Method for constructing energy-saving type disc array with double discs for fault tolerance
A technology of disk array and construction method, applied in the direction of response error generation, redundant code for error detection, input/output to record carrier, etc., can solve the problem of shortening disk life, wasting energy, high I/O throughput and I/O concurrency utilization and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
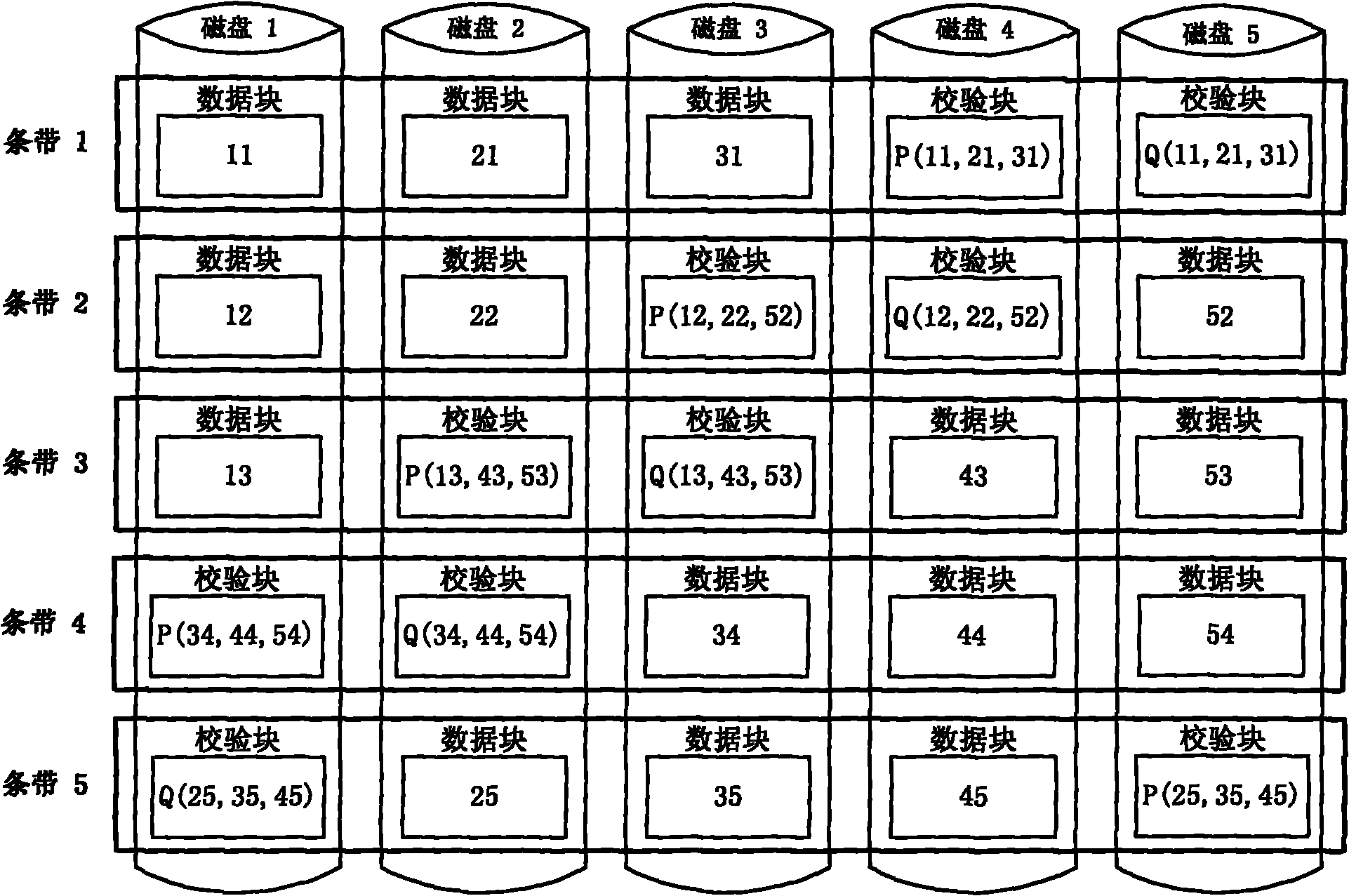
[0119] Example 1: The start address of an access is in the data block 12, and the end address is also in the data block 12.
