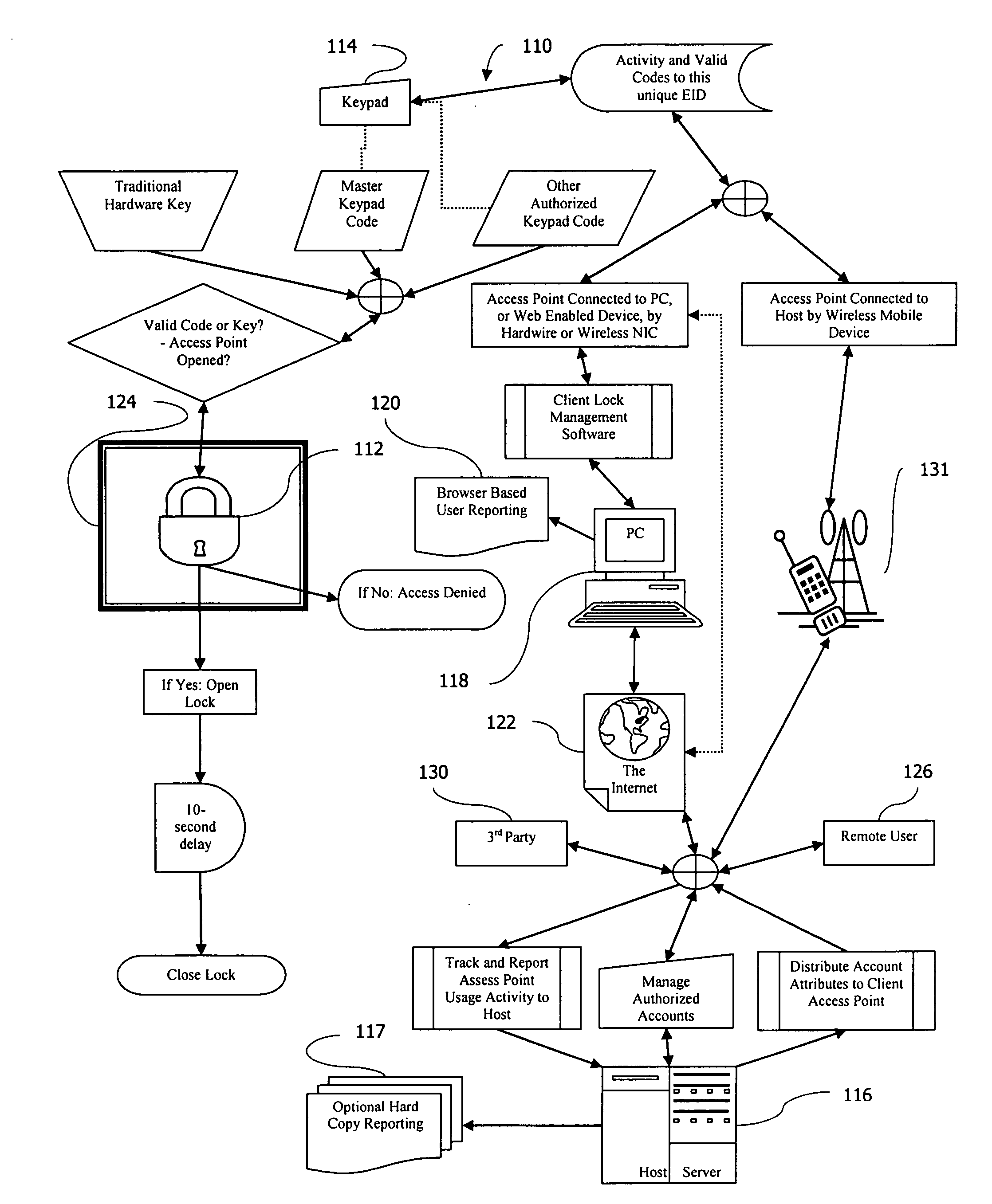
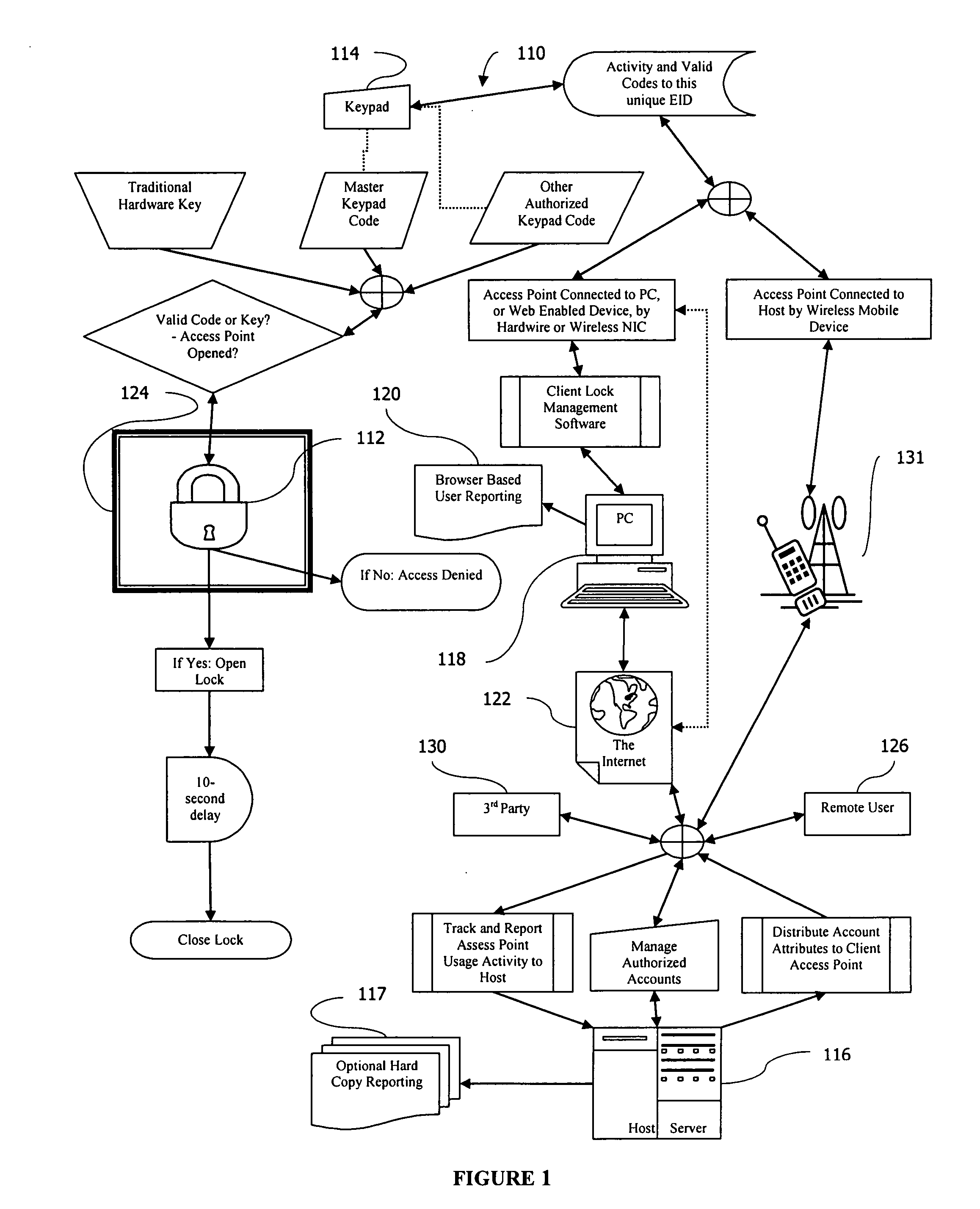
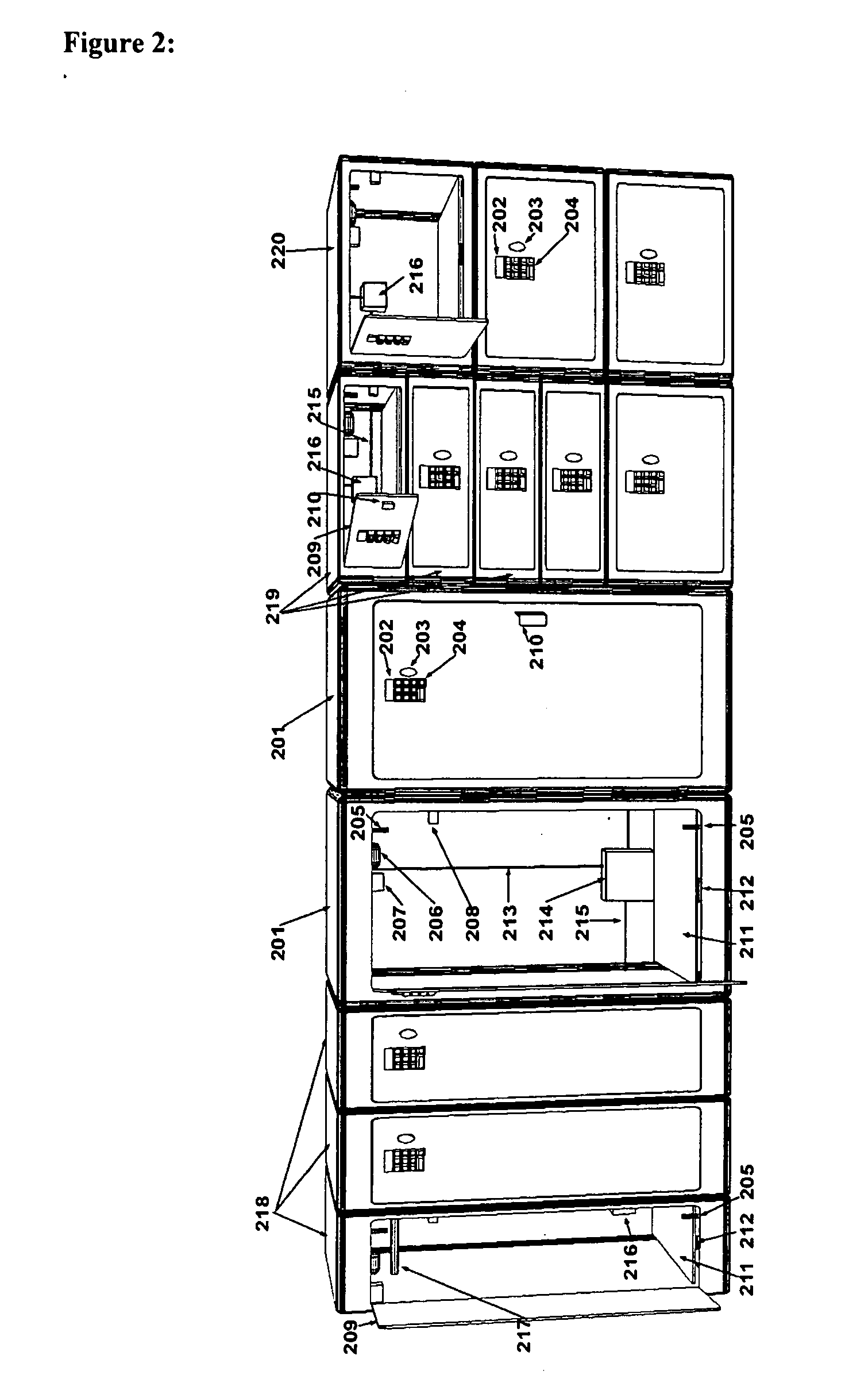
Electronic or automatic identification method to remotely manage the locks or access points to a multi-compartment secure distribution receptacle, via the internet or wireless communication network
InactiveUS20070247277A1Electric signal transmission systemsMultiple keys/algorithms usageLocking mechanismRadio access point
A multi-compartment secure delivery appliance cabinet with an independent locking mechanism at each compartment that is electronically managed or hosted at a remote central location via the Internet or wireless communication network with conditional code validations. Remote management portal software resides on host computer servers, which are in turn accessed and managed by user members through a common browser interface via the Internet or a wireless communication network via a wireless mobile device. The remote host portal software provides a variety of robust options for the user of the local access point, to program multiple access codes with varying conditions of time, date and use occurrence limitations. Additionally, the host software assigns available cabinet compartments, provides information, distributes codes, tracks and reports usage events at the respective local access points. The host interfaces with each unique local electronic locking mechanism at the respective local access location either via a web enabled device or a common PC based Internet browser or wireless mobile device.
Owner:MURCHISON KENNETH +1
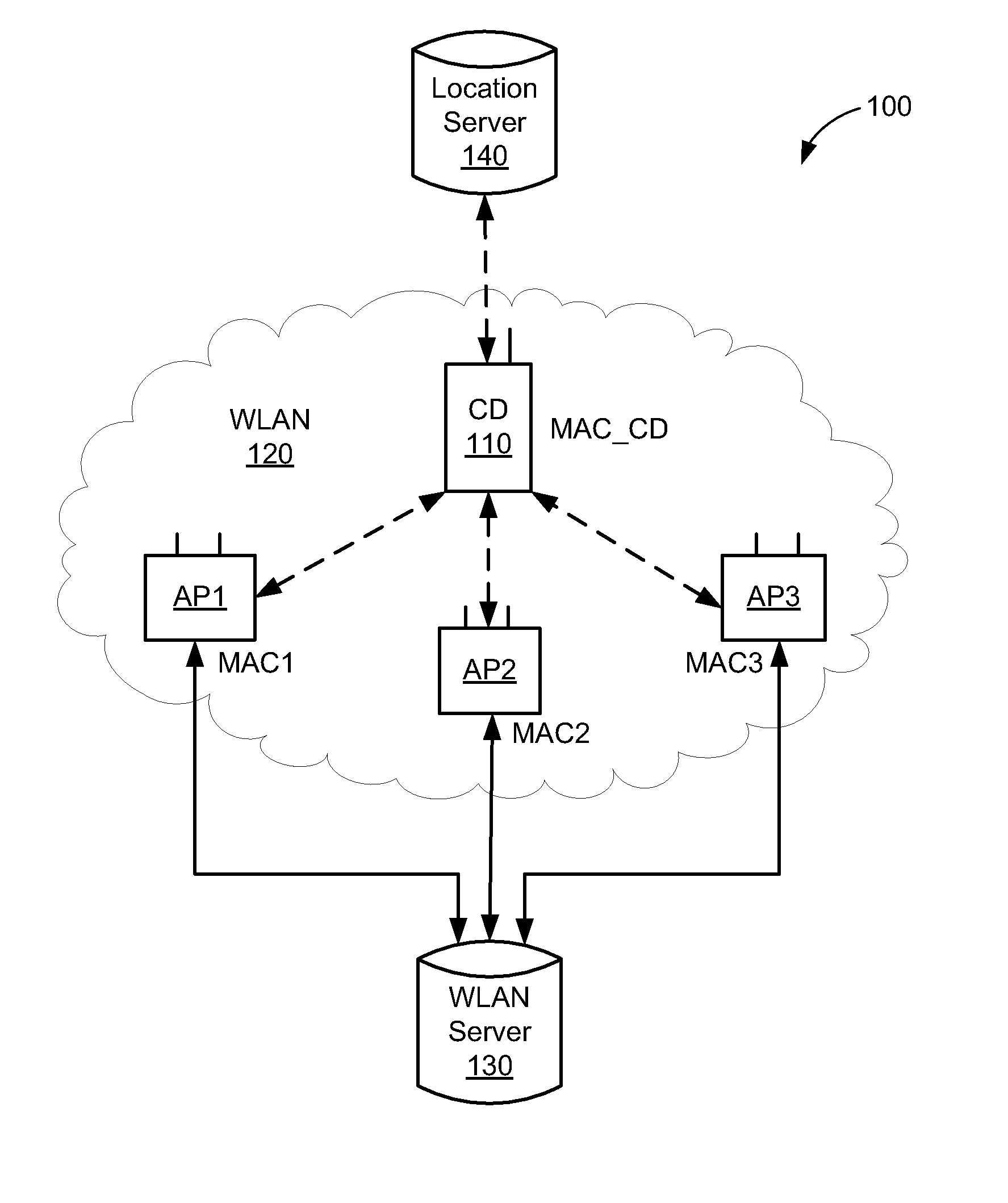
Driving hybrid location services from WLAN stations using access points
InactiveUS20130308618A1Reduce deliveryNetwork topologiesPosition fixationRadio access pointLocal area network
A wireless local area network (WLAN) positioning system is disclosed that allows the WLAN system to determine the location attributes of a client device operating in a power save mode, operating on a different channel than the WLAN's access points, and / or operating in an ad-hoc mode. The client device periodically performs scanning operations during which beacon frames broadcast by a selected AP(s) can be received. The client device parses information embedded in the beacon frames, and in response thereto selectively initiates ranging operations to determine its location attributes. After determining its location attributes, the client devices sends the location attributes back to the selected AP(s).
