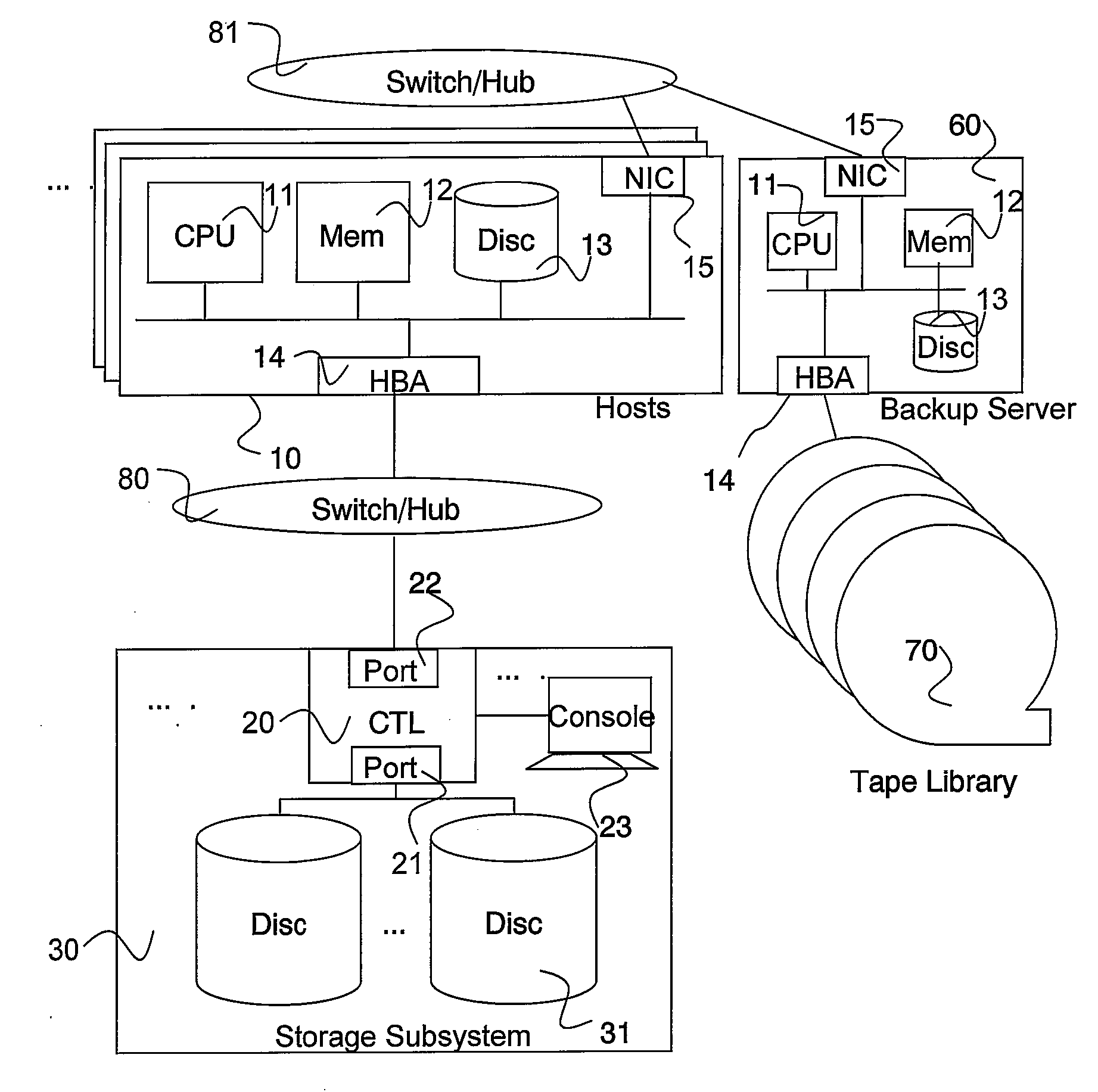
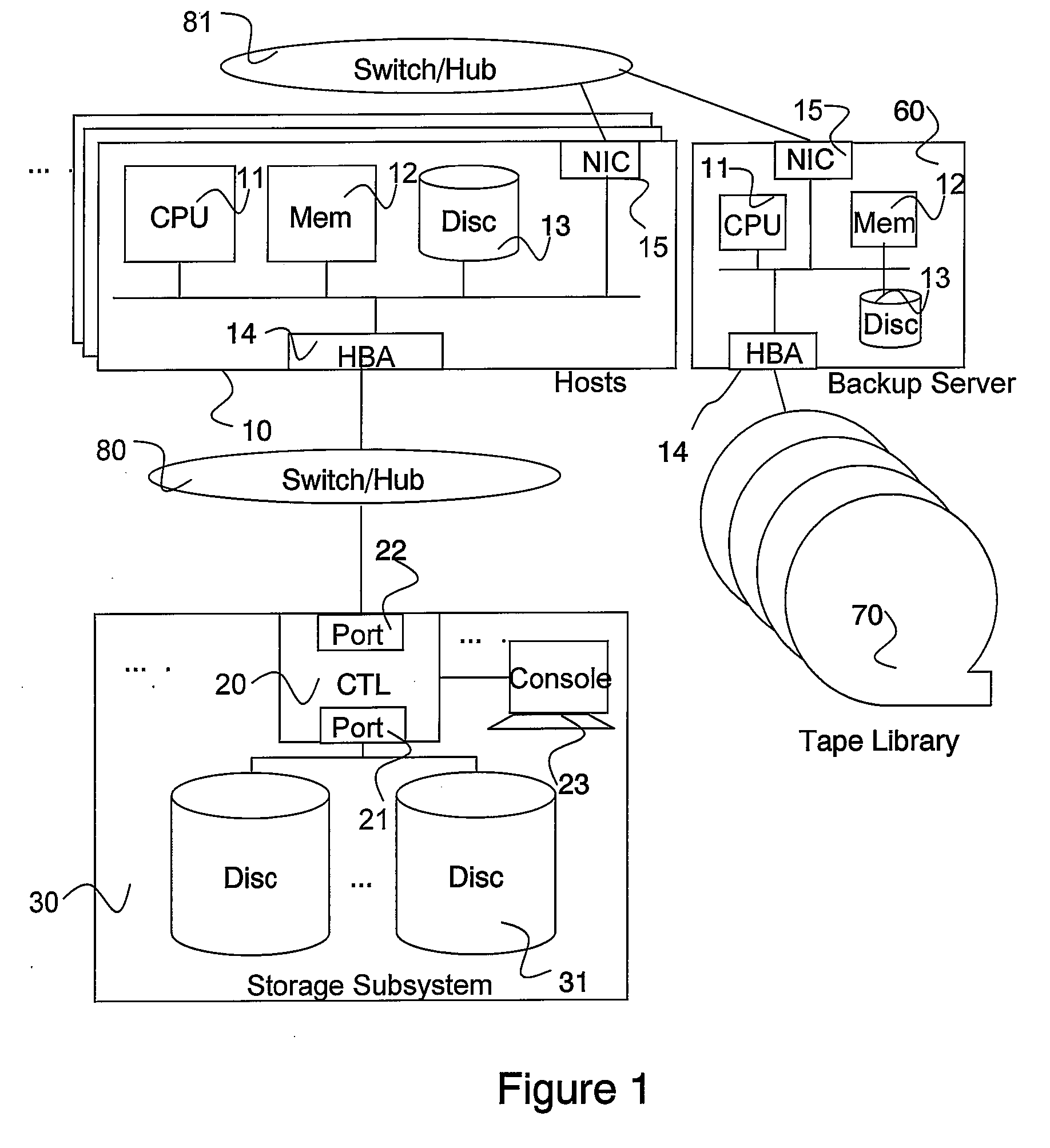
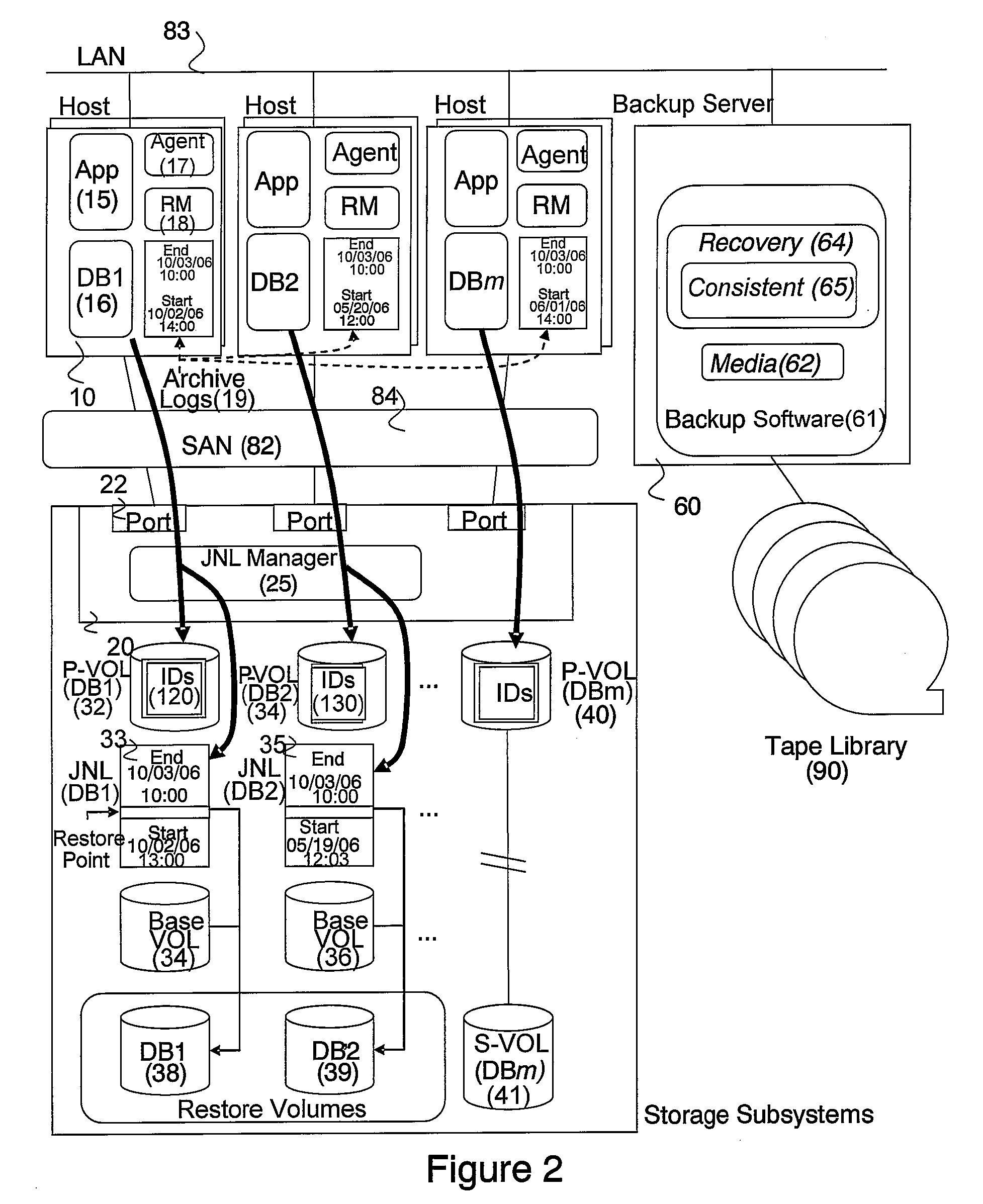
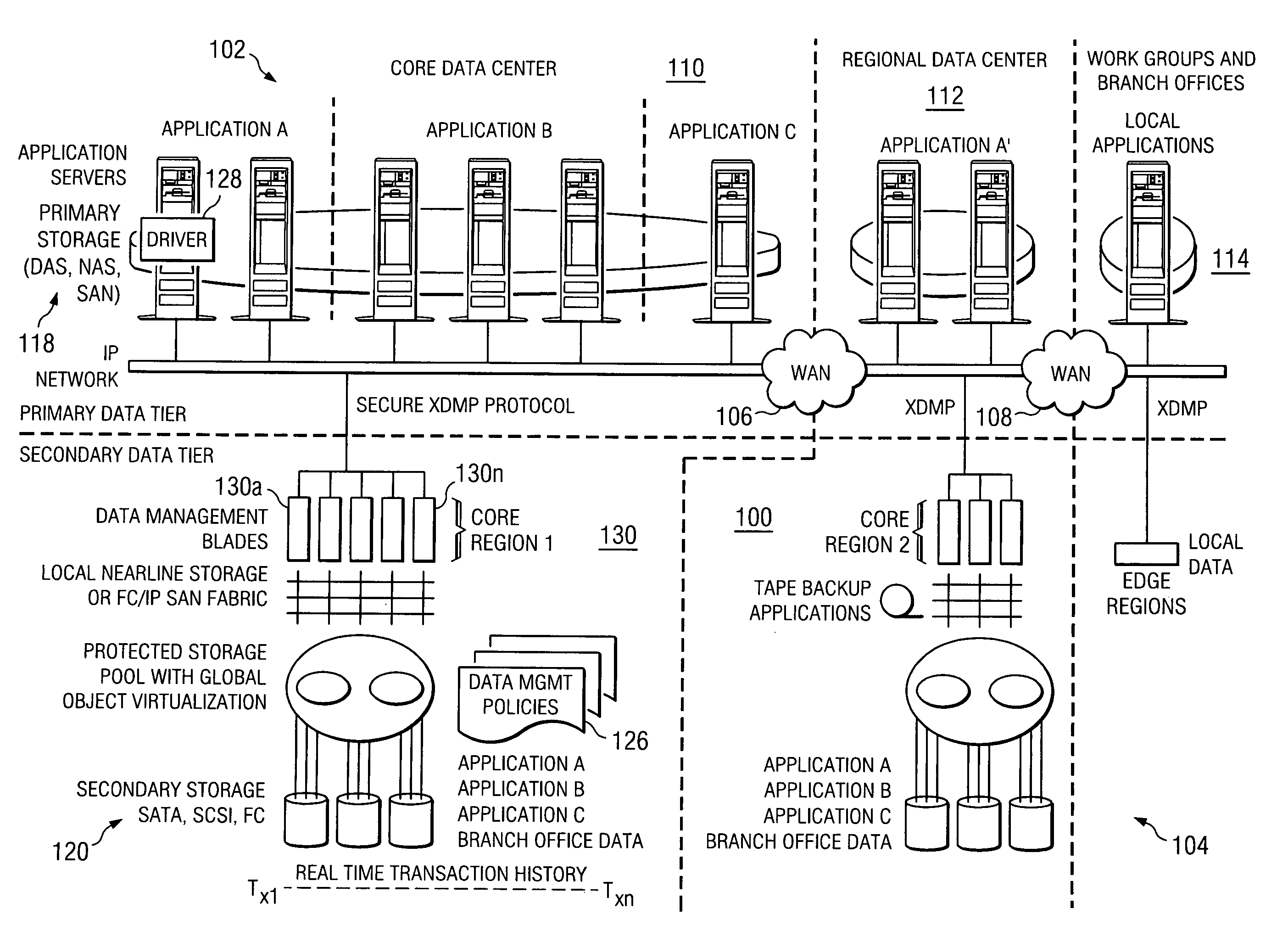
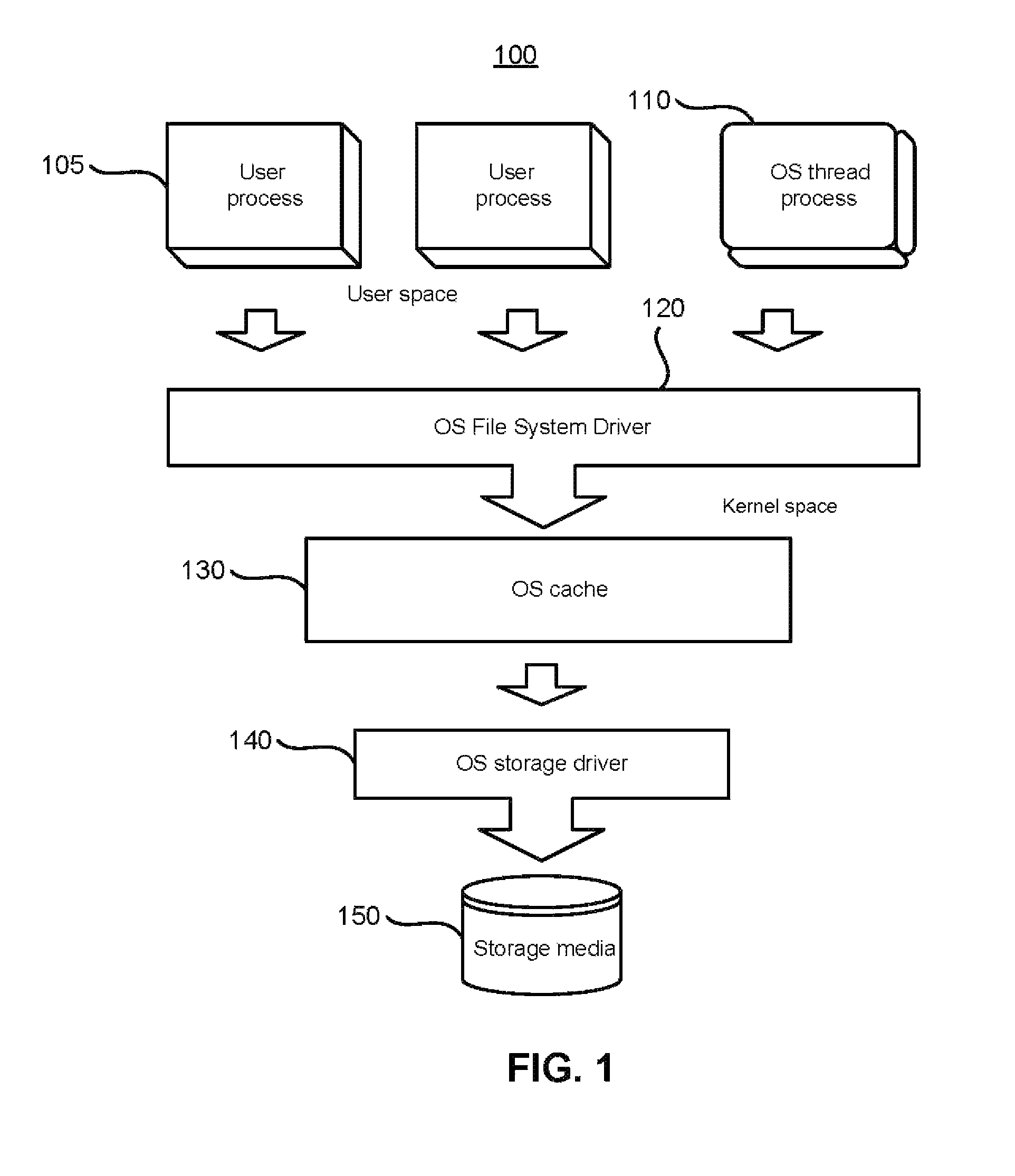
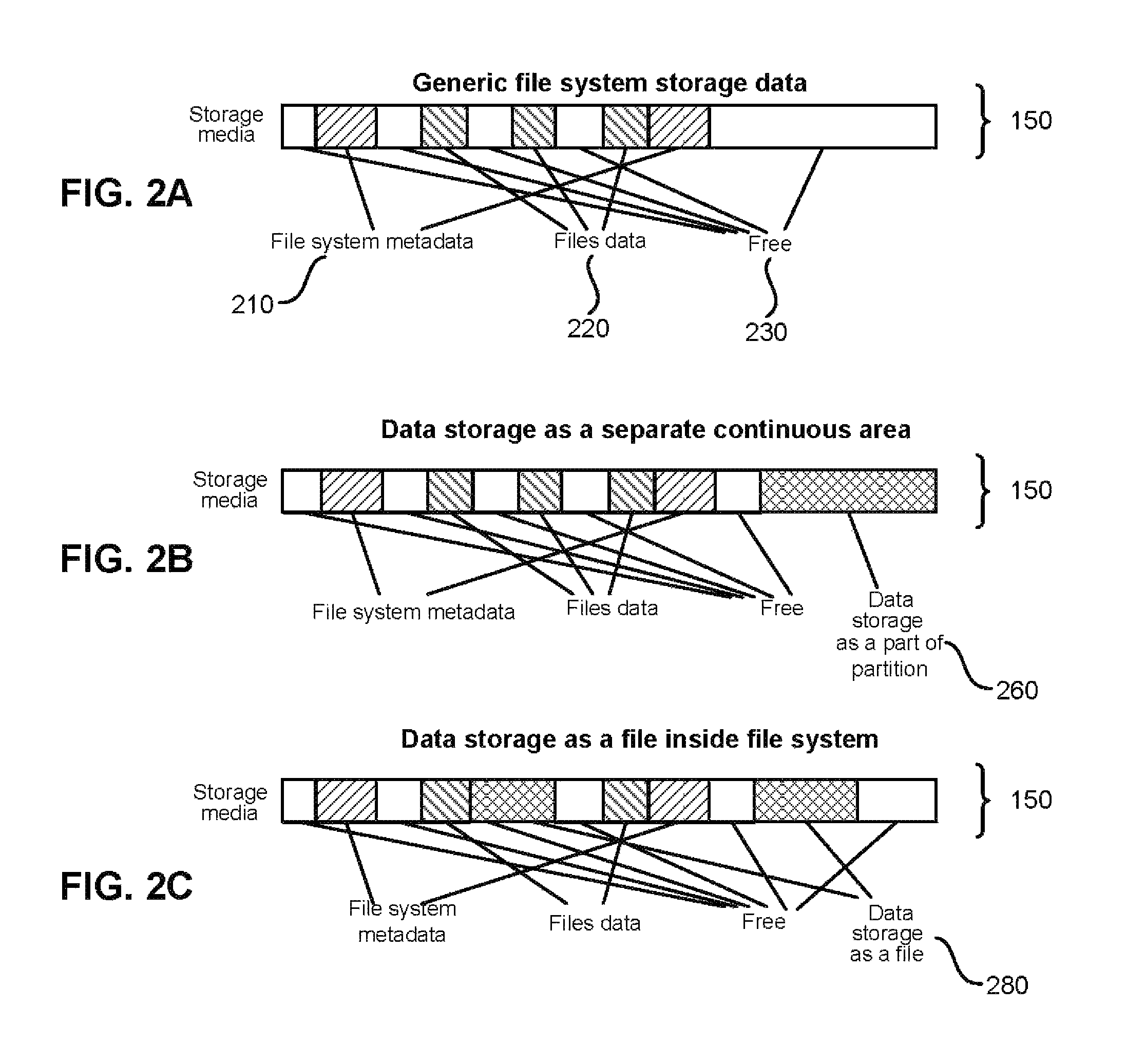
Patents
Literature
203 results about "Continuous data protection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Continuous data protection (CDP), also called continuous backup or real-time backup, refers to backup of computer data by automatically saving a copy of every change made to that data, essentially capturing every version of the data that the user saves. In its true form it allows the user or administrator to restore data to any point in time. The technique was patented by British entrepreneur Pete Malcolm in 1989 as "a backup system in which a copy [editor's emphasis] of every change made to a storage medium is recorded as the change occurs [editor's emphasis]."
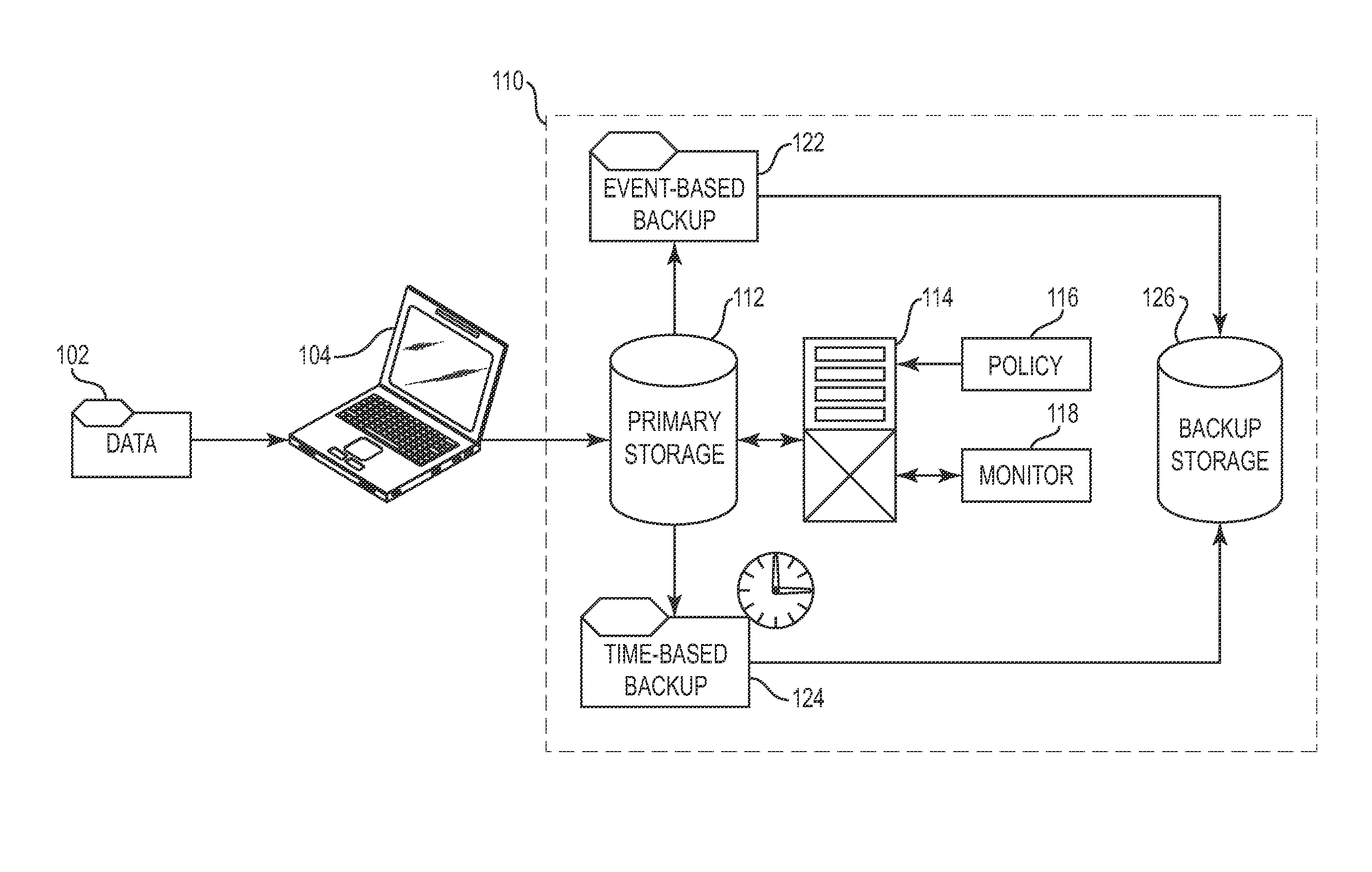
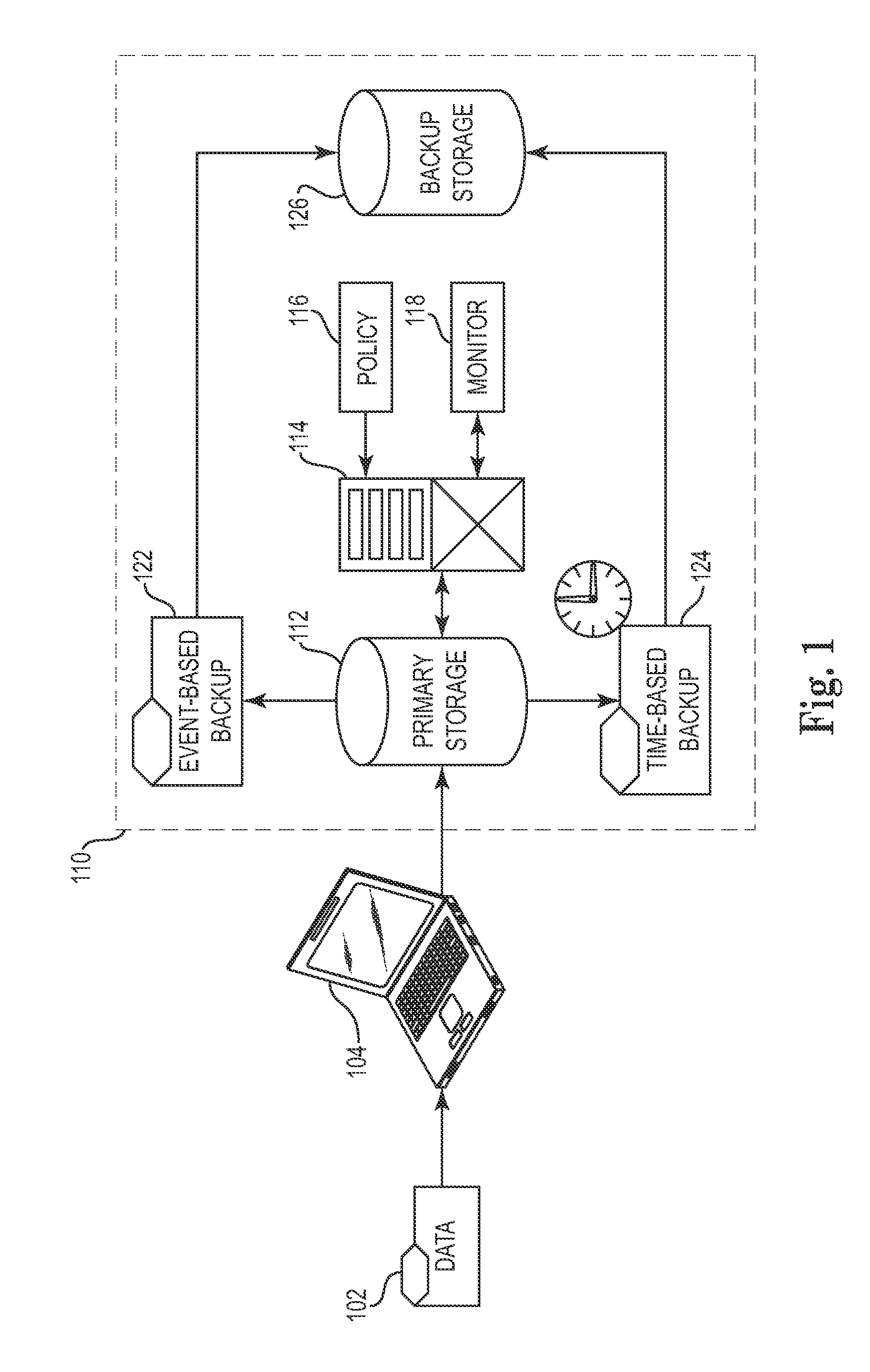
Automated and self-adjusting data protection driven by business and data activity events
InactiveUS20120089572A1Faster and more efficientMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionIncremental backupDatabase
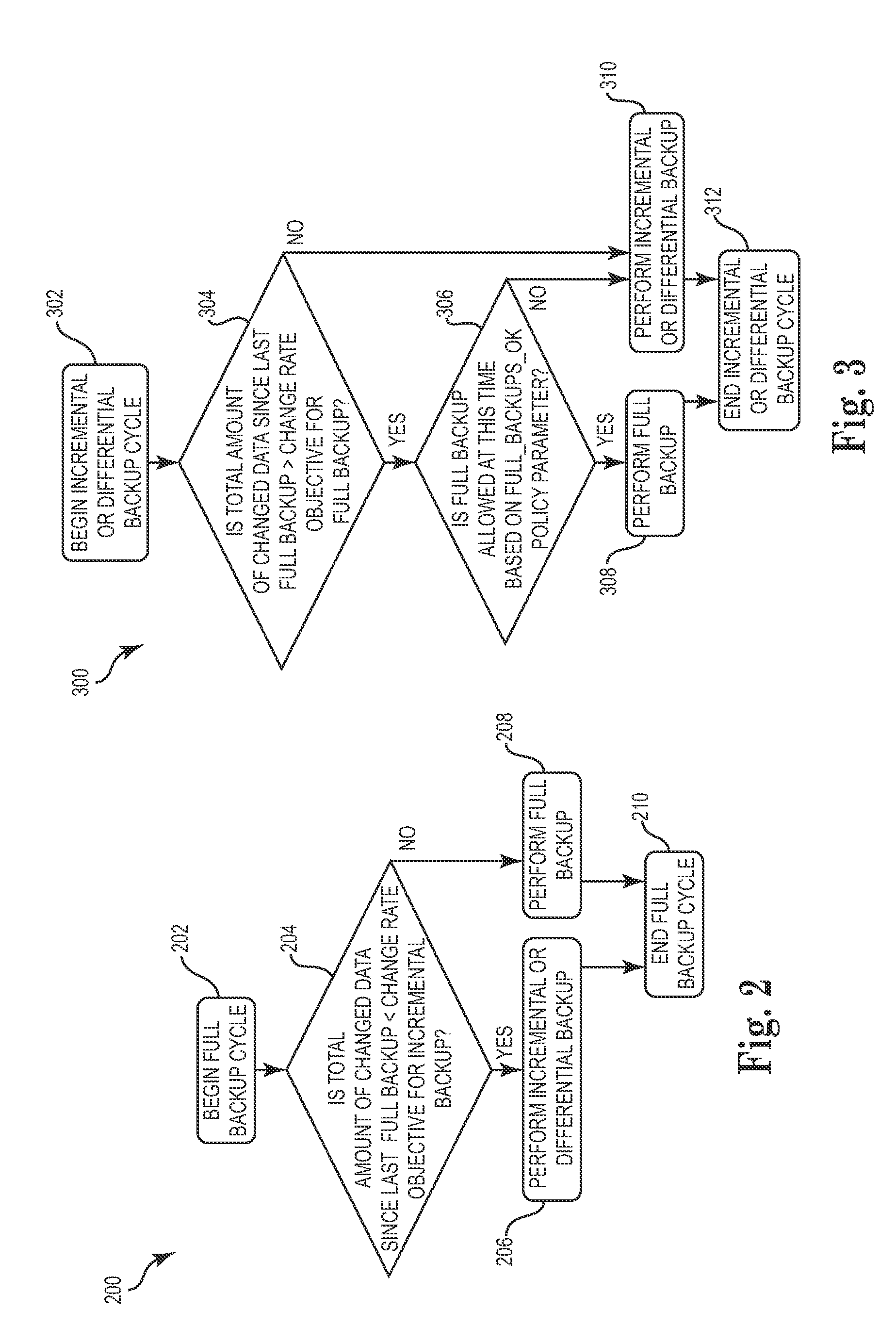
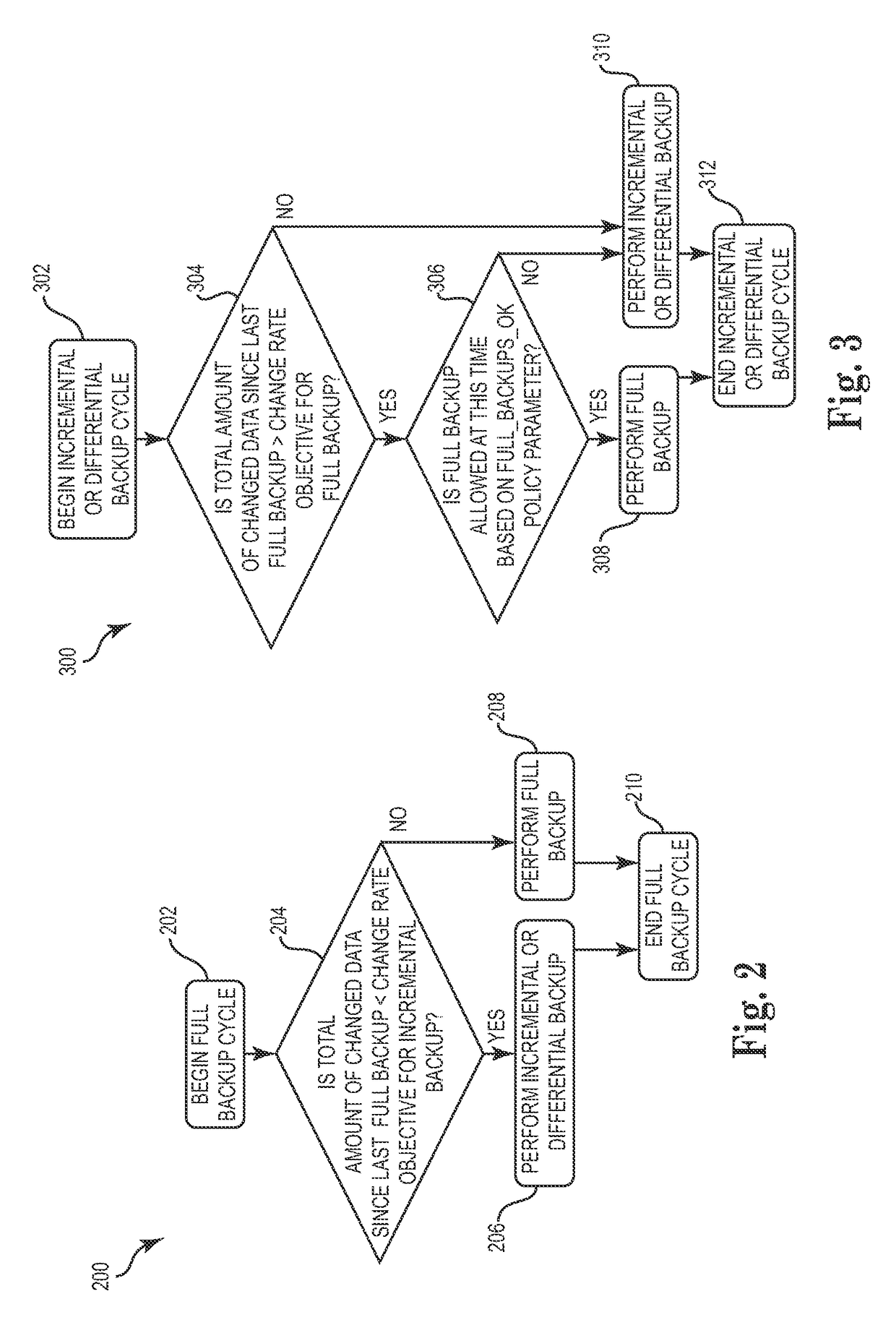
Techniques for adjusting the frequency of data backups and initiating event-driven backups in a storage system are disclosed herein. In one embodiment, a self-adjusting backup frequency, known as a “Change Rate Objective,” is defined to conduct or delay backups for one or more volumes in the storage system on the basis of an associated policy value. The Change Rate Objective may be tied to one or more business or data activity events, such as the amount and type of data changes since a last backup. The storage system may also be tailored to conduct or delay full or incremental backups on the basis of a Change Rate Objective that measures whether a full or incremental or differential backup is more appropriate. Various data or system failures, or data or business events may also be used to adjust the retention periods of continuous data protection (CDP) data and delay a rollup of CDP data.