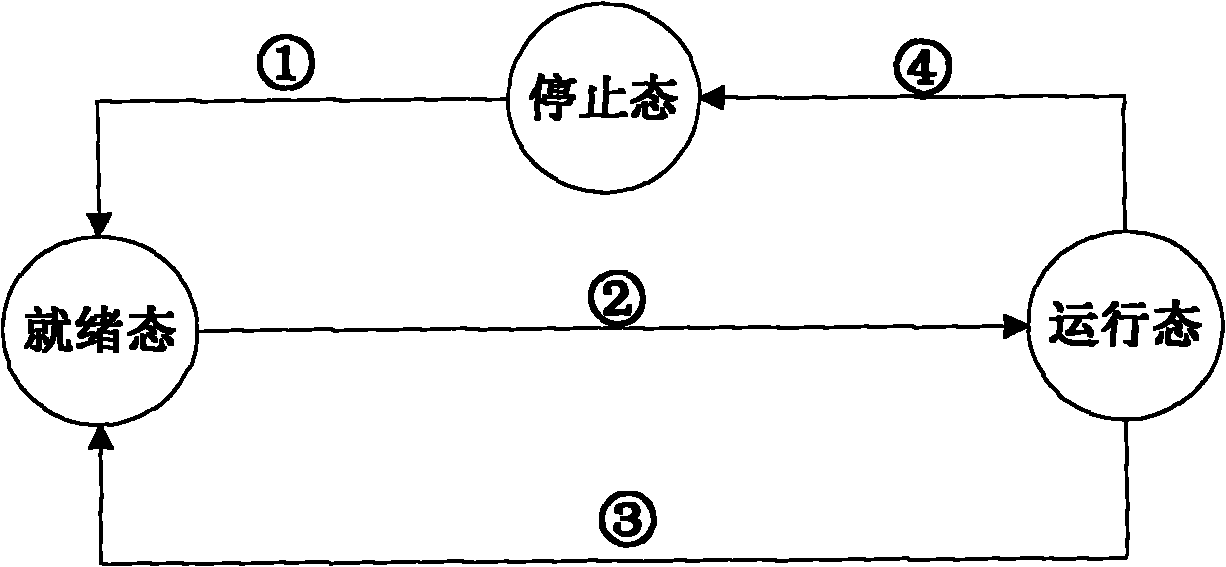
[0120] According to the logical address of the access data, find the data block 12 where it is located. The data block 12 is on disk 1, and the parity blocks located in the same stripe as data block 12 are on disk 3 and disk 4. If disks 1, 3 and 4 are located 4 is in the stop state, then it goes to the ready state; when starting to read and write data on disks 1, 3 and 4, the disks 1, 3 and 4 change from the ready state to the running state; since this access ends in data block 12, After this access is over, disks 1, 3, and 4 change from the running state to the ready state, and then exit this scheduling.
example 2
[0121] Example 2: The start address of an access is in data block 13, and the end address is in data block 21.
[0122] According to the logical address of the access data, find the data block 13 where it is located. The data block 13 is on disk 1, and the parity blocks located in the same stripe as data block 13 are on disk 2 and disk 3. If disk 1, 2, 3 is in the stop state, then go to the ready state; when starting to read and write data on disks 1, 2, and 3, the disks 1, 2, and 3 change from the ready state to the running state; since this access ends in data block 21, At time t before the end of the access to the data block 13, determine the working state of the disk 2 where the adjacent data block 21 of the data block 13 is located, and the working state of the disks 4 and 5 where the data block 21 and the stripe check block are located. Since the disk 2 is in the running state, Add 1 to its semaphore to get Sem 2 = 1, disks 4 and 5 are in the stopped state, so it turns t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com