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Radio Network Controller With IP Mapping Table
InactiveUS20120014316A1Power distribution line transmissionNetwork topologiesHandoverWireless network
Devices, systems, and methods are disclosed for seamlessly routing data to mobile devices that undergo handovers from one access point to another. A controller, such as a RNC or BSC, includes logic to map the locations of mobile devices that are connected to various access points on one or more networks. The access points include base stations, Node Bs, wireless LAN, etc., and incorporate or are coupled to network agents. The network agent reports the location of the mobile device to the controller via a plurality of means such as over an IP network, a powerline network, or a satellite network. Using the database, or IP mapping table, having the most current locations of all the mobile devices under its domain or area, the controller can route data packets to the mobile devices using the most effective routing paths.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
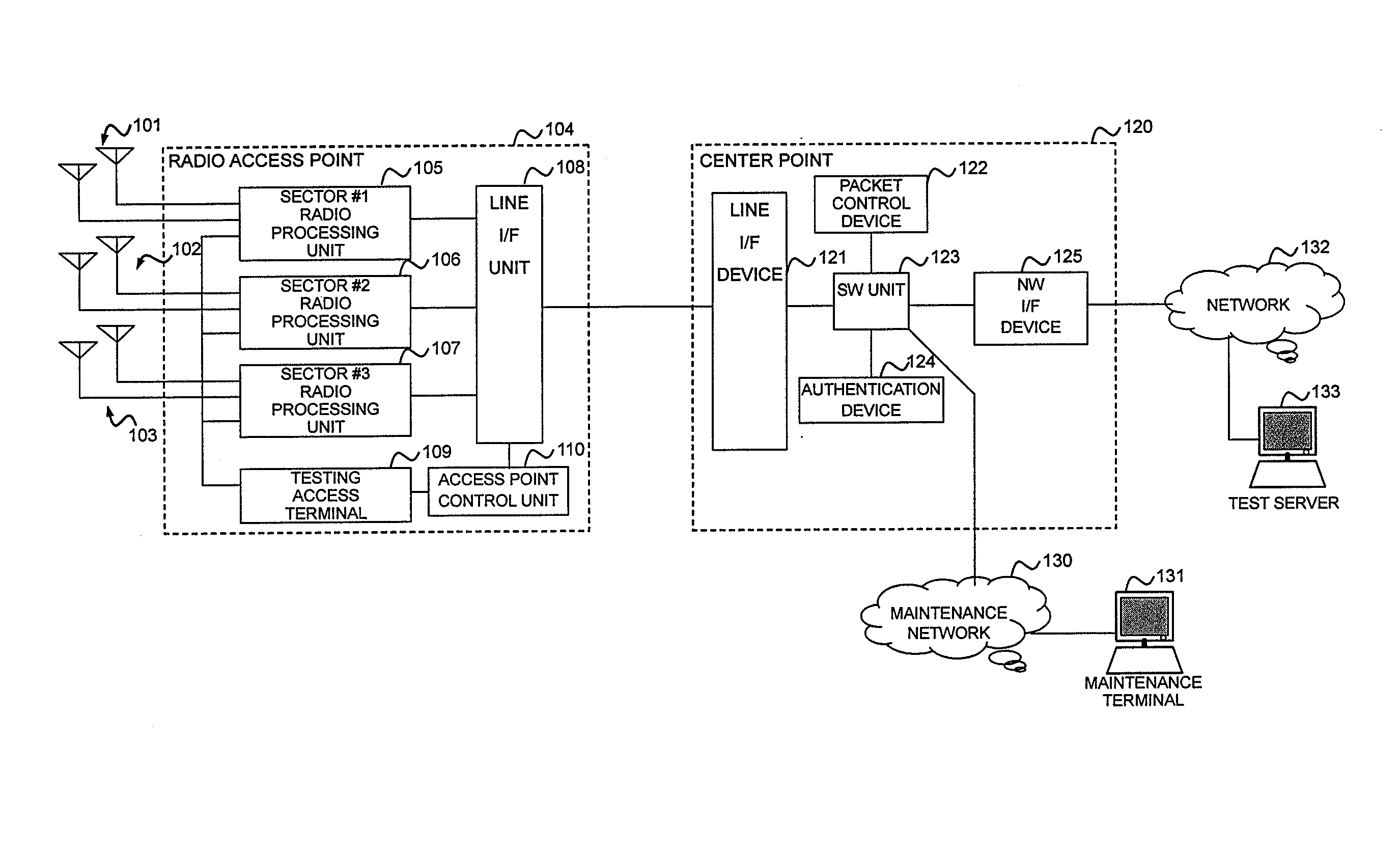
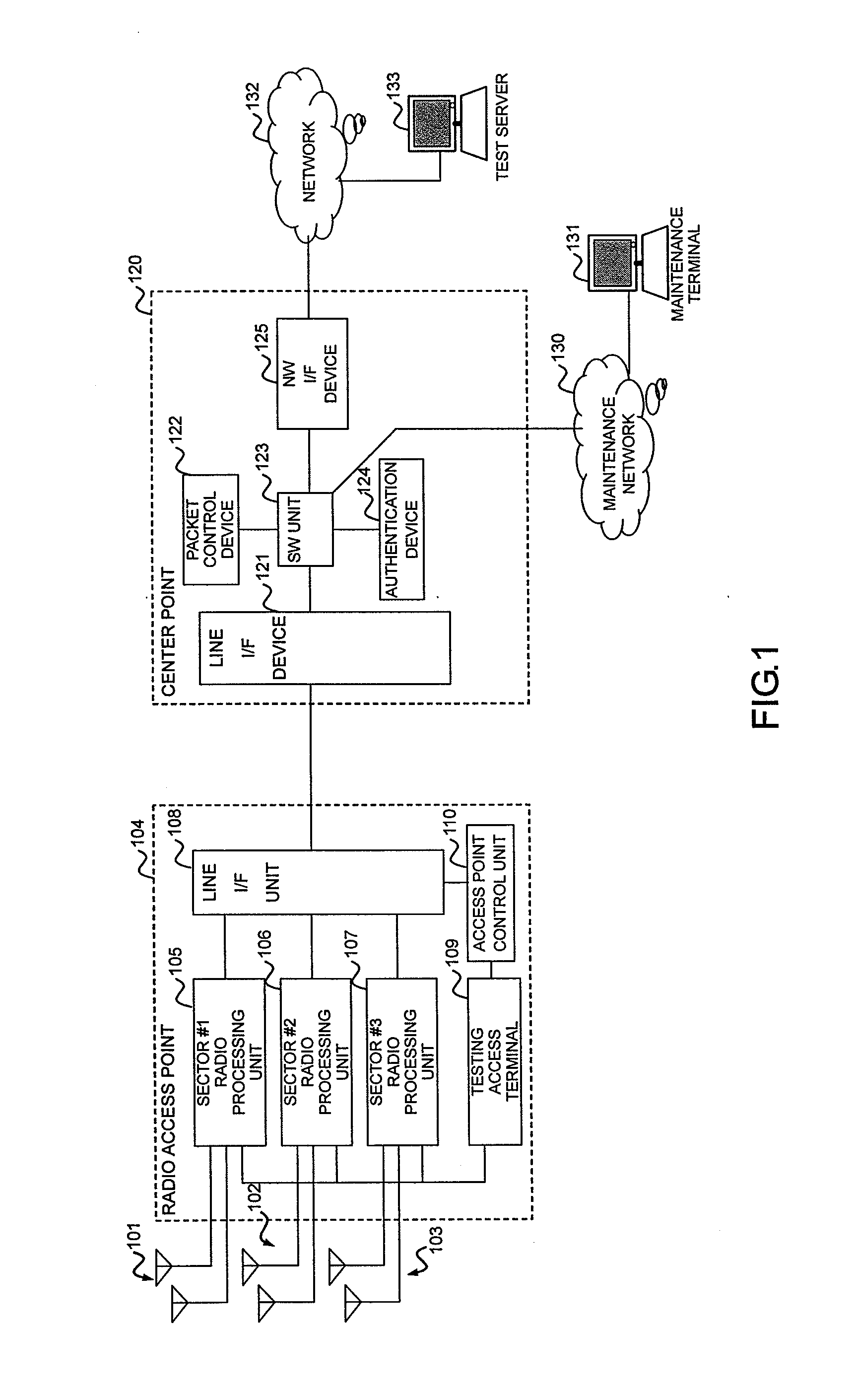
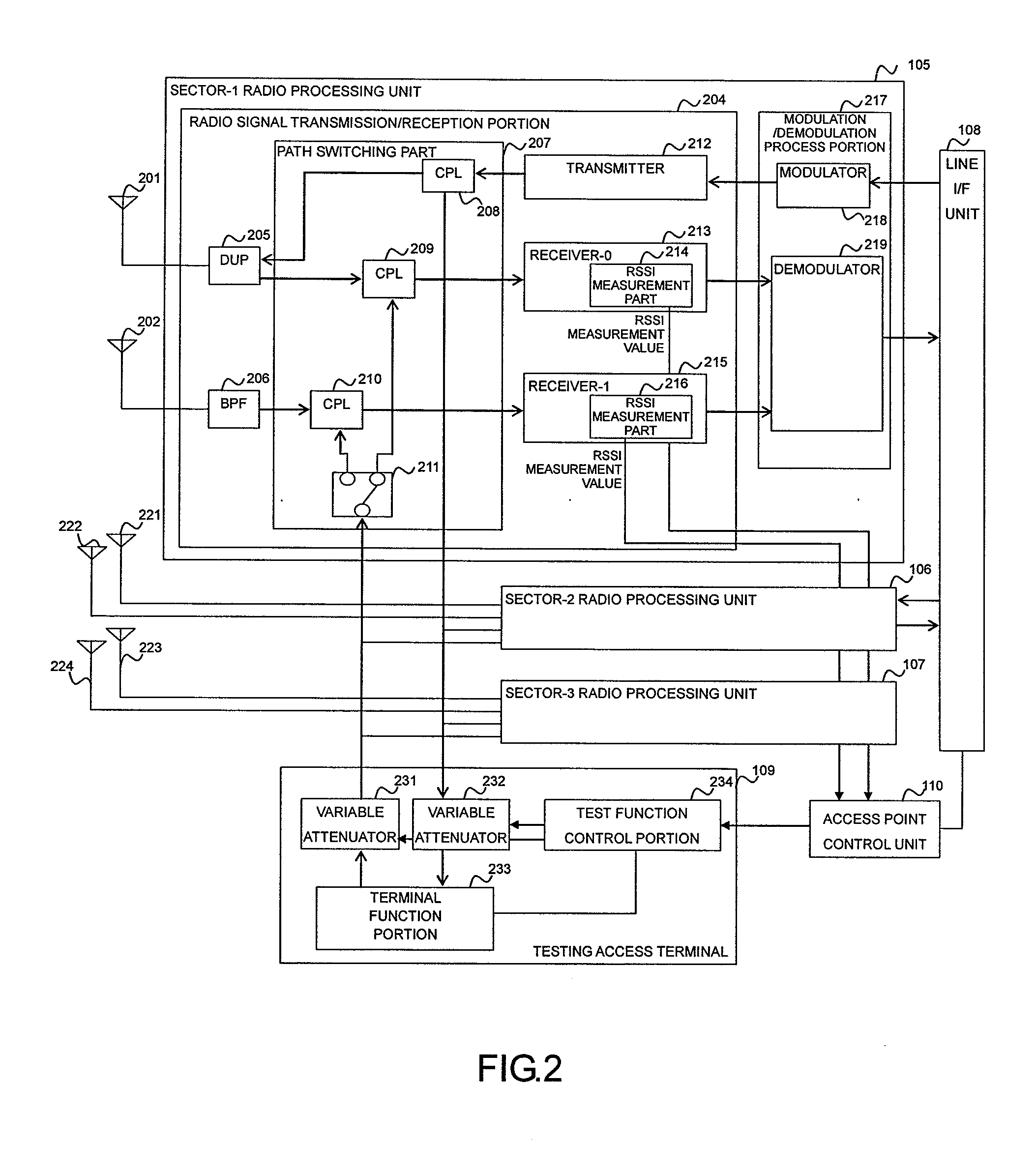
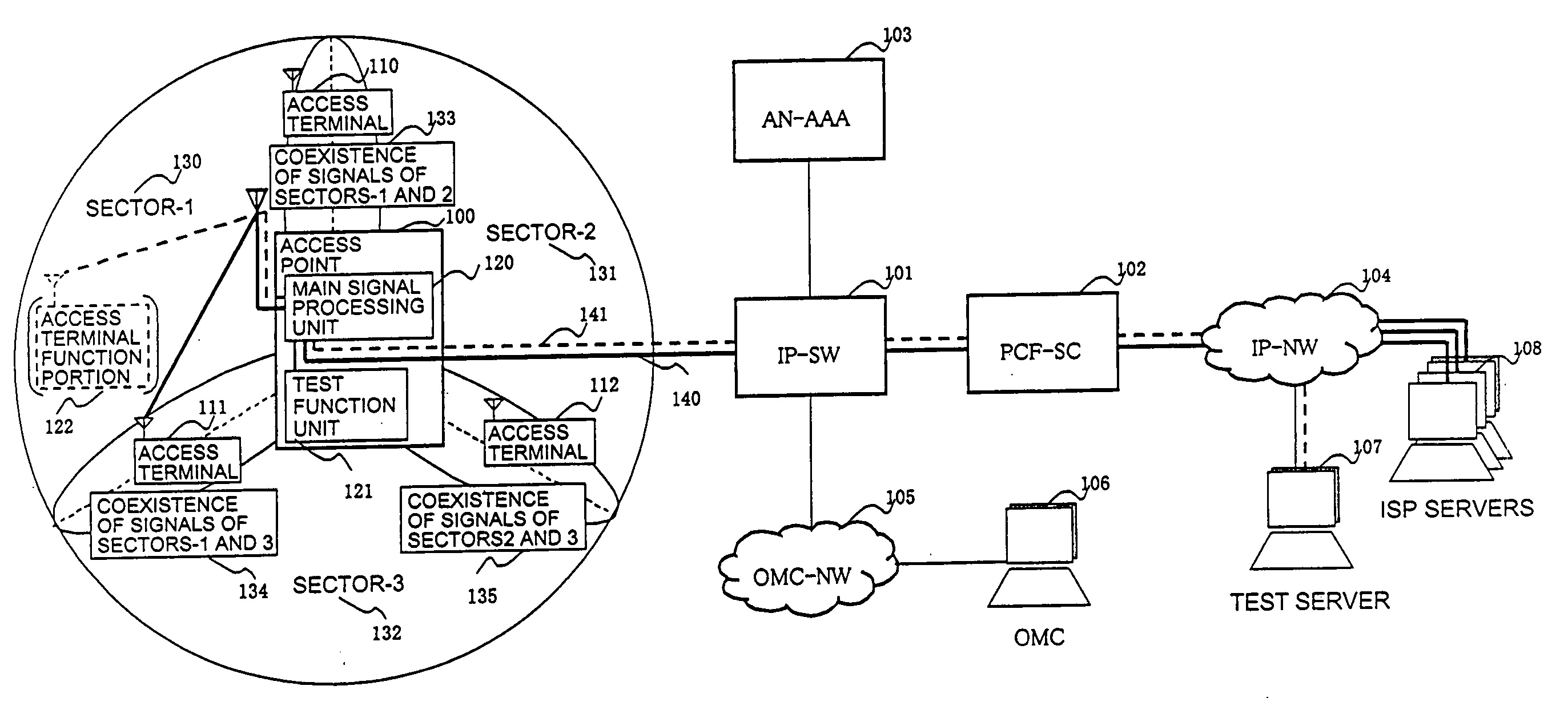
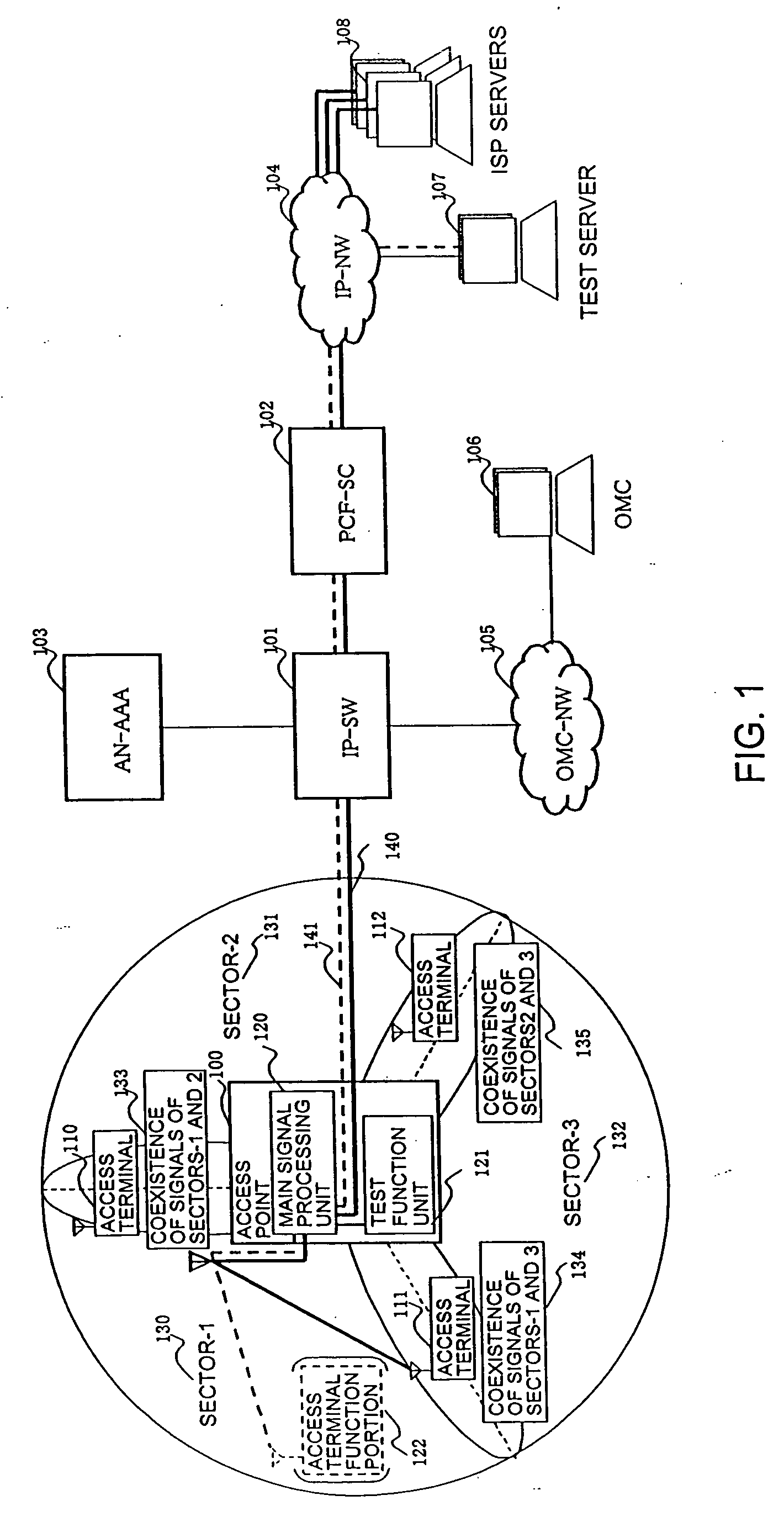
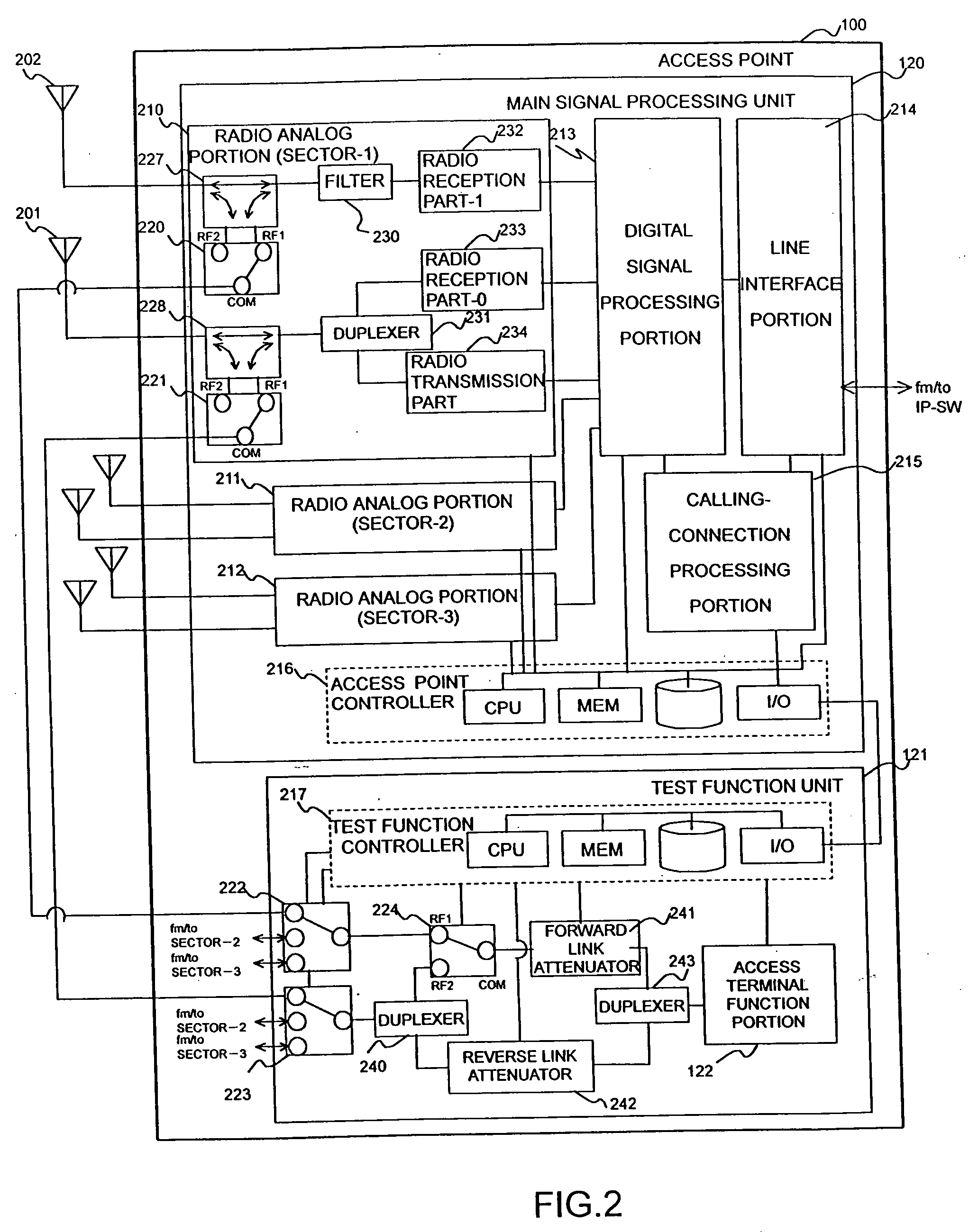
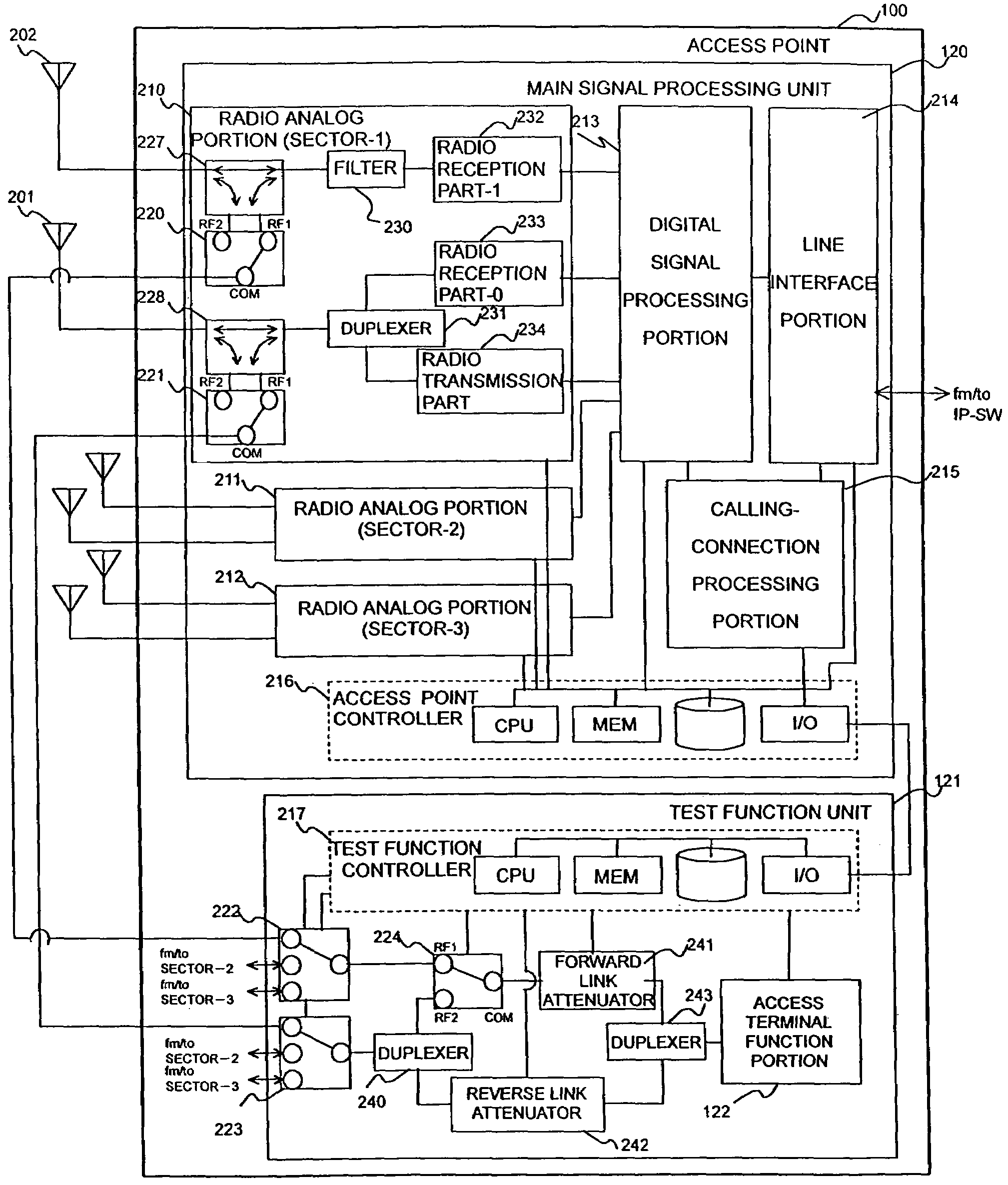
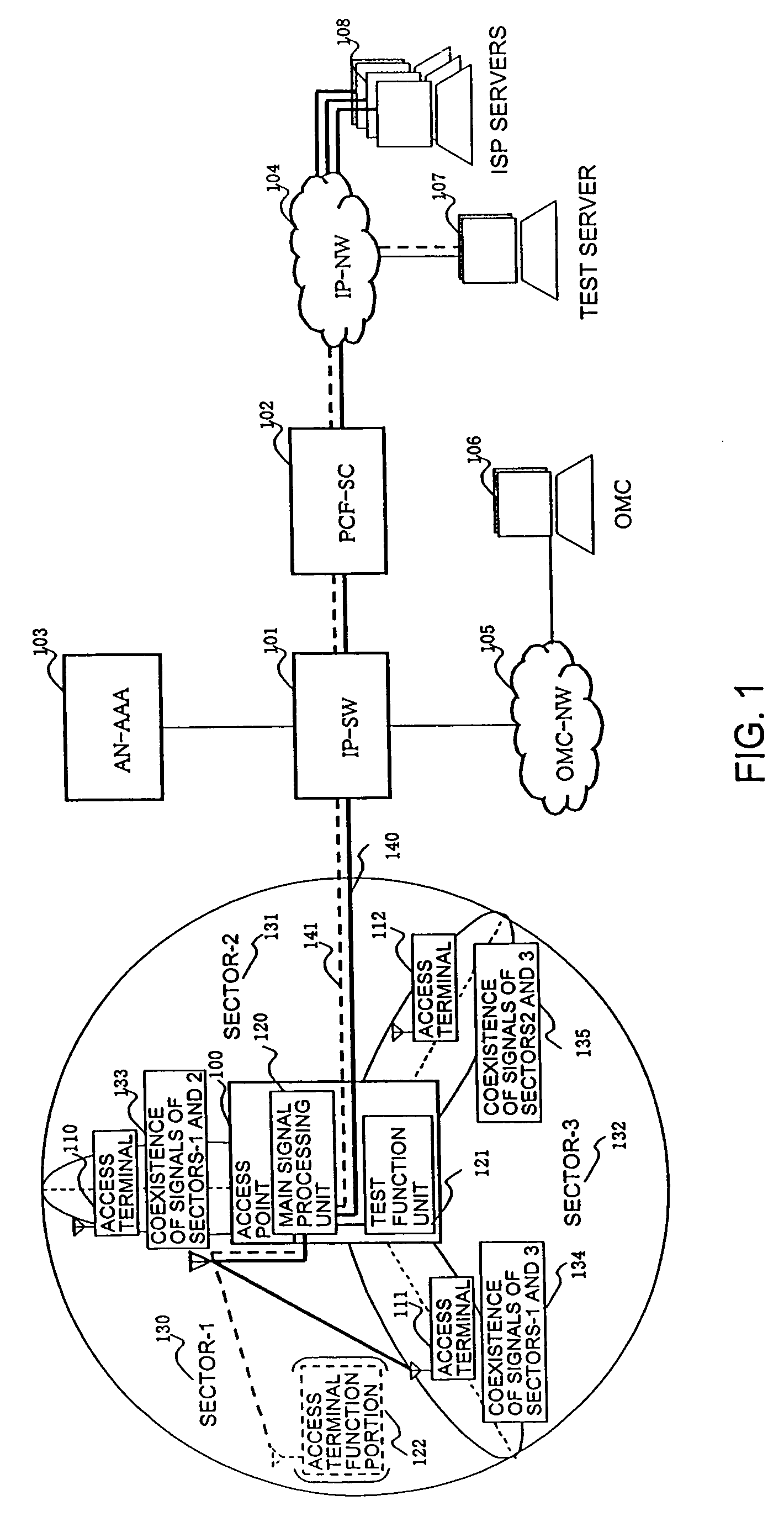
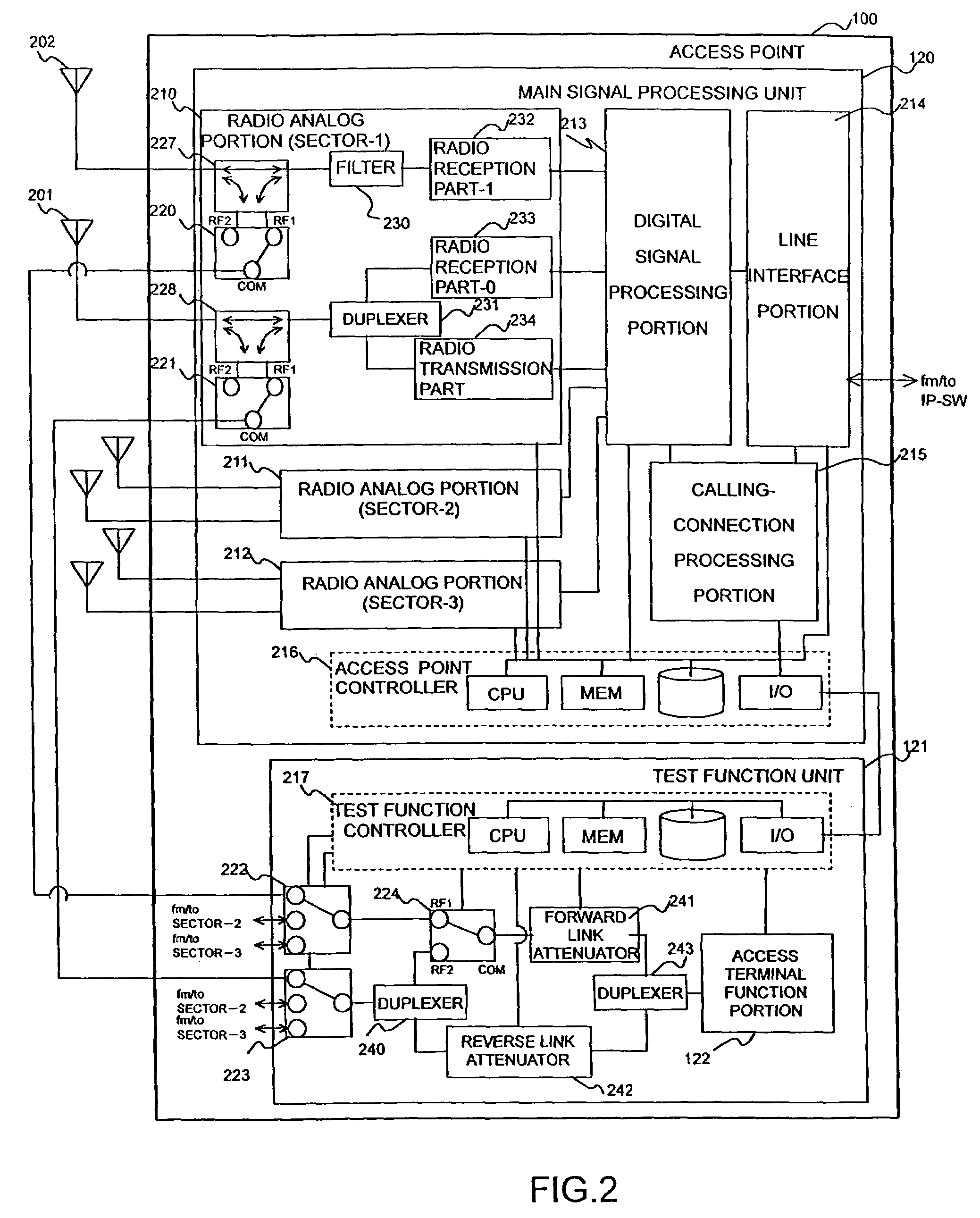
Radio access point testing apparatus