Owner:IBM CORP
Management interface for a system that provides automated, real-time, continuous data protection
ActiveUS20060101384A1Digital data information retrievalError detection/correctionDisplay deviceContent Time
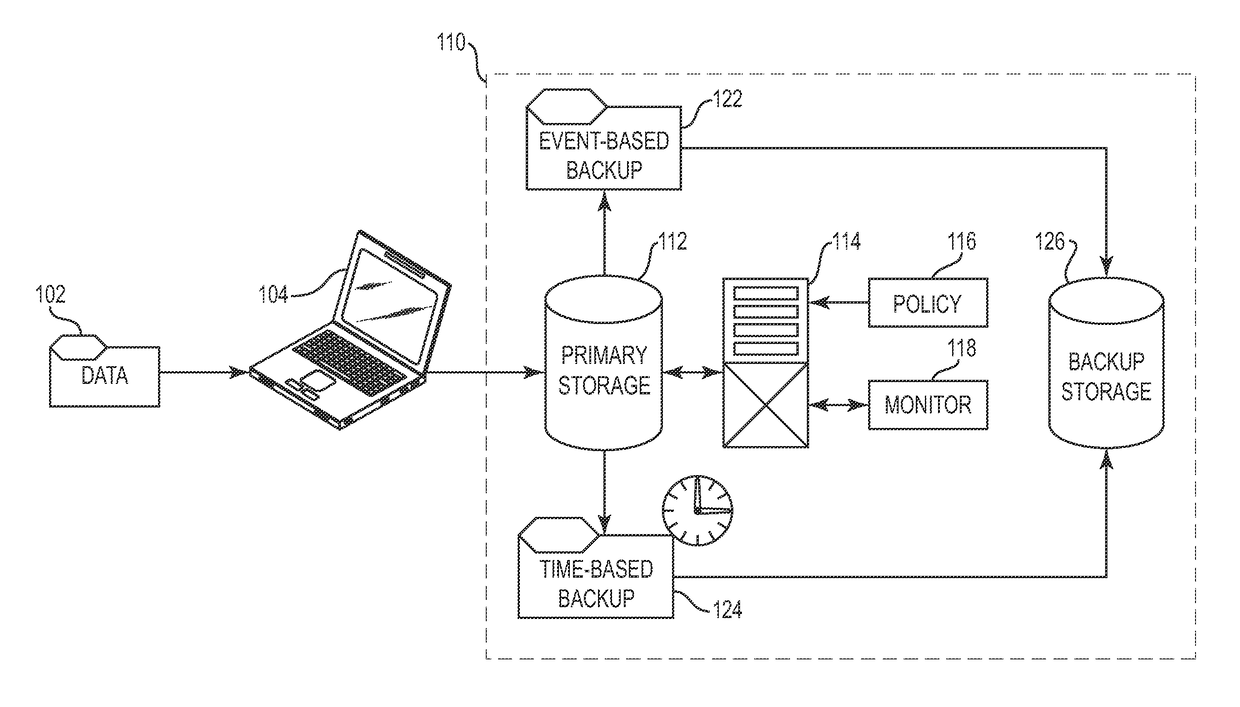
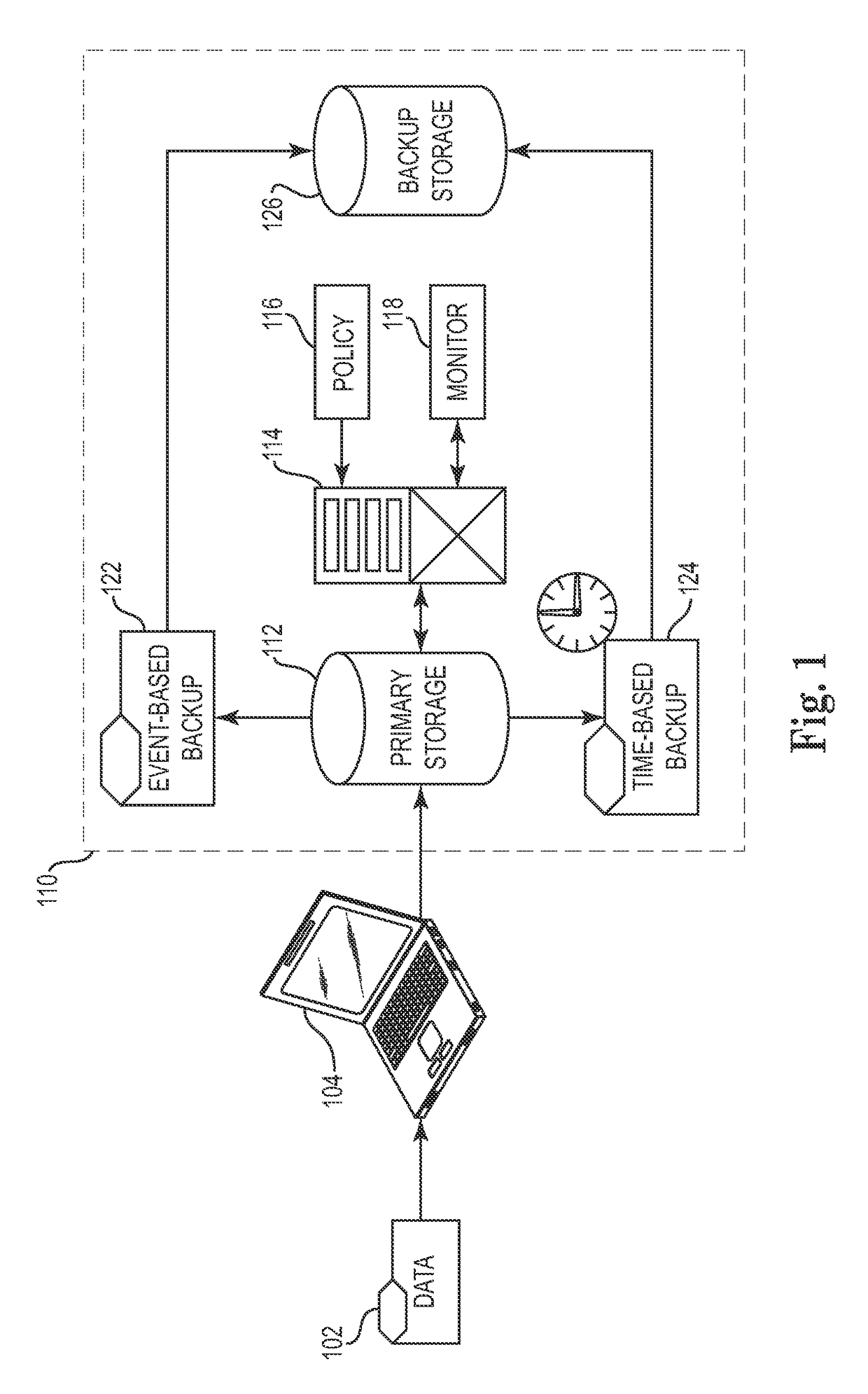
A data management system that protects data into a continuous object store includes a management interface having a time control. The time control allows an administrator to specify a “past” time, such as a single point or range. When the time control is set to a single point, a hierarchical display of data appears on a display exactly as the data existed in the system at that moment in the past. Preferably, the visualization includes both the structure of the hierarchy (e.g., the identity of the directories, their files, databases, and the like) and also the contents of the data objects themselves (i.e., what was in the files and databases). The time control enables the management interface to operate within a history mode in which the display provides a visual representation of a “virtual” point in time in the past during which the data management system has been operative to provide the data protection service. In addition, the management interface can be toggled to operate in a real-time mode, which provides an active view of the system data as it changes in real-time, typically driven by changes to primary storage. This real-time mode provides the user with the ability to view changes that occur to a set of data currently visible on the display screen. The interface also allows an administrator to specify and manage policy including, without limitation, how long data is retained in the management system. A policy engine enables the user to assert “temporal-based” policy over data objects.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
Automated and self-adjusting data protection driven by business and data activity events
InactiveUS9632875B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsRetention periodSystem failure
Techniques for adjusting the frequency of data backups and initiating event-driven backups in a storage system are disclosed herein. In one embodiment, a self-adjusting backup frequency, known as a “Change Rate Objective,” is defined to conduct or delay backups for one or more volumes in the storage system on the basis of an associated policy value. The Change Rate Objective may be tied to one or more business or data activity events, such as the amount and type of data changes since a last backup. The storage system may also be tailored to conduct or delay full or incremental backups on the basis of a Change Rate Objective that measures whether a full or incremental or differential backup is more appropriate. Various data or system failures, or data or business events may also be used to adjust the retention periods of continuous data protection (CDP) data and delay a rollup of CDP data.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
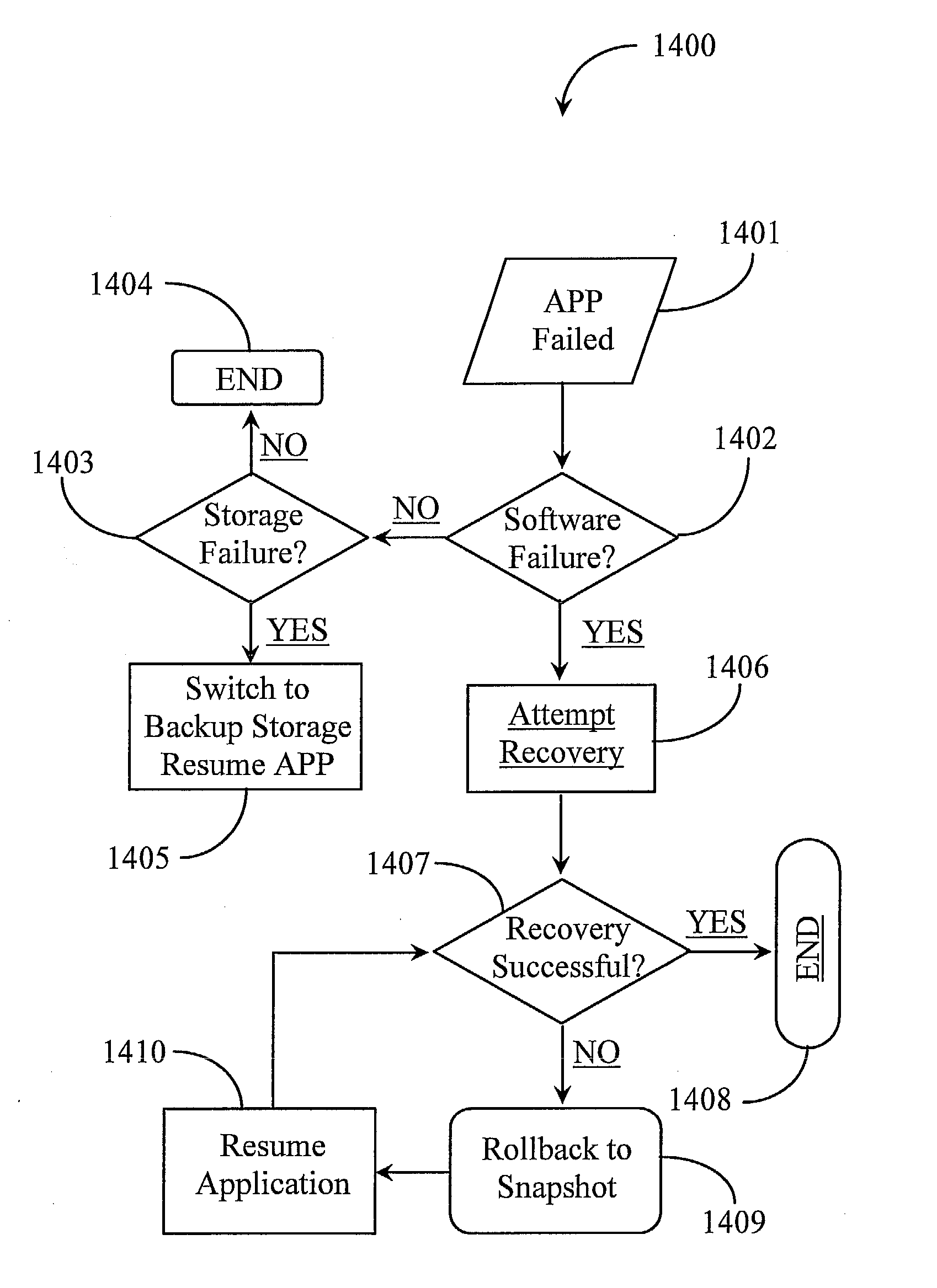
Method and system for automated, no downtime, real-time, continuous data protection
ActiveUS20050262377A1Easy to optimizeError detection/correctionGroup 6/16 element organic compoundsData streamFinite-state machine
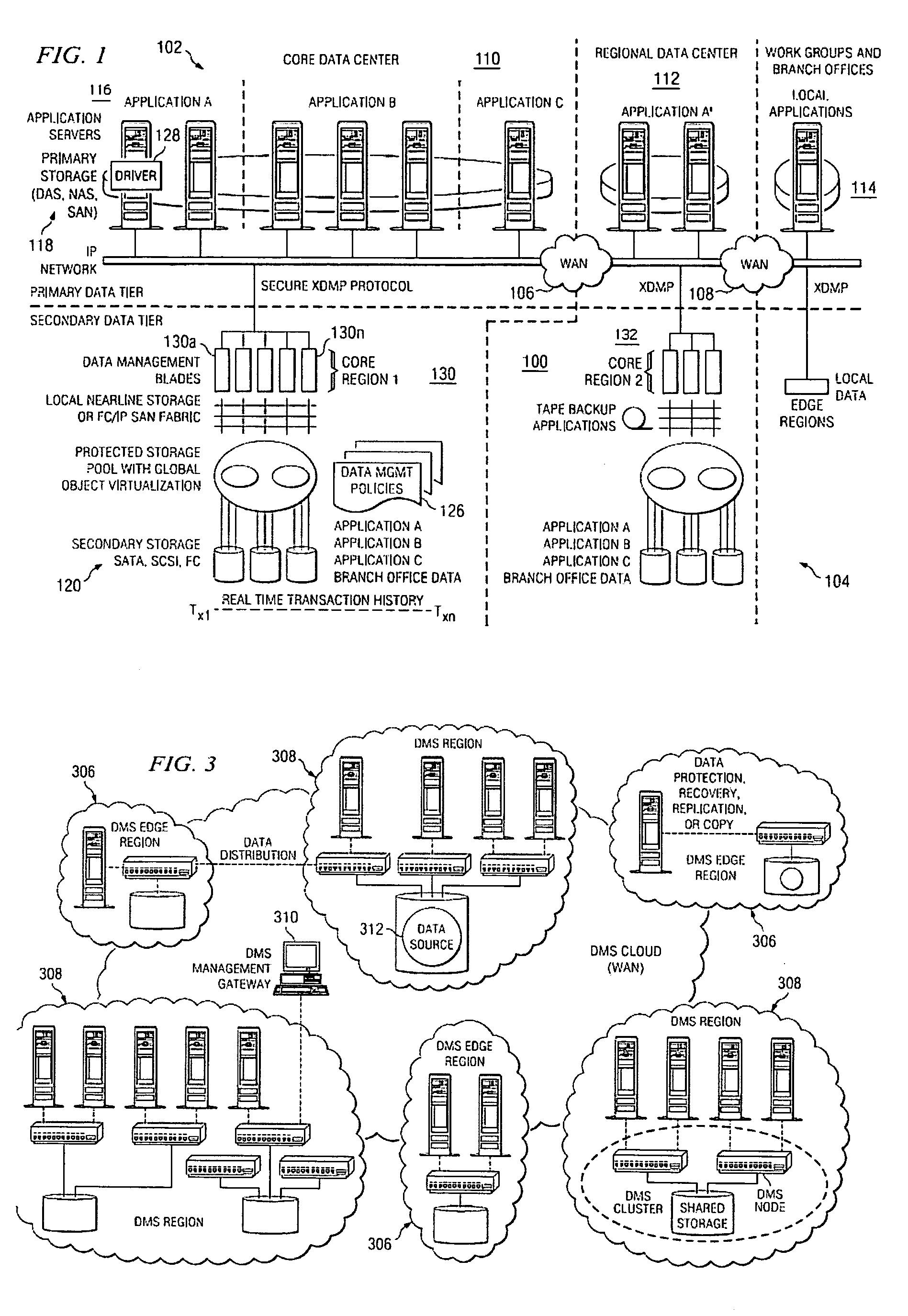
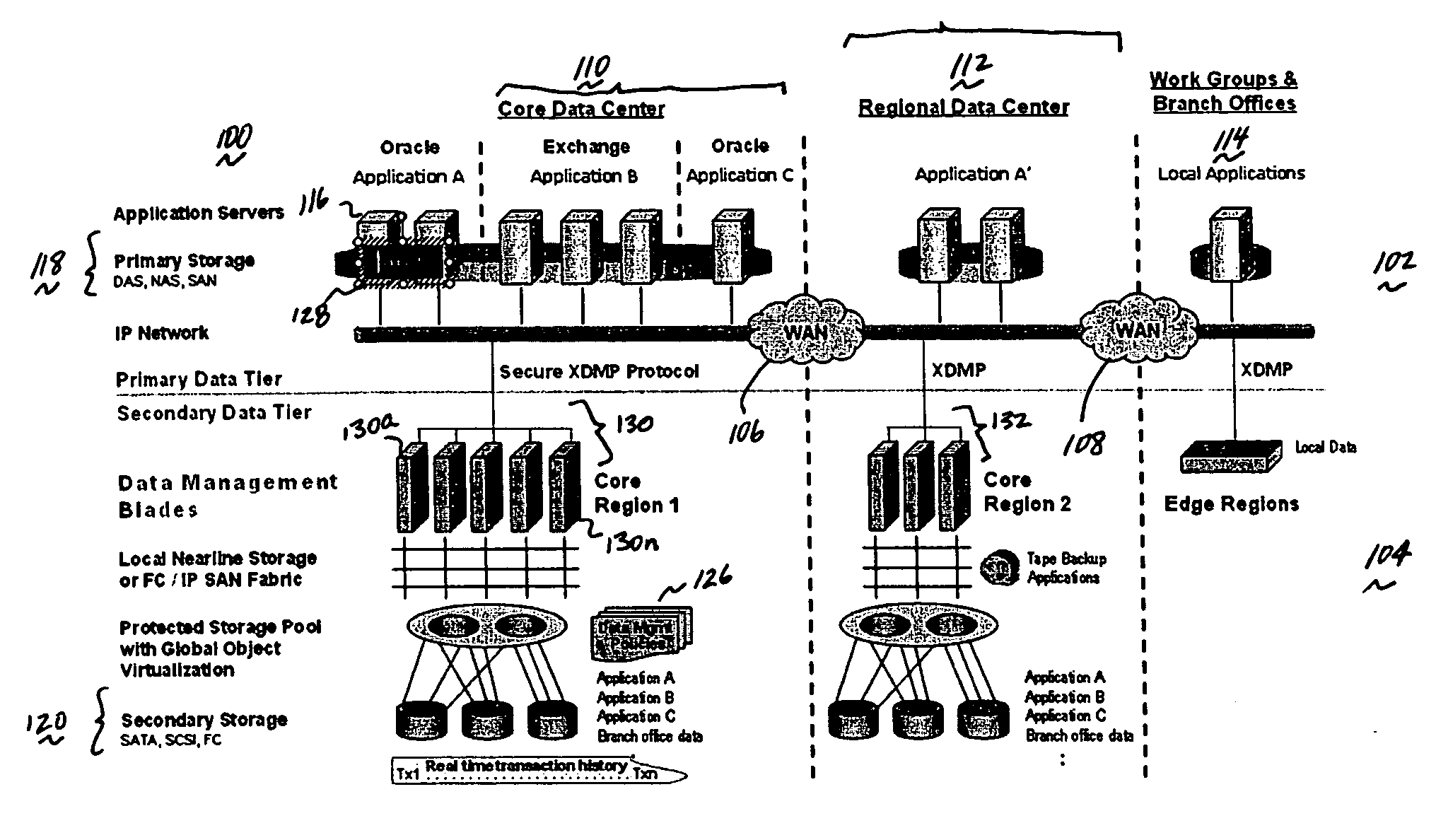
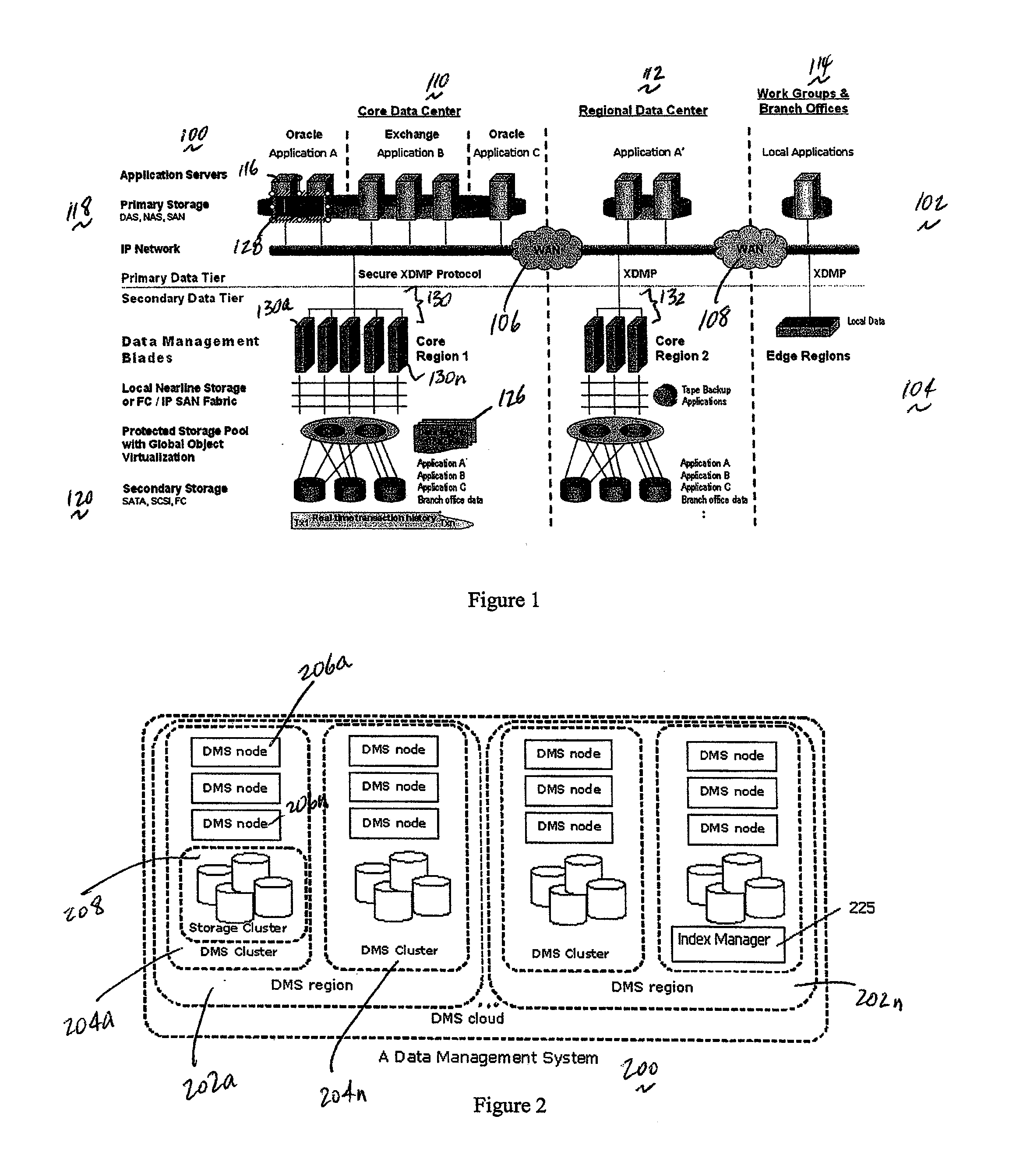
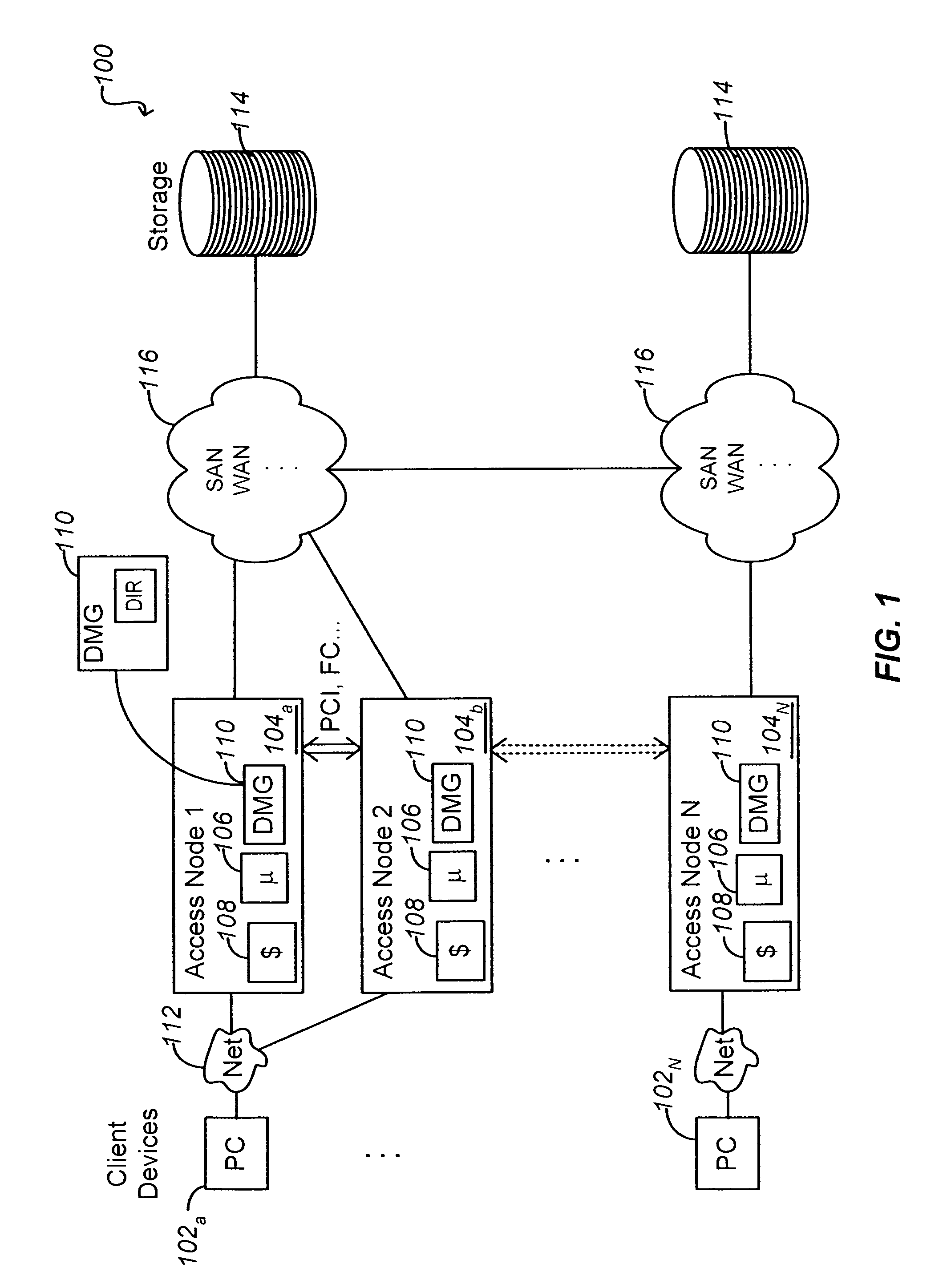
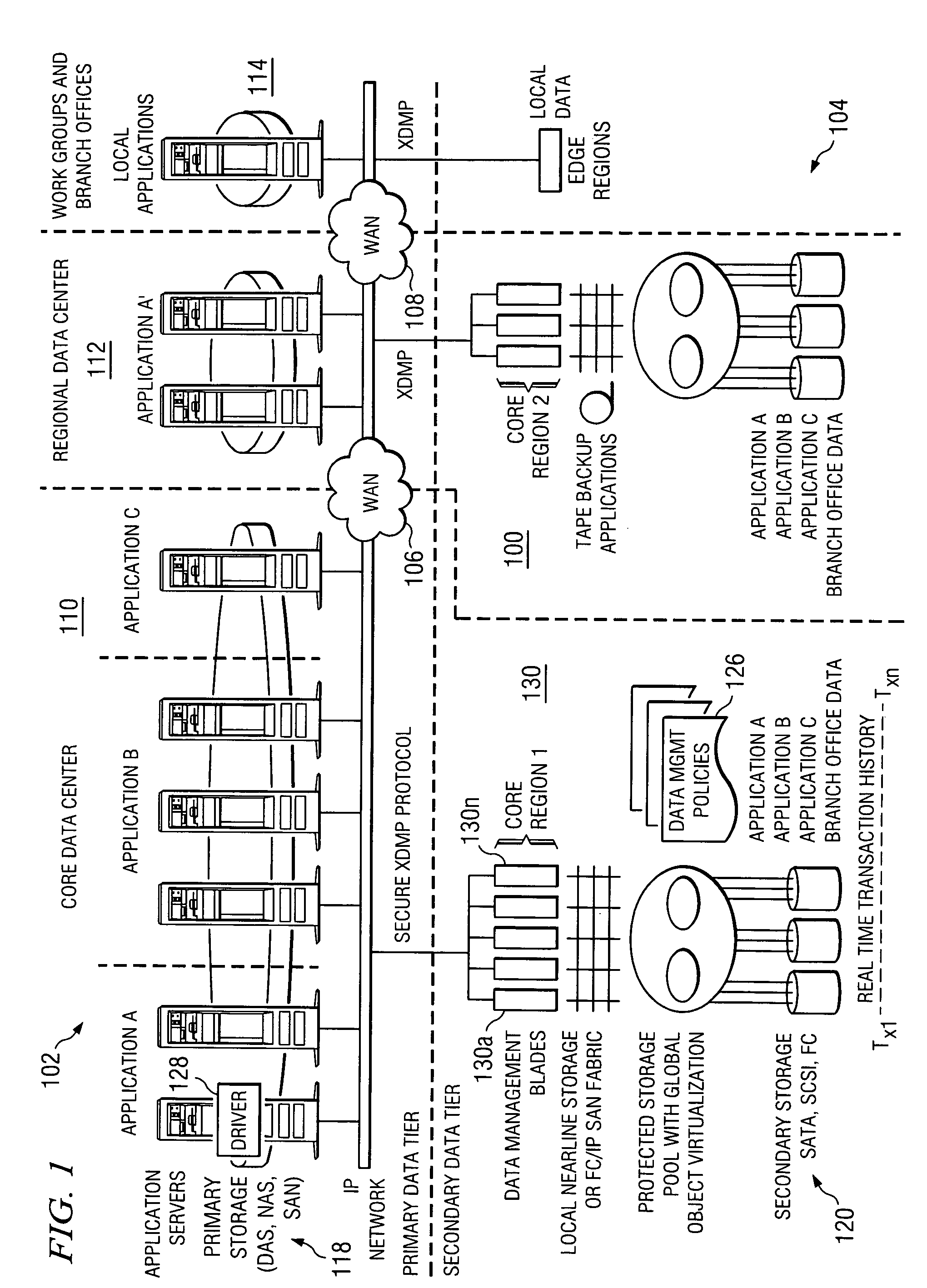
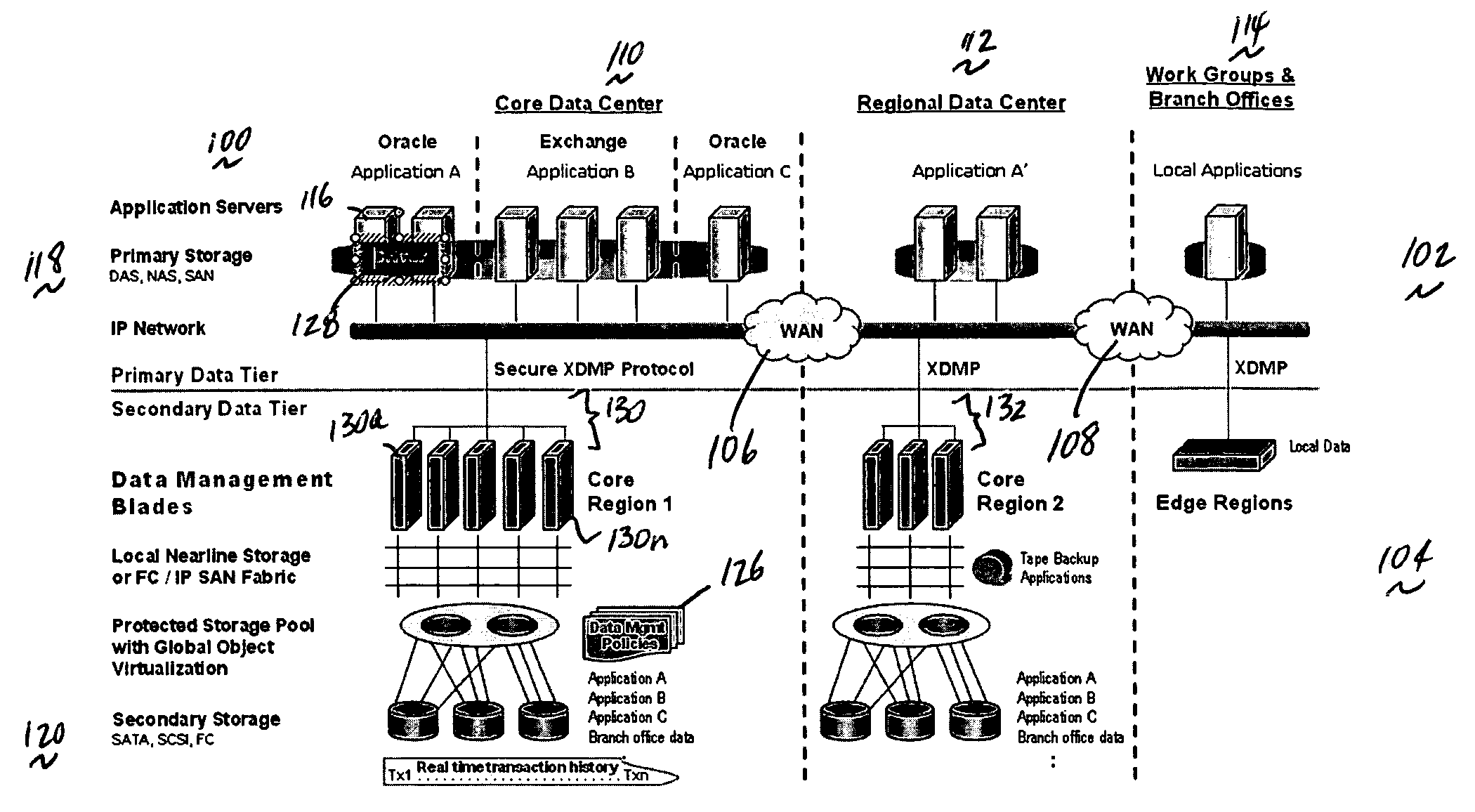
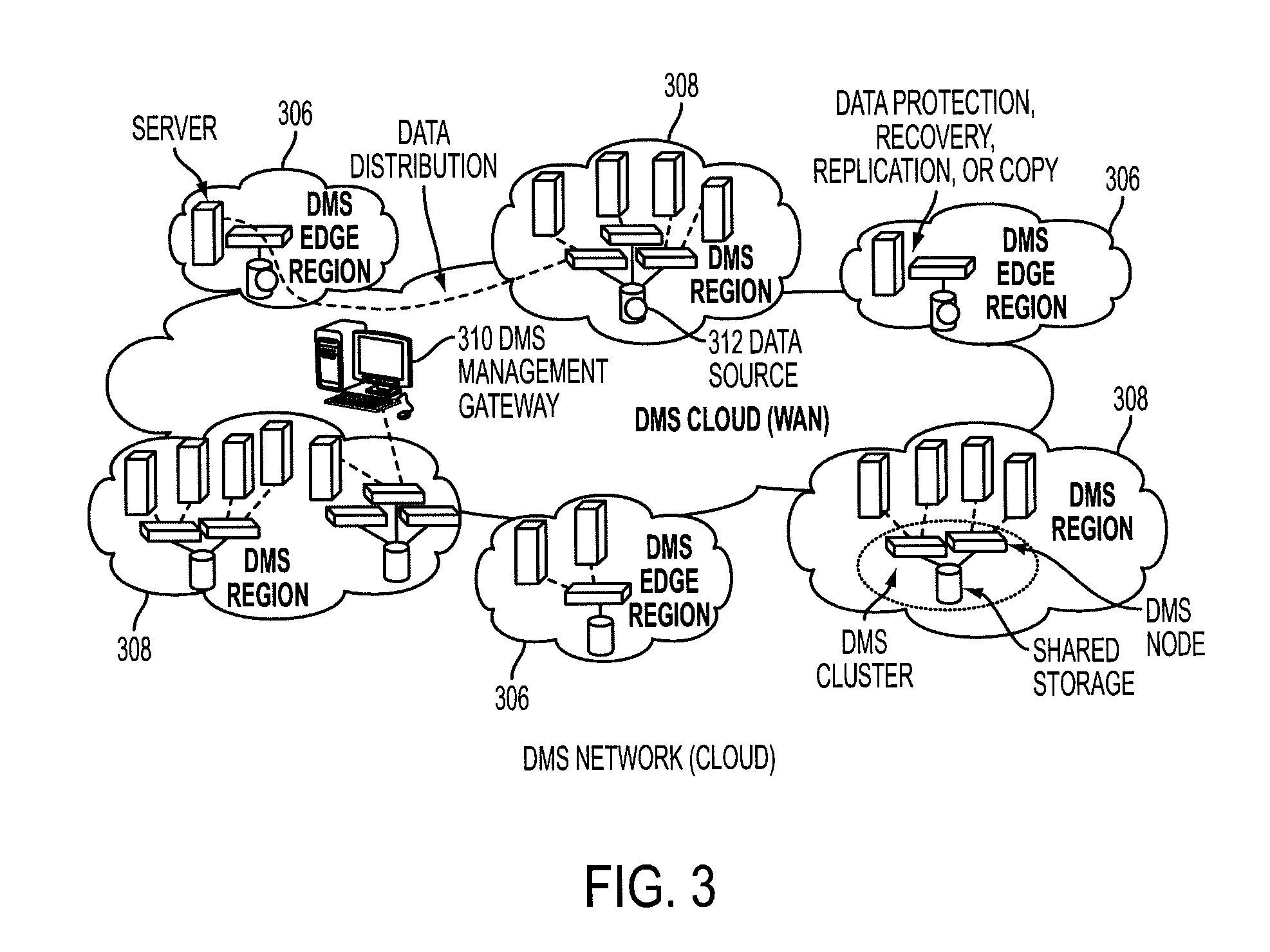
A data management system or “DMS” provides an automated, continuous, real-time, substantially no downtime data protection service to one or more data sources associated with a set of application host servers. To facilitate the data protection service, a host driver embedded in an application server captures real-time data transactions, preferably in the form of an event journal that is provided to other DMS components. The driver functions to translate traditional file / database / block I / O and the like into a continuous, application-aware, output data stream. The host driver includes an event processor that provides the data protection service, preferably by implementing a finite state machine (FSM). In particular, the data protection is provided to a given data source in the host server by taking advantage of the continuous, real-time data that the host driver is capturing and providing to other DMS components. The state of the most current data in DMS matches the state of the data in the host server; as a consequence, the data protection is provided under the control of the finite state machine as a set of interconnected phases or “states.” The otherwise separate processes (initial data upload, continuous backup, blackout and data resynchronization, and recovery) are simply phases of the overall data protection cycle. As implemented by the finite state machine, this data protection cycle preferably loops around indefinitely until, for example, a user terminates the service. A given data protection phase (a given state) changes only as the state of the data and the environment change (a given incident).
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
System for Enabling Secure and Automatic Data Backup and Instant Recovery
InactiveUS20070033356A1Improve performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory loss protectionOperational systemLatency (engineering)
A host-based system for enhancing performance for a computing appliance has a central processing unit, an operating system, a long-term disk storage medium, and a persistent low latency memory (PLLM). Writes to disk storage at random addresses are first made to the PLLM, which also stores a memory map of the disk storage medium, and later made, in sequence, to the disk storage medium according to the memory map. In another aspect the host-based system is for continuous data protection and backup for a computing appliance, and has a central processing unit, an operating system, a long-term disk storage medium, and a persistent low latency memory (PLLM). In this aspect periodic system state snapshots are stored in the PLLM associated with sequence of writes to memory made between snapshots, enabling restoration of the host to any state of a prior snapshot stored in the PLLM, and then adjustment, via the record of writes to memory between snapshots, to any state desired between the snapshot states.
Owner:BACCEL
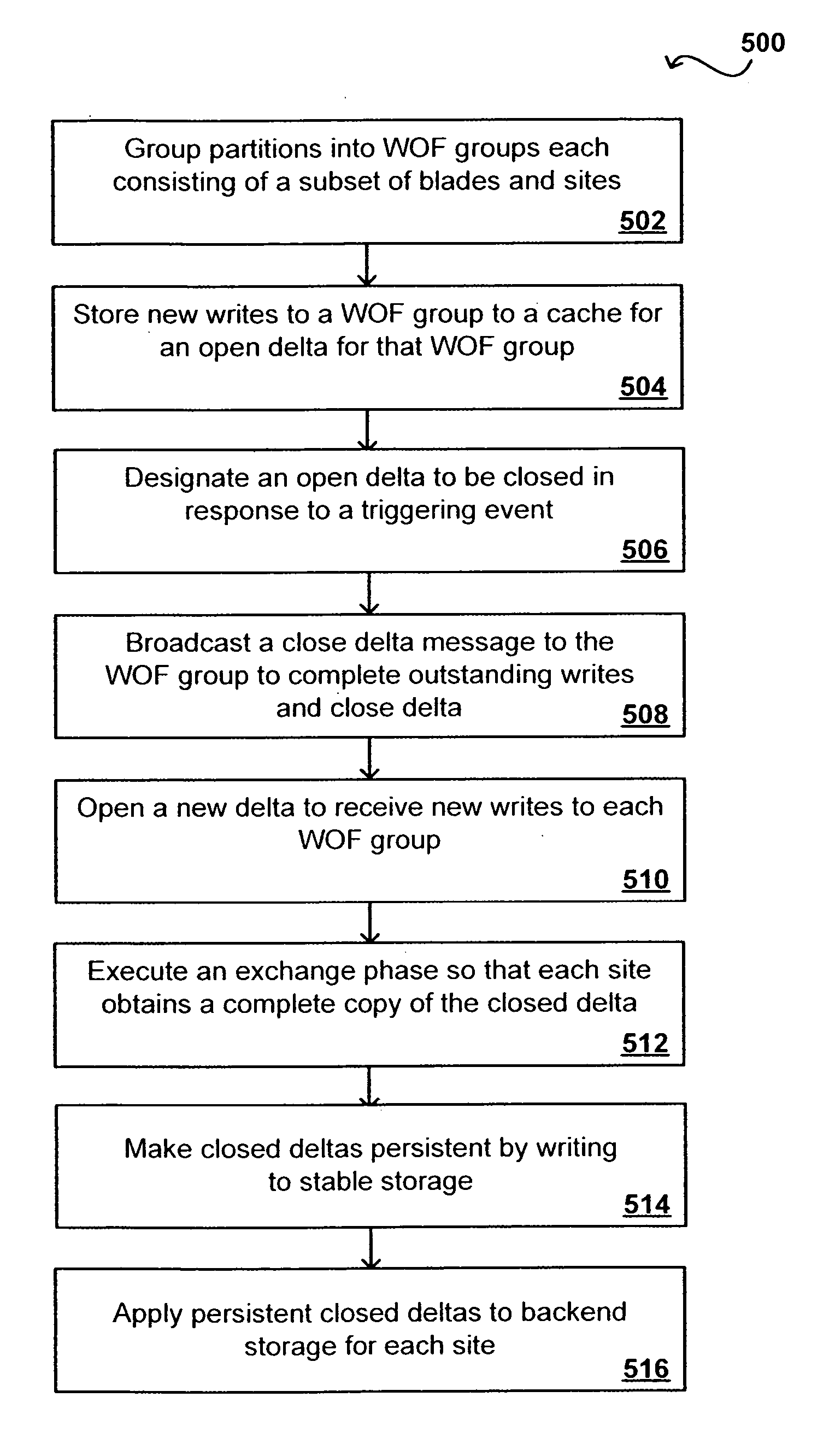
Maintaining write order fidelity on a multi-writer system
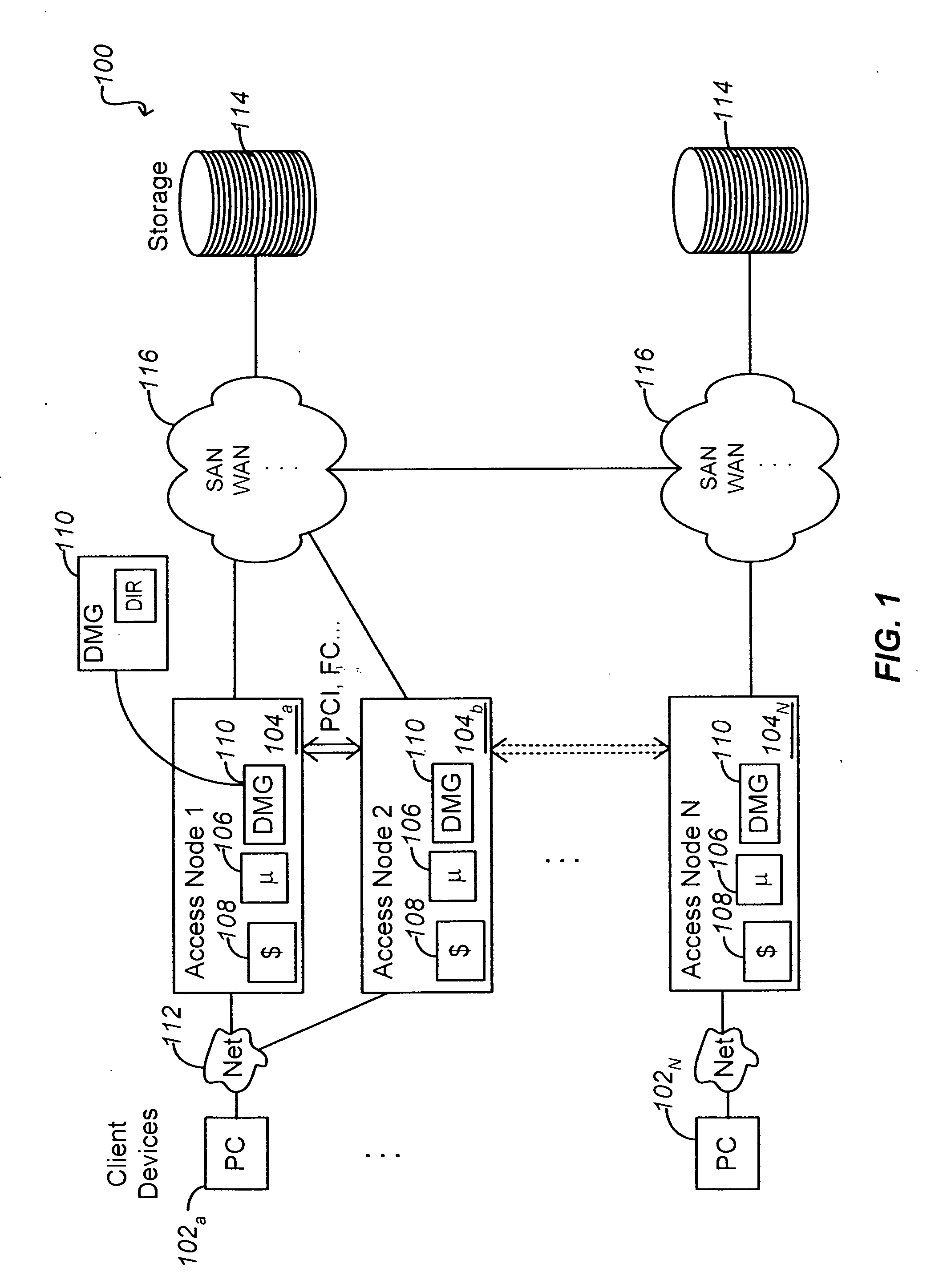
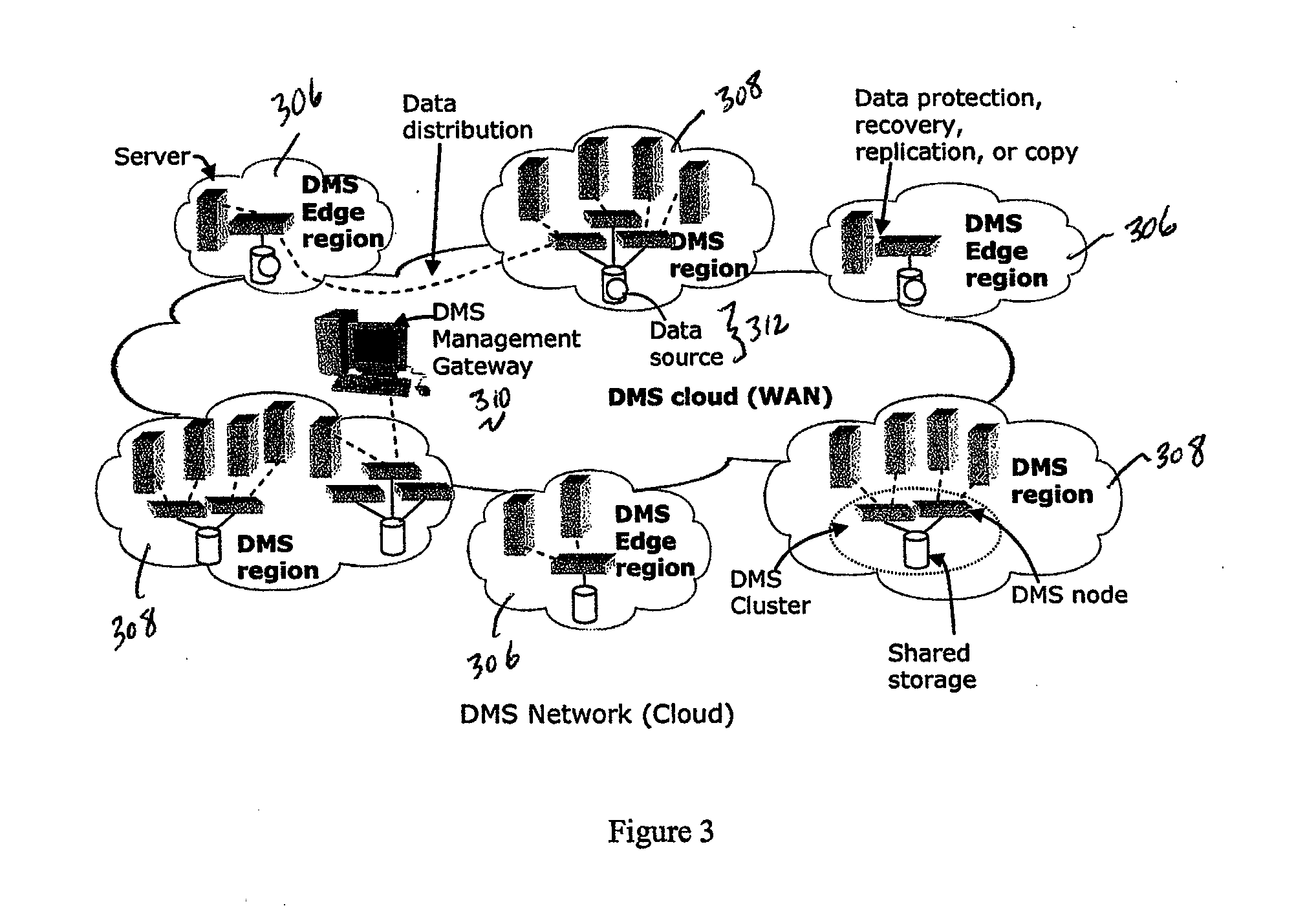
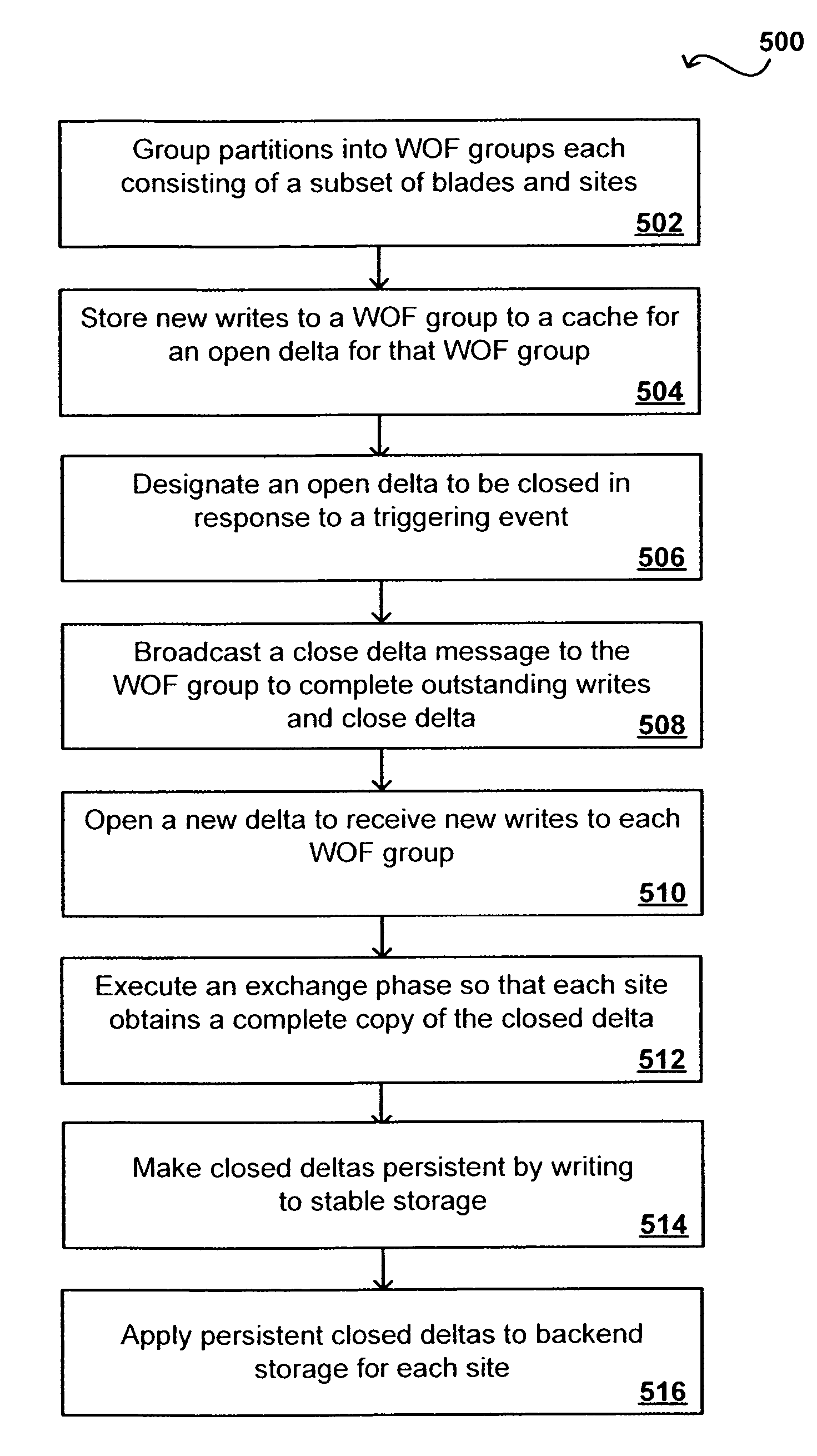
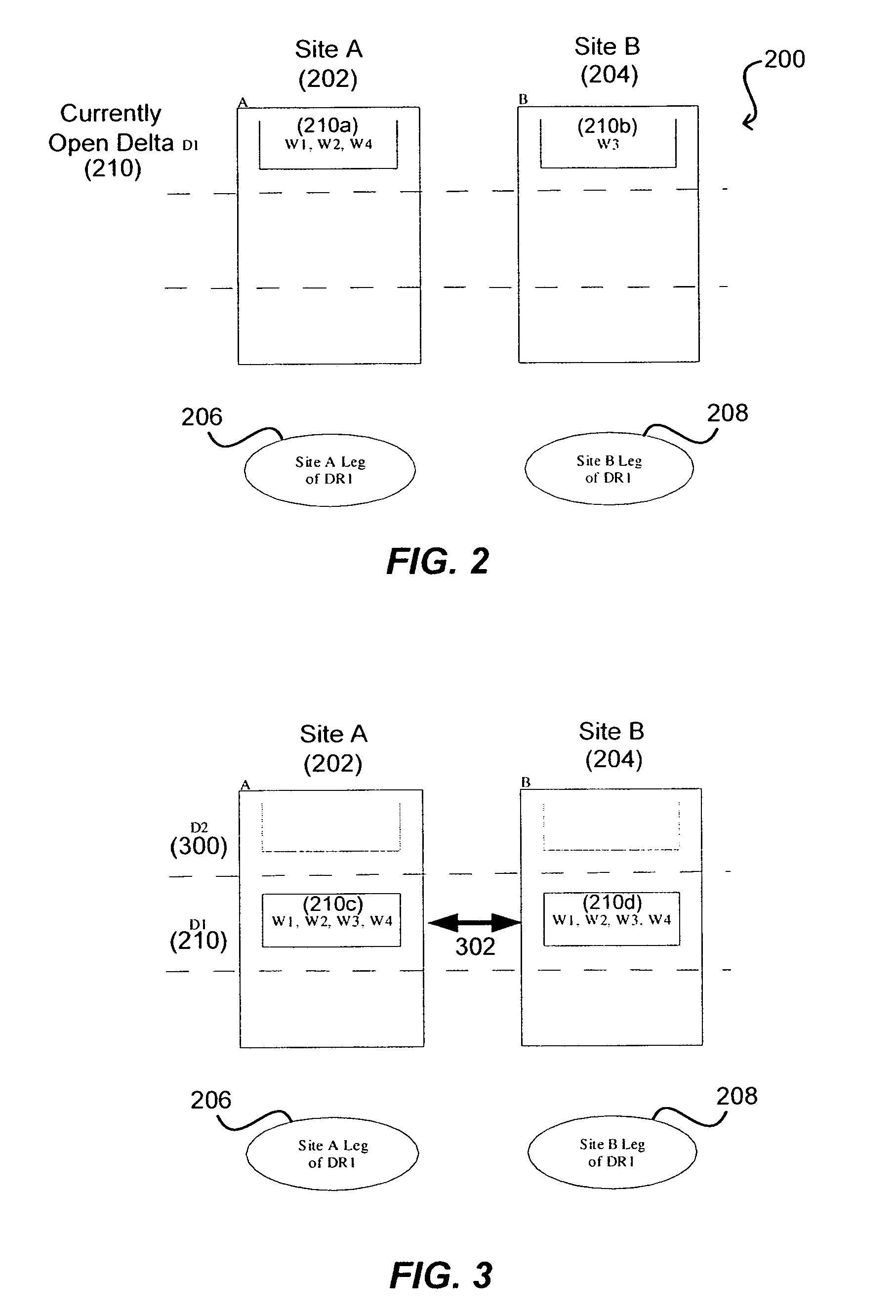
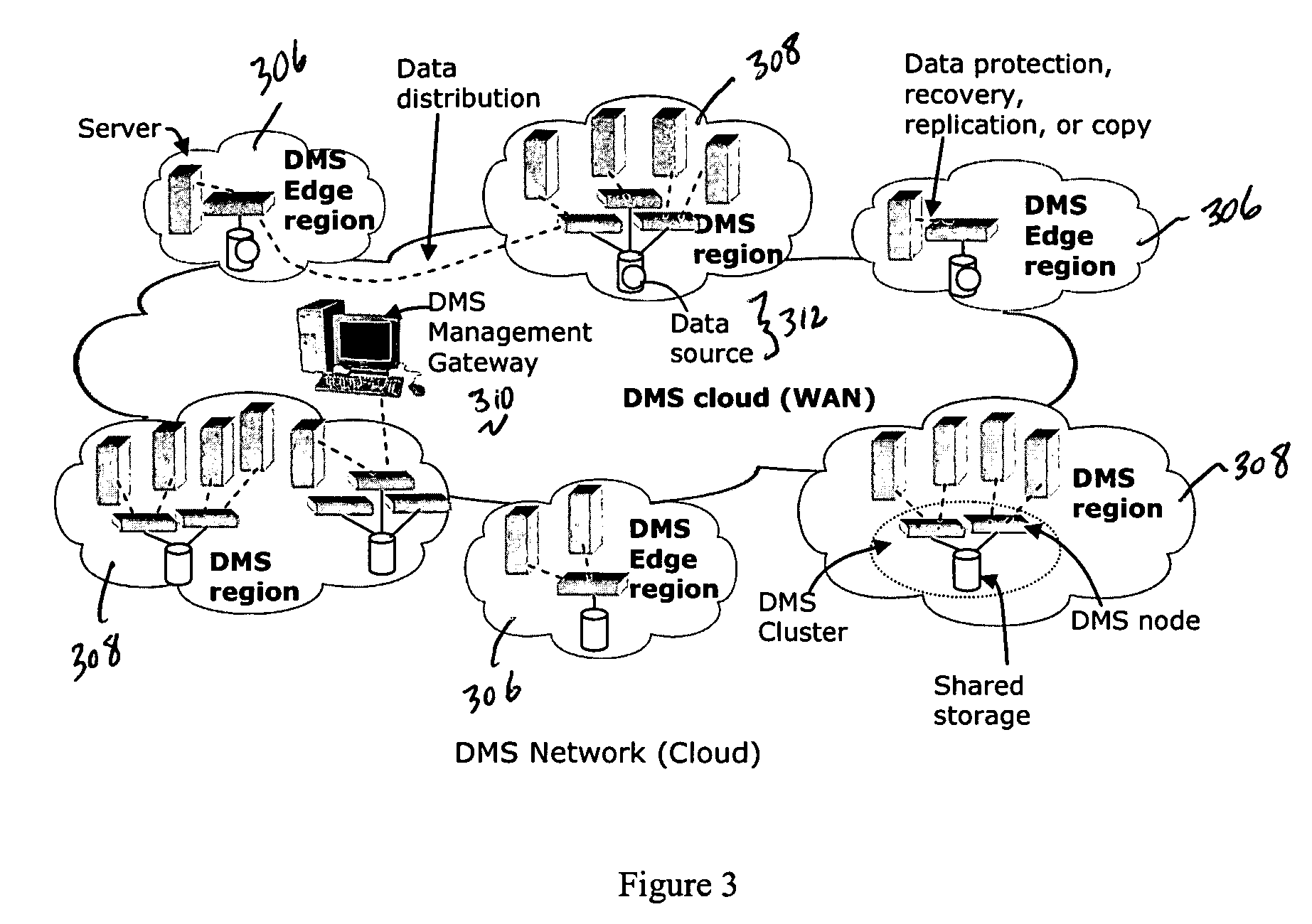
Write order fidelity (WOF) is maintained for totally-active implementations wherein a plurality of access nodes at geographically separated sites can concurrently read and / or write data in a “totally active” fashion on a distributed data system. From the hosts' perspective at diverse geographic locations, a synchronous, cache-coherent view of data is provided. Data transfer is asynchronous. A time ordered data image is created and maintained so operations can be restarted after a partial system failure that causes loss of data not yet asynchronously transferred across the network, but that has been write-acknowledged to the originating host. Time ordered asynchronous data transfer is implemented as a pipeline of changes that reflect contributions from all nodes. WOF also improves network performance and lowers bandwidth consumption. Extensions can provide, in a totally-active context, features such as point-in-time snapshots, time firewalls, on-demand backend storage allocation, synchronous / asynchronous distribution of data, and continuous data protection.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
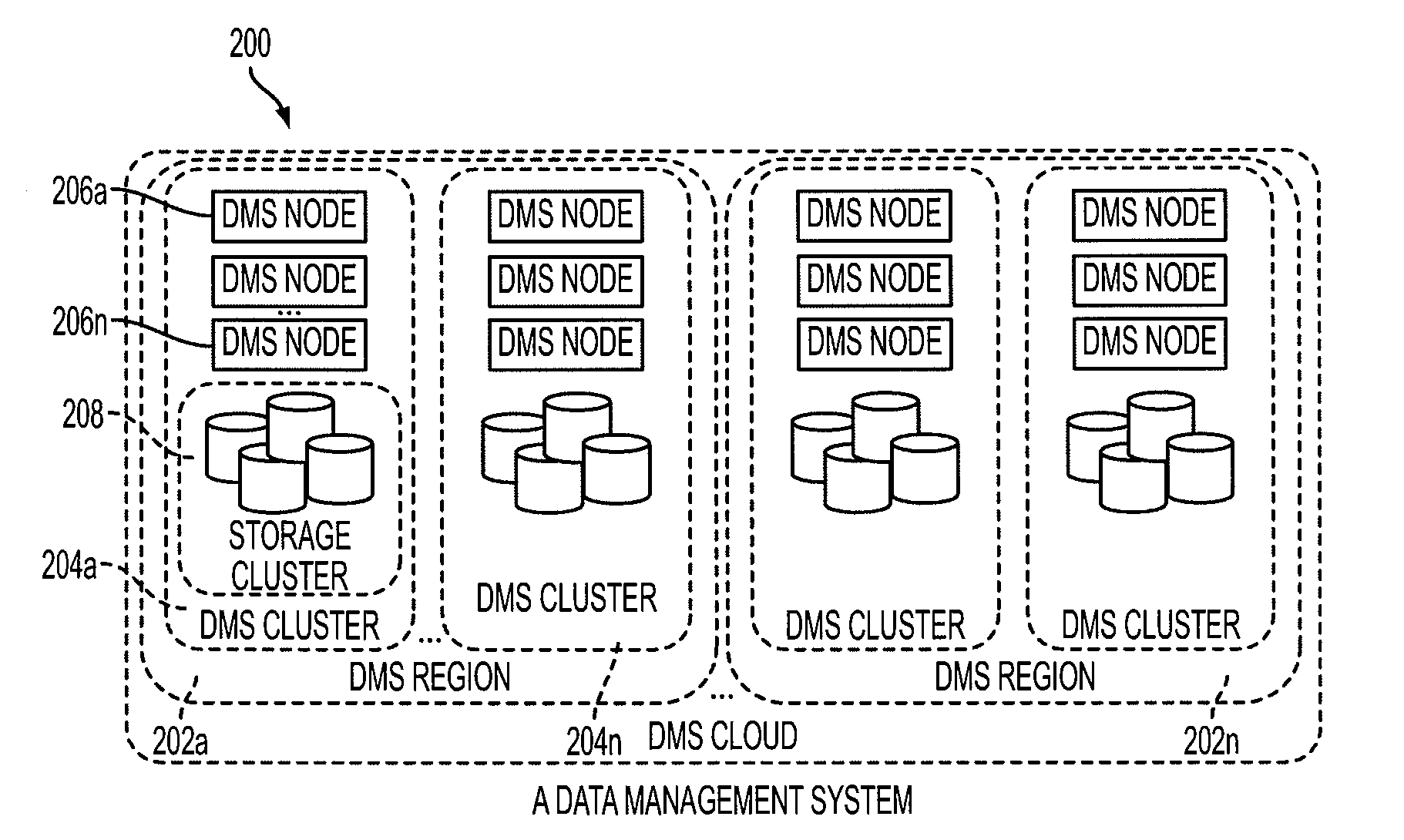
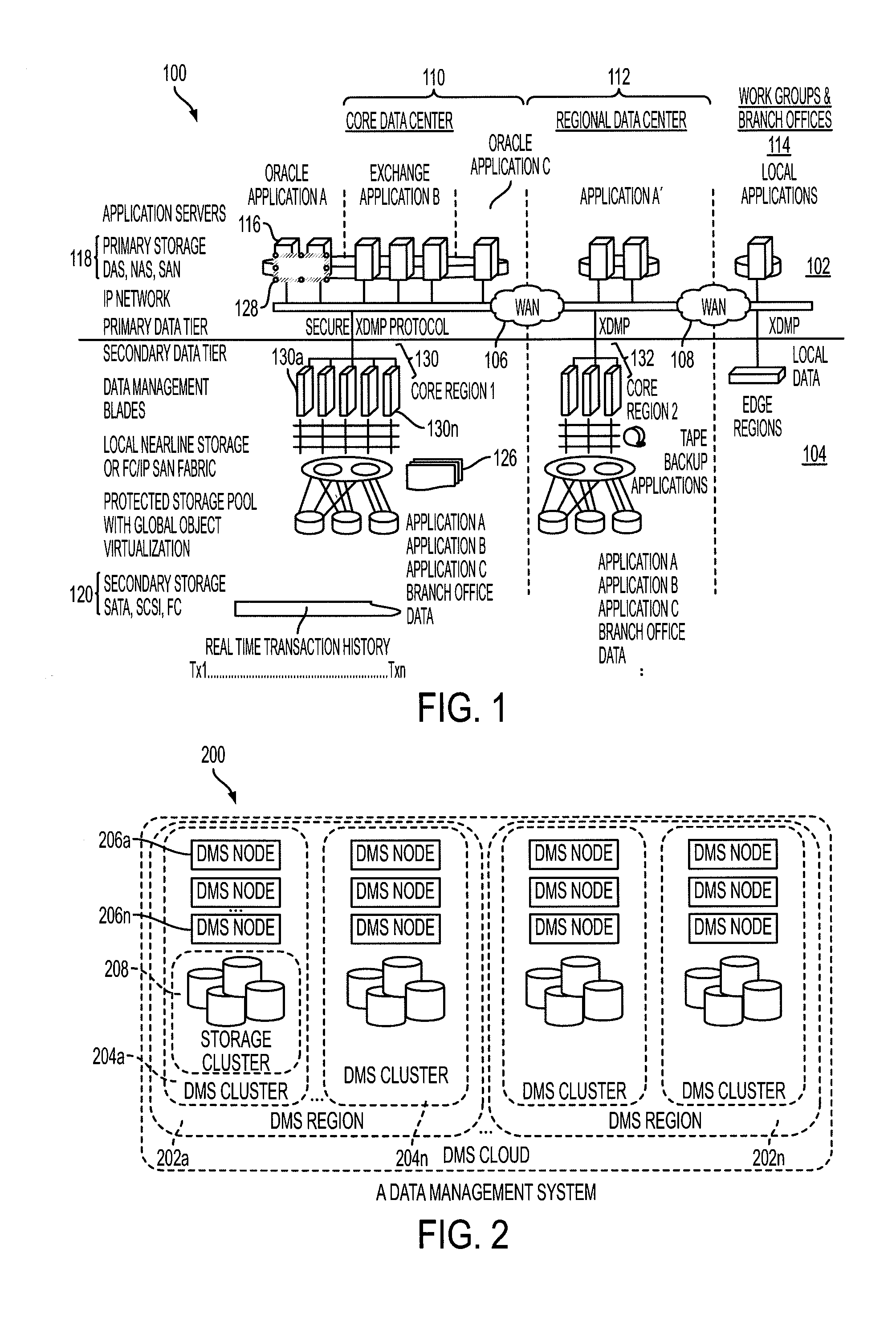
Method Of Creating Hierarchical Indices For A Distributed Object System
ActiveUS20100146004A1Easy searchImprove efficiencyError detection/correctionDigital data processing detailsReal-time dataFile system
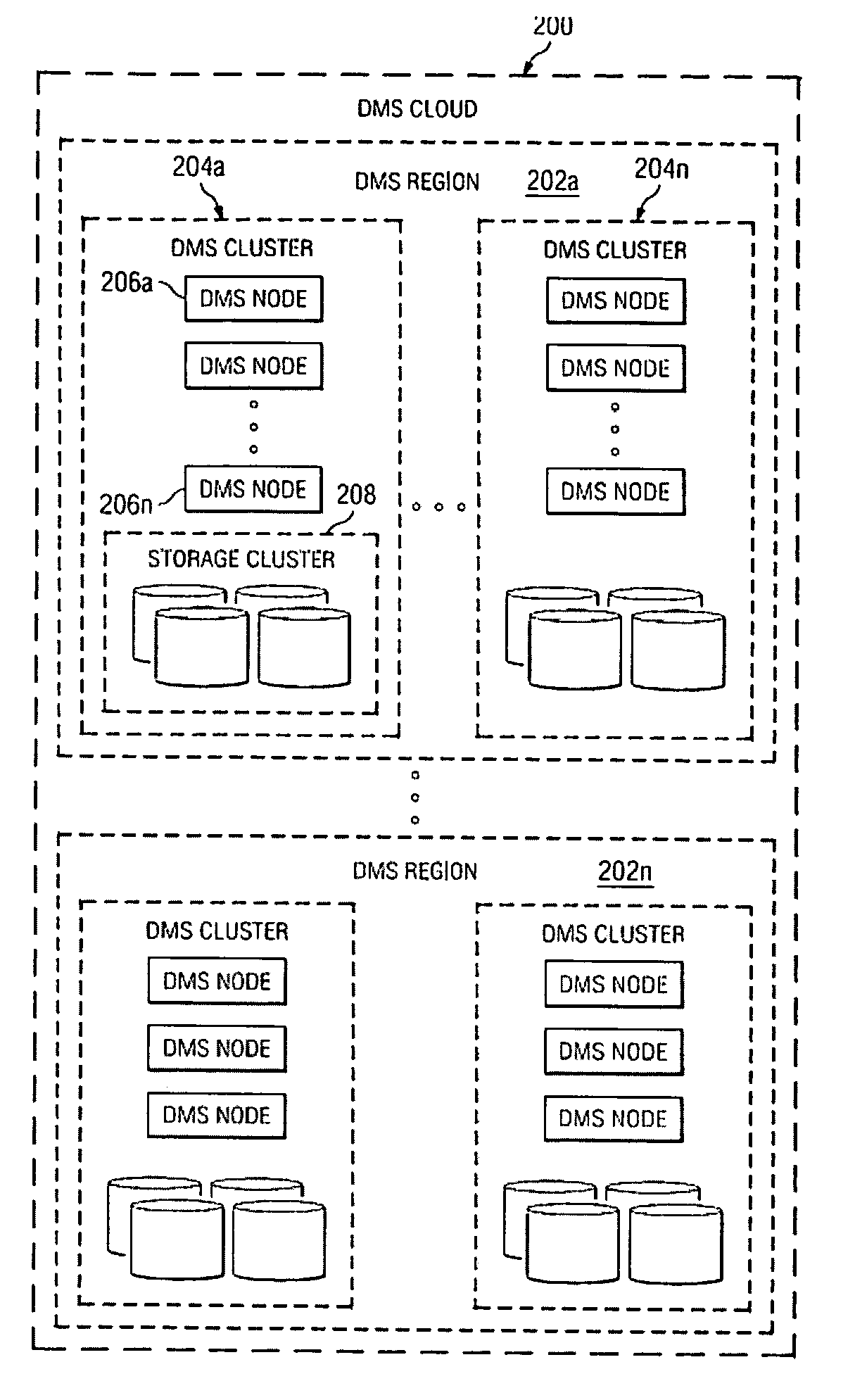
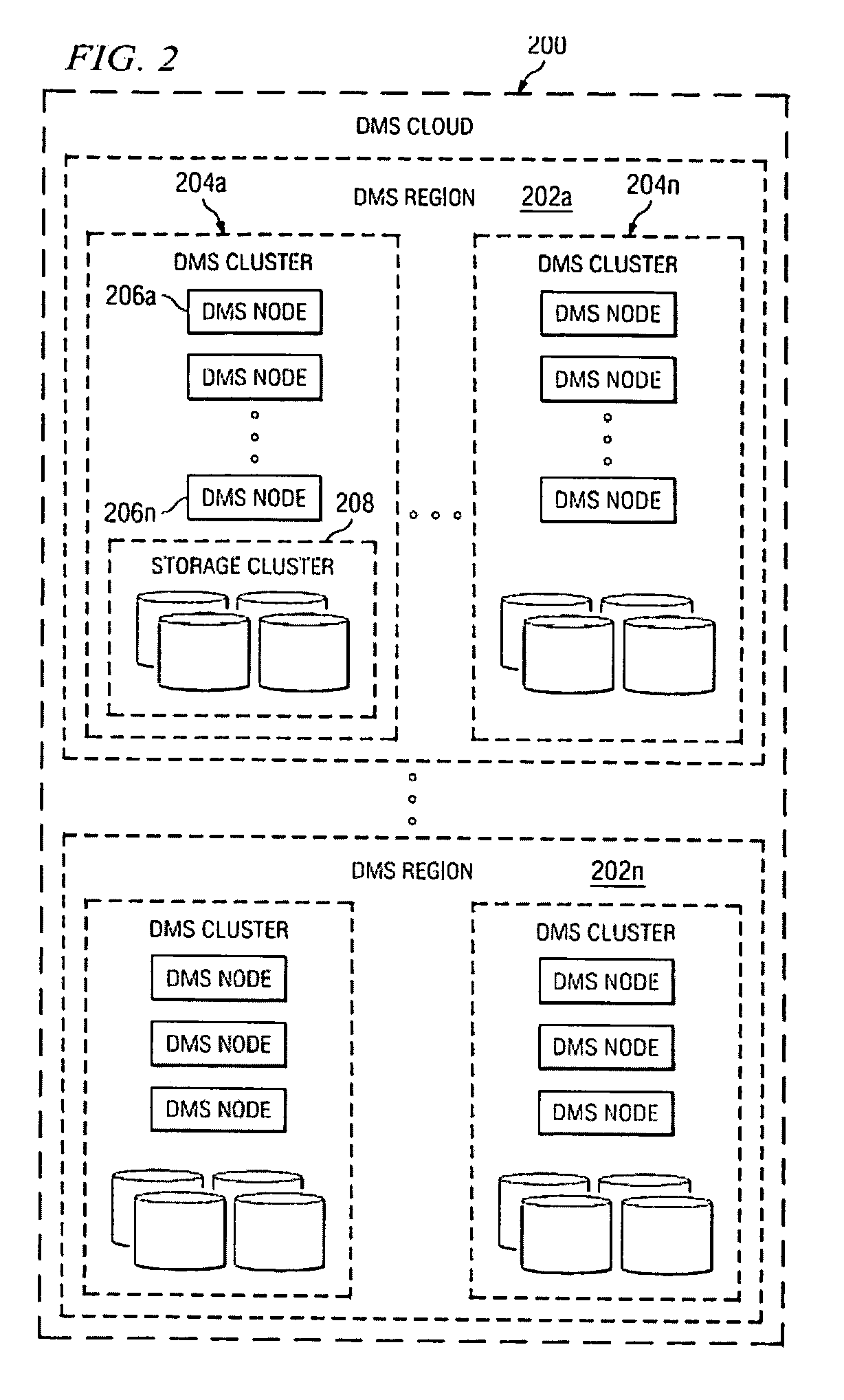
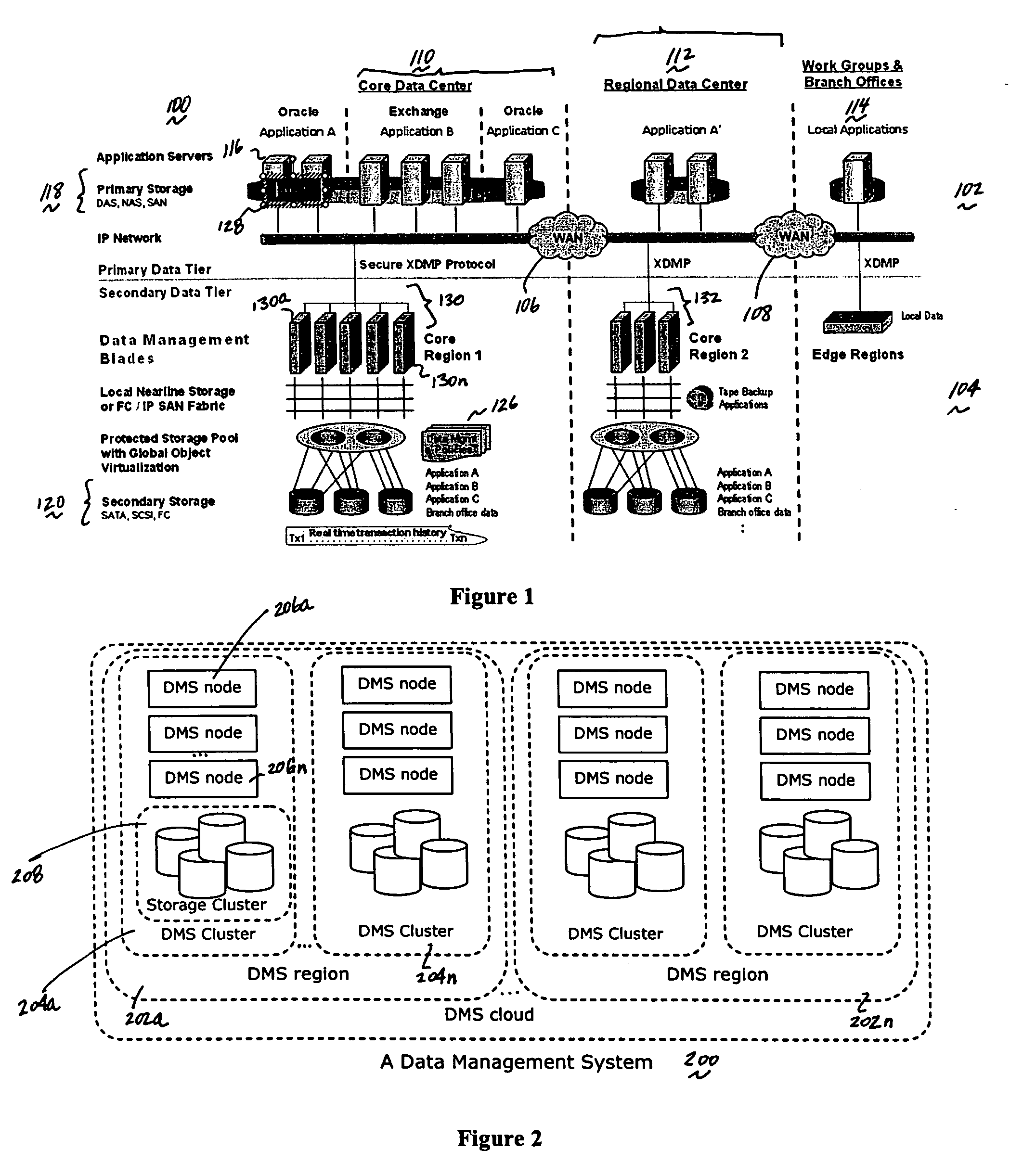
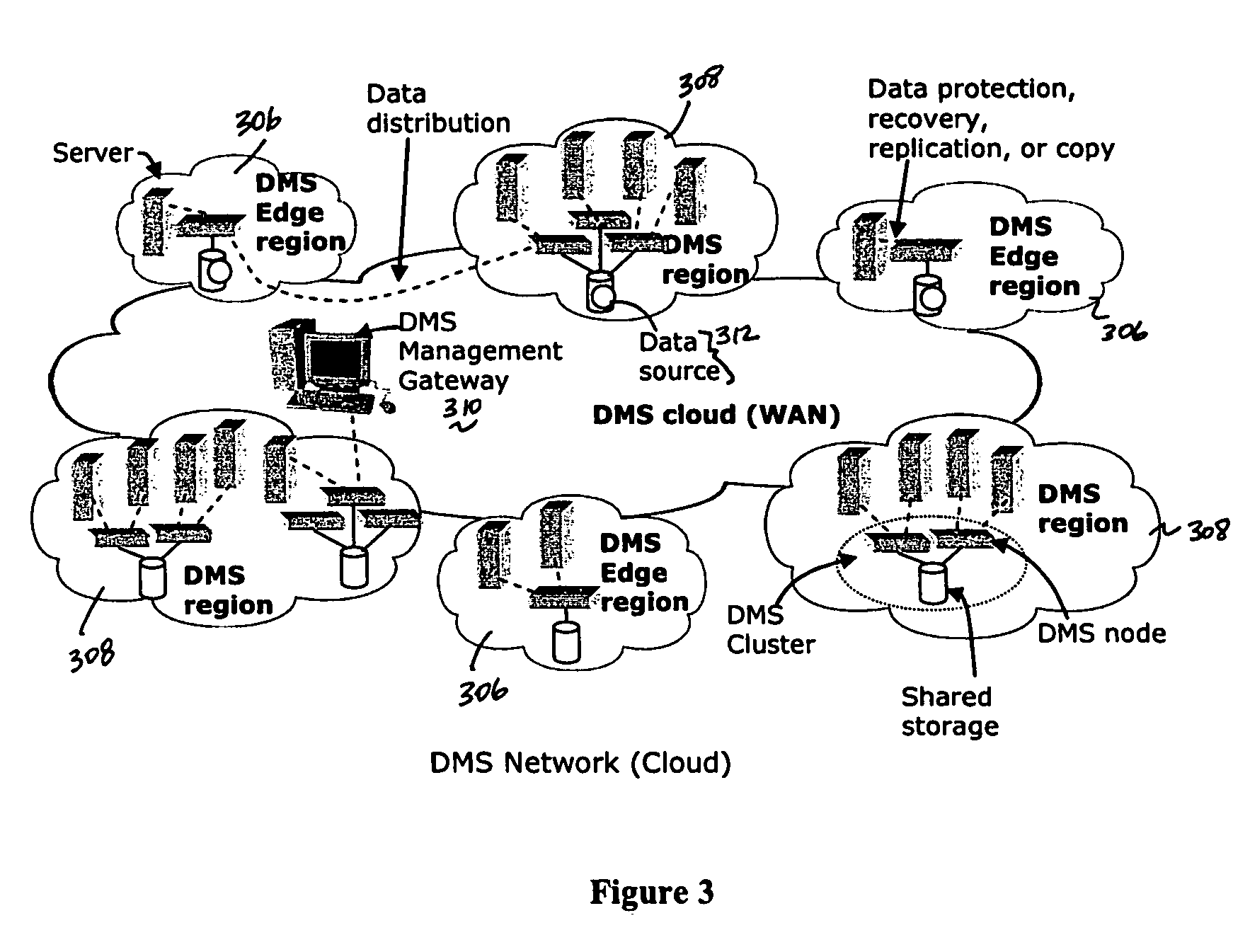
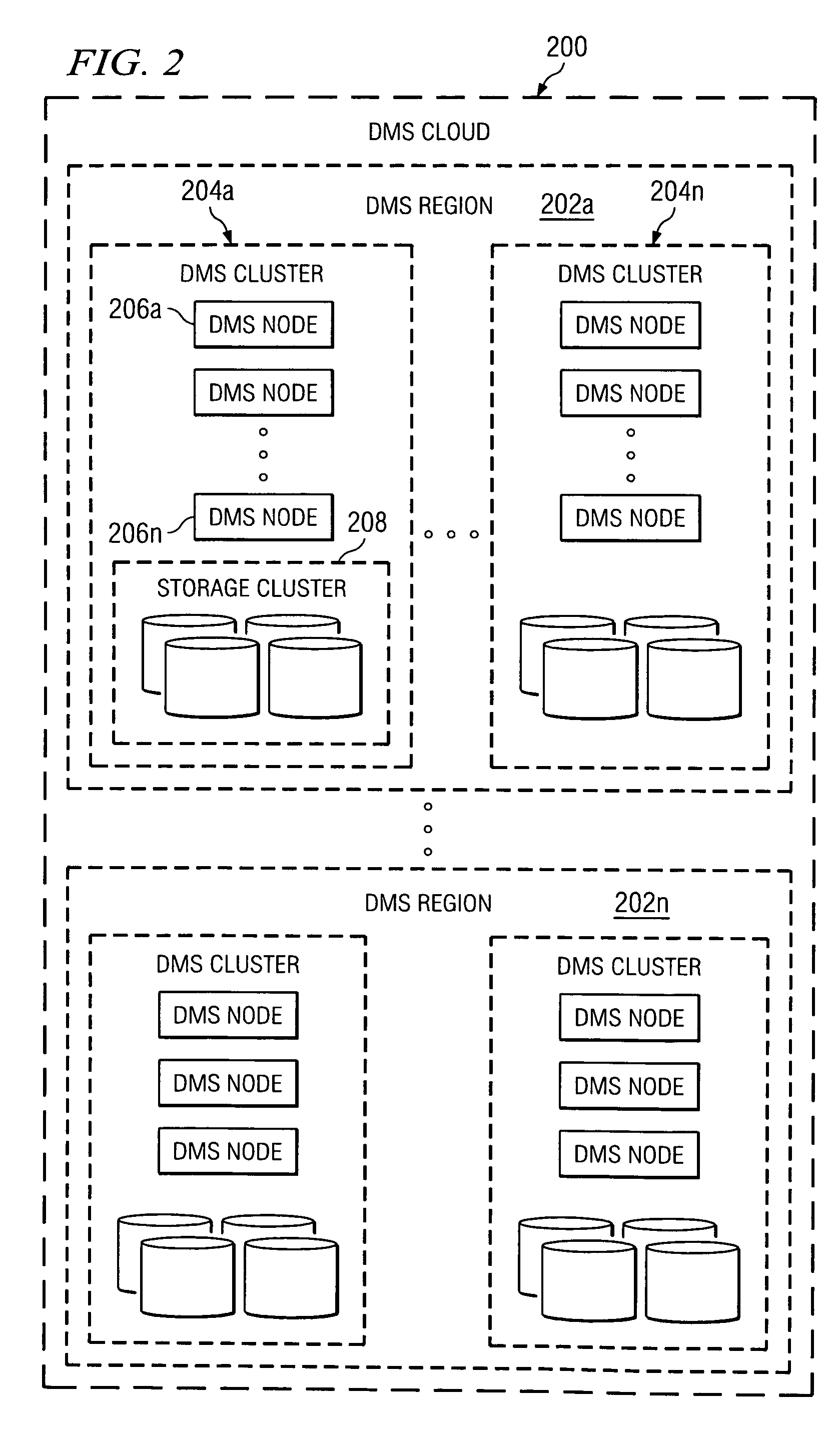
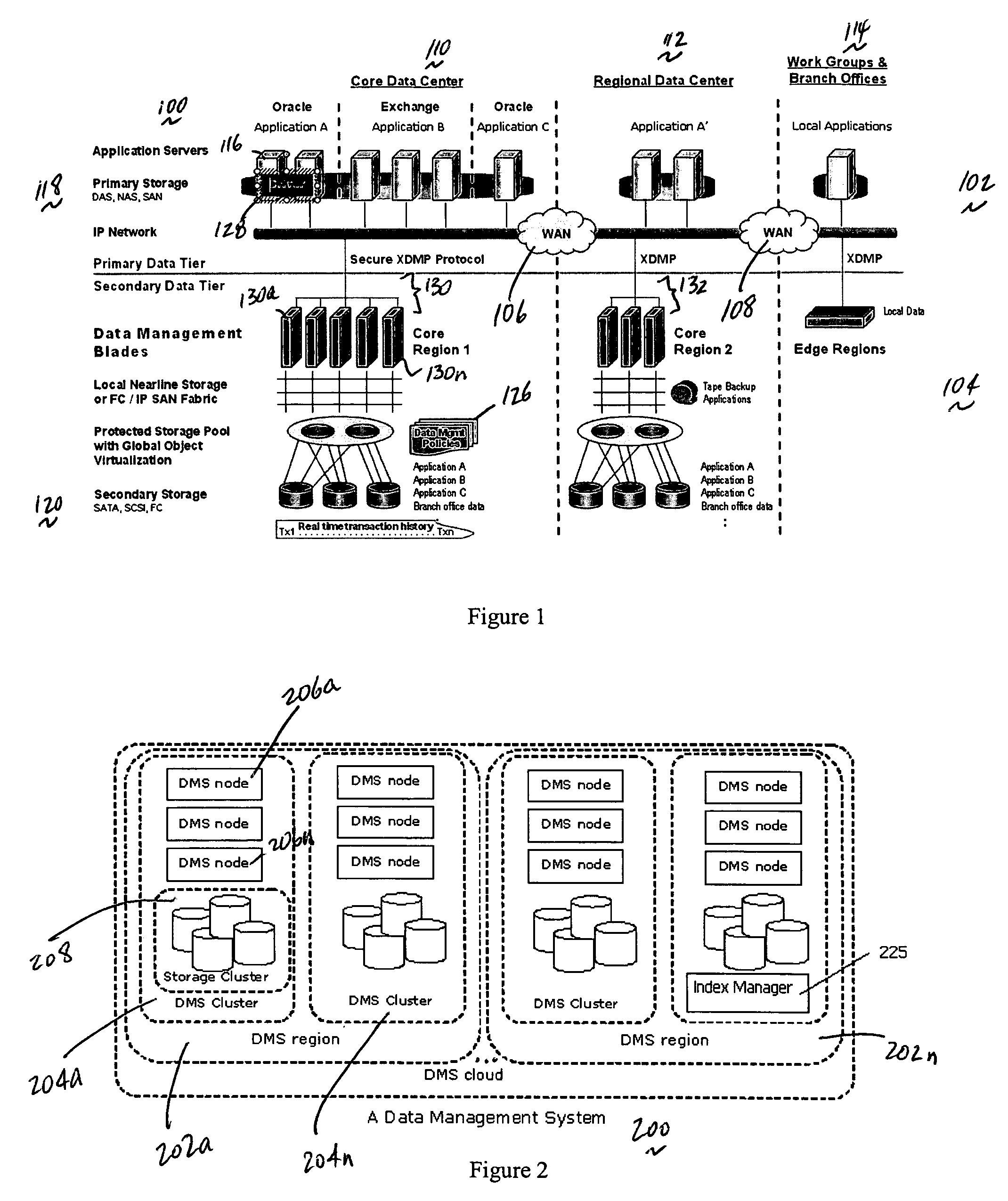
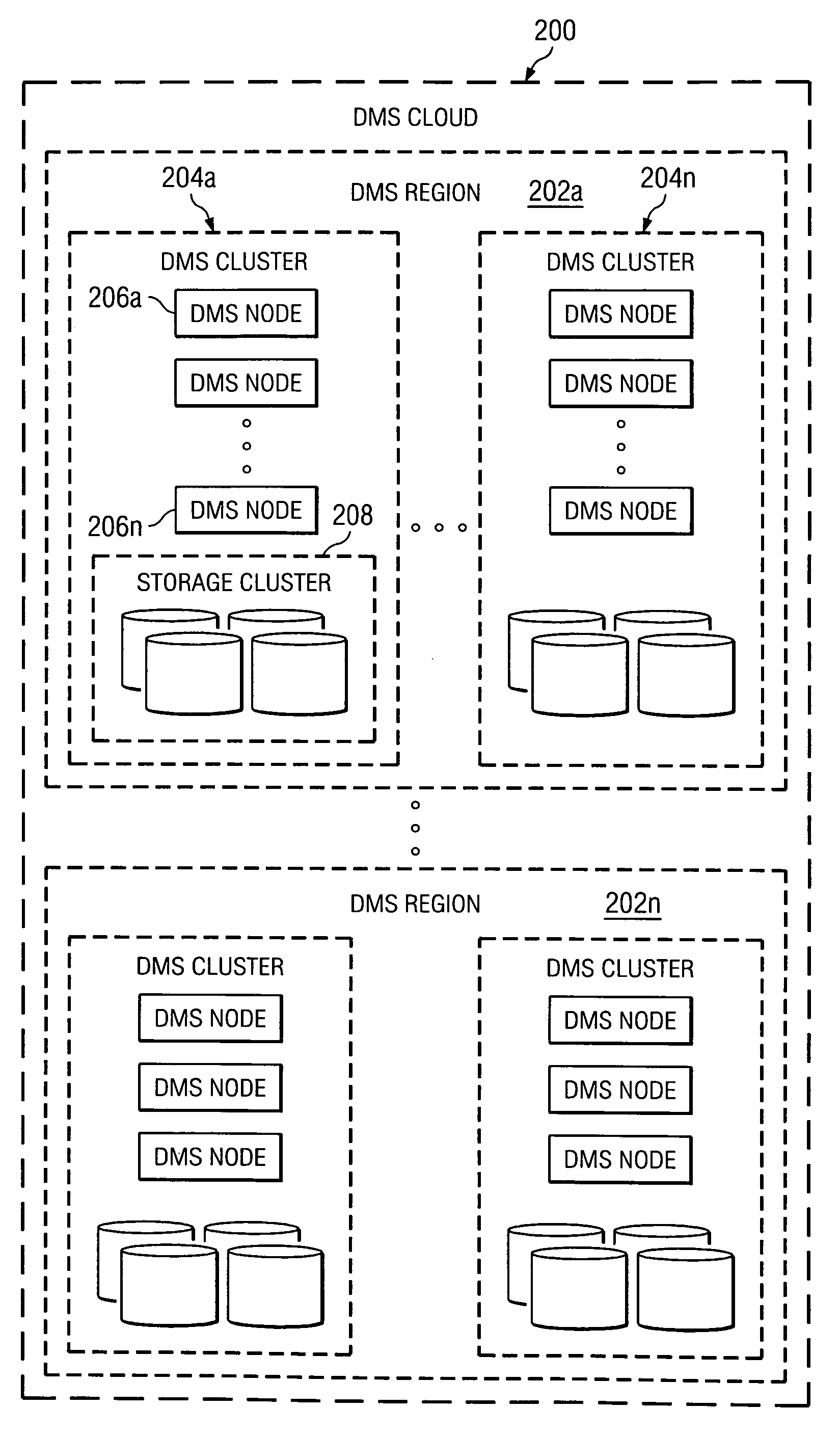
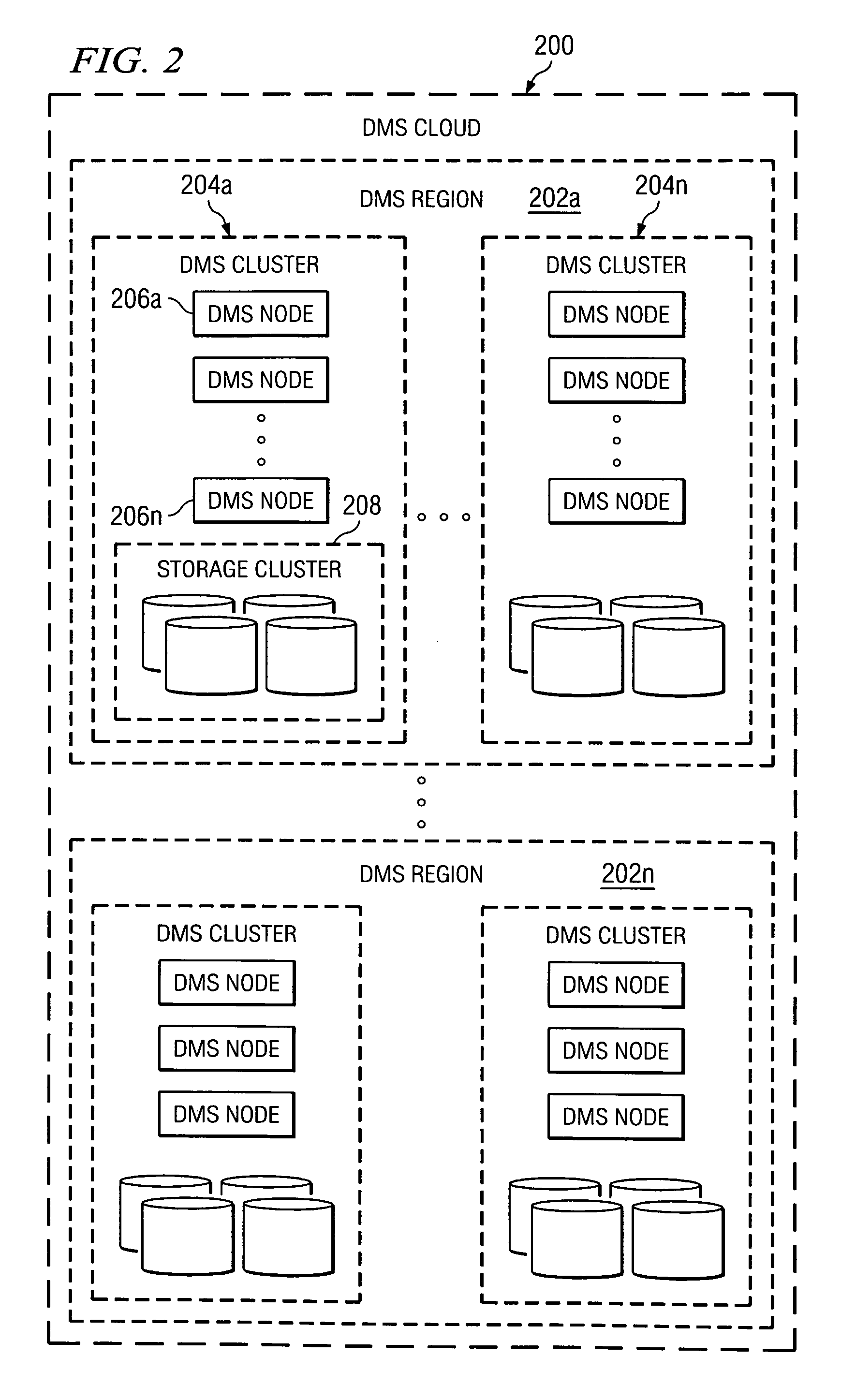
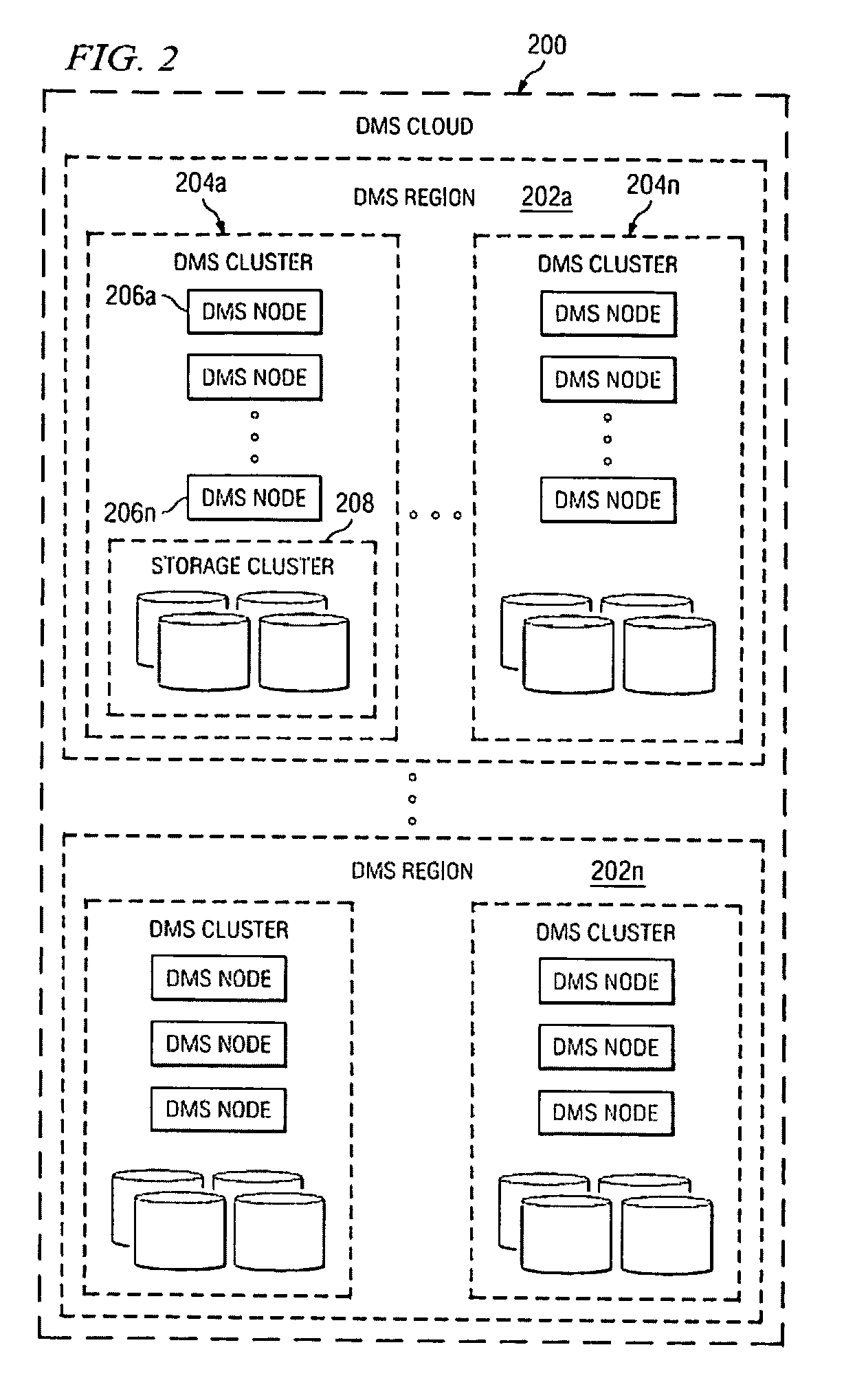