InactiveUS20080031144A1Wide marginAbnormalcy of the radio characteristicPower managementError preventionTelecommunicationsRadio access point
In a case where reception power in a radio access point is high by external noise, the normalcy of the radio access point is tested. In order to judge the normalcy of the radio characteristic of the radio access point, a test is performed through the calling connection between a testing access terminal in the radio access point and a predetermined device. An RSSI is measured before and after the transmission of a test signal. When the RSSI exceeds a threshold value, the path loss of a reverse link connected from the radio access point to the testing access terminal is increased by an attenuator. Then, reception power in the testing access terminal decreases. Thus, initial transmission power in accordance with the reception power from the testing access terminal is raised and the calling connection of the testing access terminal can be performed even under the external noise.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
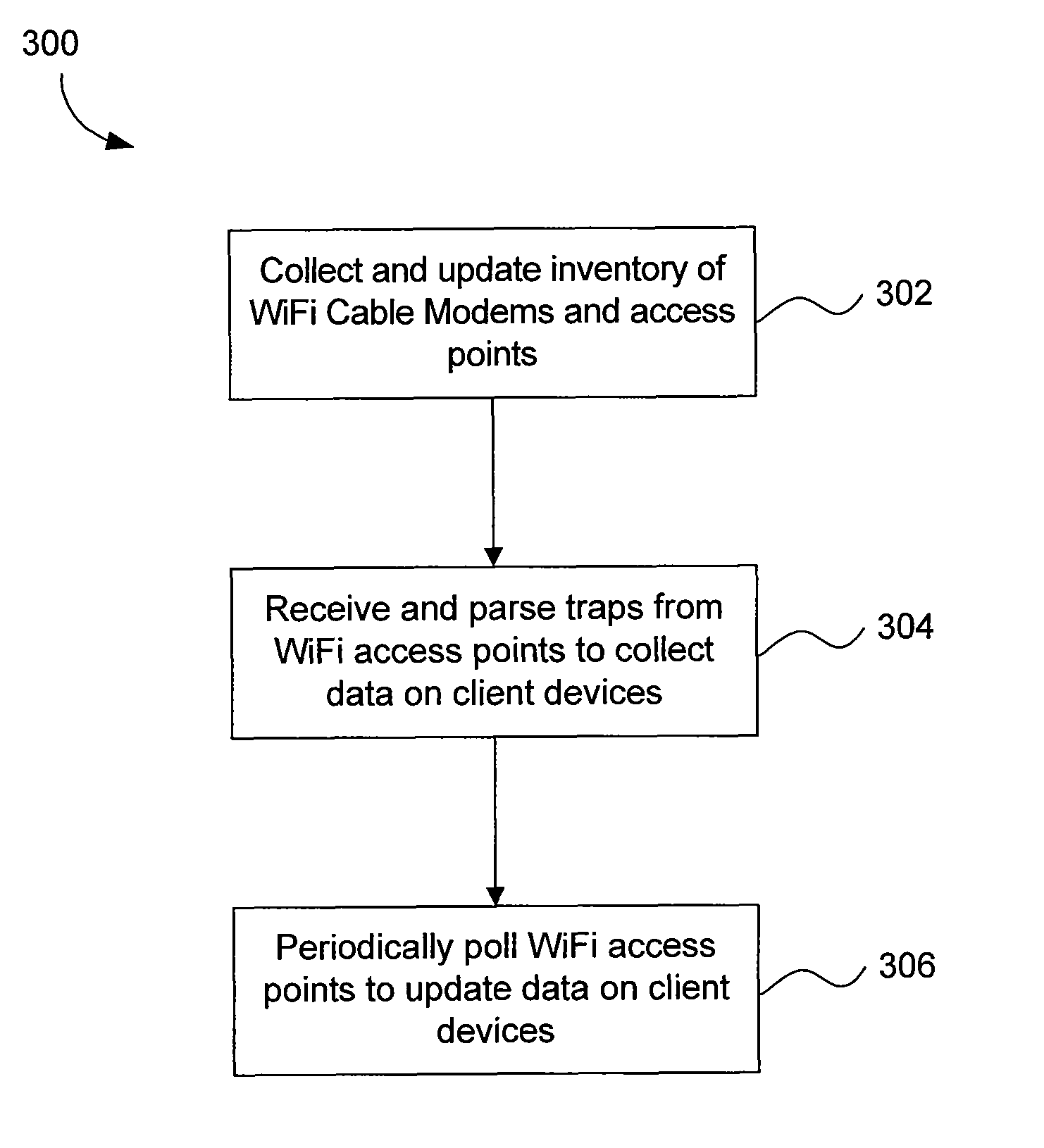
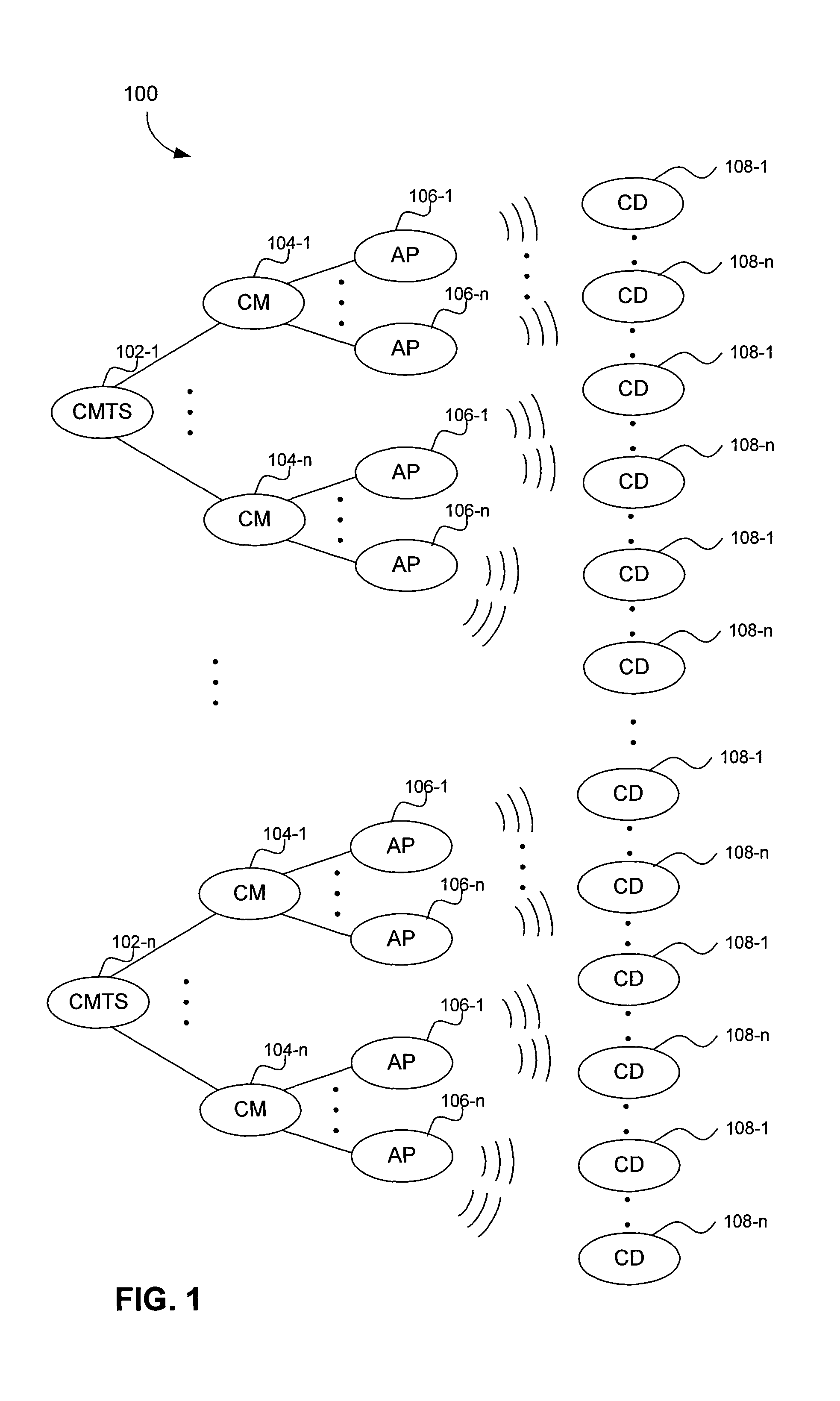
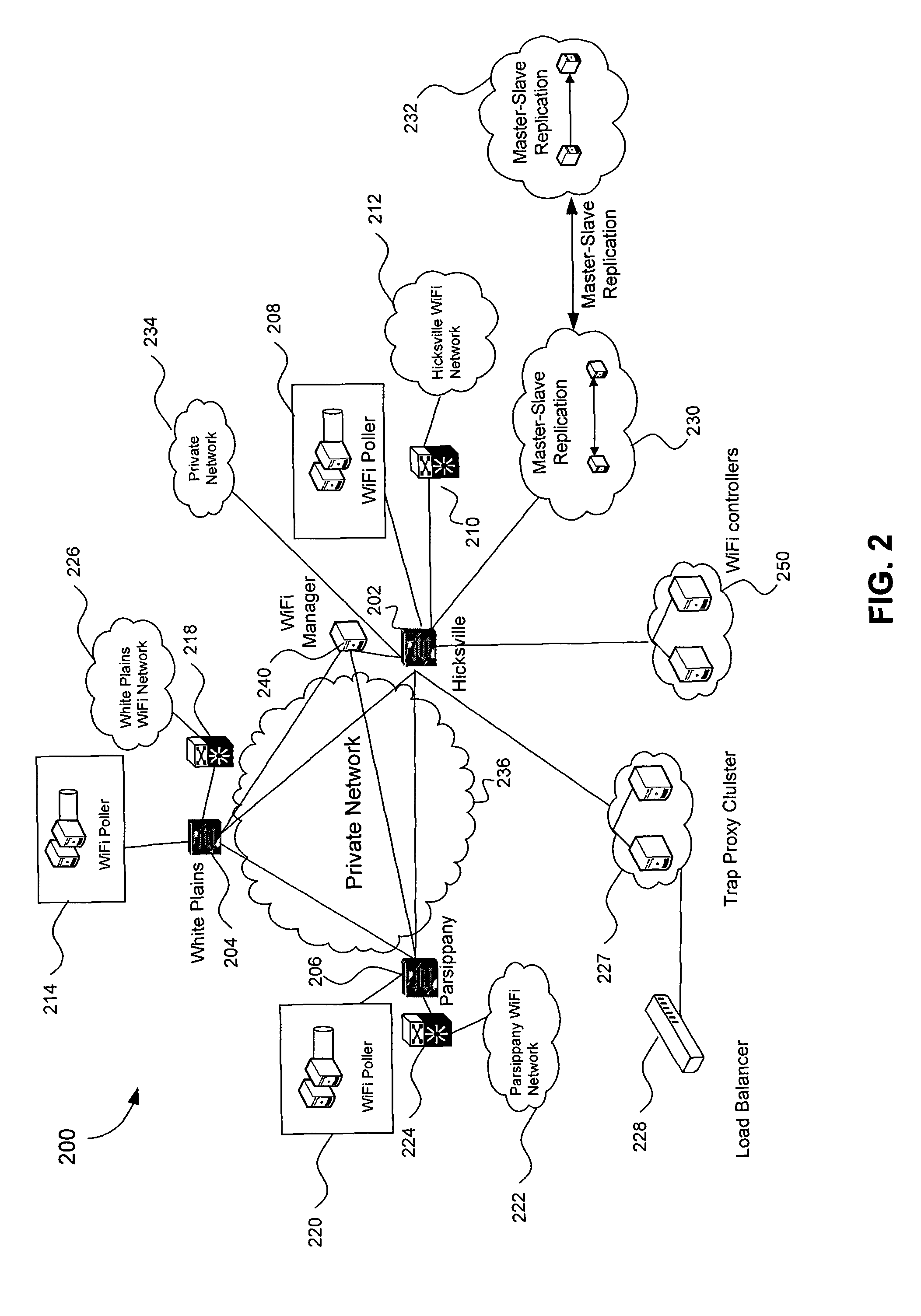
Wireless network polling and data warehousing
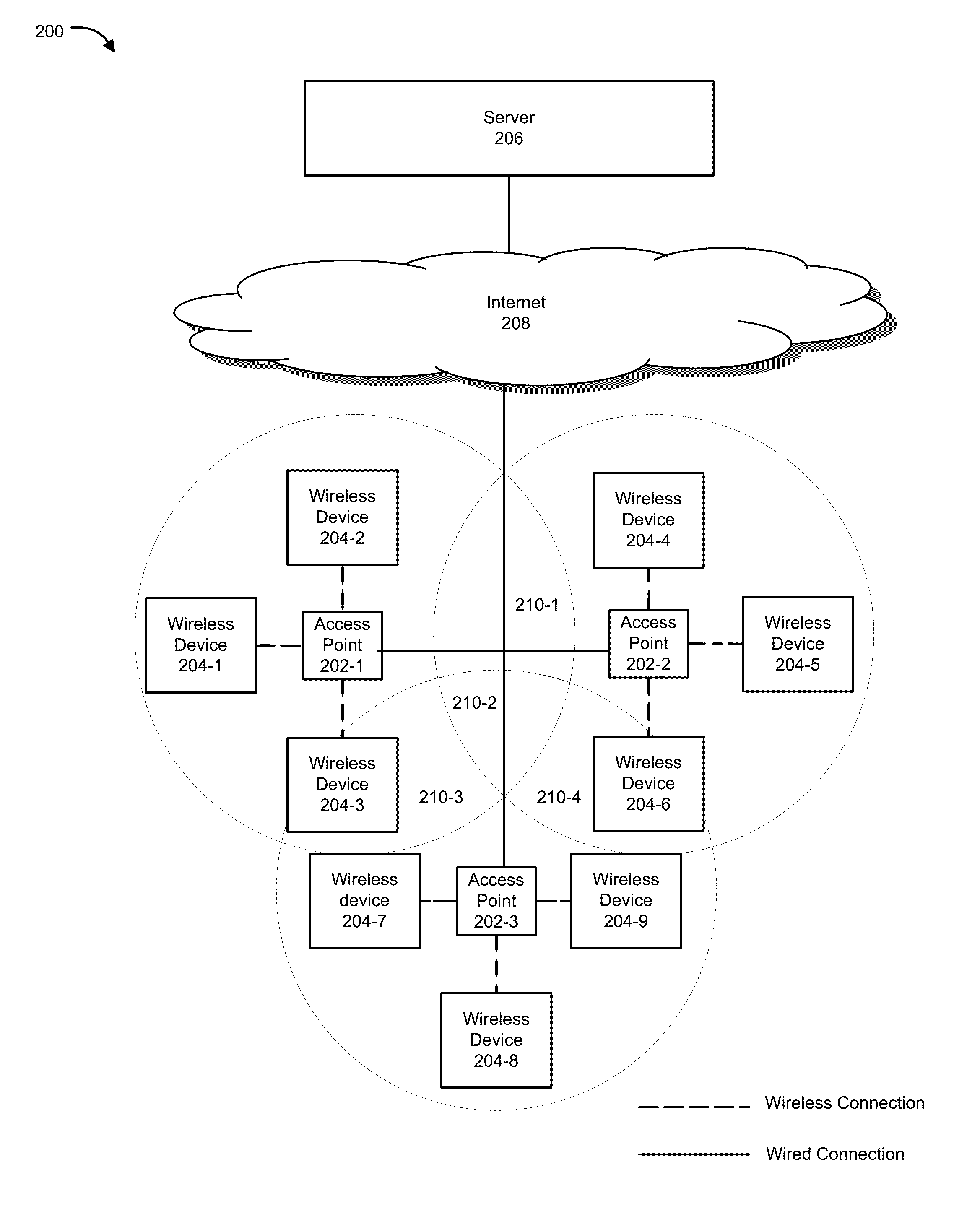
Methods and systems are provided to collect and update data on client devices connected to WiFi access points is provided. An inventory of WiFi cable modems and WiFi access points coupled to the WiFi cabled modems within a specific network is periodically collected. Internet Protocol (IP) addresses of WiFi cable modems and WiFi access points coupled to the WiFi cabled modems are periodically updated. Traps are periodically received from the WiFi access points. The traps are parsed to collect an inventory of client devices wirelessly connected to the WiFi access points and a time at which a client device connected to the WiFi access point. The WiFi access points are periodically polled to collect data on client devices, the data including a period of time that a client device has been connected to a WiFi access point and a physical location of the client device.
Owner:CSC HLDG
Wireless network having control plane segregation
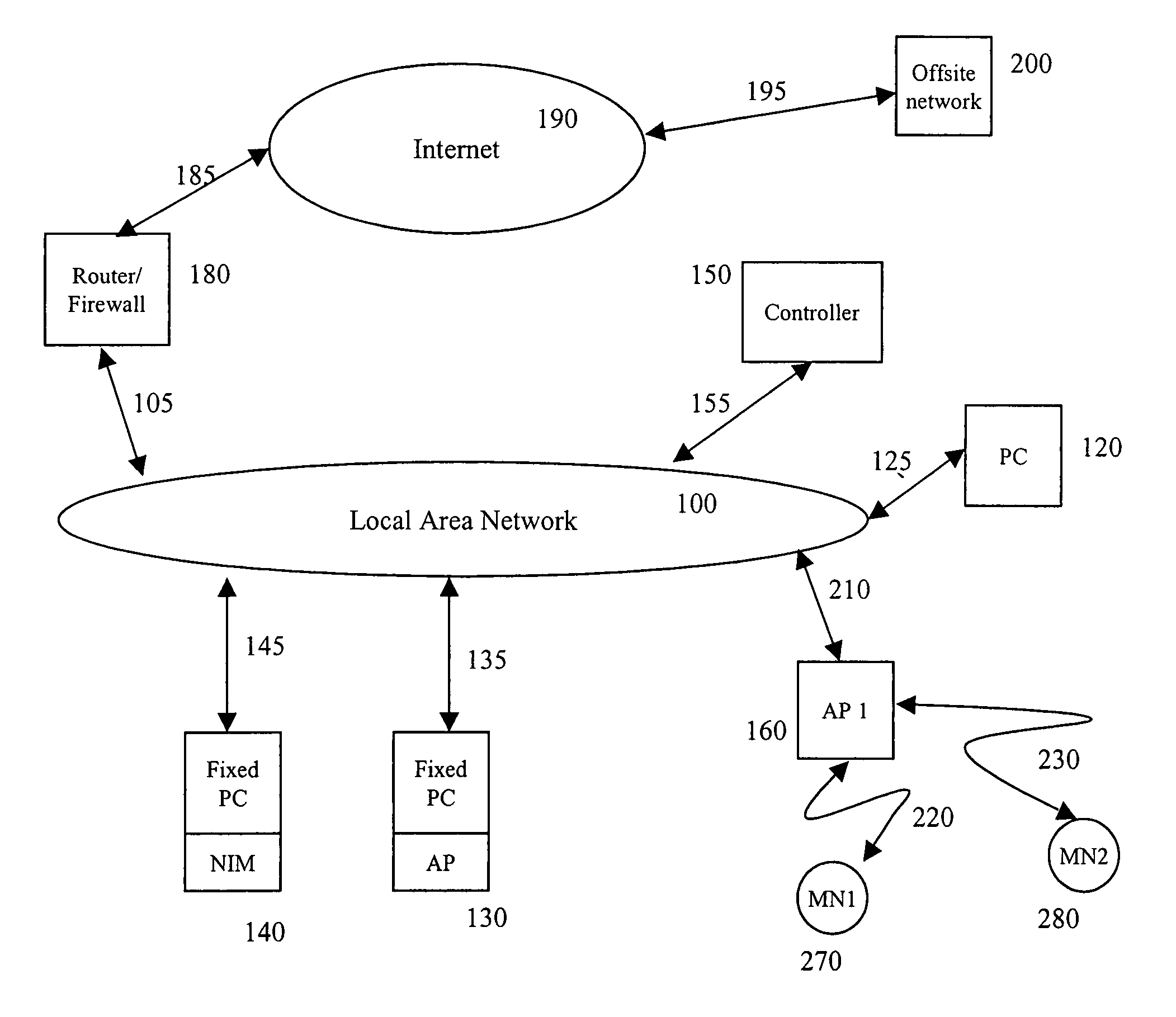
A wireless network having control plane segregation is described herein. In one embodiment, an exemplary network architecture includes, but is not limited to, multiple access points coupled to a wired network, where each of the access points is capable of communicating with one or more mobile nodes over a wireless network. The exemplary network architecture further includes a controller coupled to the access points over the wired network, where the controller maintains network traffic information of the wireless network and communicates the network traffic information with the access points to enable the access points to cooperate with each other to provide network services to the one or more mobile nodes over the wireless network. Other methods and apparatuses are also described.