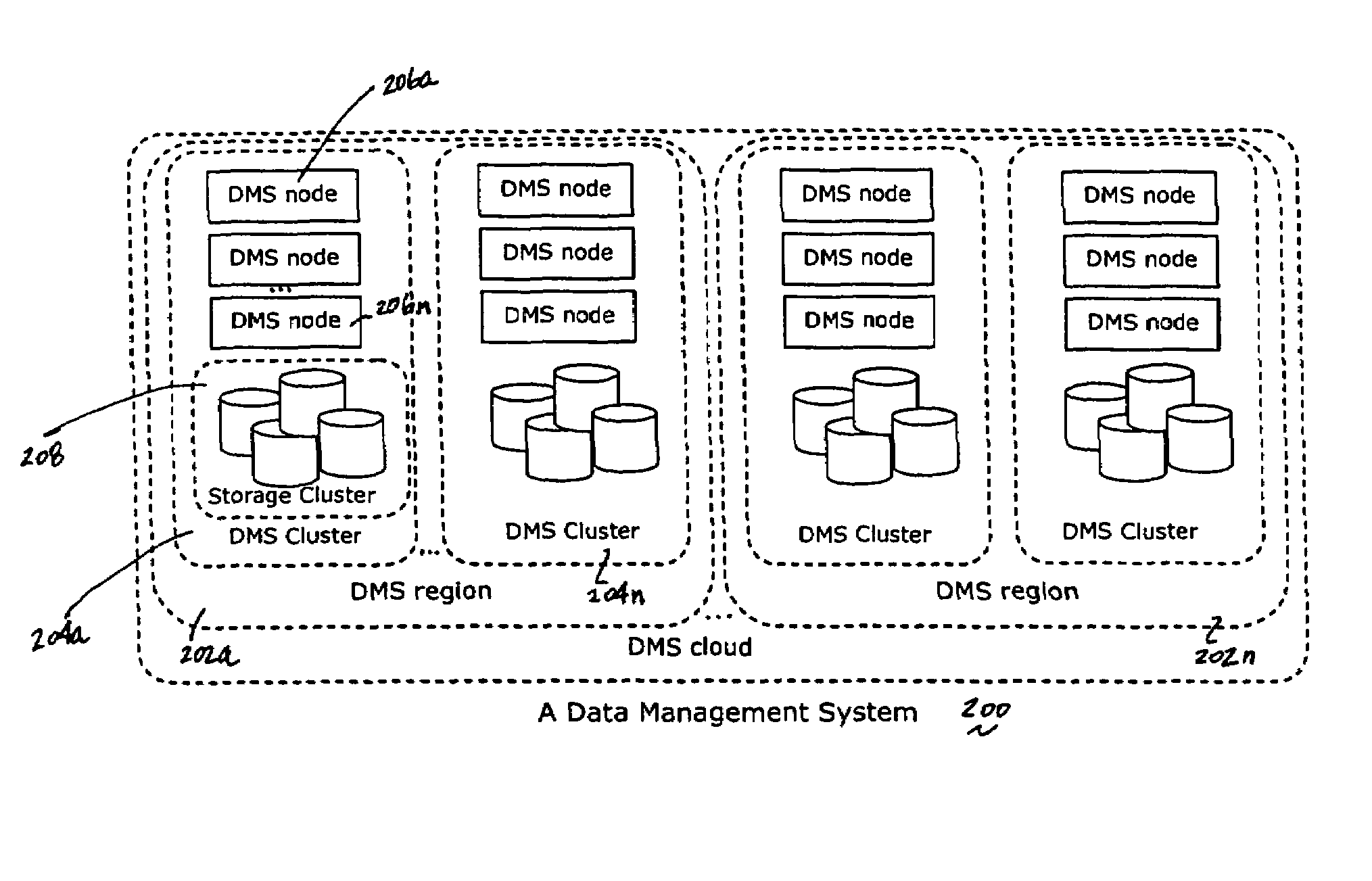
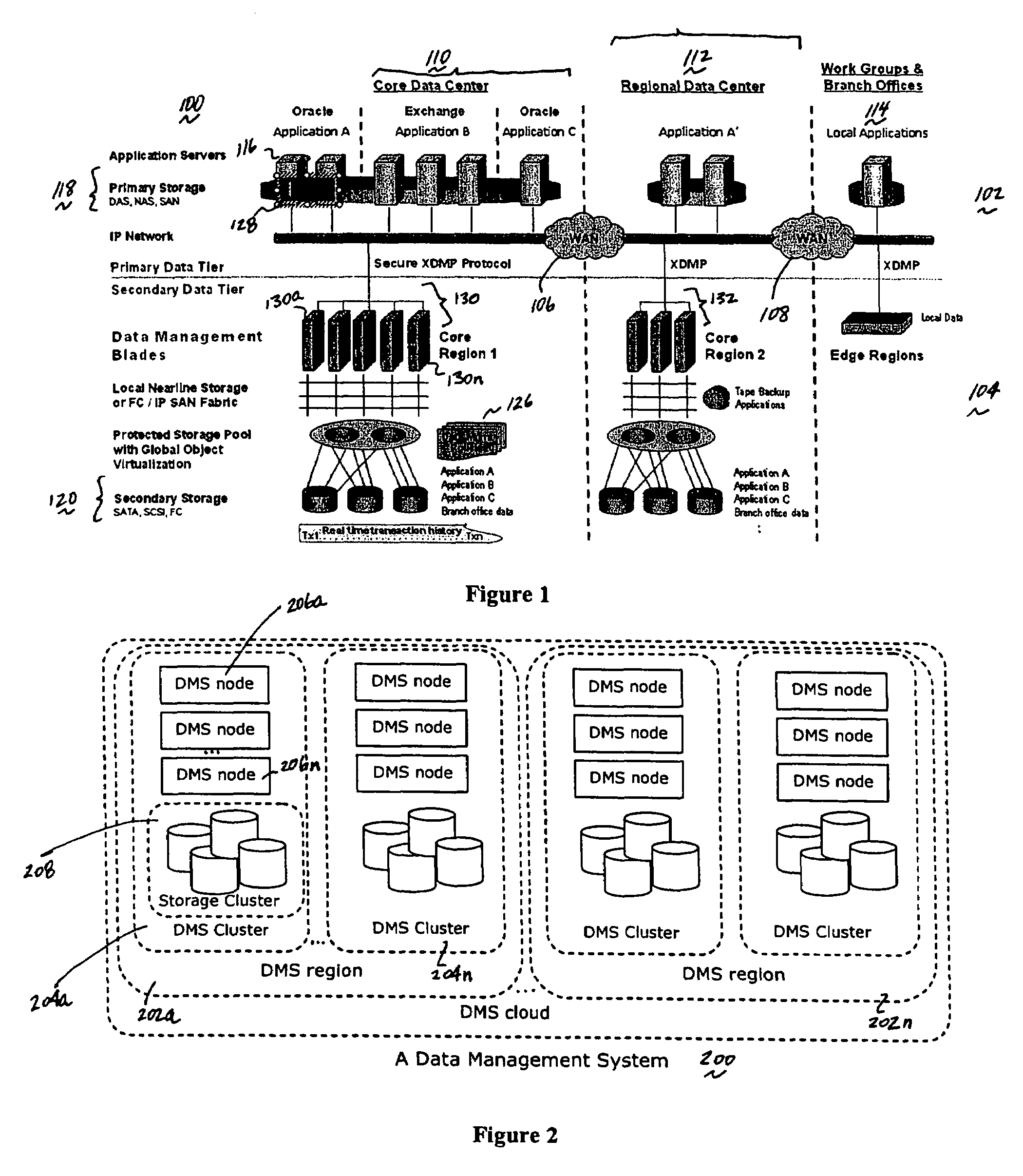
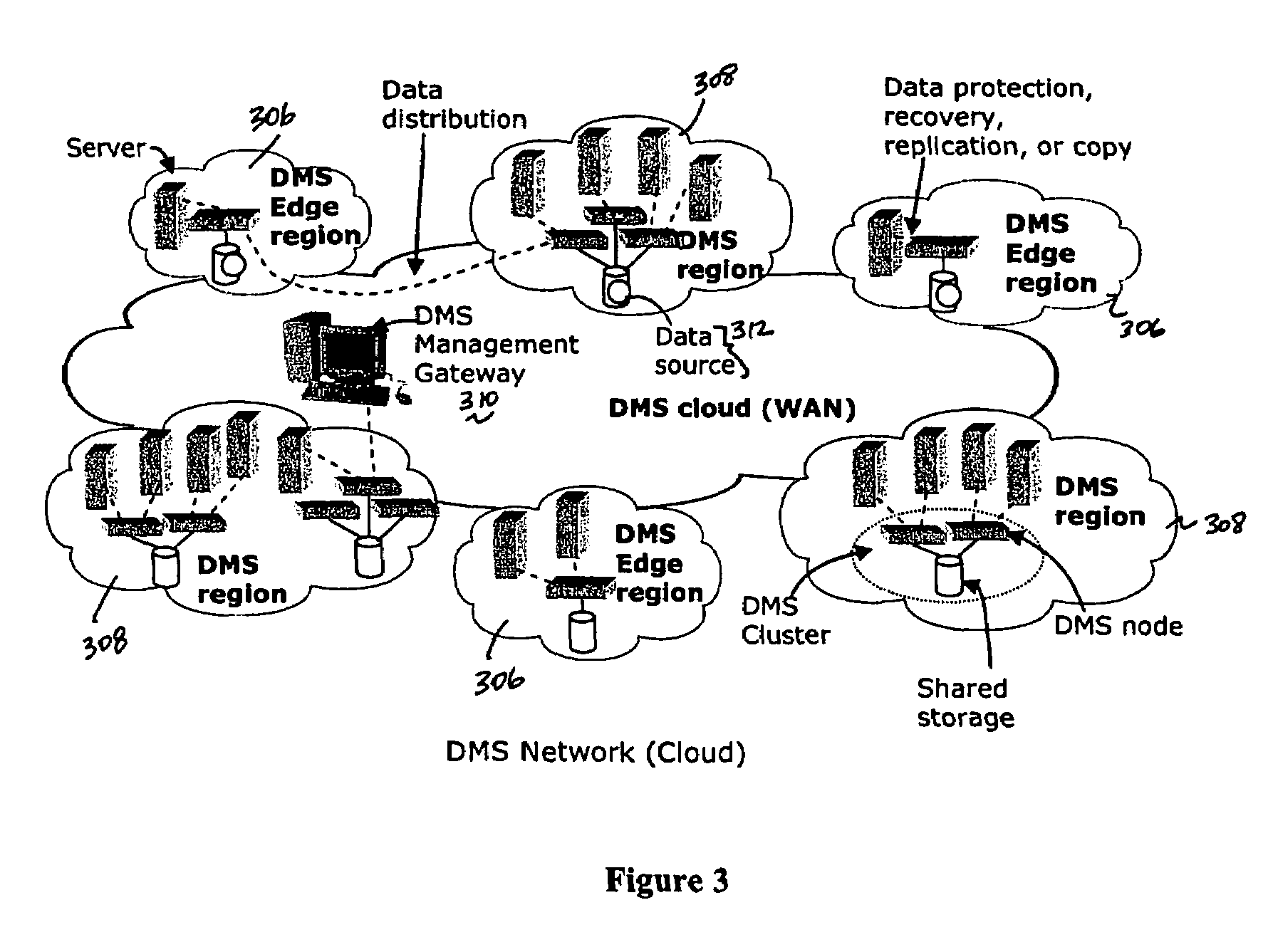
A data management system or “DMS” provides data services to data sources associated with a set of application host servers. The data management system typically comprises one or more regions, with each region having one or more clusters. A given cluster has one or more nodes that share storage. When providing continuous data protection and data distribution, the DMS nodes create distributed object storage to provide the necessary real-time data management services. The objects created by the DMS nodes are so-called active objects. The distributed object store can be built above raw storage devices, a traditional file system, a special purpose file system, a clustered file system, a database, and so on. According to the present invention, the DMS active object store provides an indexing service to the active objects. In an illustrative embodiment, any object property that has a given attribute is indexed and, as a result, the attribute becomes searchable. The DMS provides hierarchical distributed indexing using index trees to facilitate searching in a highly efficient manner.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
Maintaining write order fidelity on a multi-writer system
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
System and method for managing consistency among volumes based on application information
InactiveUS20080228833A1Eliminate the problemData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalDatabase applicationApplication software
In accordance with new technique, a computerized data recovery system includes a storage subsystem and a backup server operatively coupled to backup storage medium, the storage subsystem including a continuous data protection system. The backup server executes a recovery manager which: collects consistency points from at least two database applications executing on at least one host; collects journal terms of the continuous data protection system for each of the at least two database applications; collects log terms associated with each of the at least two database applications; displays to a user a timeline for a protected term and consistency points for the at least two database applications; receives recovery time selection from a user; receives recovery database application selection from the user; receives baseline database application selection from the user; performs crash recovery for each database application; and performs recovery of data based on transactions associated with the at least two database applications.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method and system for automated, no downtime, real-time, continuous data protection
ActiveUS7096392B2Error detection/correctionGroup 6/16 element organic compoundsData streamFinite-state machine
A data management system or “DMS” provides an automated, continuous, real-time, substantially no downtime data protection service to one or more data sources associated with a set of application host servers. To facilitate the data protection service, a host driver embedded in an application server captures real-time data transactions, preferably in the form of an event journal that is provided to other DMS components. The driver functions to translate traditional file / database / block I / O and the like into a continuous, application-aware, output data stream. The host driver includes an event processor that provides the data protection service, preferably by implementing a finite state machine (FSM). In particular, the data protection is provided to a given data source in the host server by taking advantage of the continuous, real-time data that the host driver is capturing and providing to other DMS components. The state of the most current data in DMS matches the state of the data in the host server; as a consequence, the data protection is provided under the control of the finite state machine as a set of interconnected phases or “states.” The otherwise separate processes (initial data upload, continuous backup, blackout and data resynchronization, and recovery) are simply phases of the overall data protection cycle. As implemented by the finite state machine, this data protection cycle preferably loops around indefinitely until, for example, a user terminates the service. A given data protection phase (a given state) changes only as the state of the data and the environment change (a given incident).
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
Continuous protection of data and storage management configuration
ActiveUS9128901B1Input/output to record carriersDatabase distribution/replicationEngineeringStorage management
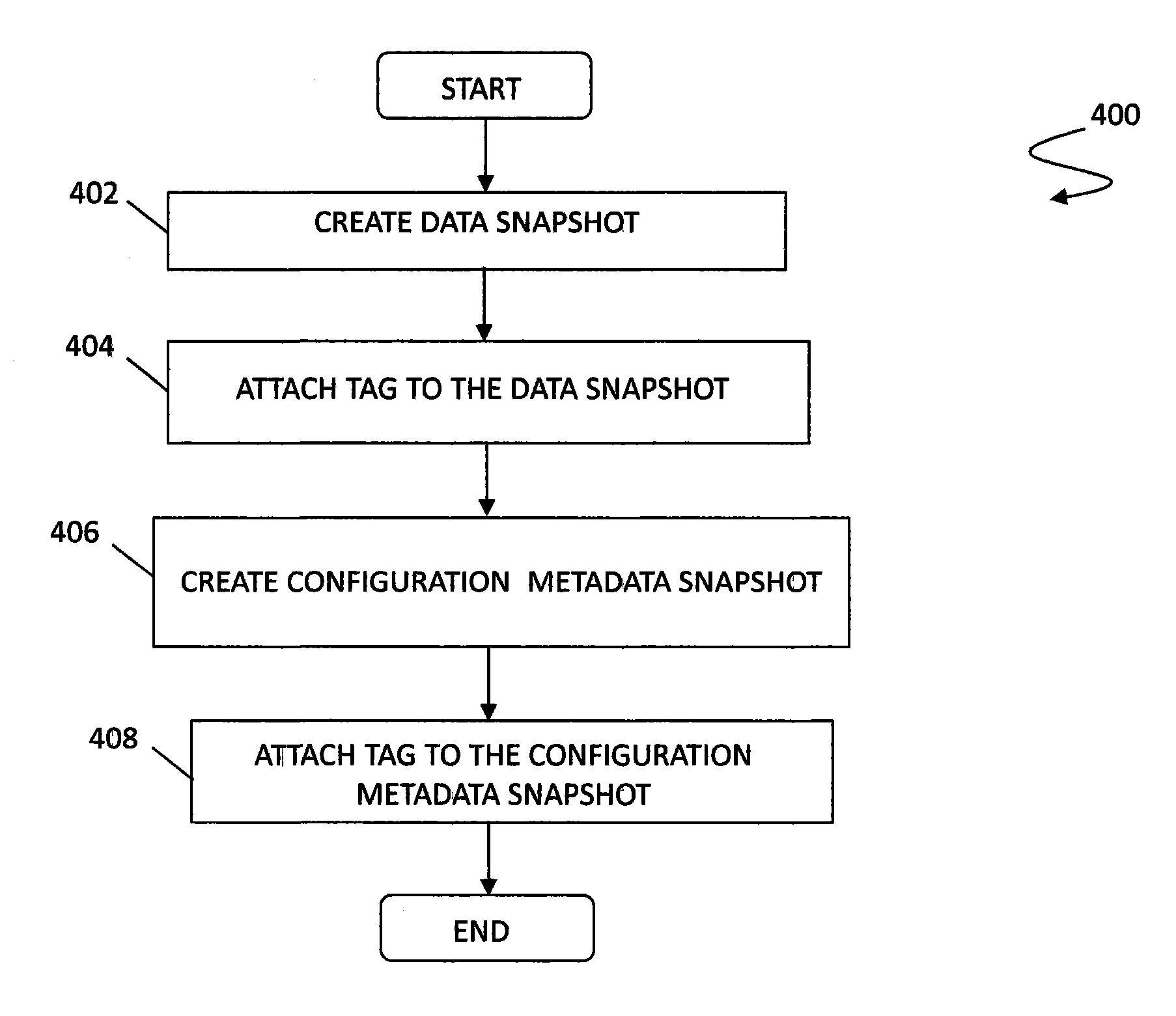
A system is provided for continuous protection of data and storage configuration metadata. Content protected by snapshots, for example, in connection with continuous snapshotting and / or continuous data protection, may be extended to include not only user data but further include configuration metadata of the storage management system. In particular, a user may want to rollback a storage management system to a past point due to performance or stability issues attributed to configuration changes. The system described herein enables rollback to prior states based on storage configuration metadata in addition to rollback of user data and provides for synchronization of the data and configuration metadata in connection with a rollback. The system also enables roll forward processing.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
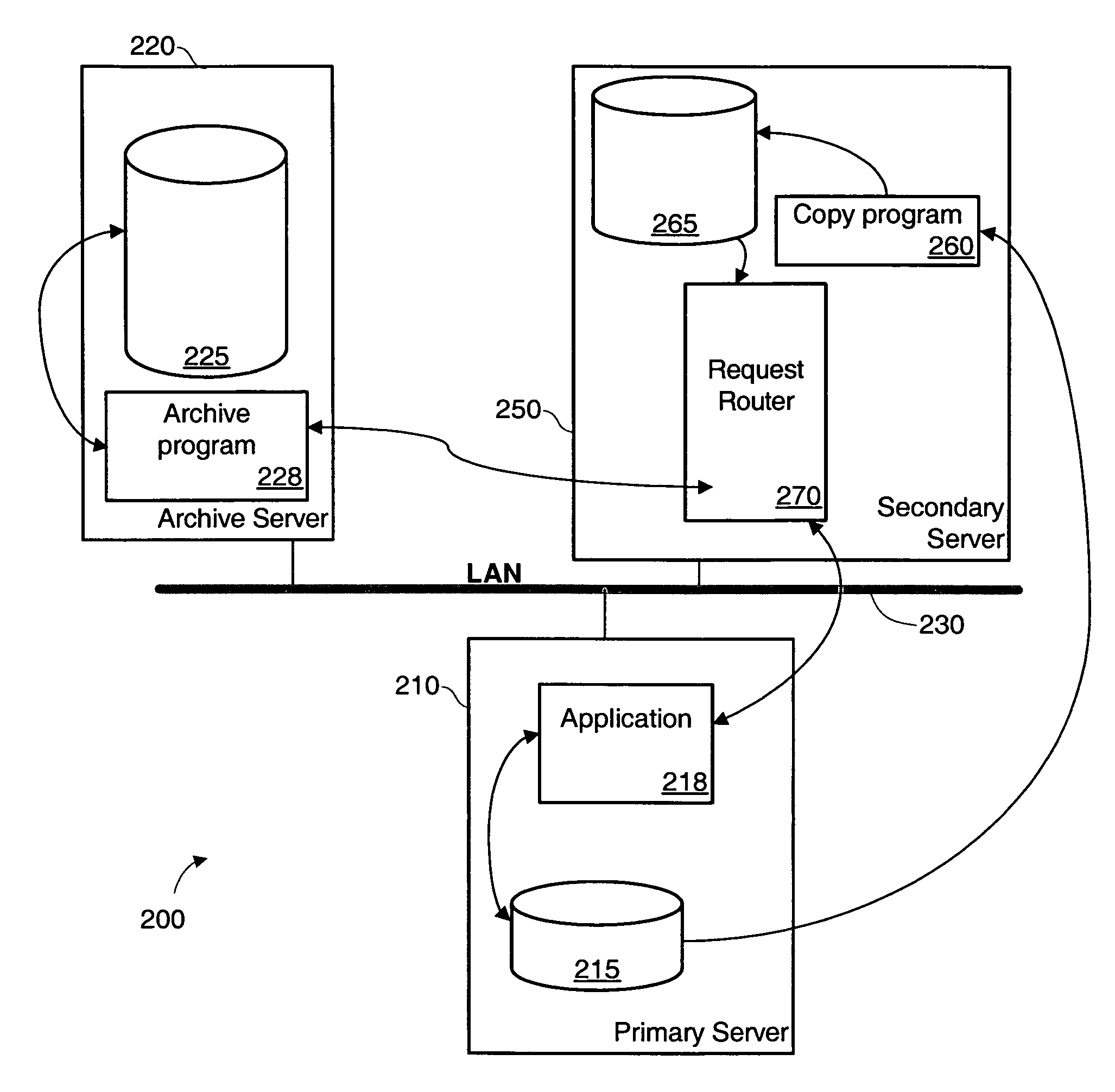
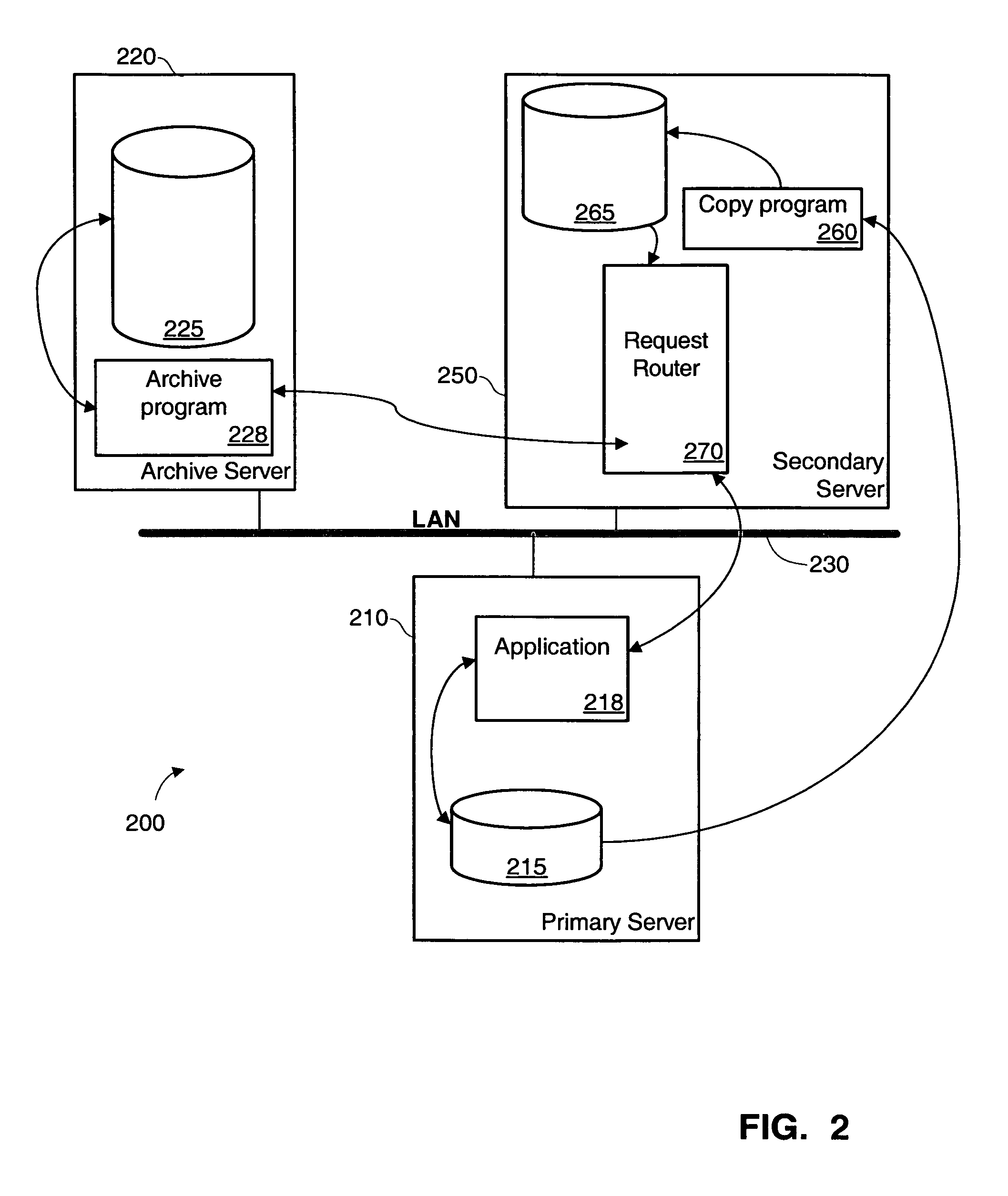
Method and system to offload archiving process to a secondary system
InactiveUS7680843B1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalData setApplication programming interface
Procedures and systems may be used for archiving data from a secondary data set that is a stable copy of a primary data set. In one implementation, the secondary data set is a continuous data protection (CDP) copy of the primary data set. One implementation of a method includes receiving an application programming interface (API) request for archive-eligible data, gathering application data from a secondary data set, obtaining archive-eligible data from the gathered application data, and responding to the request instruction with the archive-eligible data. The gathering is performed by a gathering circuit configured to obtain information from a plurality of types of secondary data sets. The method also includes receiving API modification instructions related to the archive-eligible data, and causing the modification instruction to be performed on the primary data set.