Owner:GIDWANI SANJAY M
Method and device for selecting WIFI (Wireless Fidelity) access point to access to network
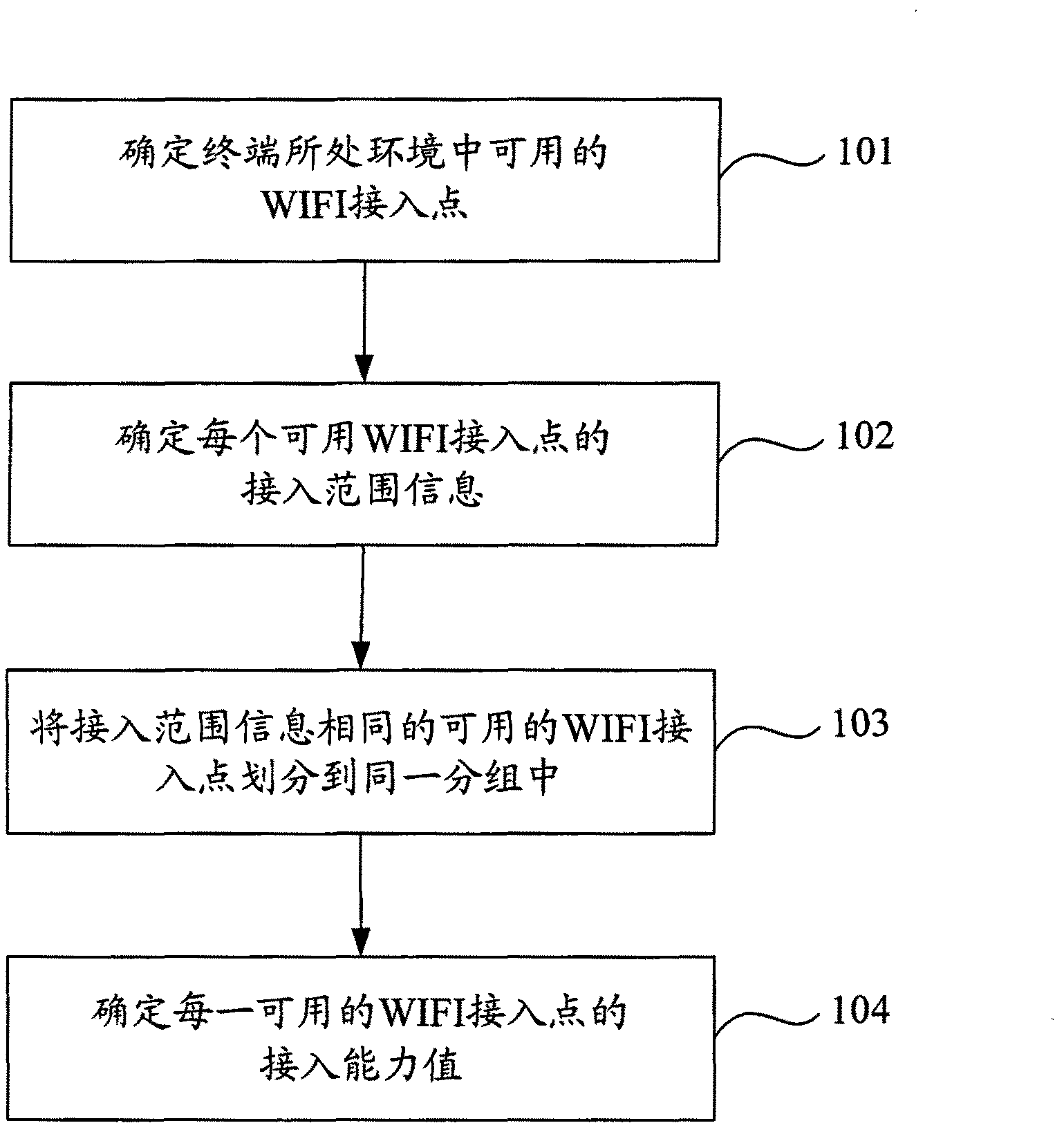
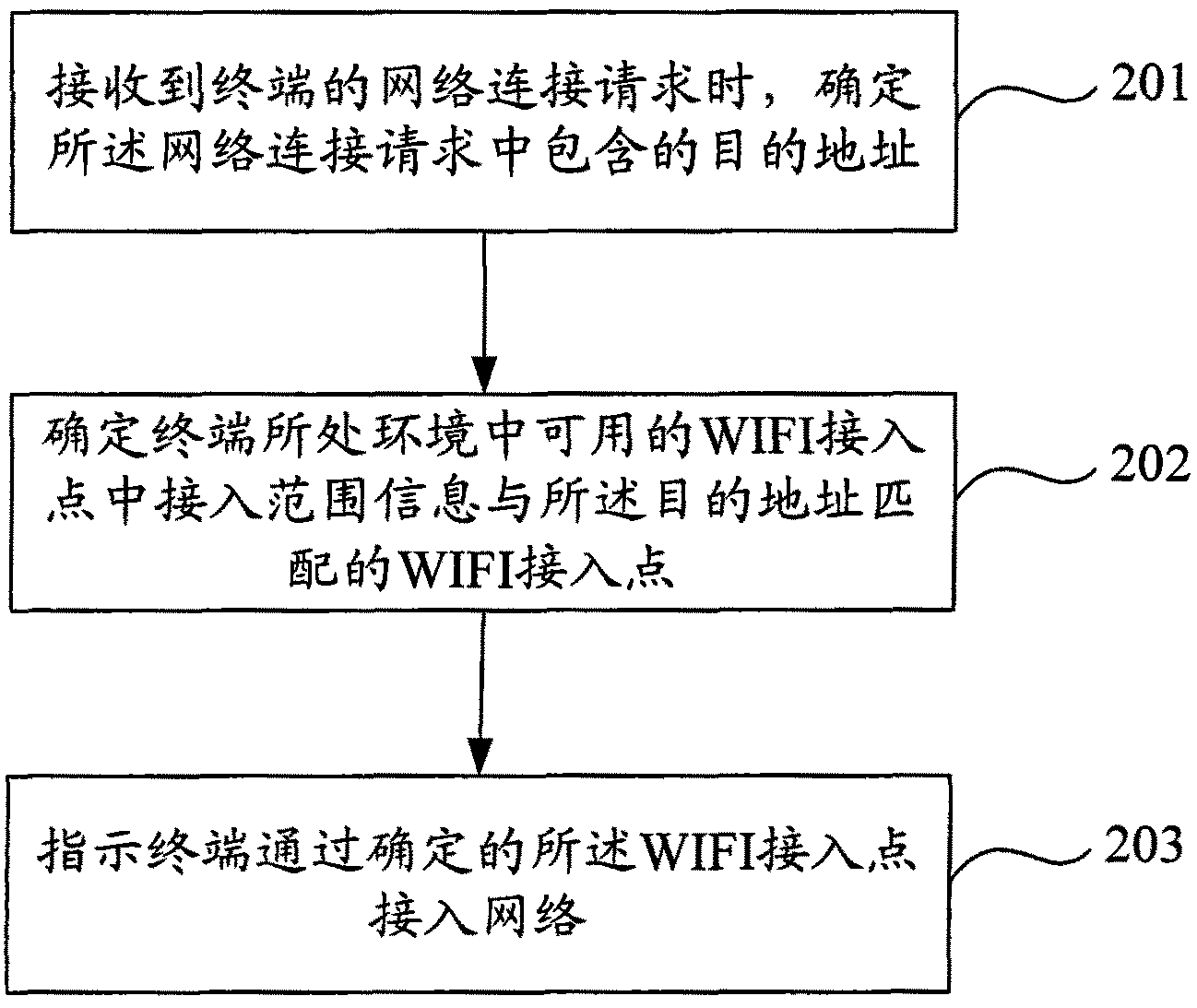
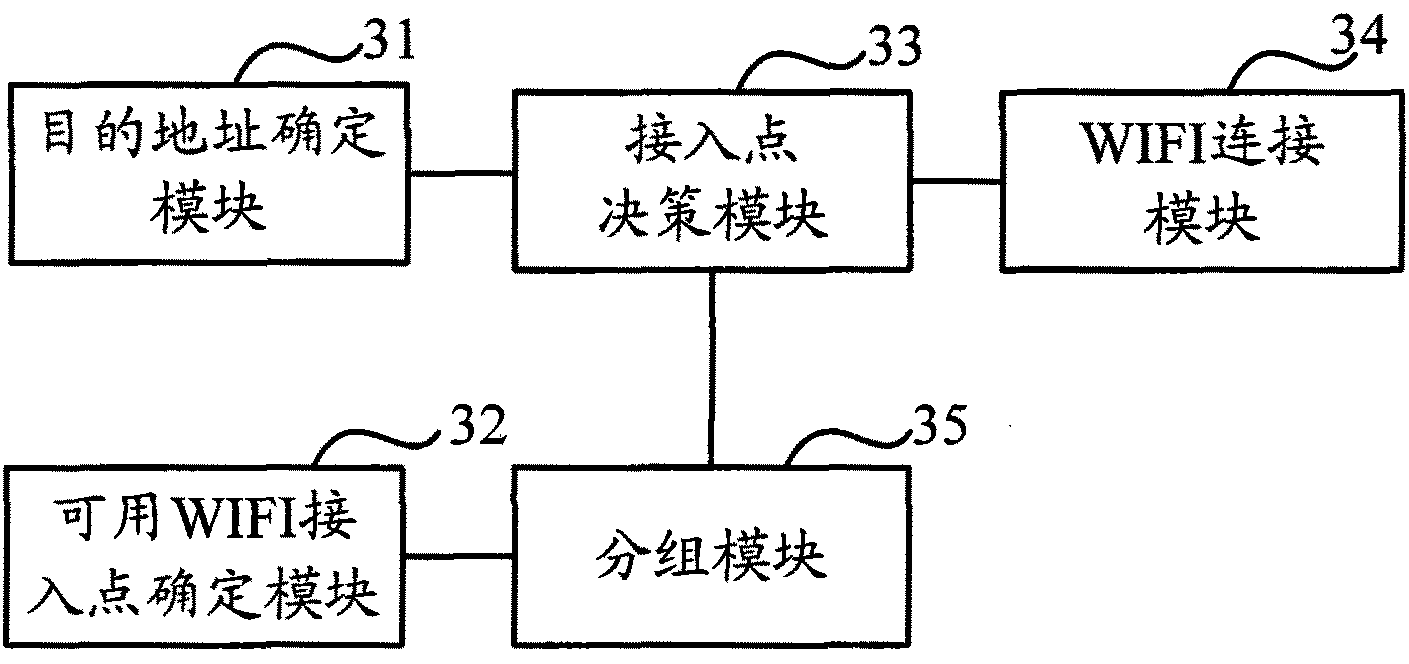
ActiveCN102378303ASatisfy the requirements for the connection requestGuaranteed smooth executionAssess restrictionNetwork connectionRadio access point
The invention provides a method and device for selecting a WIFI (Wireless Fidelity) access point to access to a network. The method specifically comprises the following steps that: when a terminal initiates a network connection request, the terminal is matched with the access range of each usable WIFI access point according to a target address contained in the network connection request; and when at least one WIFI access point of which the access range can reach a target network appointed by the network connection request exists, any one WIFI access point can be selected for the terminal to access to the target network. Each selectable WIFI access point is the usable WIFI access point and can realize the access function, and the connection range meets the requirements of the network connection request, so that the terminal can successfully access to the target network appointed by the network connection request, and services can be executed smoothly.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM CO LTD
Provisioning remote access points
InactiveUS20100313262A1Web data indexingUser identity/authority verificationElectricityTelecommunications network
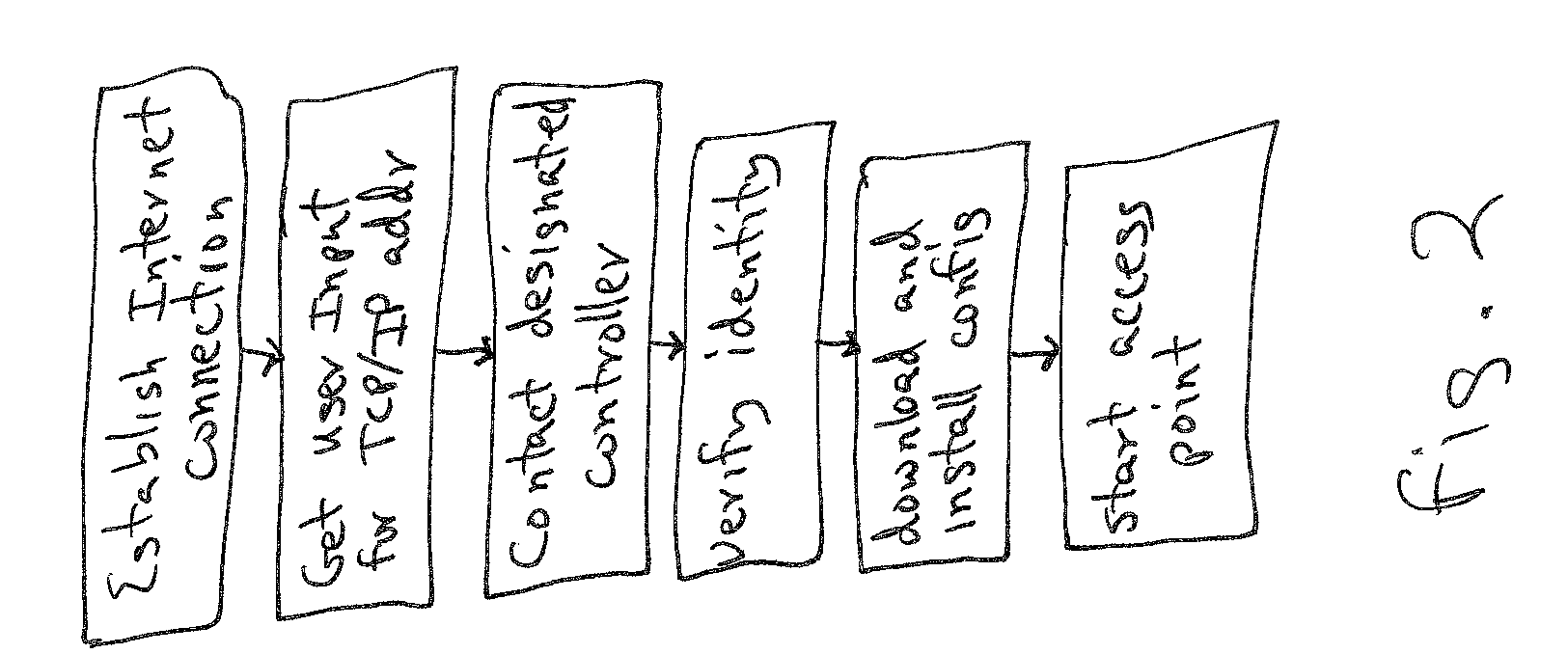
Provisioning remote access points for use in a telecommunication network. A remote access point contains identity information established during manufacturing; this identity information may be in the nature of a digital certificate. The identity information is stored in the remote access point, and may be stored in a Trusted Platform Module if present. When the remote access node is powered up in unprovisioned state, outside the manufacturing