Owner:SYMANTEC OPERATING CORP
Method of creating hierarchical indices for a distributed object system
ActiveUS7689602B1Easy searchImprove efficiencyError detection/correctionDigital data processing detailsIndexing ServiceDistributed object systems
A data management system or “DMS” provides data services to data sources associated with a set of application host servers. The data management system typically comprises one or more regions, with each region having one or more clusters. A given cluster has one or more nodes that share storage. When providing continuous data protection and data distribution, the DMS nodes create distributed object storage to provide the necessary real-time data management services. The objects created by the DMS nodes are so-called active objects. The distributed object store can be built above raw storage devices, a traditional file system, a special purpose file system, a clustered file system, a database, and so on. According to the present invention, the DMS active object store provides an indexing service to the active objects. In an illustrative embodiment, any object property that has a given attribute is indexed and, as a result, the attribute becomes searchable. The DMS provides hierarchical distributed indexing using index trees to facilitate searching in a highly efficient manner.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
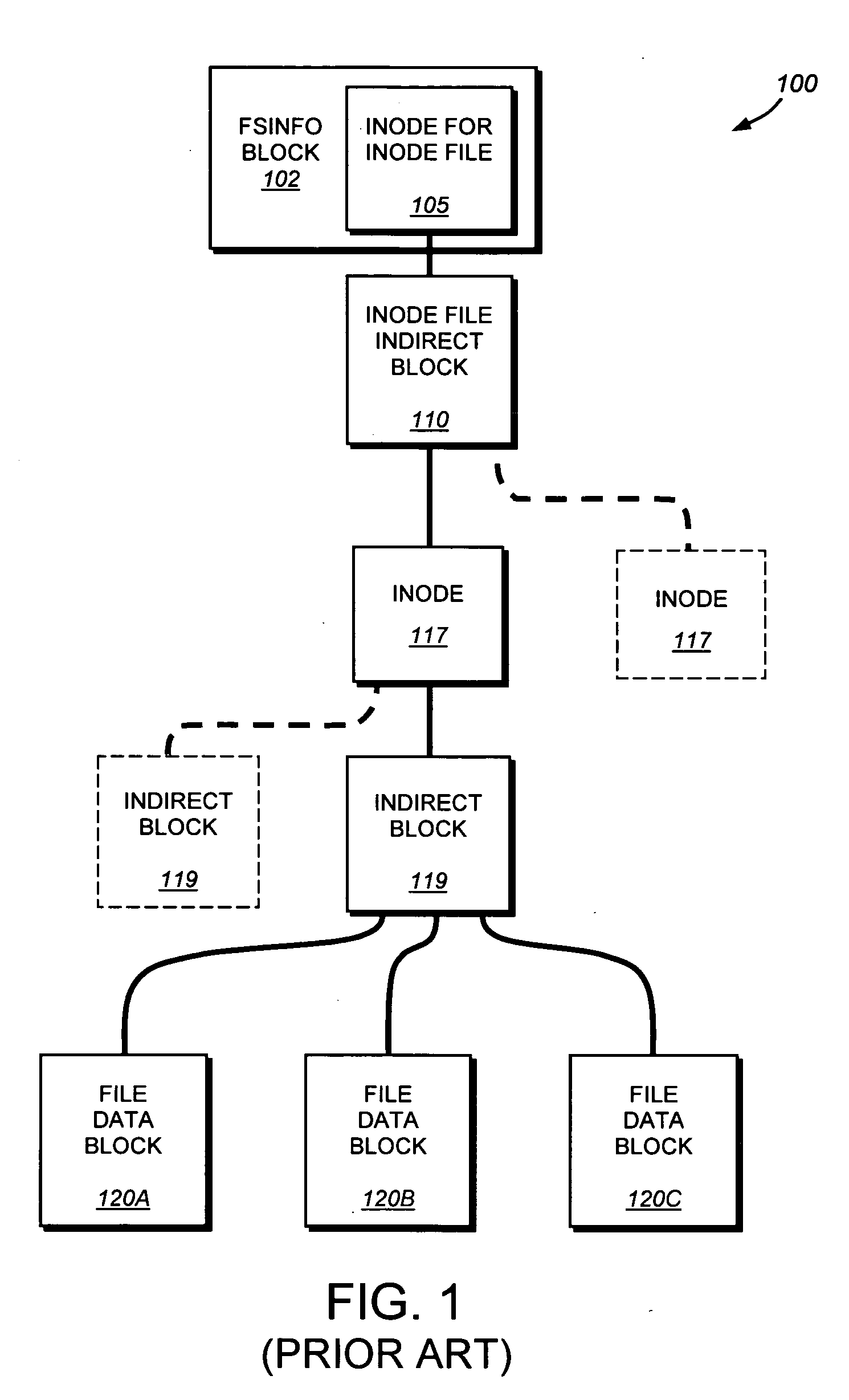
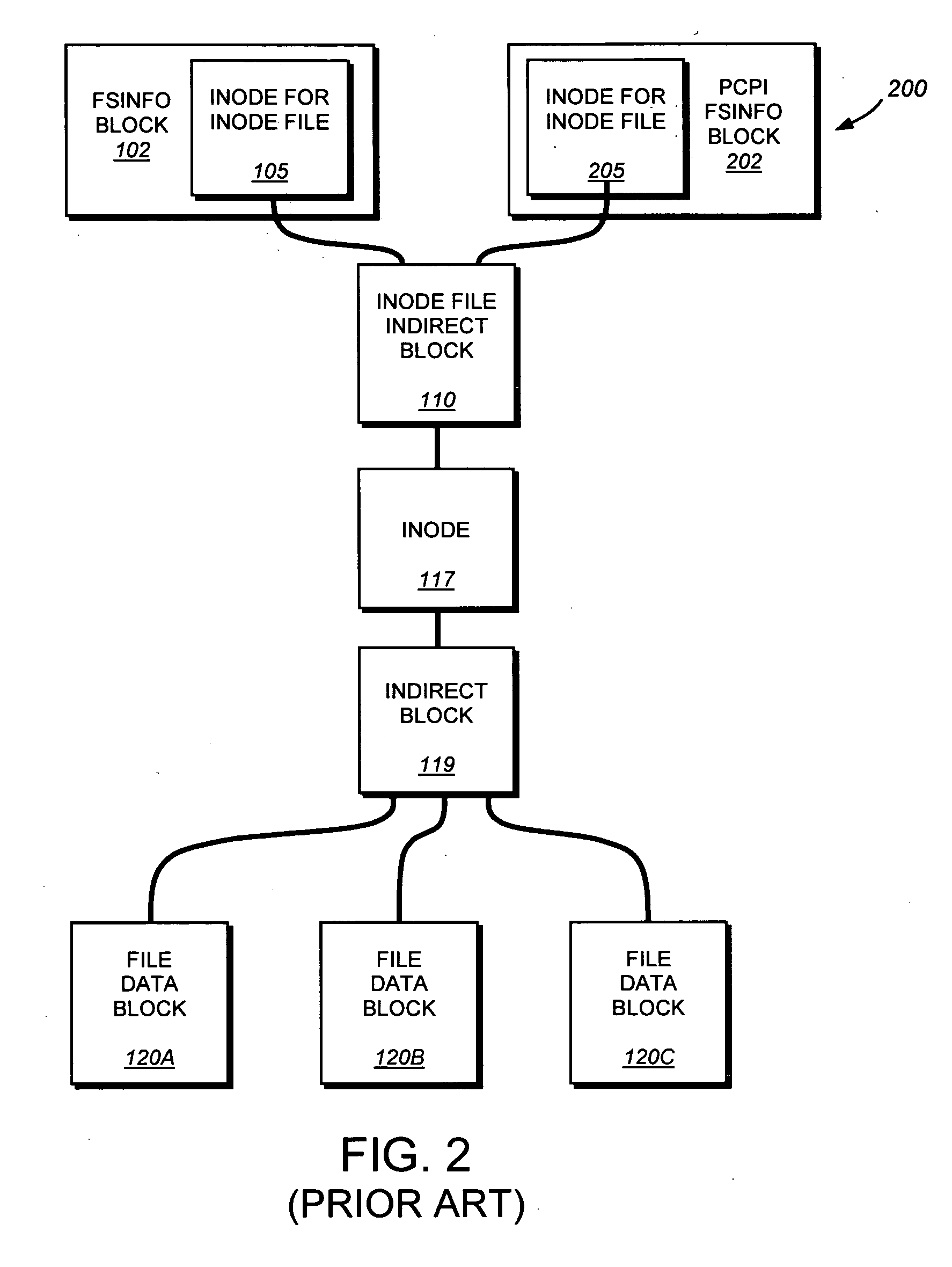
System and method for providing continuous data protection
ActiveUS20070276878A1Easy to useDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsFile systemContinuous data protection
A system and method provides continuous data protection using checkpoints in a write anywhere file system. During a consistency point of a write anywhere file system, freed blocks are identified and are appended to a delete log for retention. A consistency point log is updated with a new entry associated with the consistency point. If the file system needs to retrieve its state at a particular point in time, the stored blocks of the delete log may be recovered
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
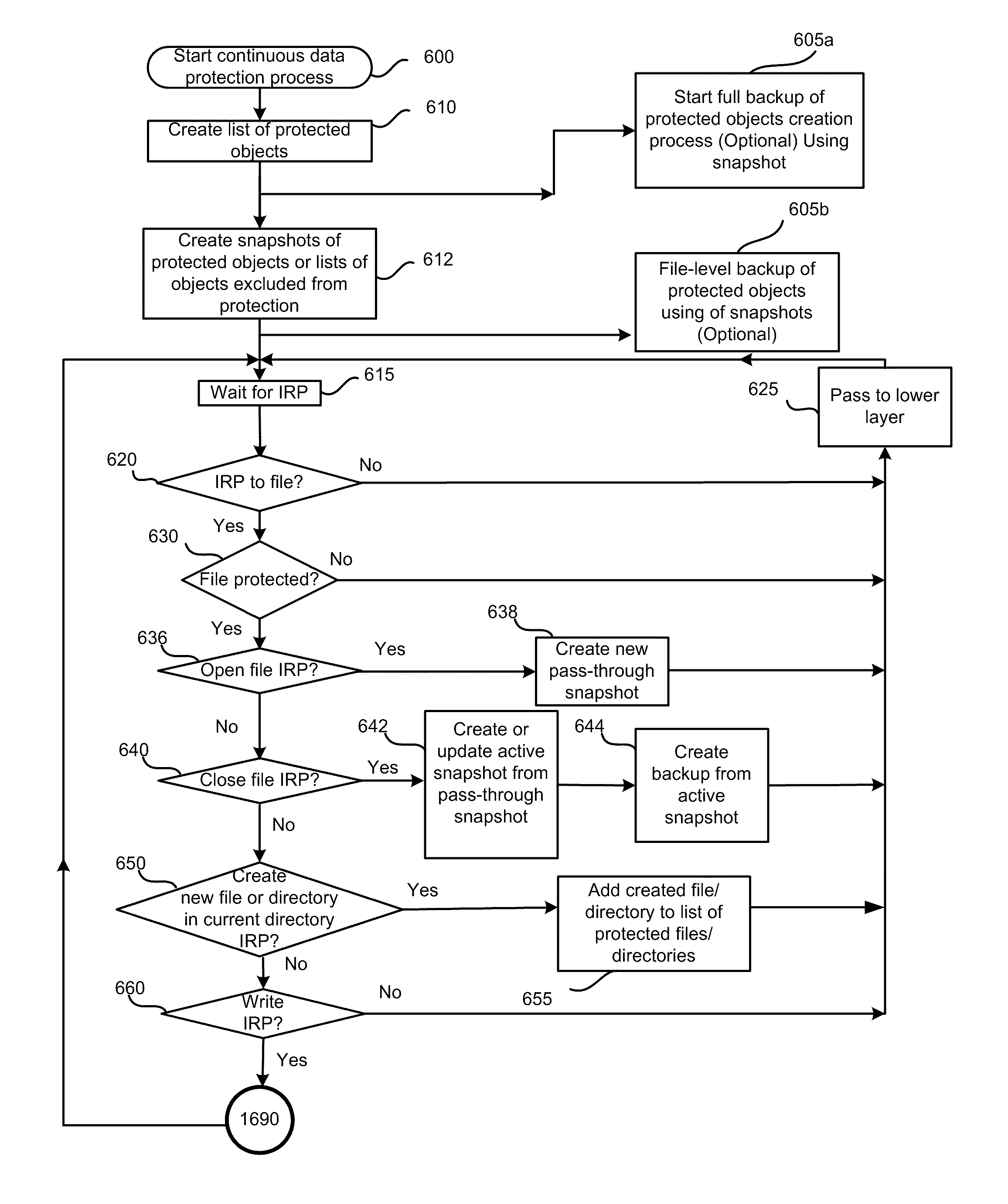
File-level continuous data protection with access to previous versions
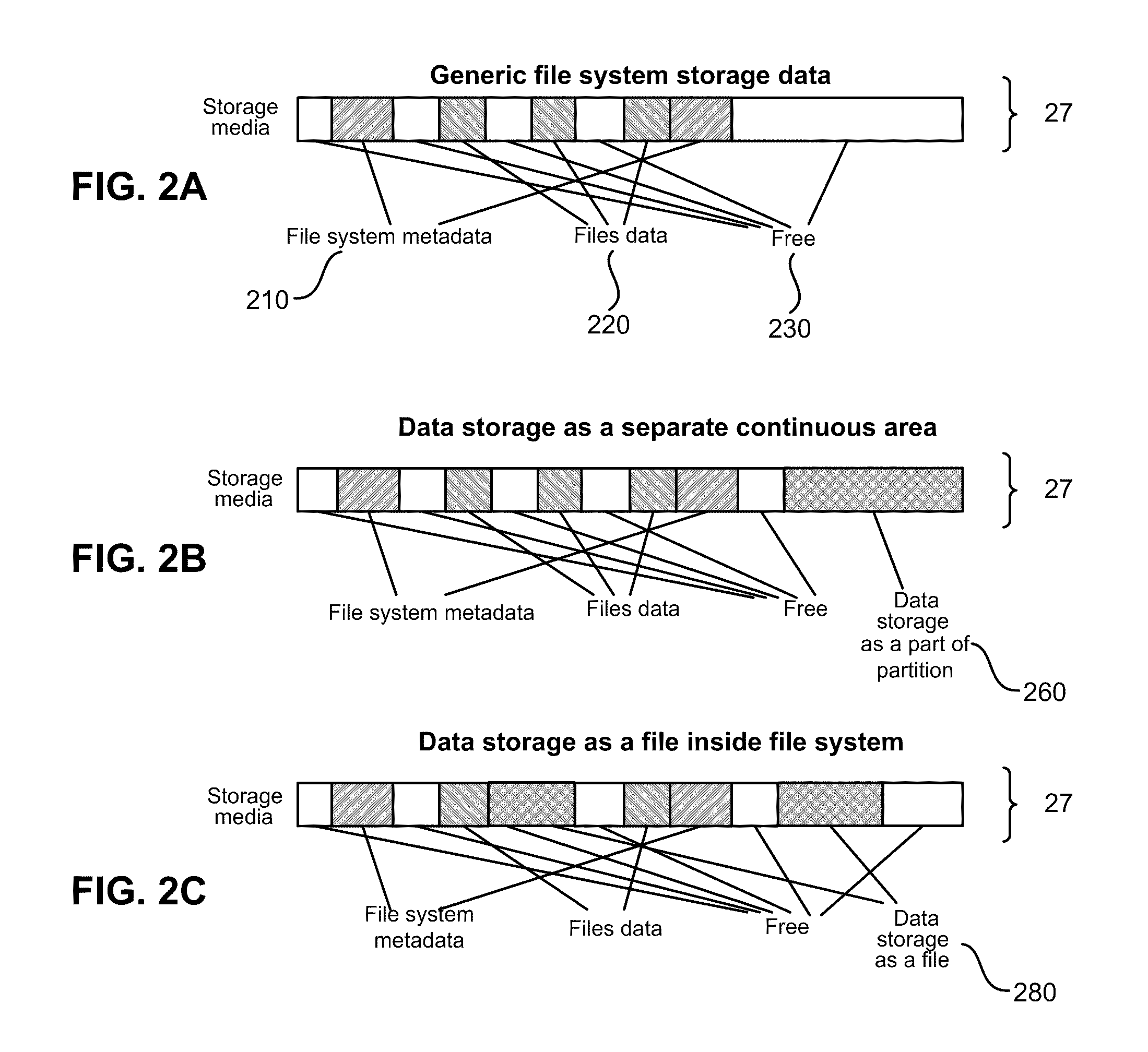
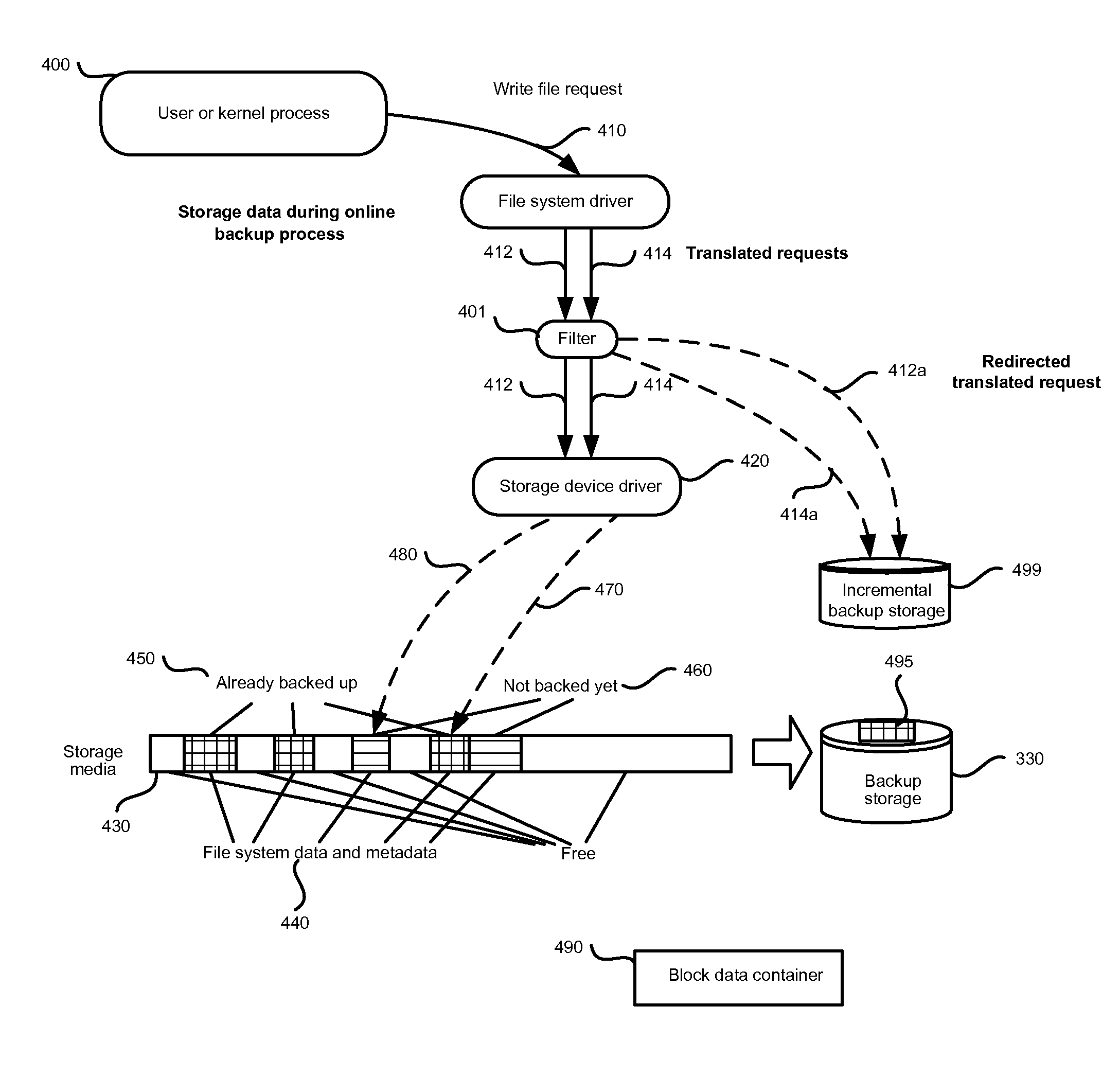
ActiveUS8005797B1View effectivelyOvercome disadvantagesDigital data processing detailsError detection/correctionFile systemData memory
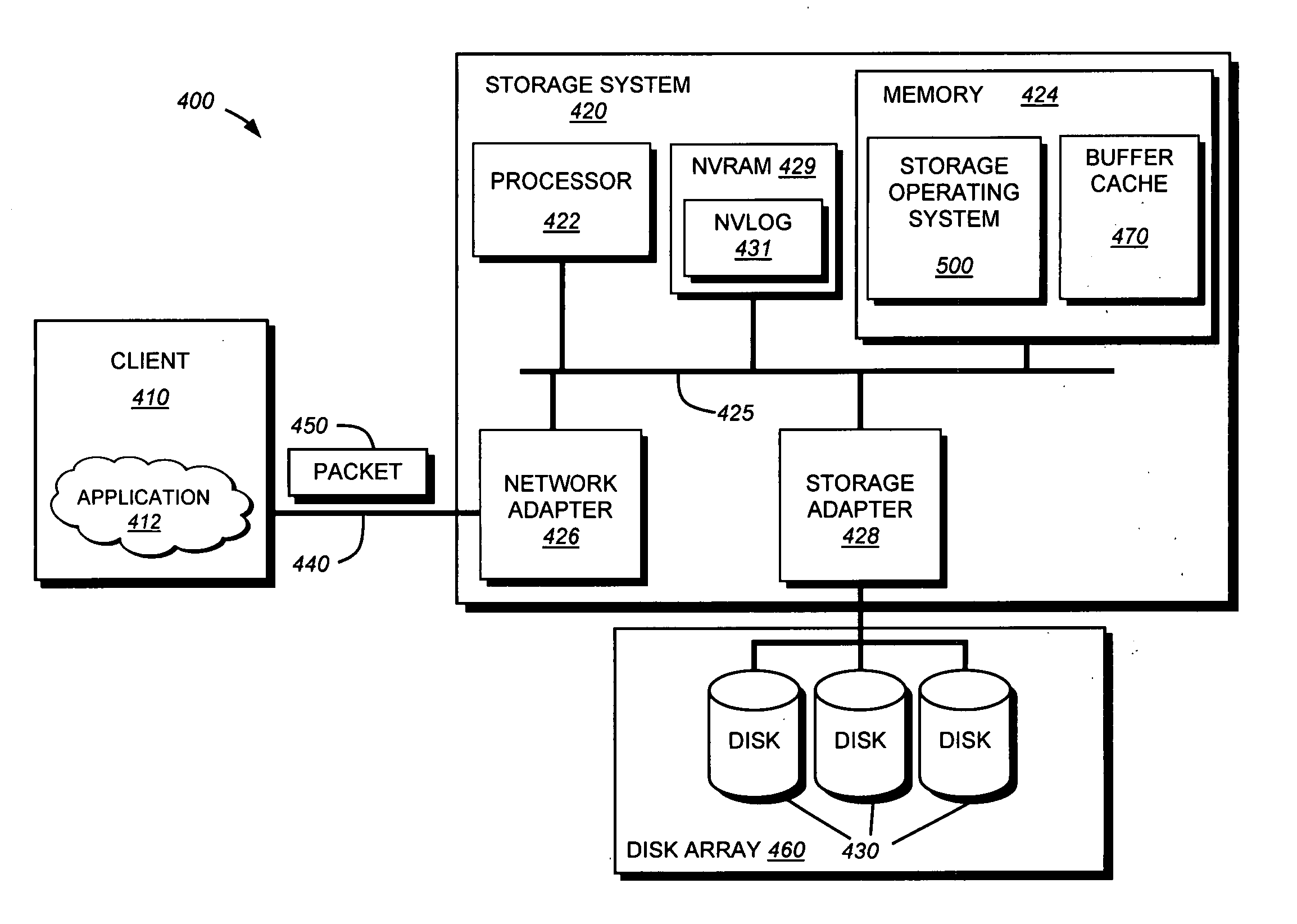
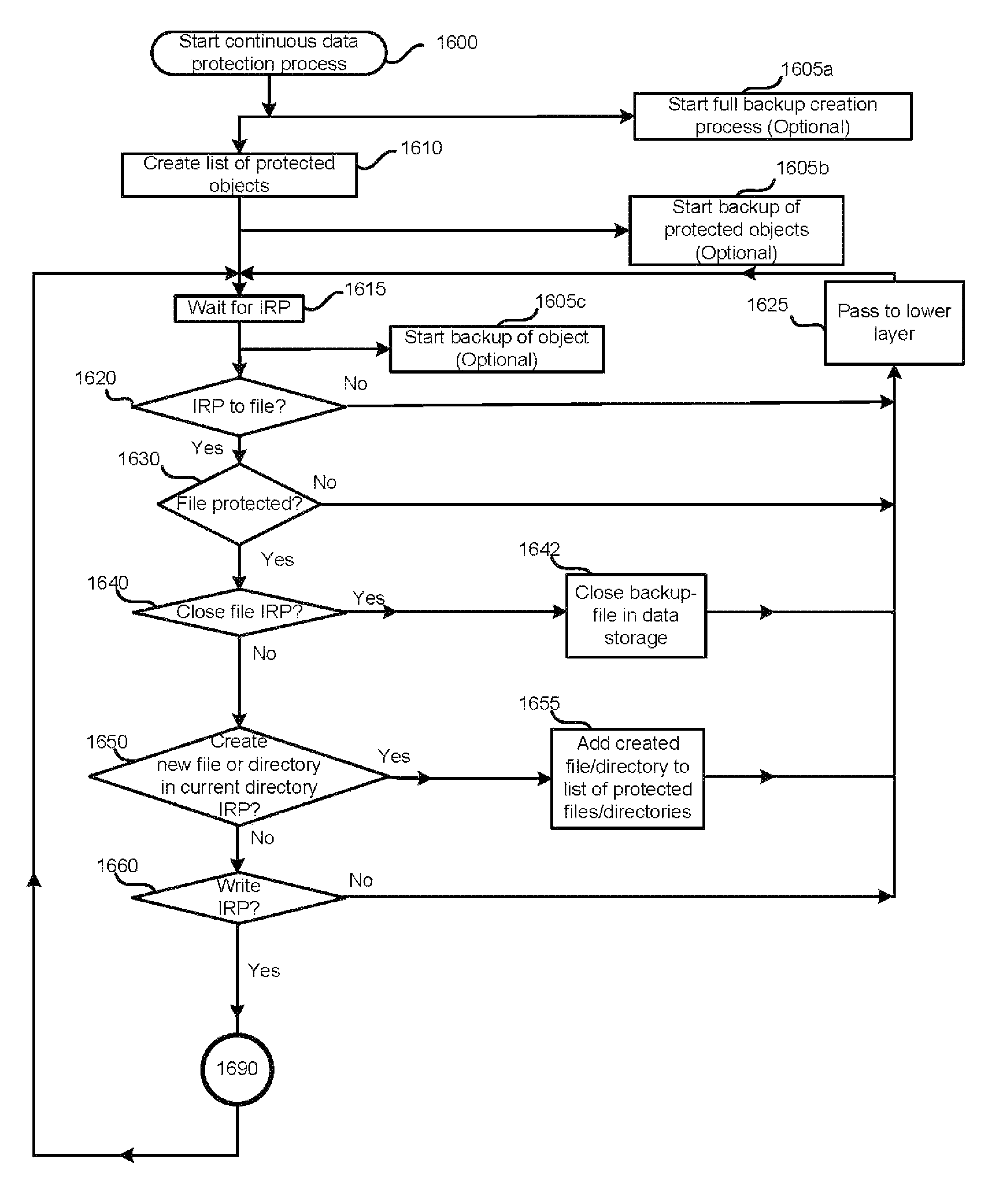
A system for continuous data protection includes a storage device and a backup storage device. The continuous data protection procedure is performed as two parallel processes: creating an initial backup by copying a data as a file / directory from the storage device into the backup storage device, and copying the data to be written to the data storage as a part of a file / directory into the incremental backup. When a write command is directed to a file system driver, it is intercepted and redirected to the backup storage, and the data to be written in accordance with the write request, is written to the incremental backup on the backup storage. If the write command is also directed to a data (a file / directory) that has been identified for backup, but has not yet been backed up, the identified data (a file / directory) is copied from the storage device to the intermediate storage device. Then, the write command is executed on the identified file / directory on the storage device and the file / directory is copied from the intermediate storage device.
Owner:MIDCAP FINANCIAL TRUST
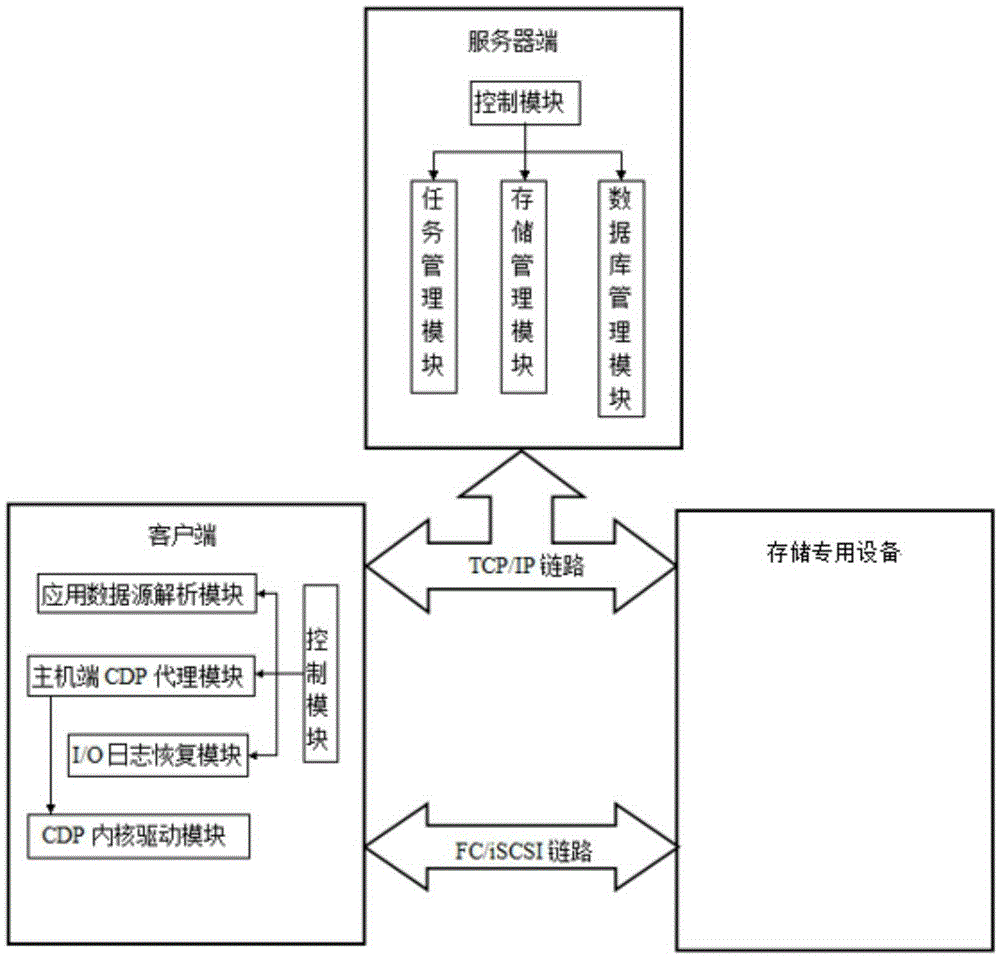
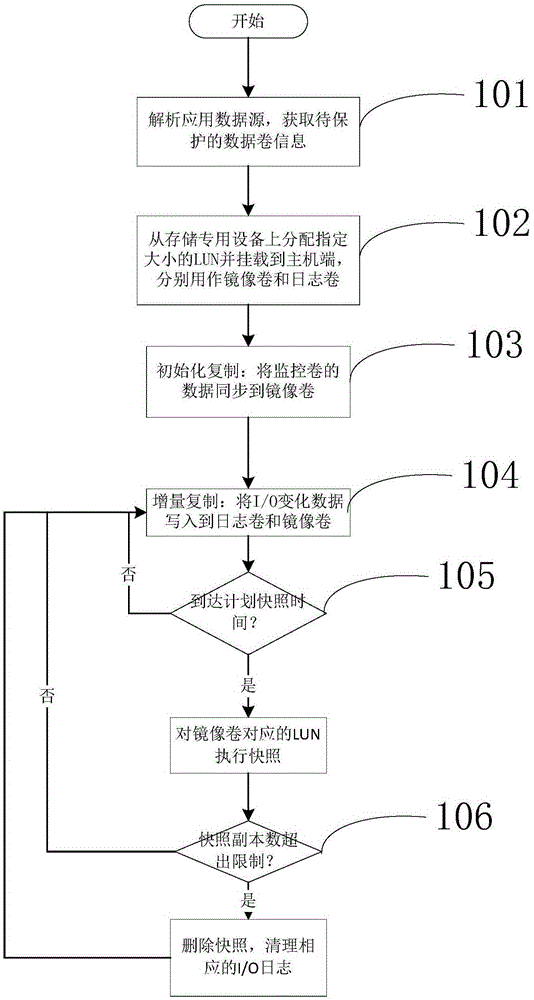
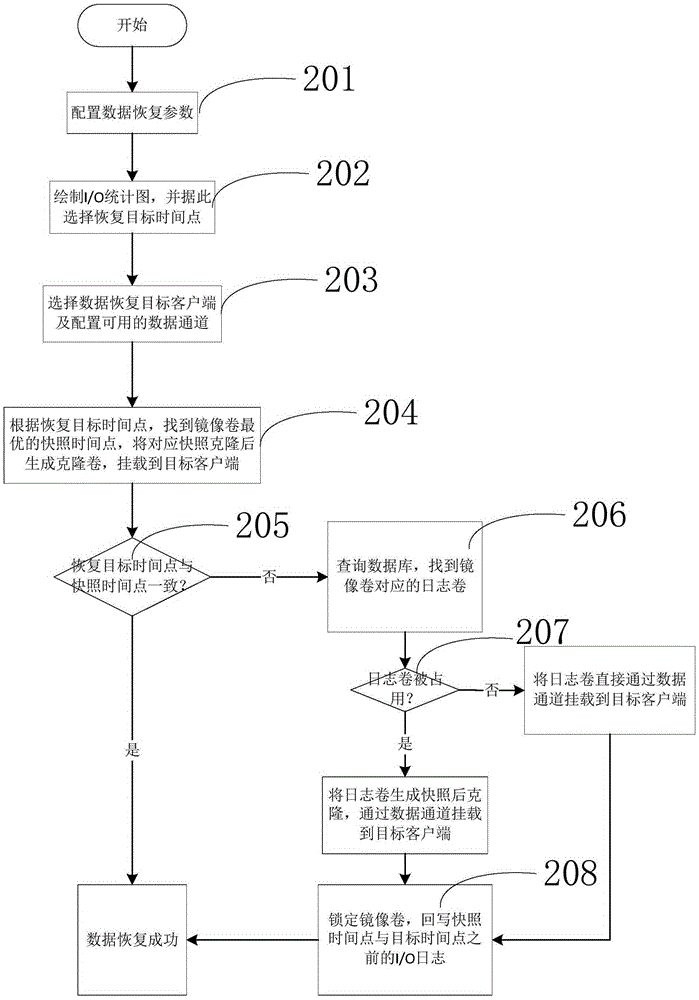
A continuous data protection system and its realization method
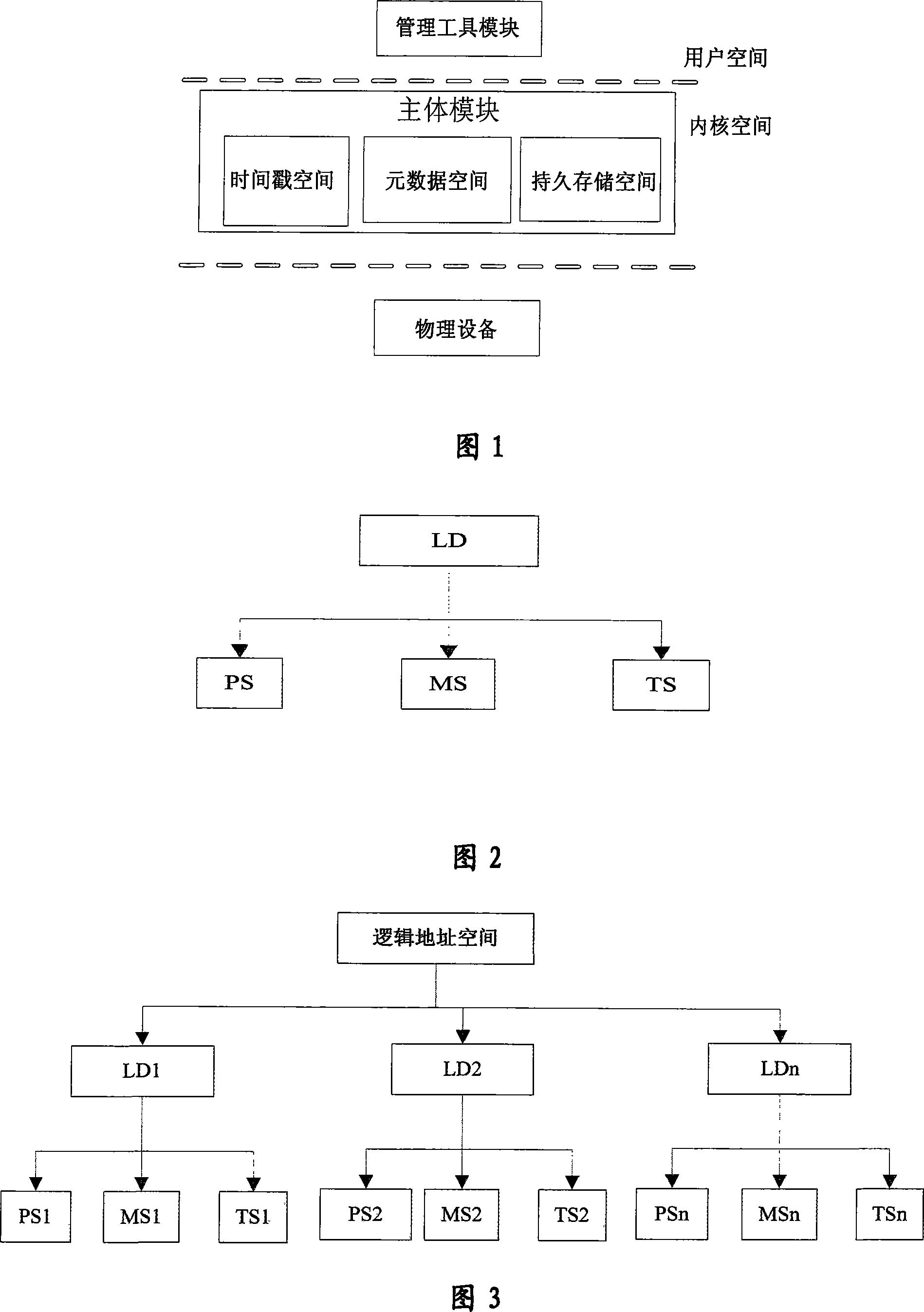
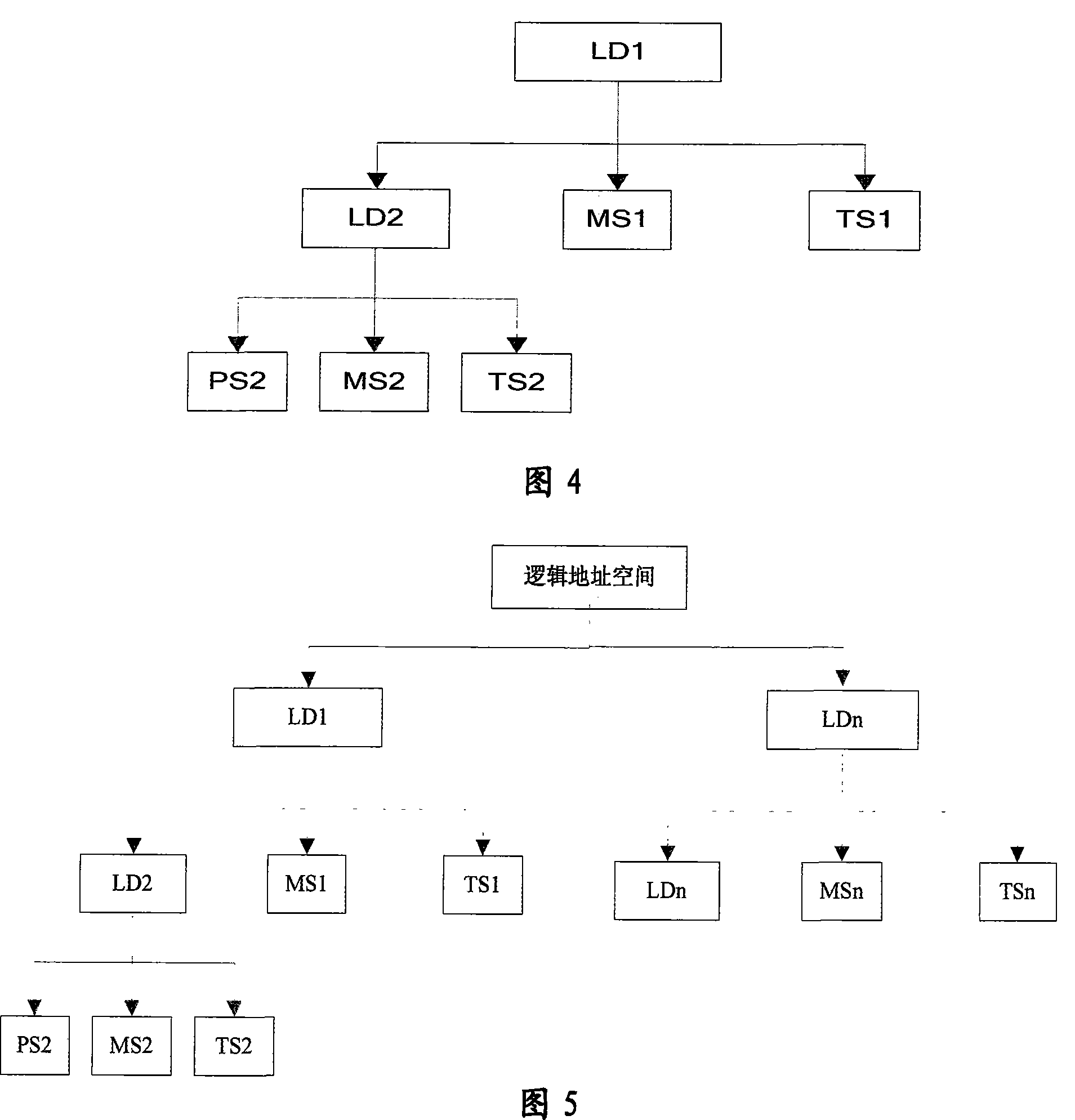
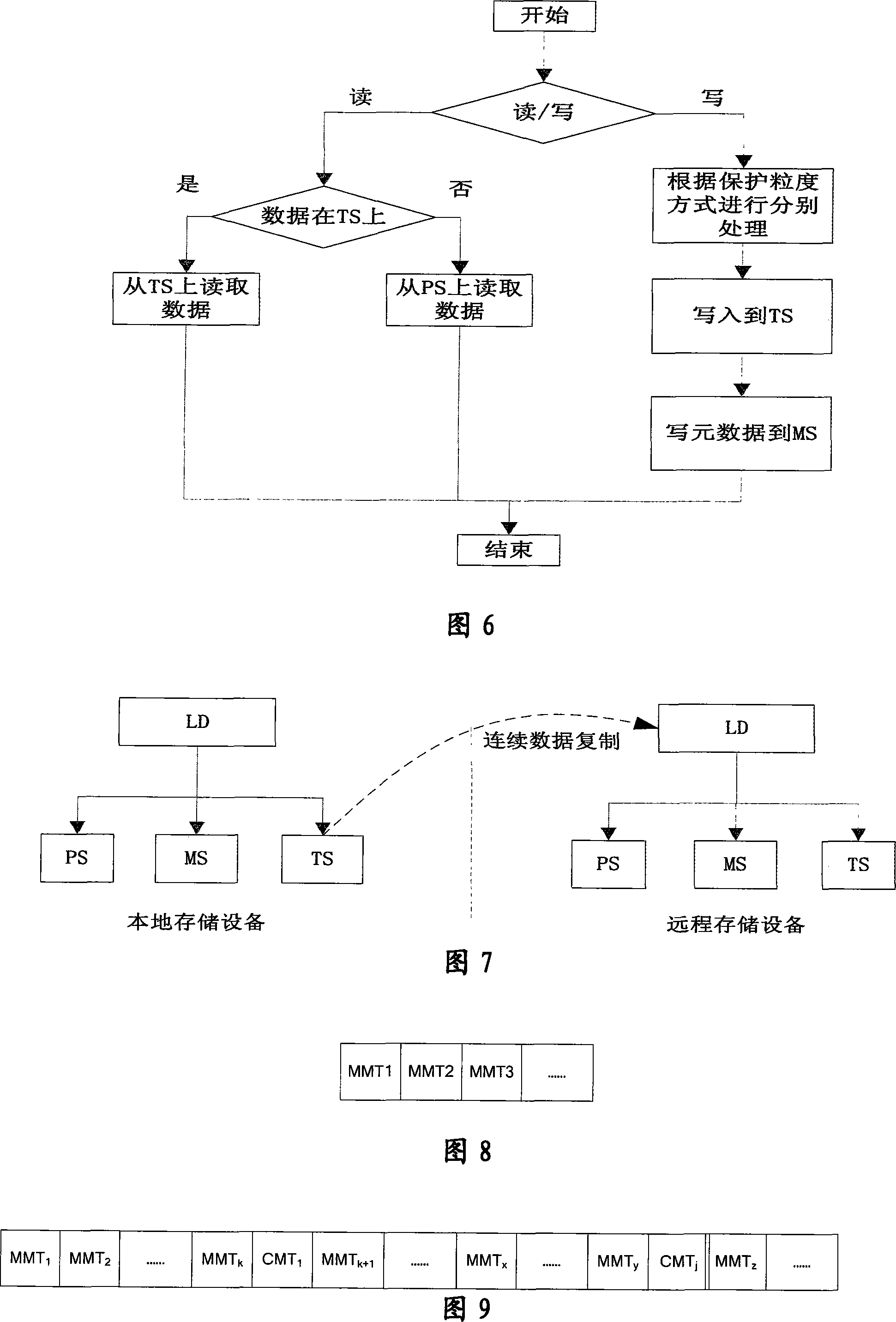
ActiveCN101187948AReliability is not reducedRedundant operation error correctionSpecial data processing applicationsManagement toolGranularity
The invention provides a Continuous Data Protection CDP system and the realizing method thereof. The system comprises a management tool module, a main body module and physical equipment. The system can perform flexible stack. The management tool module is used for building the main body module with a temporal point, and performing the operations of reading, writing and storing to the main body module, according to the difference of the data access frequency and the data level, the important data which is accessed recently adopts a CDP technique with a fine grit, the non-important data which is not accessed often adopts a back-up protection technique with a coarse particle size, thereby the invention can support continuous data protection of different protection granularities, through the flexible stack structure, the requirement of the data memory capacity is reduced, while the reliability for the data continuous protection is not reduced.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and system for virtual on-demand recovery for real-time, continuous data protection