environment, it attempts to establish an internet connection via a first wired interface, and queries a user for information representing the TCP / IP address of its controller via a second wired interface. Once an internet connection is present, and a TCP / IP address has been provided, the remote access point attempts to connect to the controller at that address. The controller may filter connection requests through a whitelist of approved remote access points. Once a connection is established, controller and access point exchange and verify each other's identities. This may be done through the exchange and verification of digital certificates. Provisioning information is downloaded from controller to remote access point and installed. This may be done via a tunnel such as an encrypted tunnel. Software updates may be applied. The provisioned remote access point is placed in operation.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Mobile terminal and radio access point in radio access system
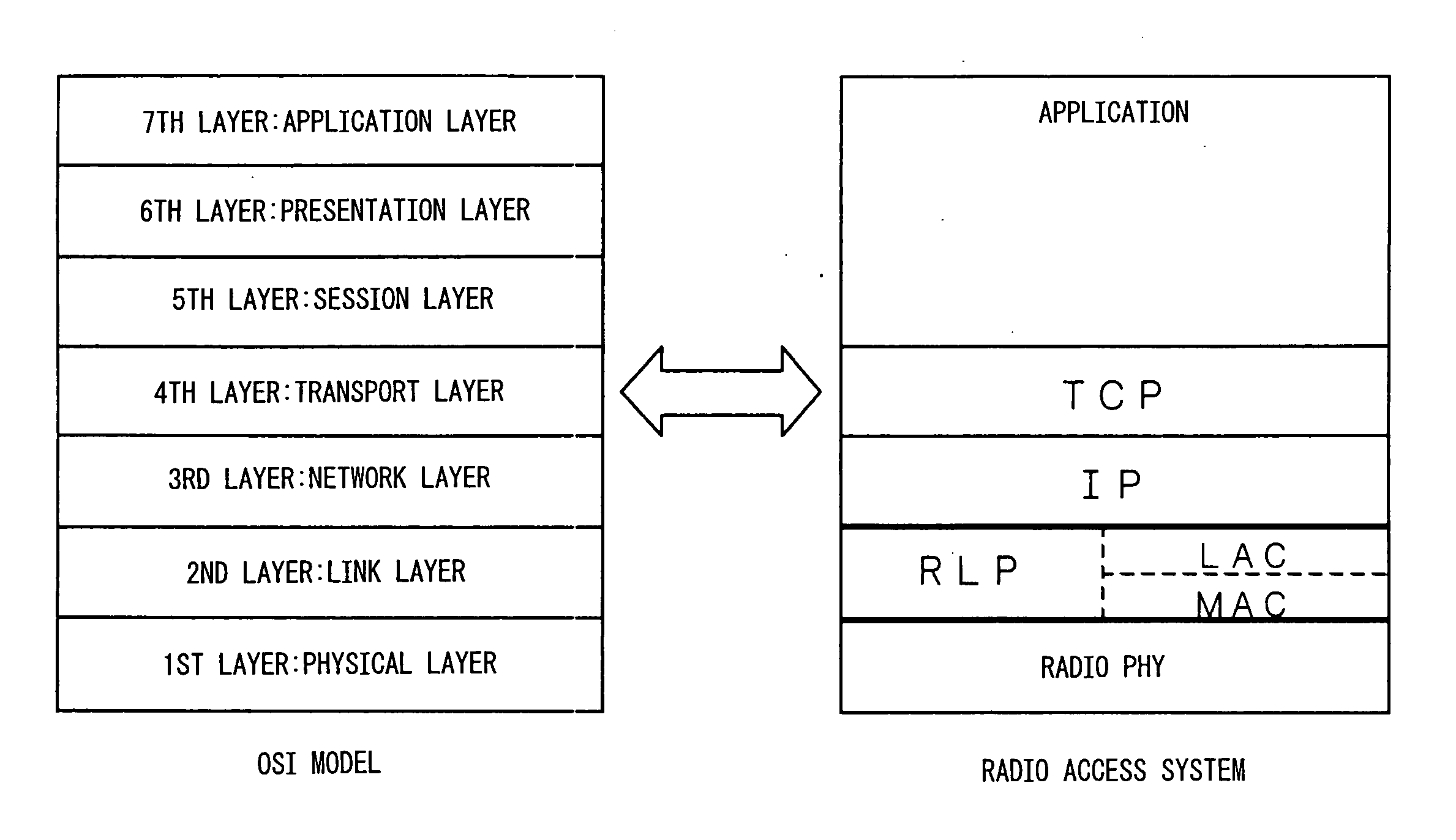
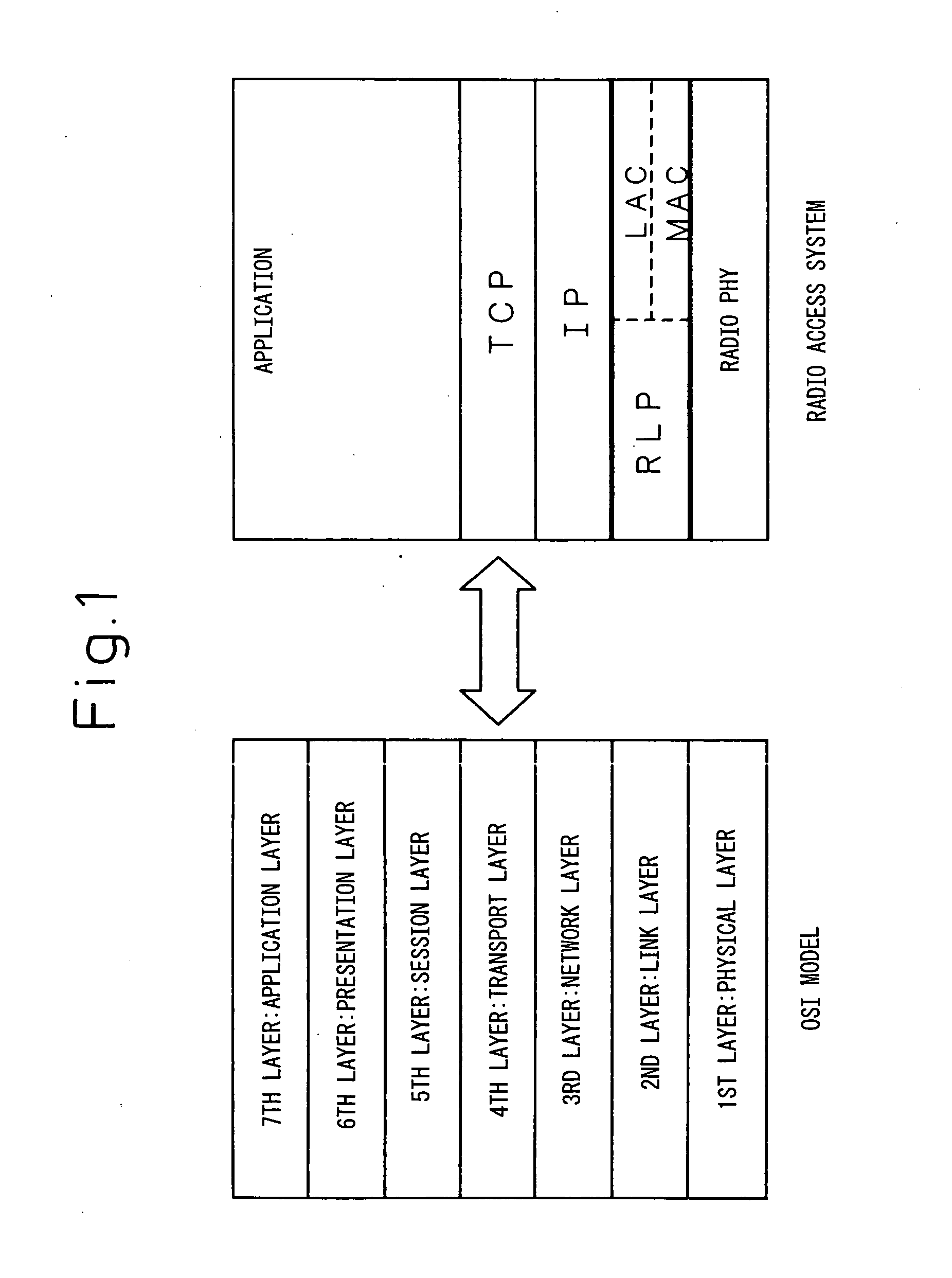
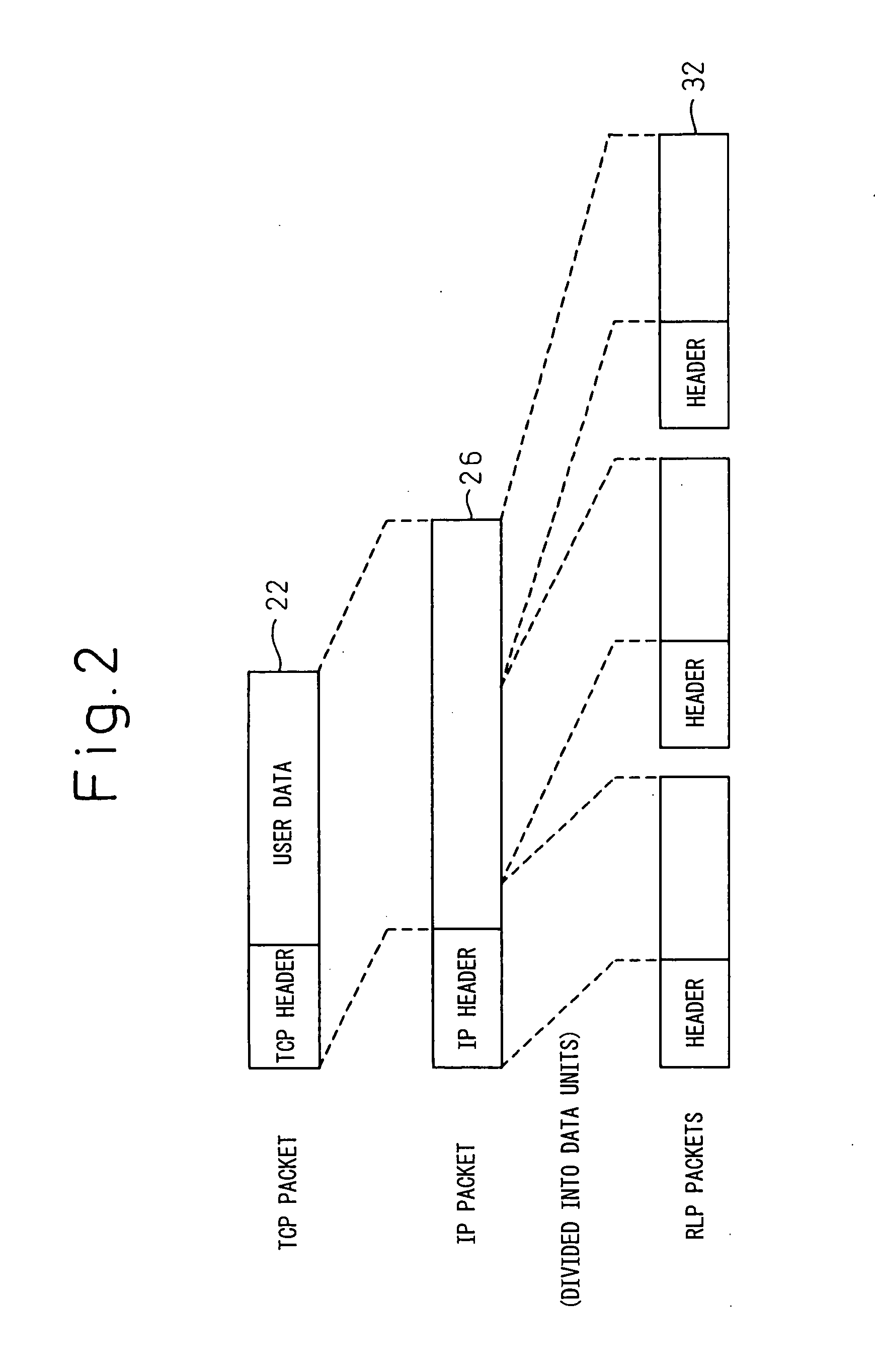
InactiveUS20050169305A1Increase heightNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexCommunication qualityRadio access point
A mobile terminal (10) in a radio access system detects communication quality such as frequency of retransmission, packet error rate, etc. on an RLP-based radio link, and converts the communication quality into a traffic class in IP or a window size in TCP. Based on the thus converted communication quality, flow control is performed at IP or TCP. At a radio access point (12) also, quality information is extracted from an IP header or a TCP header, and the number of packets into which the IP or TCP packet is to be fragmented, retransmission count, etc. are set based on the extracted information.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
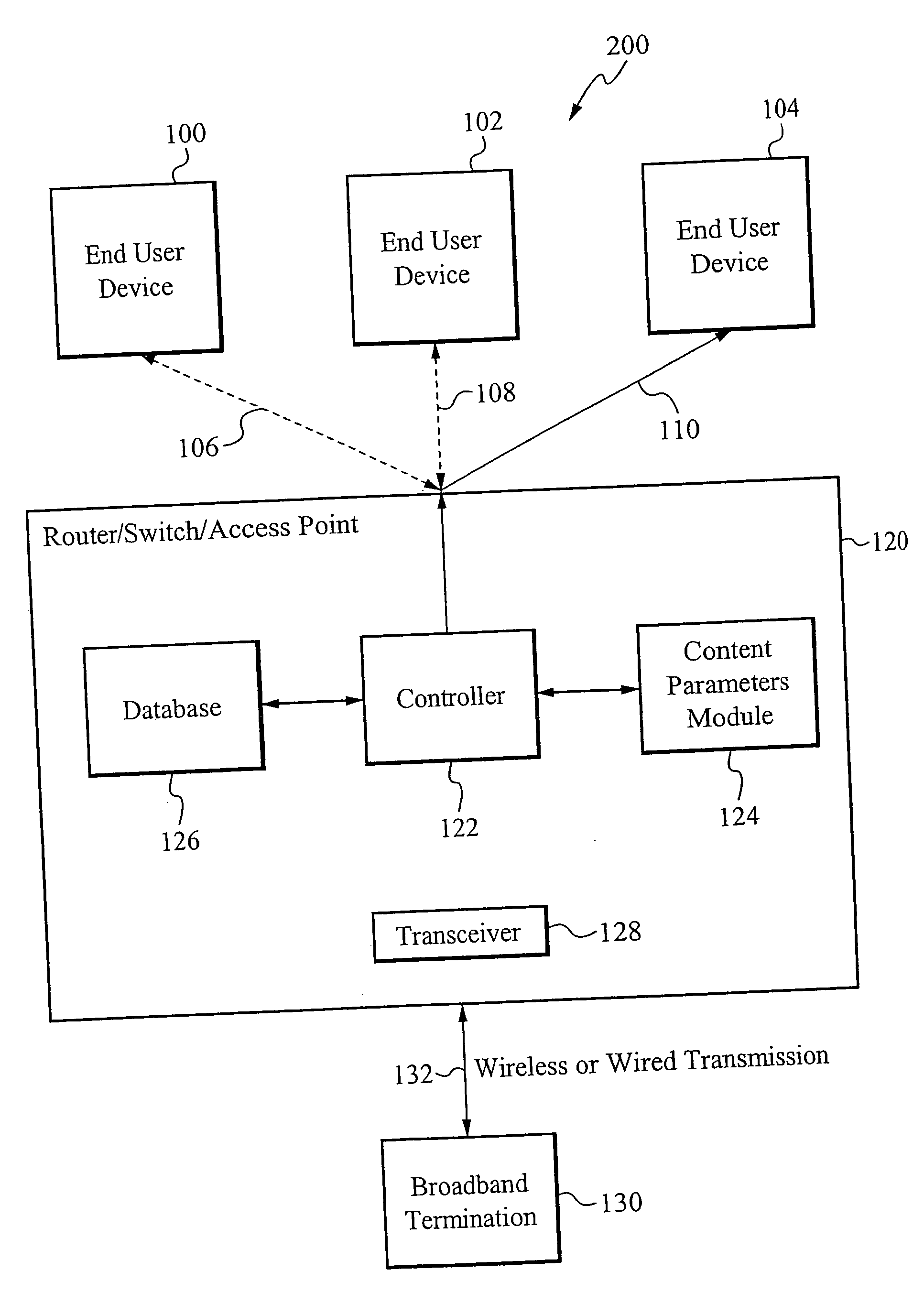
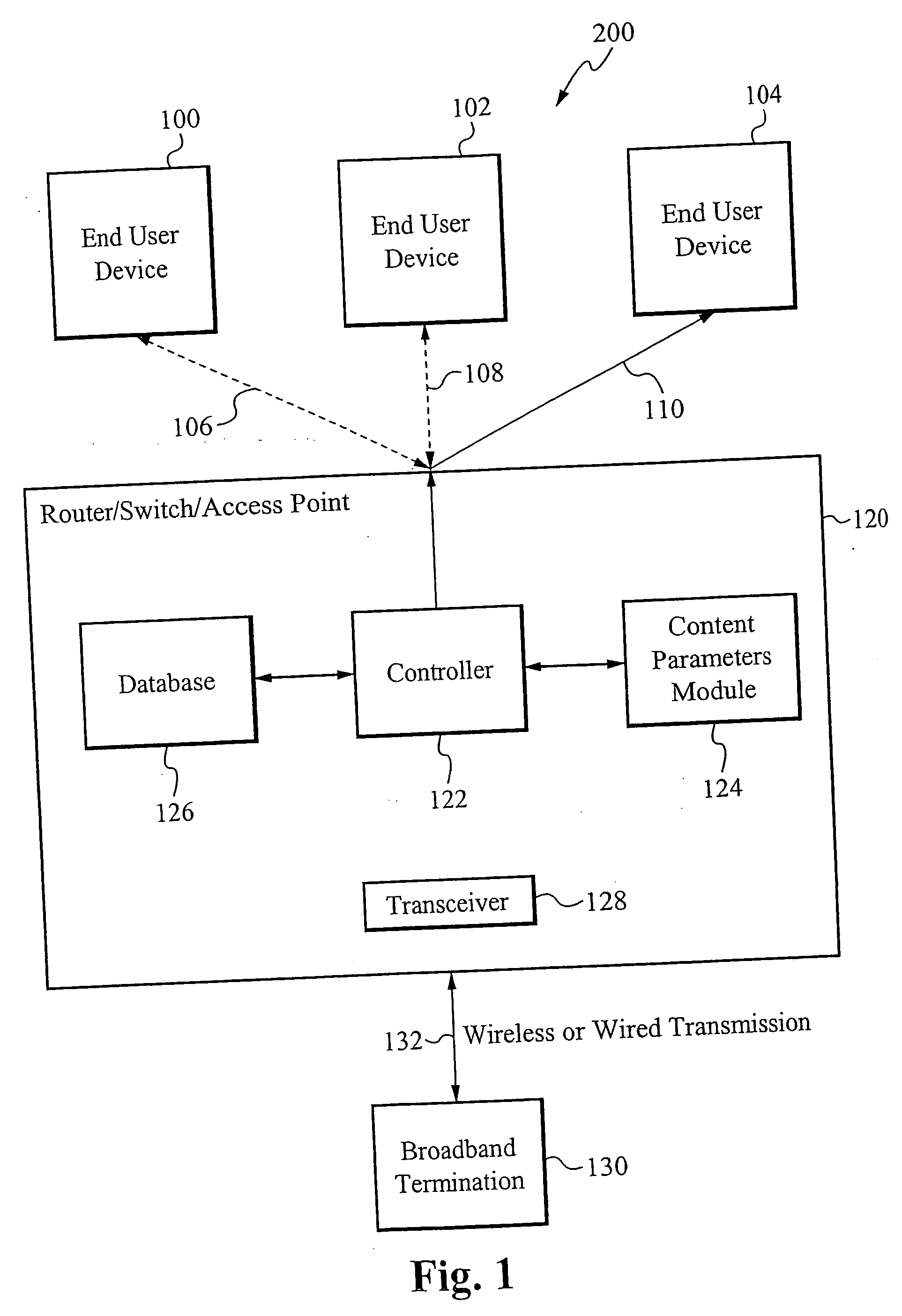
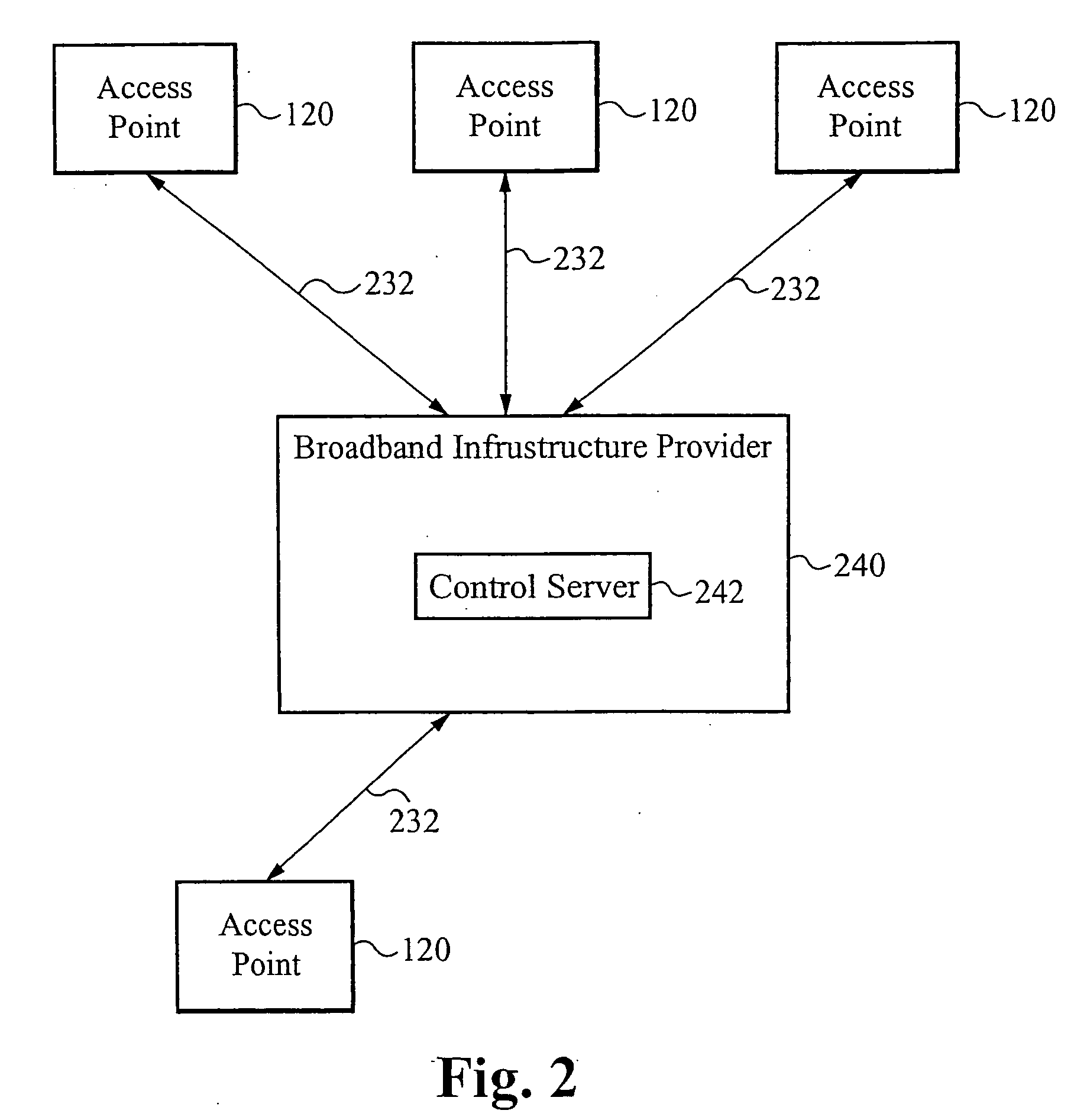