A data management system or “DMS” provides an automated, continuous, real-time, substantially no downtime data protection service to one or more data sources associated with a set of application host servers. To facilitate the data protection service, a host driver embedded in an application server captures real-time data transactions, preferably in the form of an event journal that is provided to other DMS components. The driver functions to translate traditional file / database / block I / O and the like into a continuous, application-aware, output data stream. The host driver includes an event processor. When an authorized user determines that a primary copy of the data in the host server has become incorrect or corrupted, the event processor can perform a recovery operation to an entire data source or a subset of the data source using former point-in-time data in the DMS. The recovery operation may have two phases. First, the structure of the host data in primary storage is recovered to the intended recovering point-in-time. Thereafter, the actual data itself is recovered. The event processor enables such data recovery in an on-demand manner, in that it allows recovery to happen simultaneously while an application accesses and updates the recovering data.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
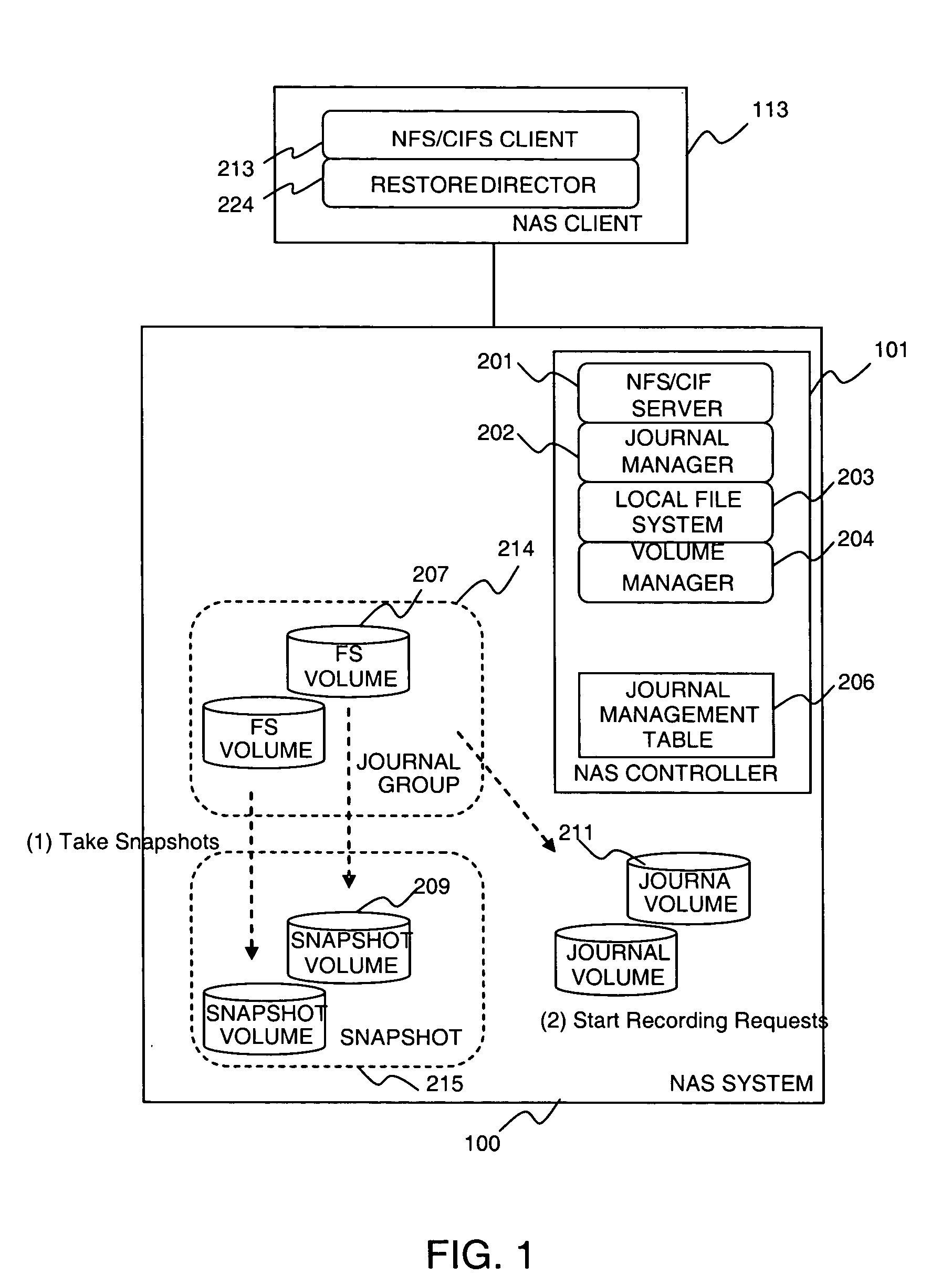
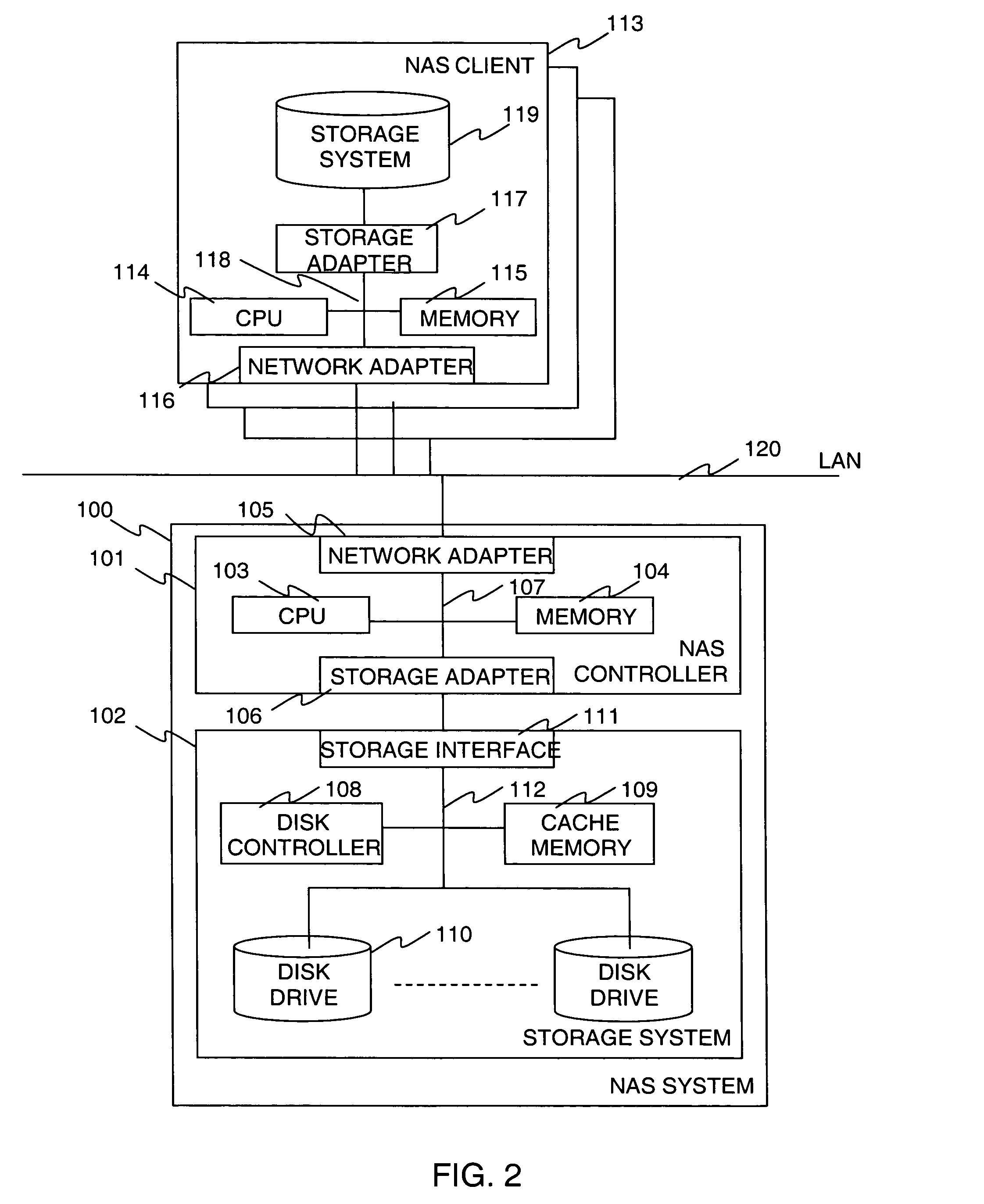
Method and apparatus of continuous data protection for NAS
InactiveUS20080027998A1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsFile systemClient-side
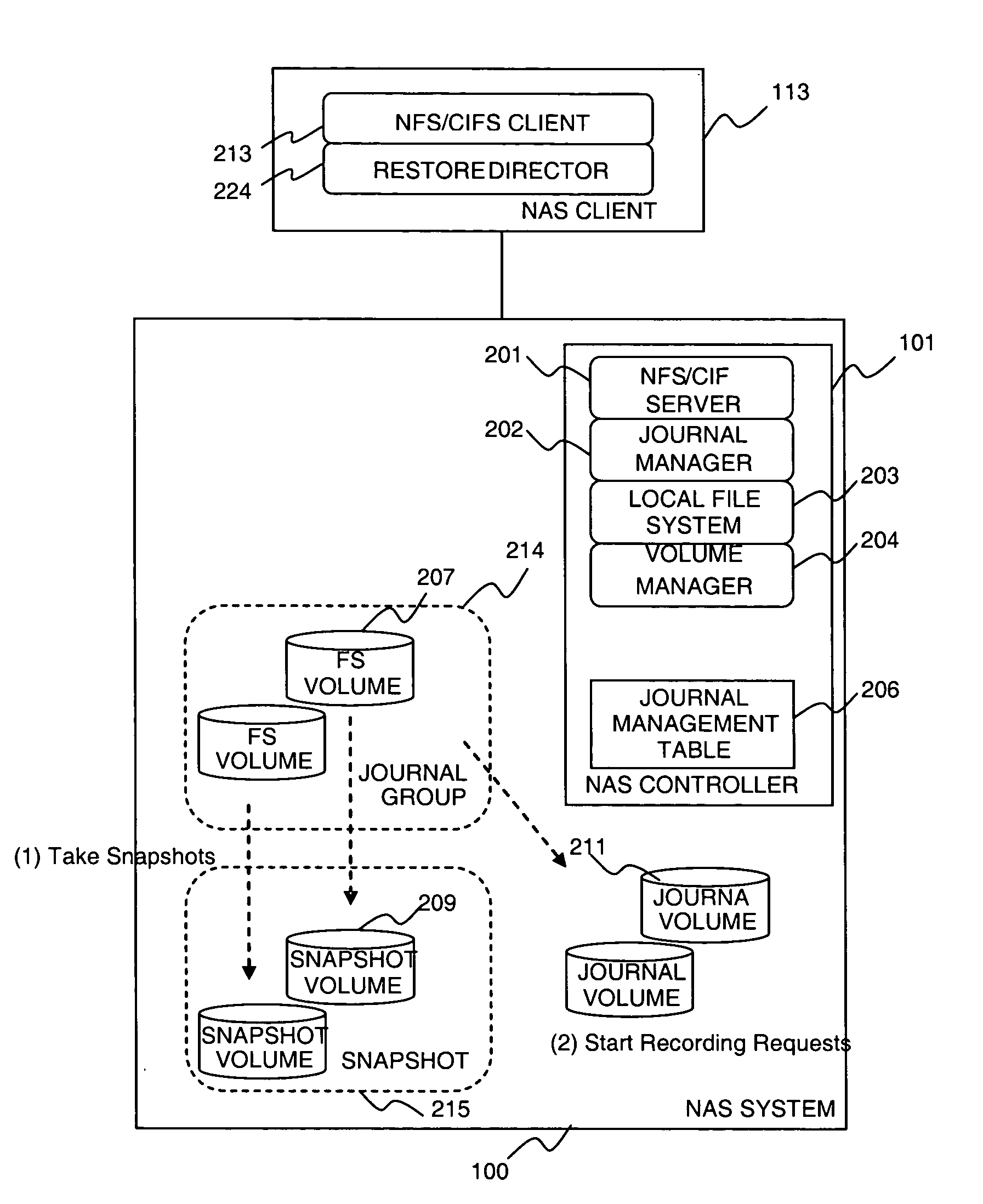
A system includes a NAS System and one or more NAS Clients. The NAS system manages volumes containing file system data, volumes containing snapshot (copy) of the file system data, and volumes containing journal (log) of requests sent from NAS Clients. The system takes a snapshot of the volume containing file system data periodically, and records requests to the file system data after the snapshot is taken. When the system needs to restore an image of file system data at a certain point, it restores the snapshot, and then it replays the recorded requests in order. The system protects a file system using CDP function on a storage system by implementing a function in the NAS system, which determines a time point at which each storage system operation is completed, and a function in the storage system for keeping the information in the journal.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
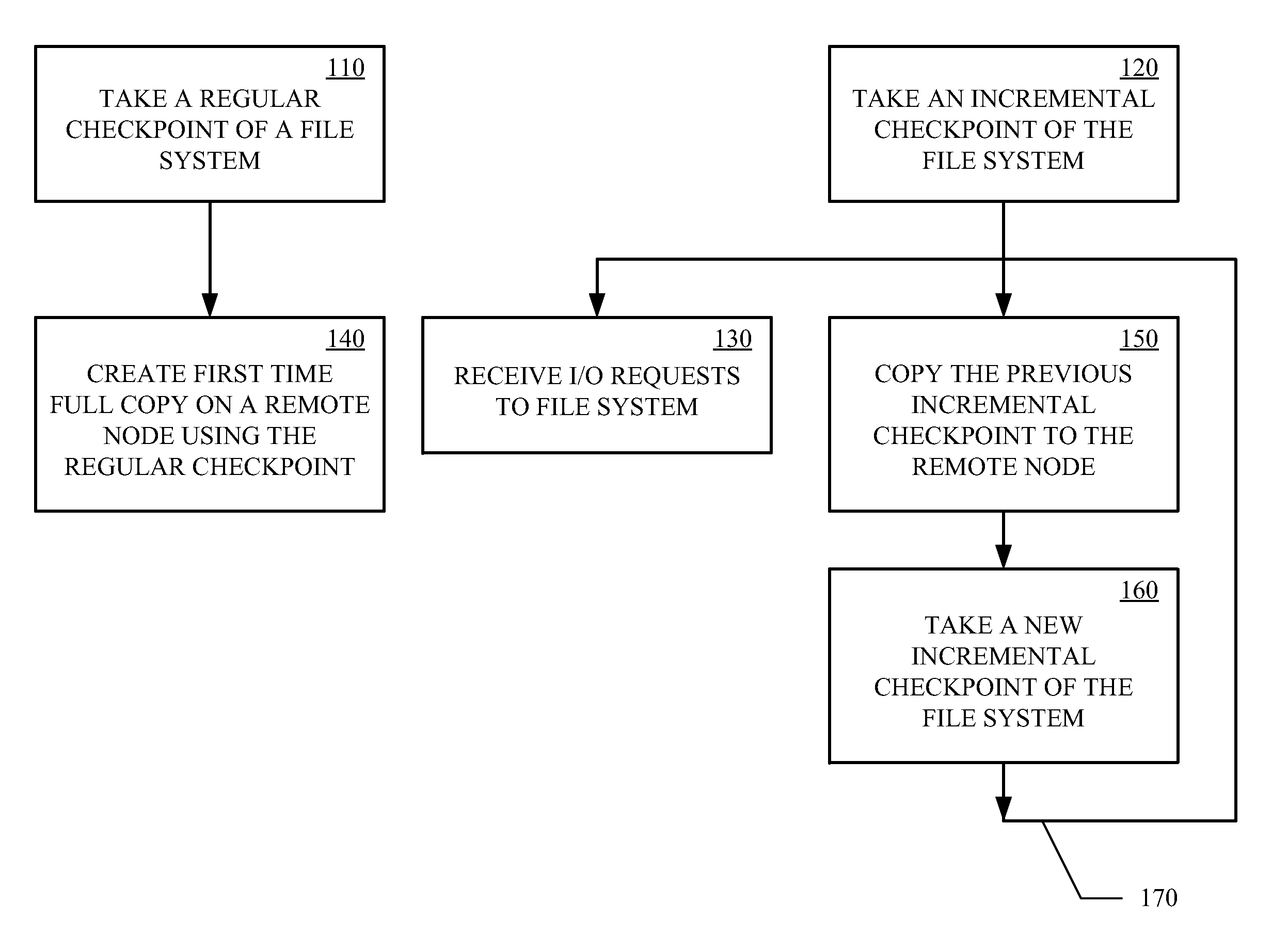
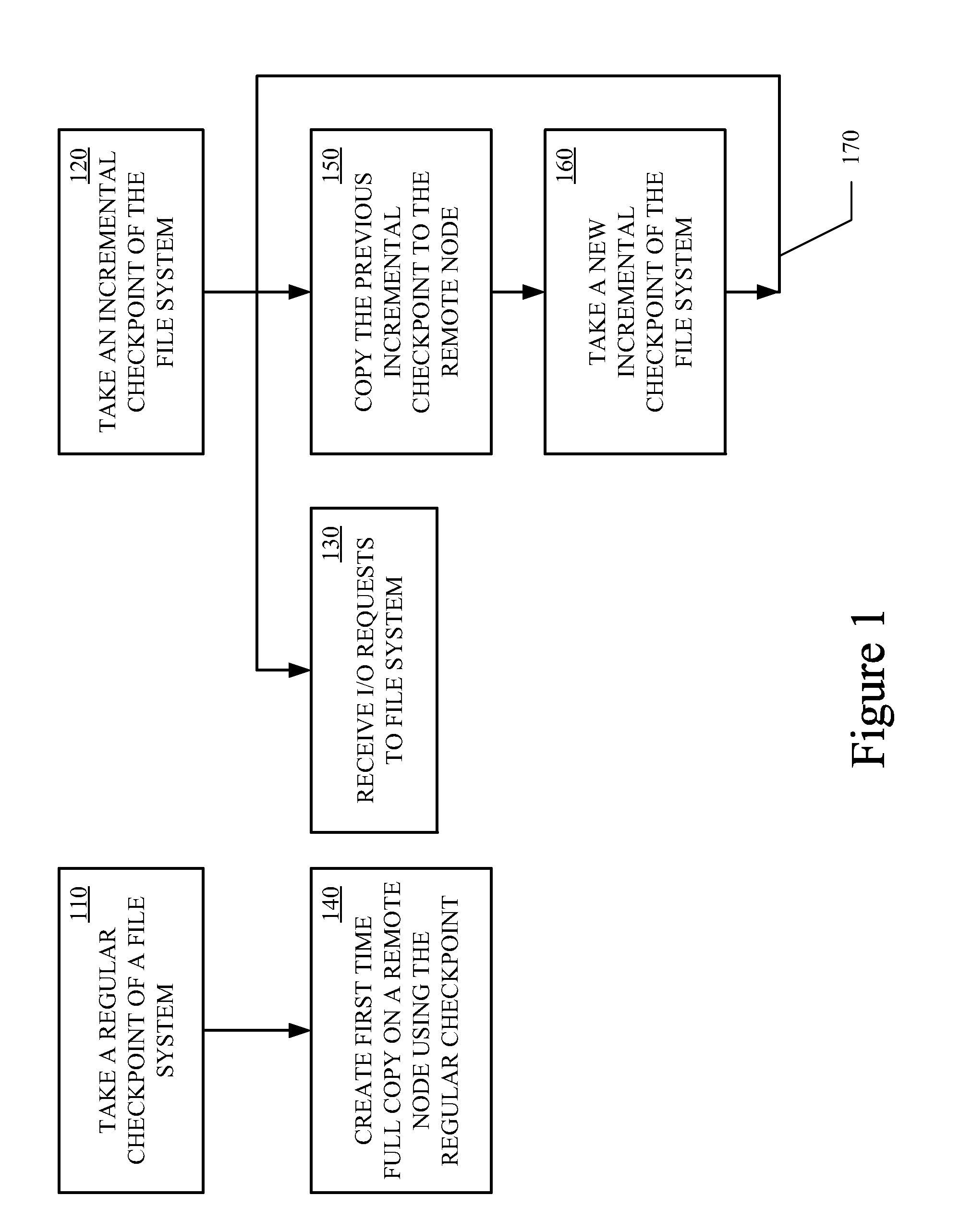
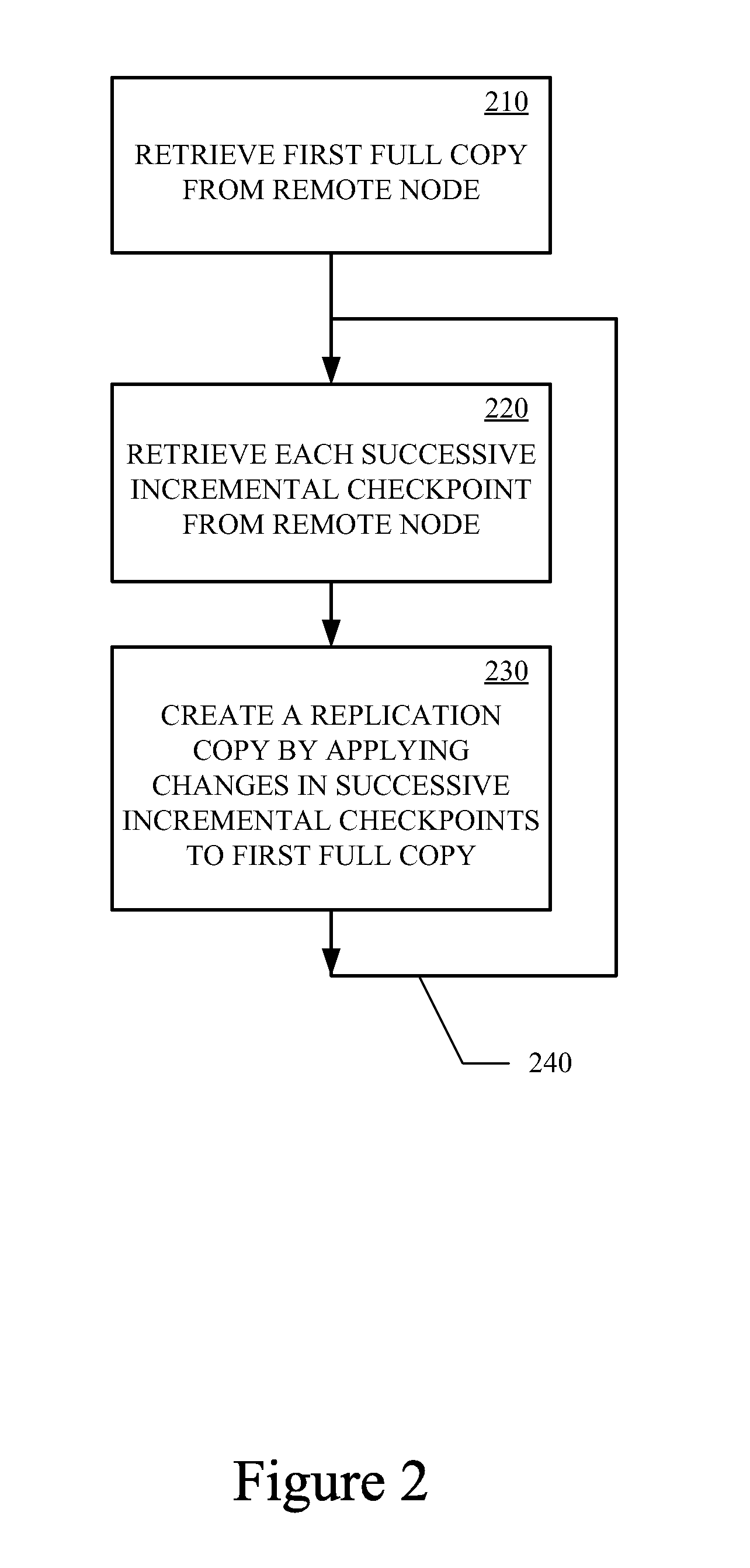
Data Replication Techniques Using Incremental Checkpoints
ActiveUS20120036106A1Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsFile systemContinuous data protection
Incremental checkpoint, for use in data replication, track the changes made to a file system after a point in time at which the incremental checkpoint is created. Data replication techniques using the incremental checkpoints may include taking a regular checkpoint of the file system and creating the first time full copy on remote node using the regular checkpoint. Changes made to the file system are then tracked in an incremental checkpoint that are stored on the remote node. The processes of taking the incremental checkpoint and storing the incremental checkpoint are iteratively performed. The first time fully copy and the incremental checkpoints may then be used for data replication, backup, continuous data protection (CDP), or the like.
Owner:VERITAS TECH
Method and system for continuous data protection
ActiveUS8051044B1Digital data processing detailsError detection/correctionData capacityIncremental backup
Continuous data protection is performed as two parallel processes: copying a data block from the storage device into the backup storage device (creating initial backup) and copying the data block to be written to the data storage into the incremental backup. When a write command is directed to a data storage block, it's intercepted and redirected to the backup storage, and data, which is to be written in accord to the write request, is written to the incremental backup on the backup storage. If write command is also directed to a data storage block identified for backup that has not yet been backed up, the identified data storage block is copied from the storage device to the intermediate storage device, the write command is executed on the identified data storage block from the storage device, and the data storage block is copied from the intermediate storage device to the backup storage device. In case of an error accessing a block on the storage device, the block is marked as invalid. The system suspends a write command to the storage device during the initial data backup process if the intermediate storage device has reached a selected data capacity; and copies a selected amount of data from the intermediate storage device to the backup storage device.
Owner:MIDCAP FINANCIAL TRUST
Snapshot storage and data recovery method of continuous data protection system
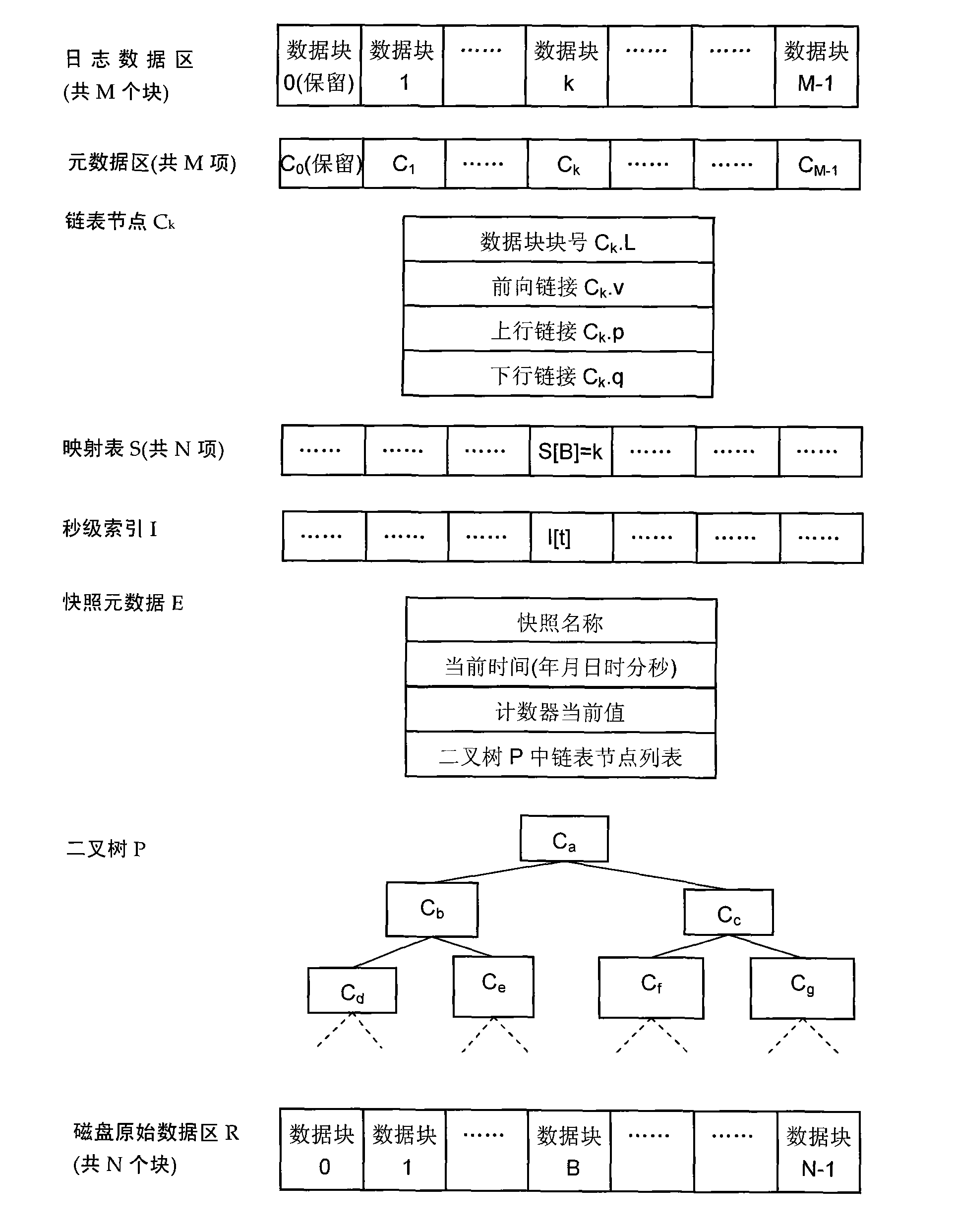
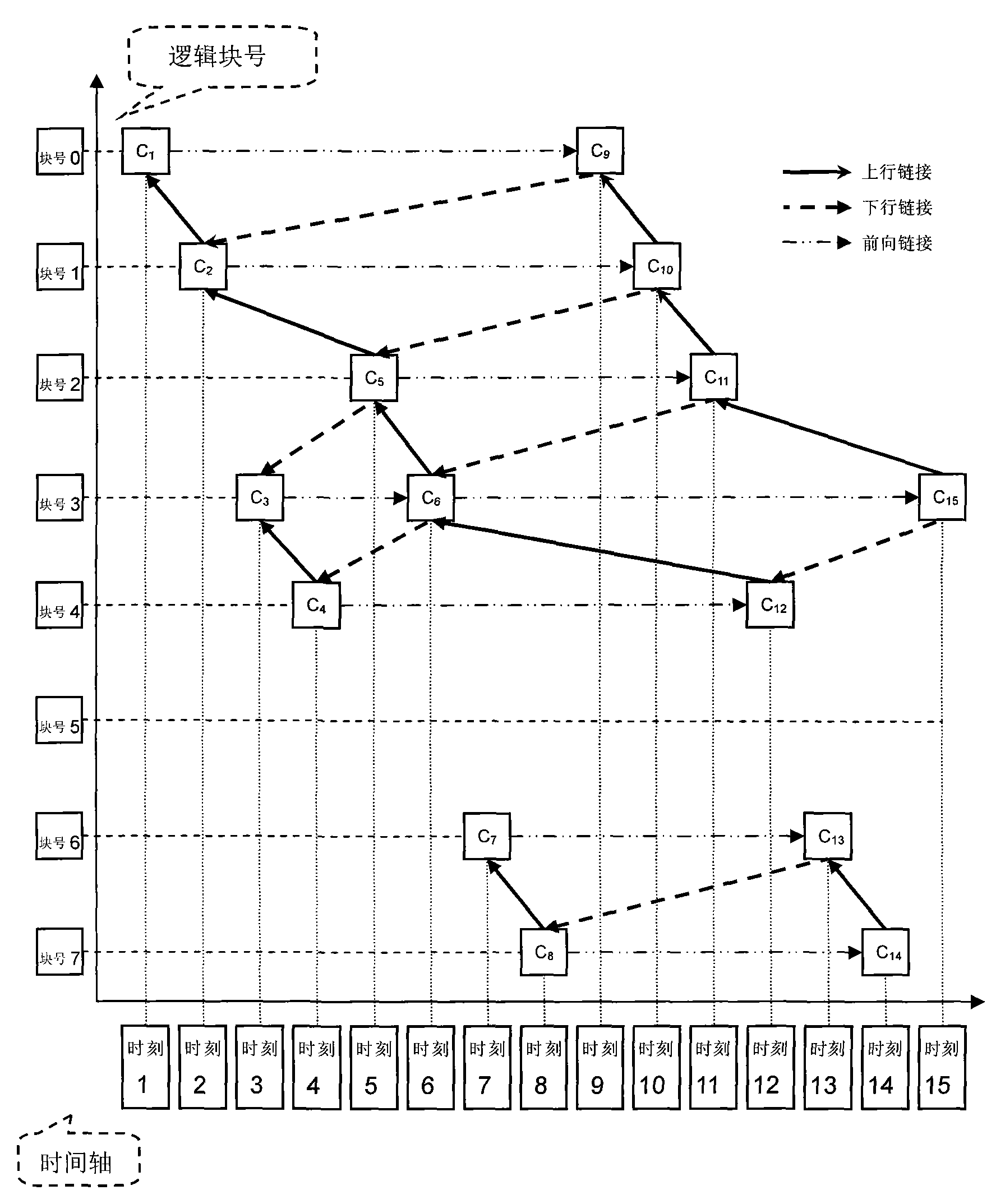
ActiveCN101777016AImprove storage efficiencySave storage spaceMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRedundant operation error correctionRecovery methodBinary tree
The invention discloses a snapshot storage and data recovery method of a continuous data protection system. In a block-level continuous data protection (CDP) system, each write operation of a disk data block has a CDP metadata for recording the write operation. The CDP metadata is taken as a chain table node, and besides a block number containing the data block, the node also sets up three fields of forward link, uplink and downlink. On the basis, a binary tree is constructed to record the table head of each key chain table node, thereby forming a key node set, and the chain table starting from the table heads can reflect the mapping relation from each block address of the disk of the current time to the log data block. The invention can store the mapping relation of the snapshot time by using less storage space, thereby supporting more intensive data snapshot and being beneficial to shortening the data recovery time.