Method of determing broadband content usage within a system
An end user network access point monitors and collects usage statistics associated with all content accessed by the end user devices through the access point. One or more external control servers collect the usage statistics from each access point, thereby compiling macro-level statistics related to content accessed by the end user devices. The one or more external control servers can be co-located with the network equipment of the broadband infrastructure provider, or the one or more external control servers can be independent of the broadband infrastructure.
Owner:VASU NETWORKS CORP
Radio access point testing method and testing apparatus
InactiveUS20050107080A1Transmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringCommunications systemRadio access point
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Radio access point testing method and testing apparatus
InactiveUS7366508B2Transmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringCommunications systemRadio access point
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Access network clusterhead for providing local mobility management of a roaming IPv4 node
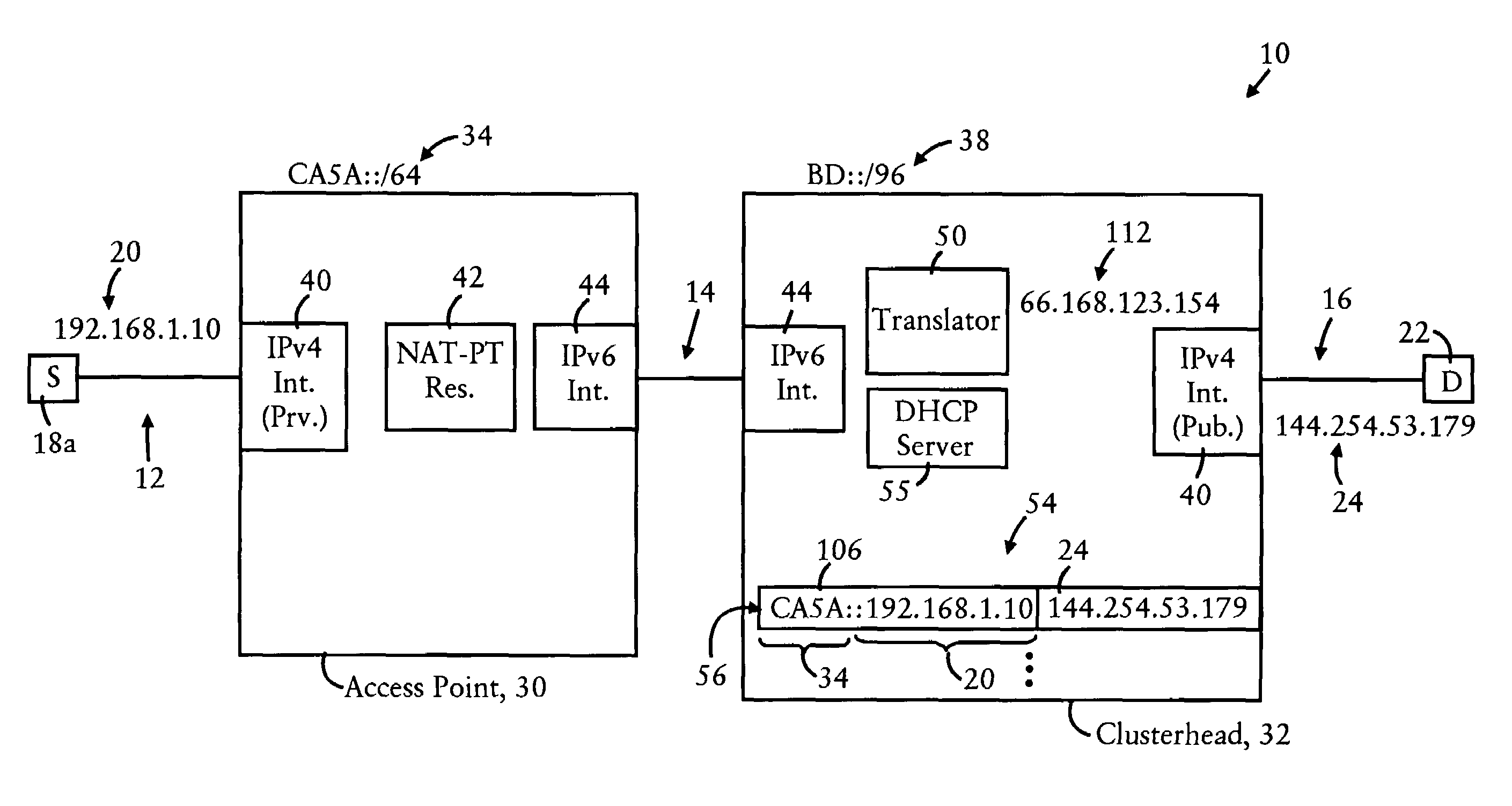
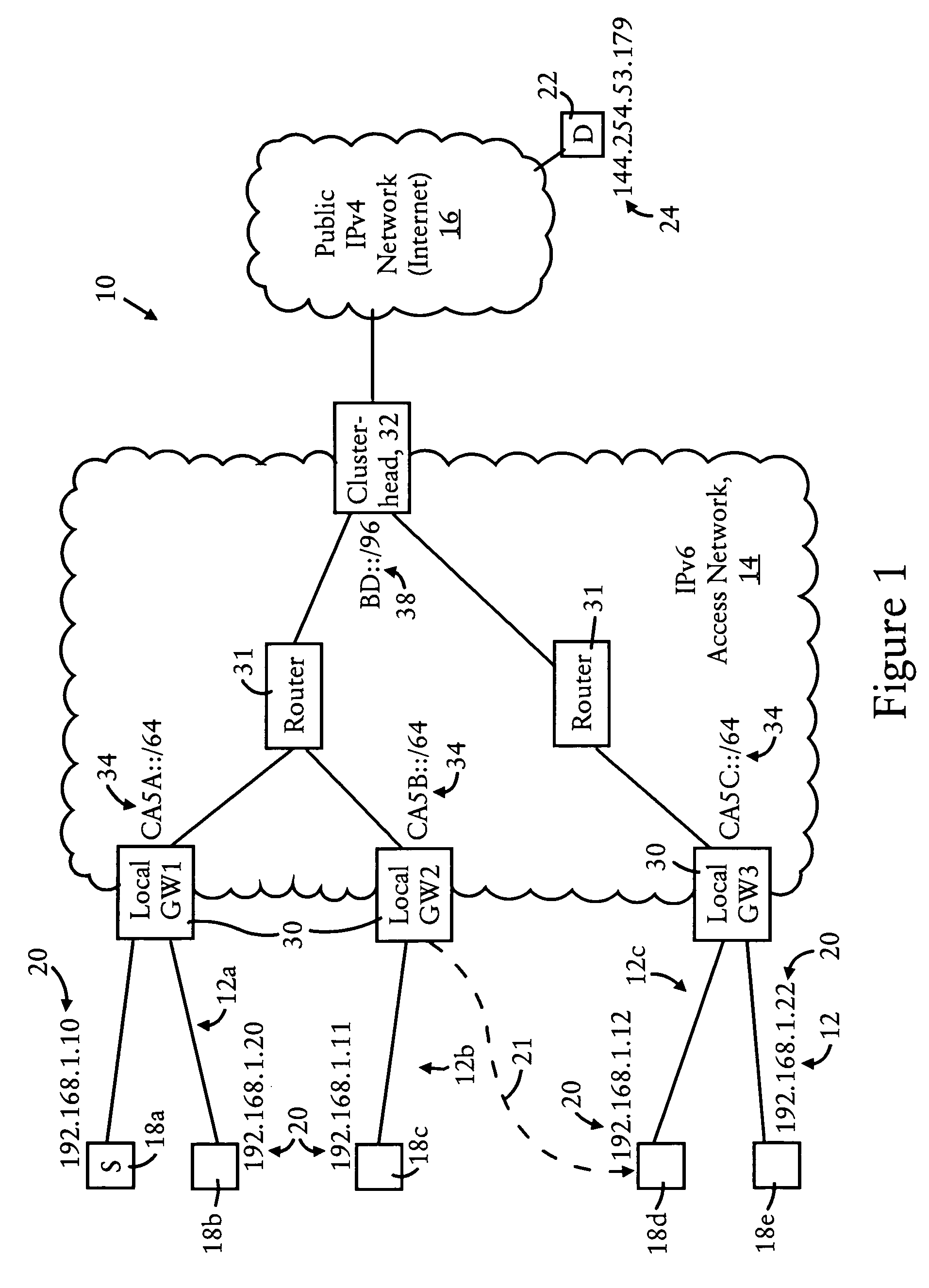
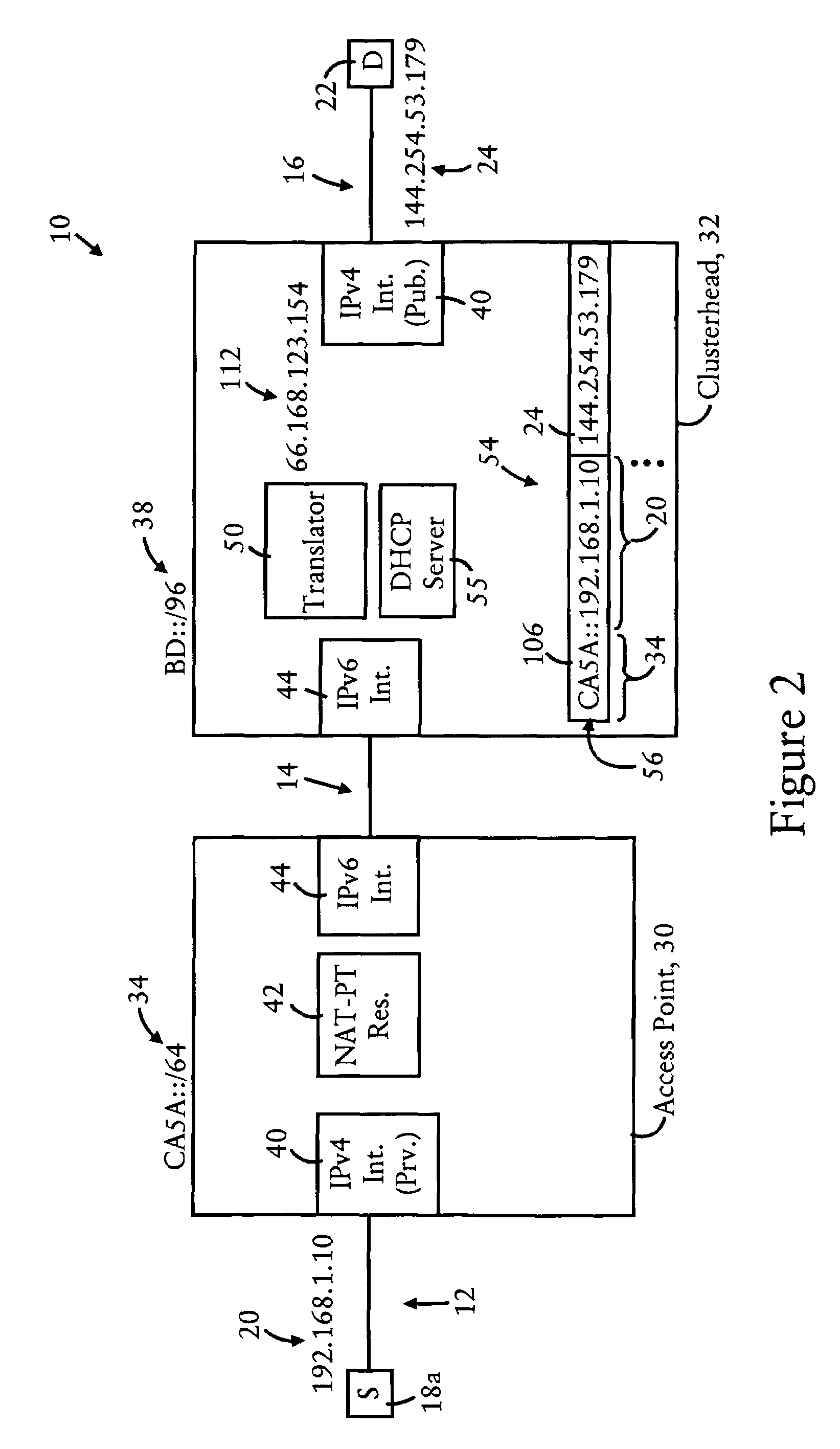
InactiveUS7639686B2Stay connectedTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationAccess networkRadio access point
An IPv4 host is able to maintain connectivity within an access network while moving among access points of the access network, based on receiving a unique assigned IPv4 address from a clusterhead of the access network. Any DHCP request by the IPv4 host is sent via the connecting access point to the clusterhead. The clusterhead, providing connectivity for hosts in the access network to a wide area network based on respective entries, assigns the IPv4 address to the IPv4 host, based on storing an entry including the IPv4 address and an IP-based identifier of the connecting access point, and sends a DHCP response to the IPv4 host via the connecting access point. A second DHCP request from the IPv4 host to a second access point causes the clusterhead to update the entry with the second access point identifier, enabling the IPv4 host to continue use of the assigned IPv4 address.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
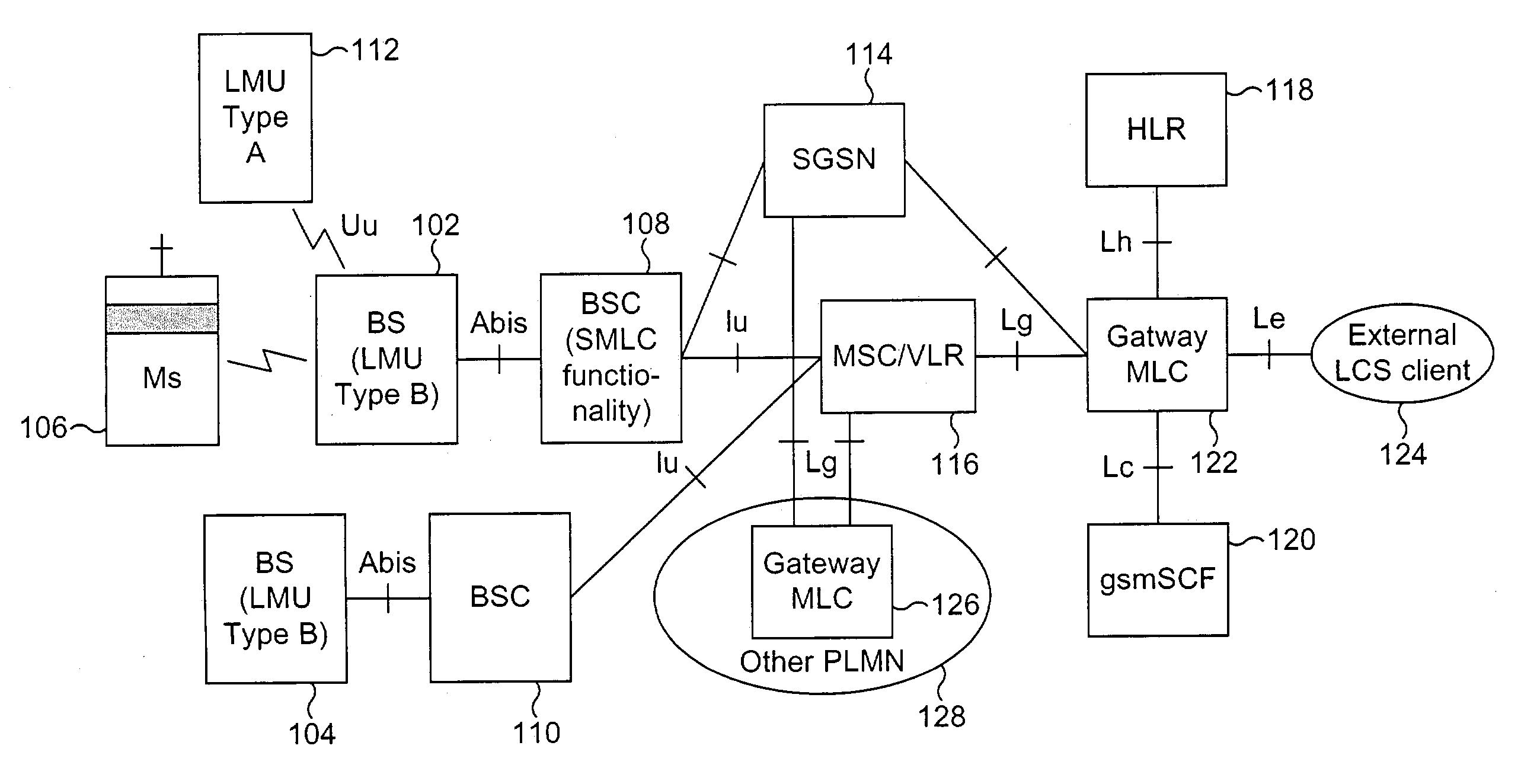
Location services
InactiveUS20040203882A1Huge savingsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesRadio access pointMobile communication systems
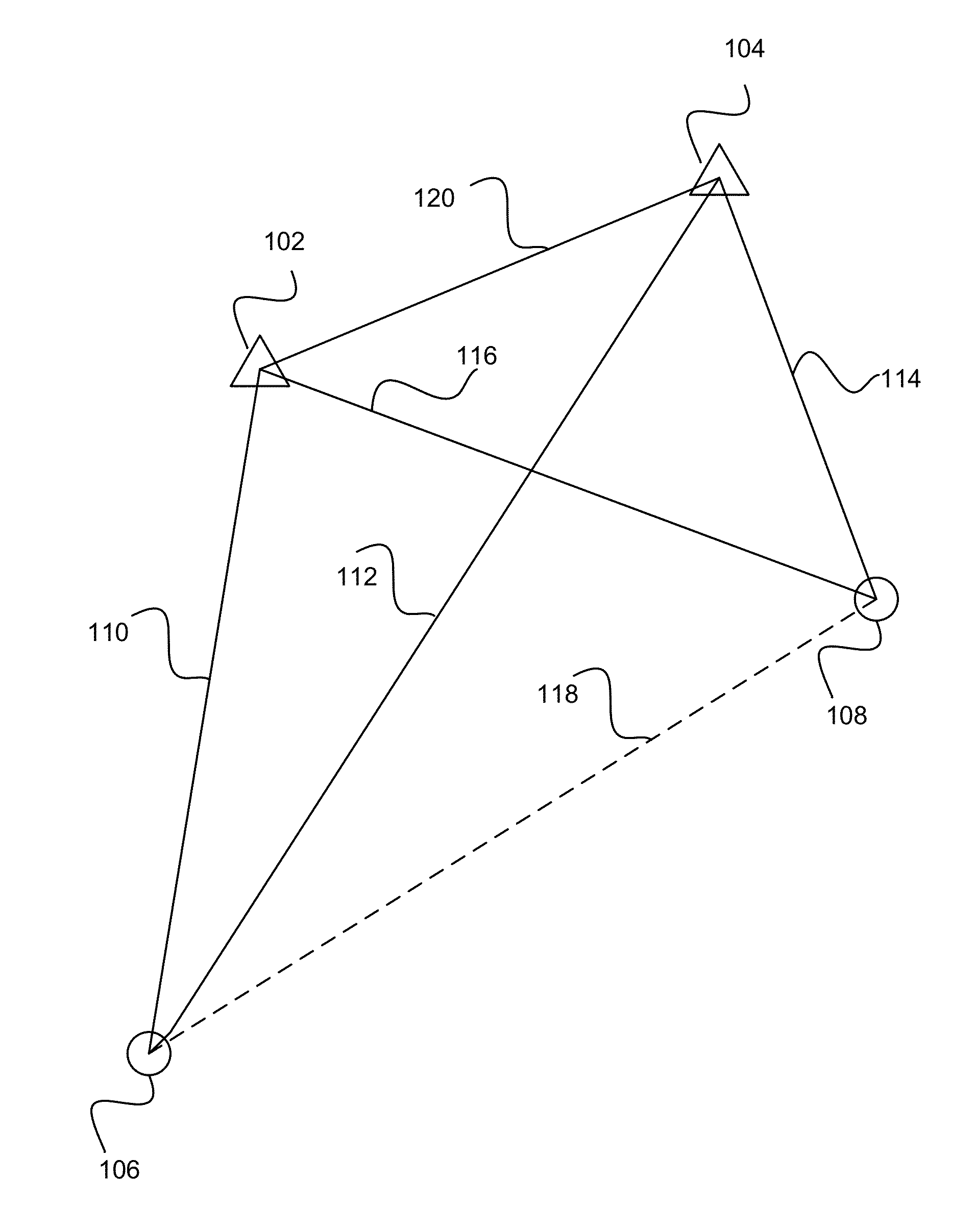
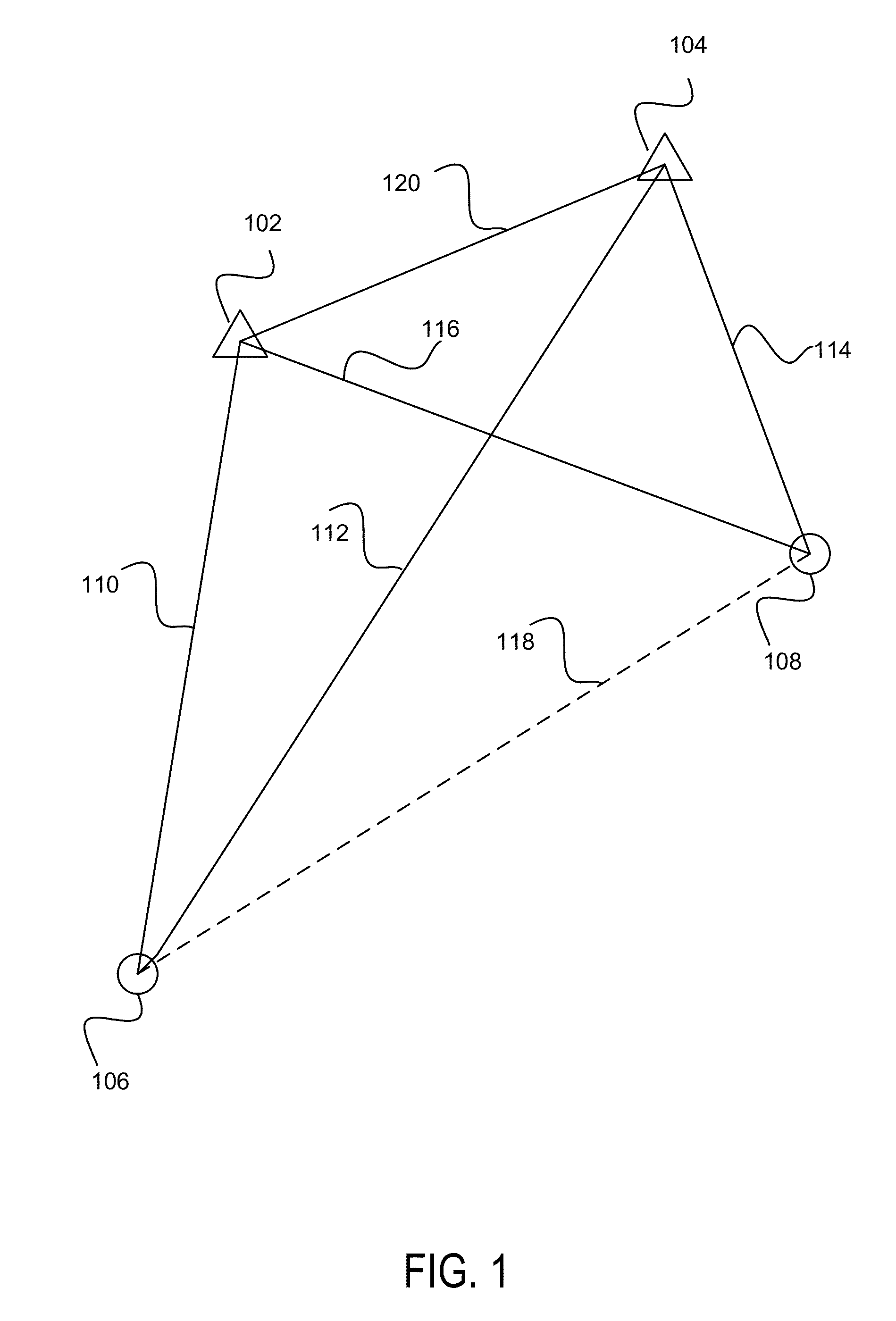
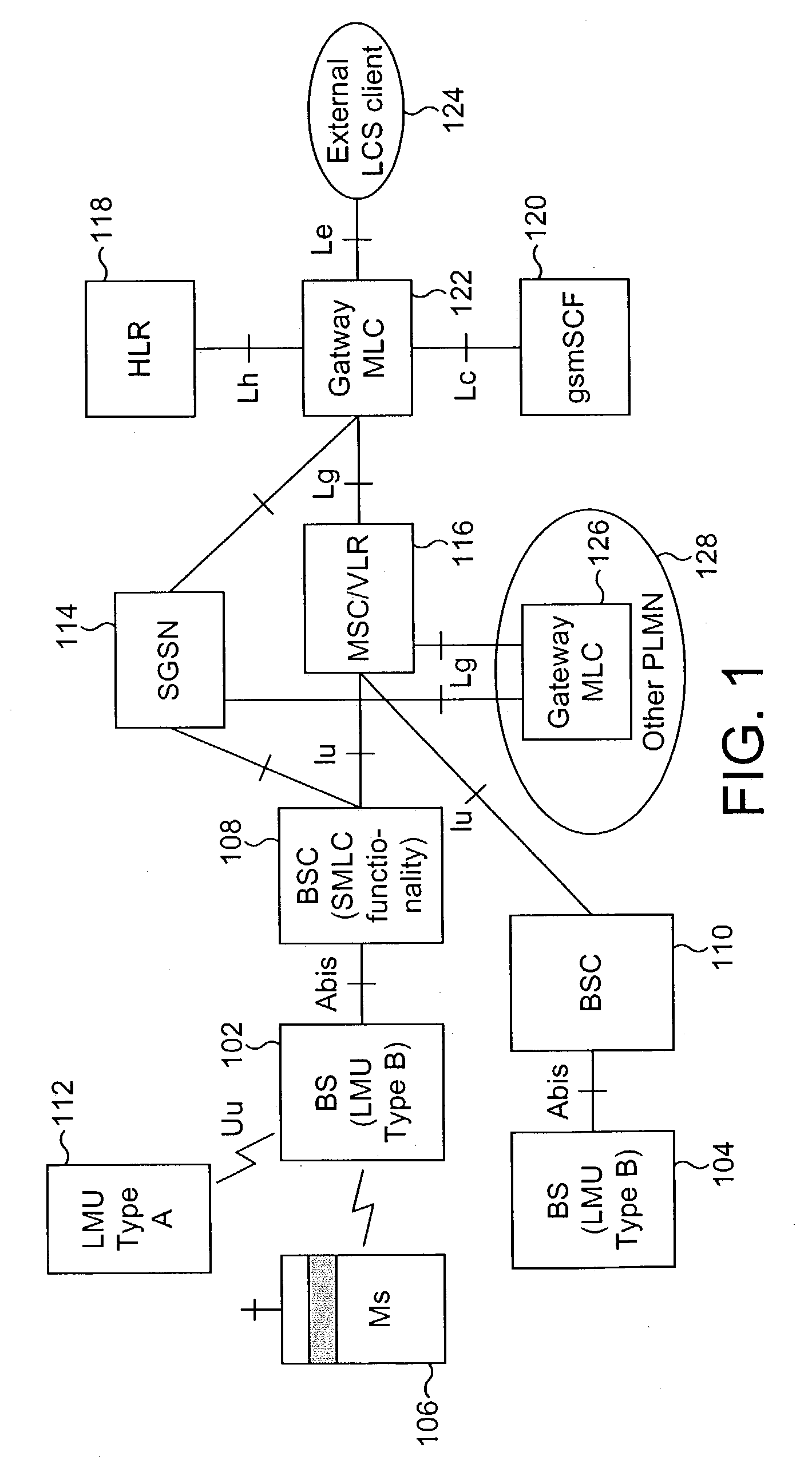
There is disclosed a mobile communication system including a plurality of cells each associated with a plurality of radio access points, and at least one mobile user connected in one cell via a radio access point, the system further including a network element associated with said plurality of cells for maintaining a neighbour list for location position determination of the mobile user, the network element including: means for generating an initial neighbour list, comprising the identity of those radio access points determined to be neighbouring the radio access point with which the mobile user is connected; means for temporarily including a candidate neighbour in the neighbour list, comprising the identity of a radio access point determined to be a potential neighbour of the radio access point with which the mobile user is connected; means for collecting measurement reports for each neighbour in the neighbour list, including the candidate neighbour; means for comparing the measurement reports for each neighbour; and means for adding the candidate neighbour to the neighbour list if measurement reports for the candidate neighbour determine that the candidate neighbour is a neighbour of the radio access point, and thereby automatically maintaining a location services neighbour list for a mobile user.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com