Owner:TOYOU FEIJI ELECTRONICS
Management interface for a system that provides automated, real-time, continuous data protection
ActiveUS7904913B2Digital data information retrievalError detection/correctionDisplay deviceObject store
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
Transient point-in-time images for continuous data protection
ActiveUS7523277B1Reduce the amount requiredError detection/correctionMemory systemsUse of timeContinuous data protection
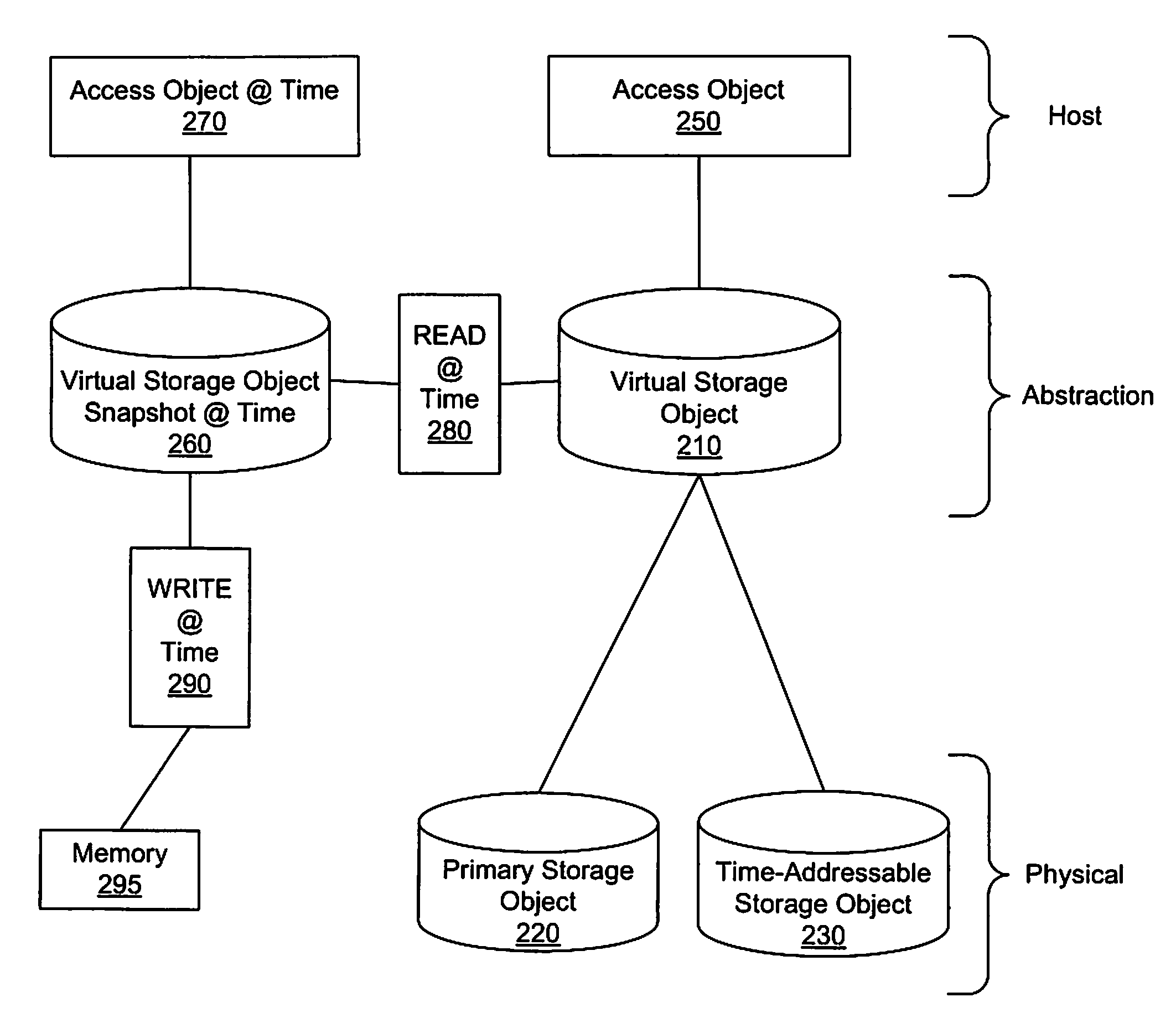
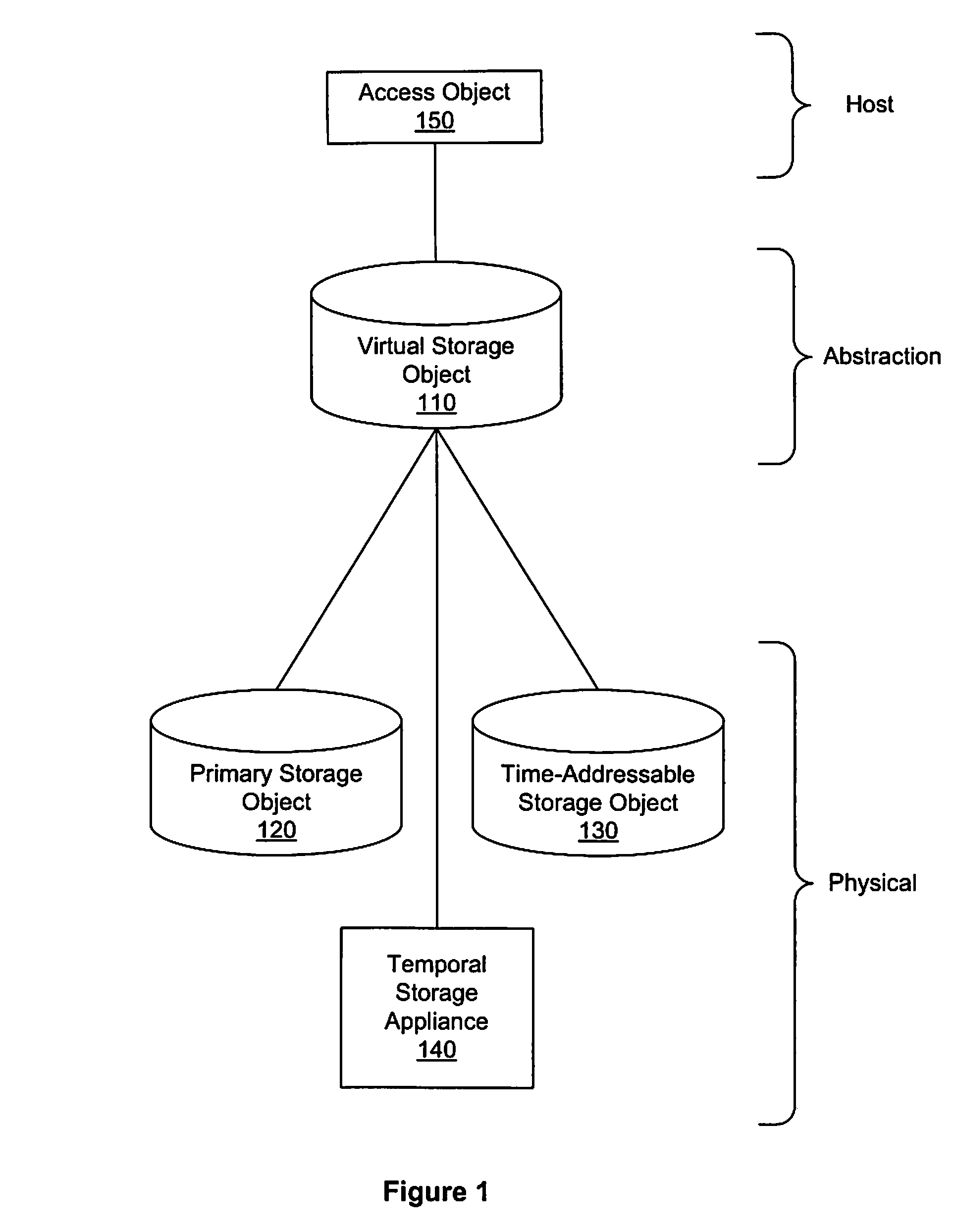
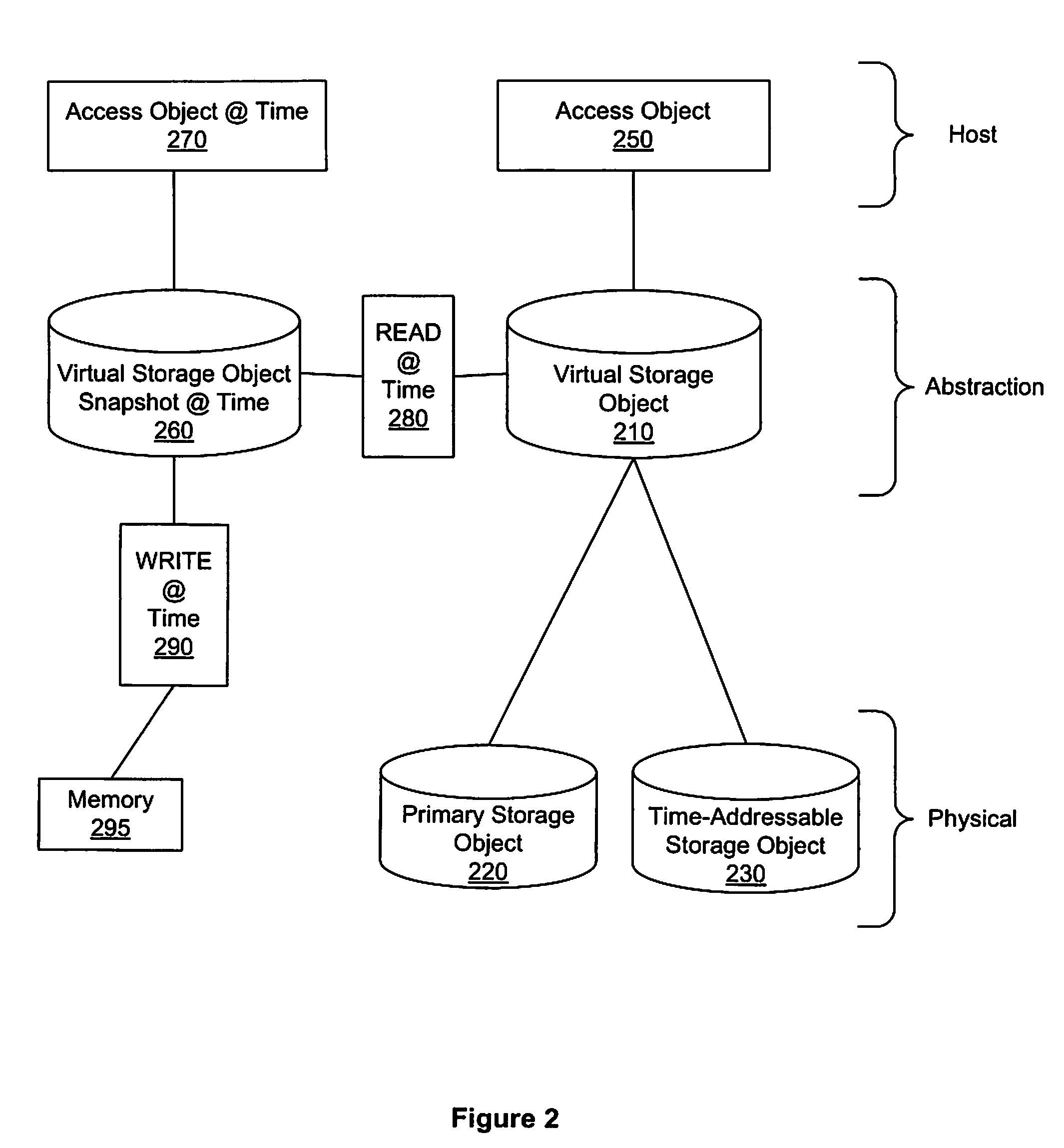
A method, system, and apparatus that provide an equivalent of persistent frozen image snapshots through the use of a time-addressable storage object, such as a time-indexed storage volume, are presented. These virtual snapshot images are presented to a system in a manner such that the image is not persistent and therefore (i) do not take up additional storage resources, and (ii) reduce the amount of volume management overhead that must be maintained since information about the snapshot can be discarded when the snapshot is no longer needed.
Owner:SYMANTEC OPERATING CORP
Continuous data protection method
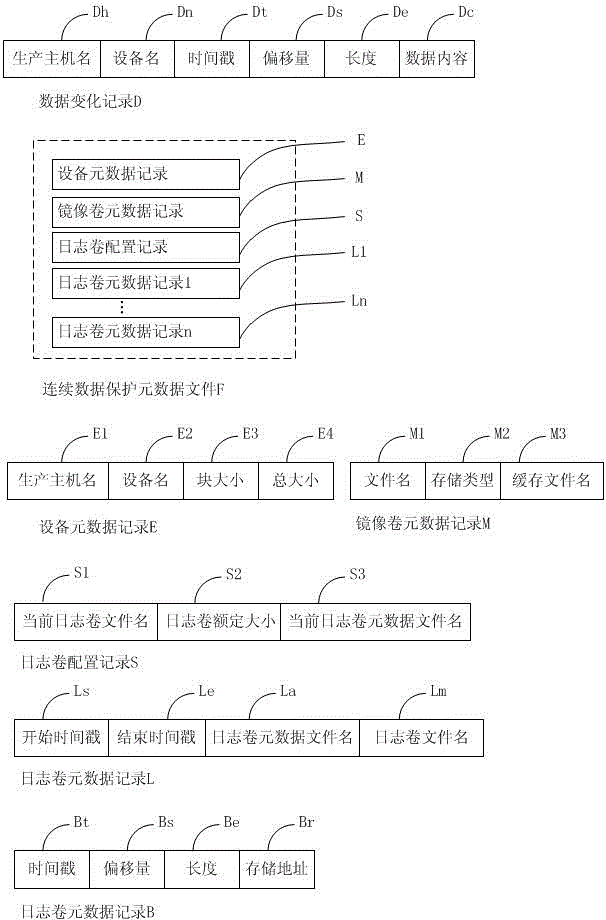
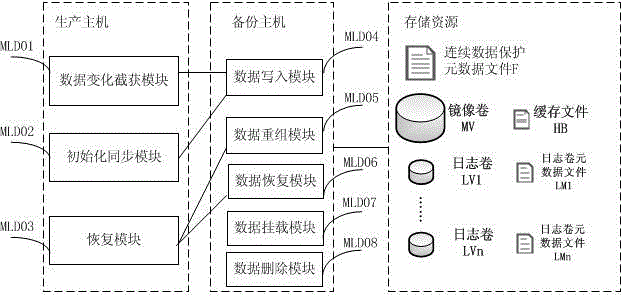
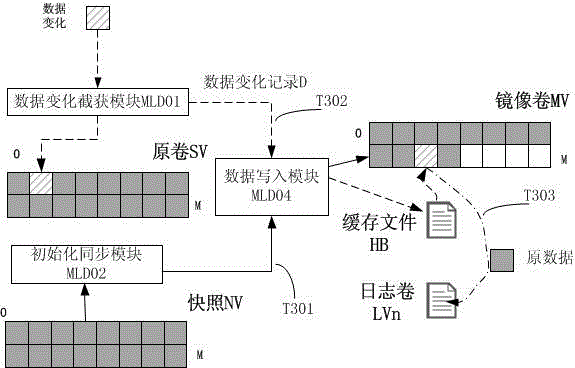
ActiveCN104866435AQuick verificationWrite quicklyMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital data protectionRecording durationState variation
The invention provides a continuous data protection method. Data can be recovered to any time point; data mounting in a short time can be realized; and the fast verification, write-in and immediate use of the data are realized. The method comprises the following steps that: initialization synchronization is executed at first; the initial state of production host block equipment is synchronized to a backup host; meanwhile, a data variation capturing module is started for capturing the data variation and transmitting the data variation to the backup host; the data variation is written into a mirrored volume; original data of a data variation address is written into a journal volume; the timestamp, the offset, the length and the storage address are recorded; and the recording of any data variation is realized. The reconfiguration of a virtual volume is used; the actual data access is redirected to the mirrored volume, the journal volume and a write time volume through a virtual volume index block; and the data read-out and the data write-in are realized. The data recovery is realized by using data read-out. Obsolete data can be deleted only through finding and deleting all of the journal volume and journal volume metadata files with the ending timestamp before the time point.
Owner:成都云祺科技有限公司
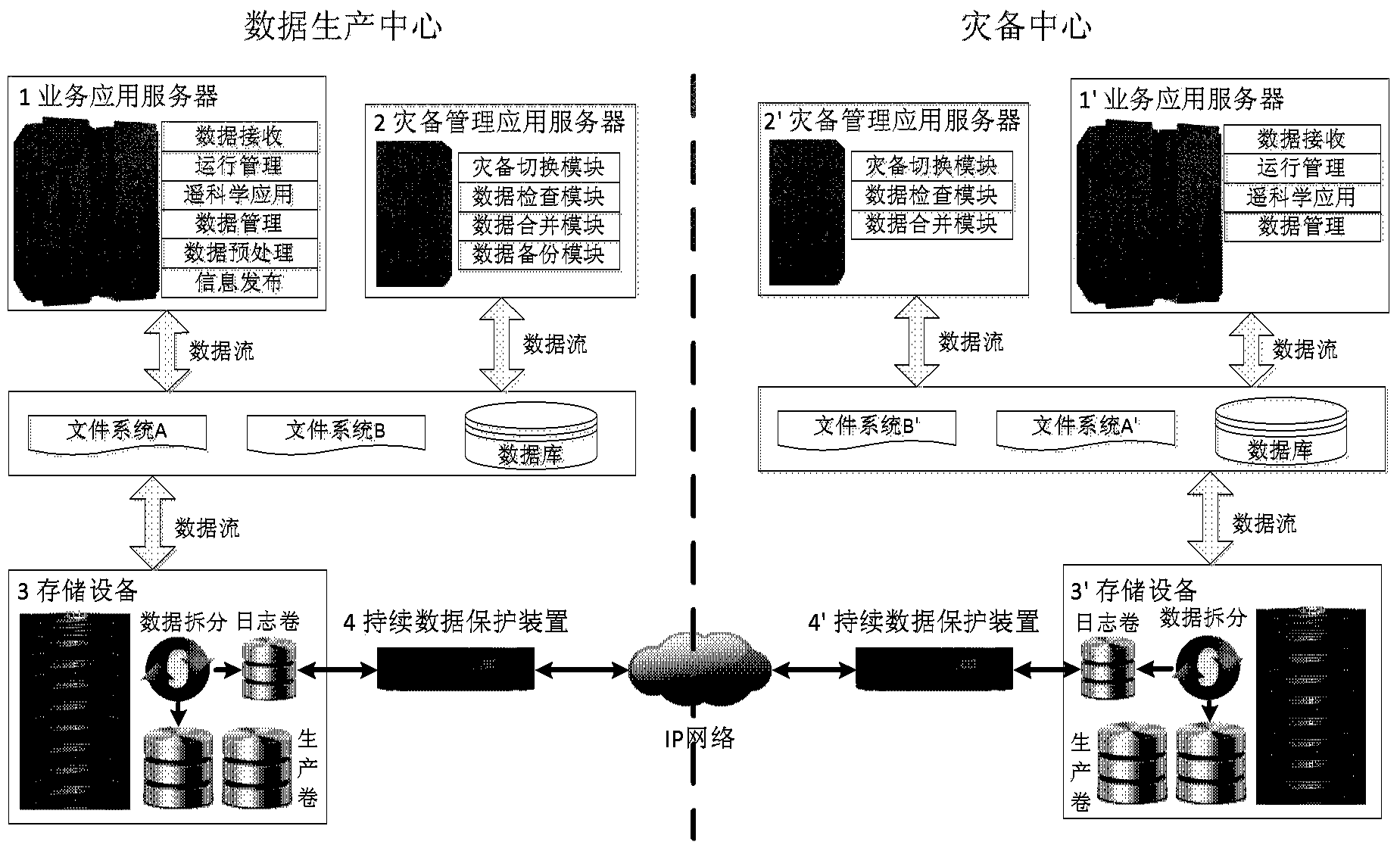
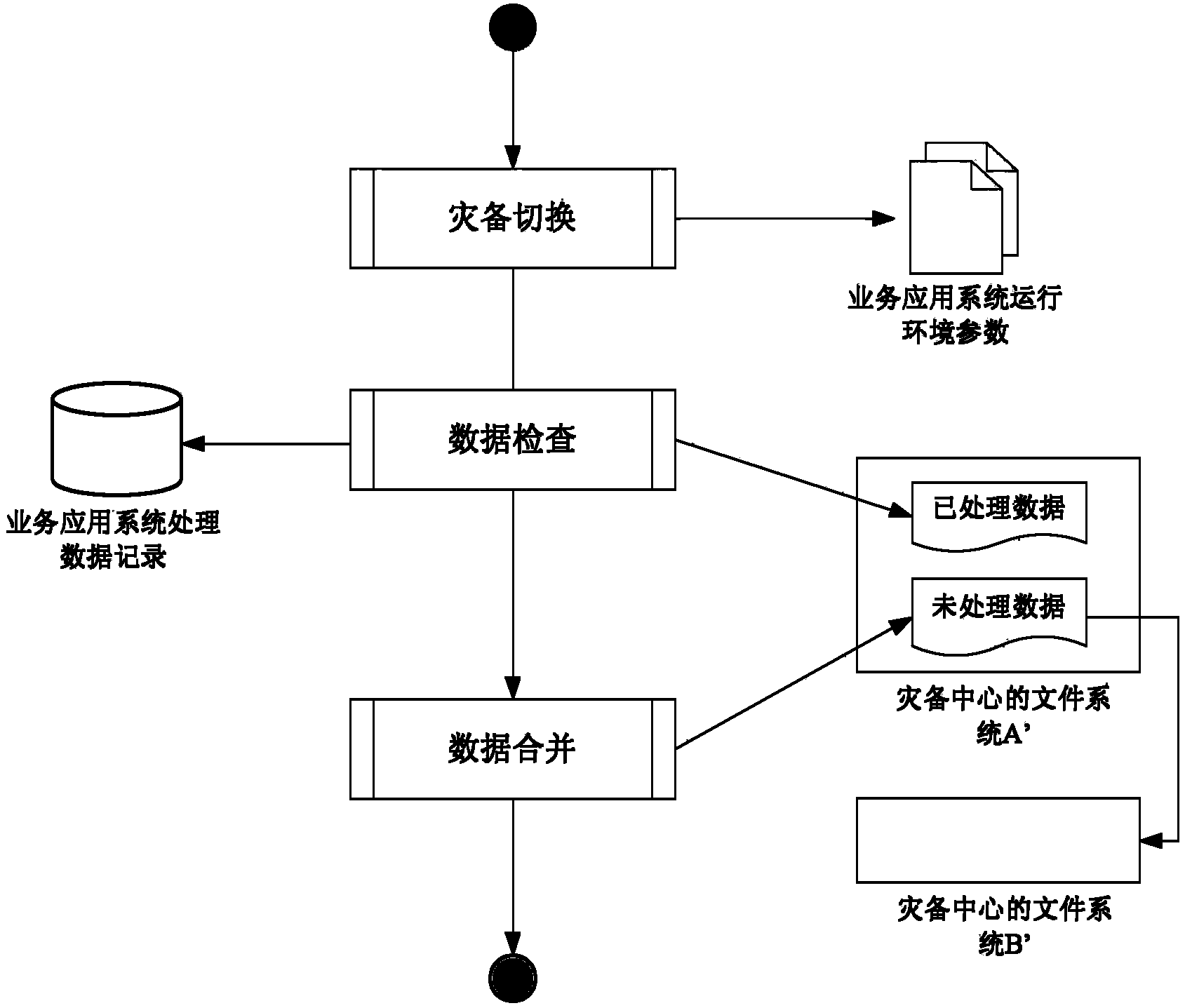
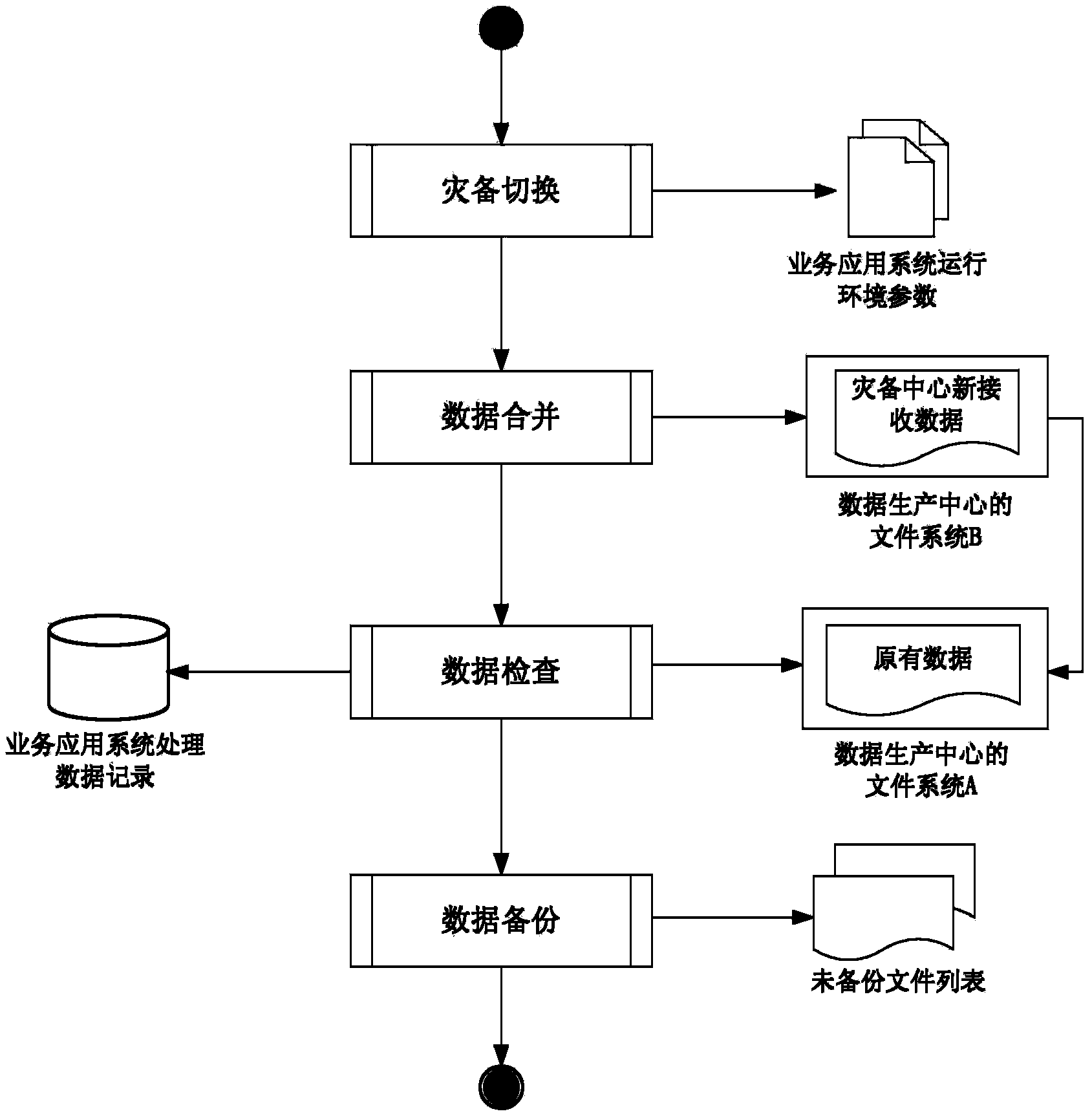
System and method for big data remote disaster recovery backup of ground application
ActiveCN103838646AAchieve separationEfficient separationTransmissionRedundant operation error correctionApplication serverData needs
The invention discloses a system and method for big data remote disaster recovery backup of ground application. In the system, a service application server deployed on a data production central terminal is used for operating service application under the normal circumstances; a service application server deployed on a disaster recovery backup central terminal is used for taking over and operating core services of the data production center when disasters occur; a disaster recovery backup management application server is used for switching the core services of the data production center into a disaster recovery backup center when the disasters occur and switching the core services back to the data production center after disaster recovery; a storage system deployed on the data production central terminal is used for storing all produced data; a storage system deployed on the disaster recovery backup central terminal is used for storing all data needing the disaster recovery backup and data newly received and processed by the disaster recovery backup center after service switching when the disasters occur; a continuous data protection application device is used for sending data written in an area to be protected to the opposite-terminal storage systems in real time to achieve continuous data backup protection.
Owner:NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORIES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method and system for no downtime resynchronization for real-time, continuous data protection
InactiveUS20100198788A1Data processing applicationsError detection/correctionBaseline dataReal-time data
A data management system or “DMS” provides an automated, continuous, real-time data protection service to one or more data sources associated with a set of application host serves. To facilitate the service, a host driver embedded in an application server captures real-time data transactions. When a data protection command for a given data source is forwarded to a host driver, an event processor enters into an initial upload state. During this state, the event processor gathers a list of data items to be protected and creates a data list. Then, the event processor moves the data to a DMS core to create initial baseline data. The upload is a stream of application-aware data chunks that are attached to upload events. A resynchronization state is entered when there is a suspicion that the state of the data in the host is out-of-sync with the state of the most current data in the DMS.
Owner:BAKBONE SOFTWARE INC
Continuous data protection system and method combining with snapshot technology
ActiveCN105389230AShorten the timeReduce protection vacuum periodRedundant operation error correctionProtection systemBlock level
Owner:EISOO SOFTWARE
Method and system for no downtime resychronization for real-time, continuous data protection
ActiveUS7680834B1Easy to optimizeError detection/correctionDatabase distribution/replicationBaseline dataReal-time data
A data management system or “DMS” provides an automated, continuous, real-time data protection service to one or more data sources associated with a set of application host servers. To facilitate the service, a host driver embedded in an application server captures real-time data transactions. When a data protection command for a given data source is forwarded to a host driver, an event processor enters into an initial upload state. During this state, the event processor gathers a list of data items to be protected and creates a data list. Then, the event processor moves the data to a DMS core to create initial baseline data. The upload is a stream of application-aware data chunks that are attached to upload events. A resynchronization state is entered when there is a suspicion that the state of the data in the host is out-of-sync with the state of the most current data in the DMS. During upload or upward resynchronization, the application does not have to be shut down.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
Method and system for file-level continuous data protection
ActiveUS8296264B1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsFile systemData memory
Continuous data protection is performed as two parallel processes: creating an initial backup by copying a data as a file / directory from the storage device into the backup storage, and copying the data to be written to the data storage as a part of a file / directory into the incremental backup. Alternatively, it can be performed as one process: copying the data to be written to the data storage as a part of a file / directory on the storage. A write command to a file system driver is intercepted and redirected to the backup, and the data is written to the incremental backup. If the write command is also directed to a not yet backed up data (a file / directory), the identified data is copied from the storage device to intermediate storage. The write command is executed on the file / directory from the storage device, and the file / directory is copied from the intermediate storage.
Owner:MIDCAP FINANCIAL TRUST
Storage system, data protection method, and program
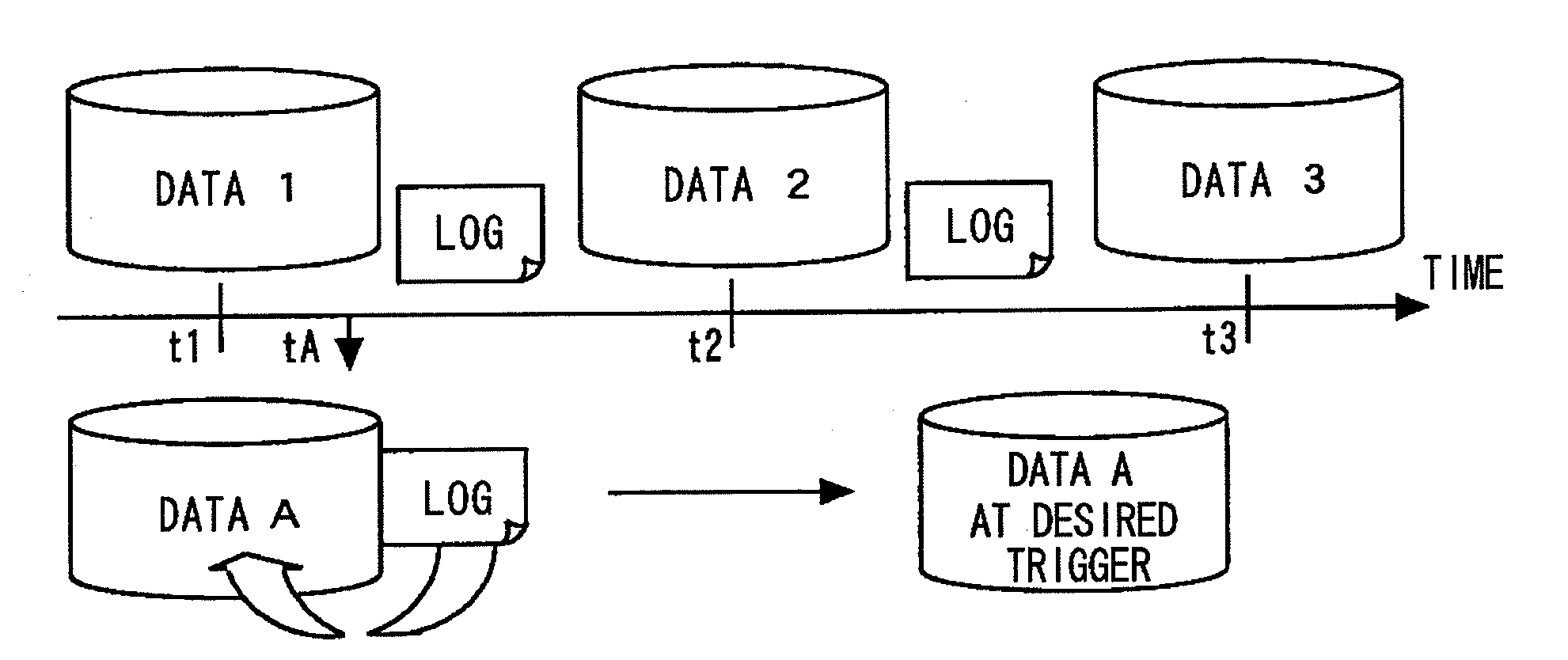
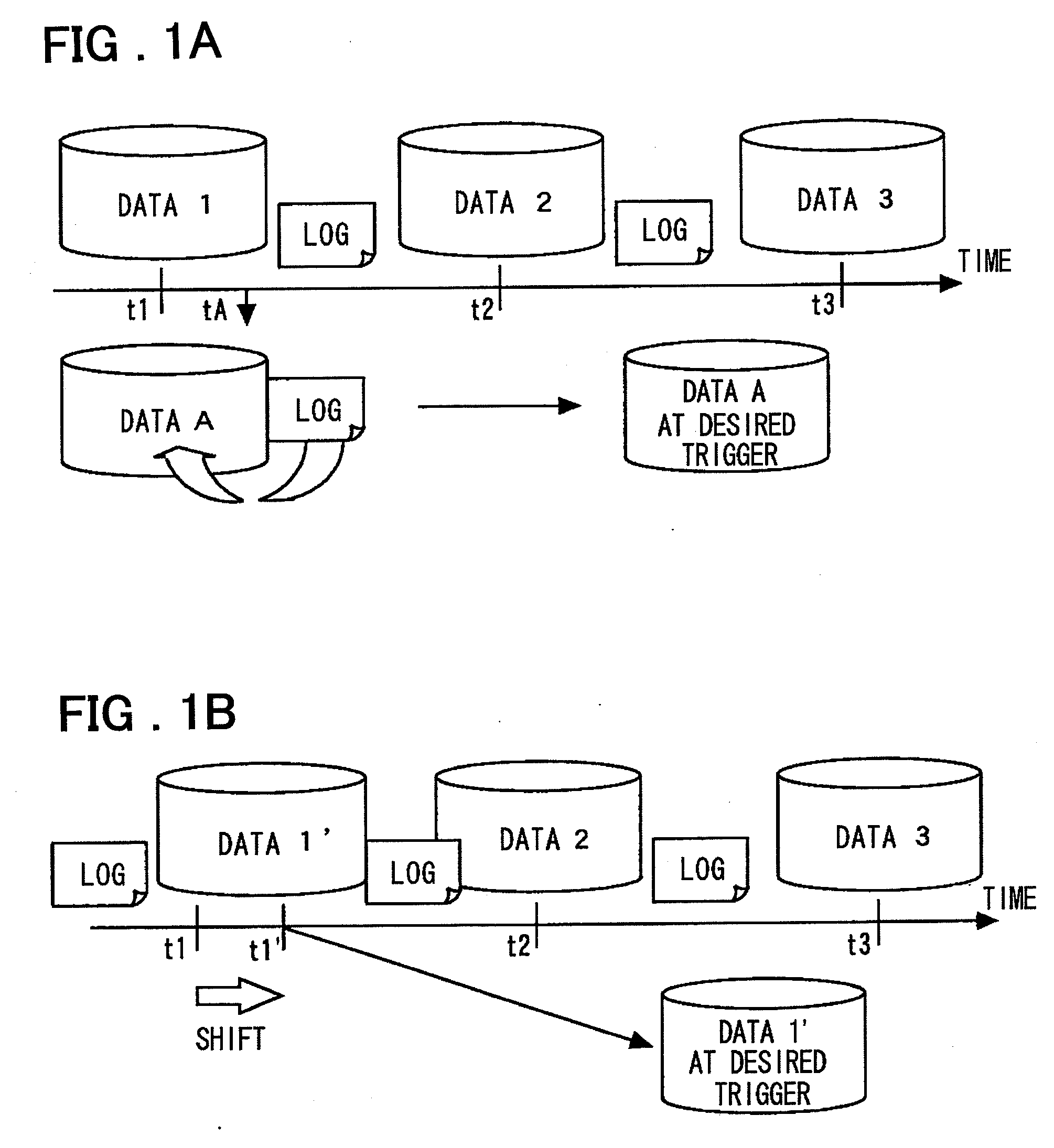
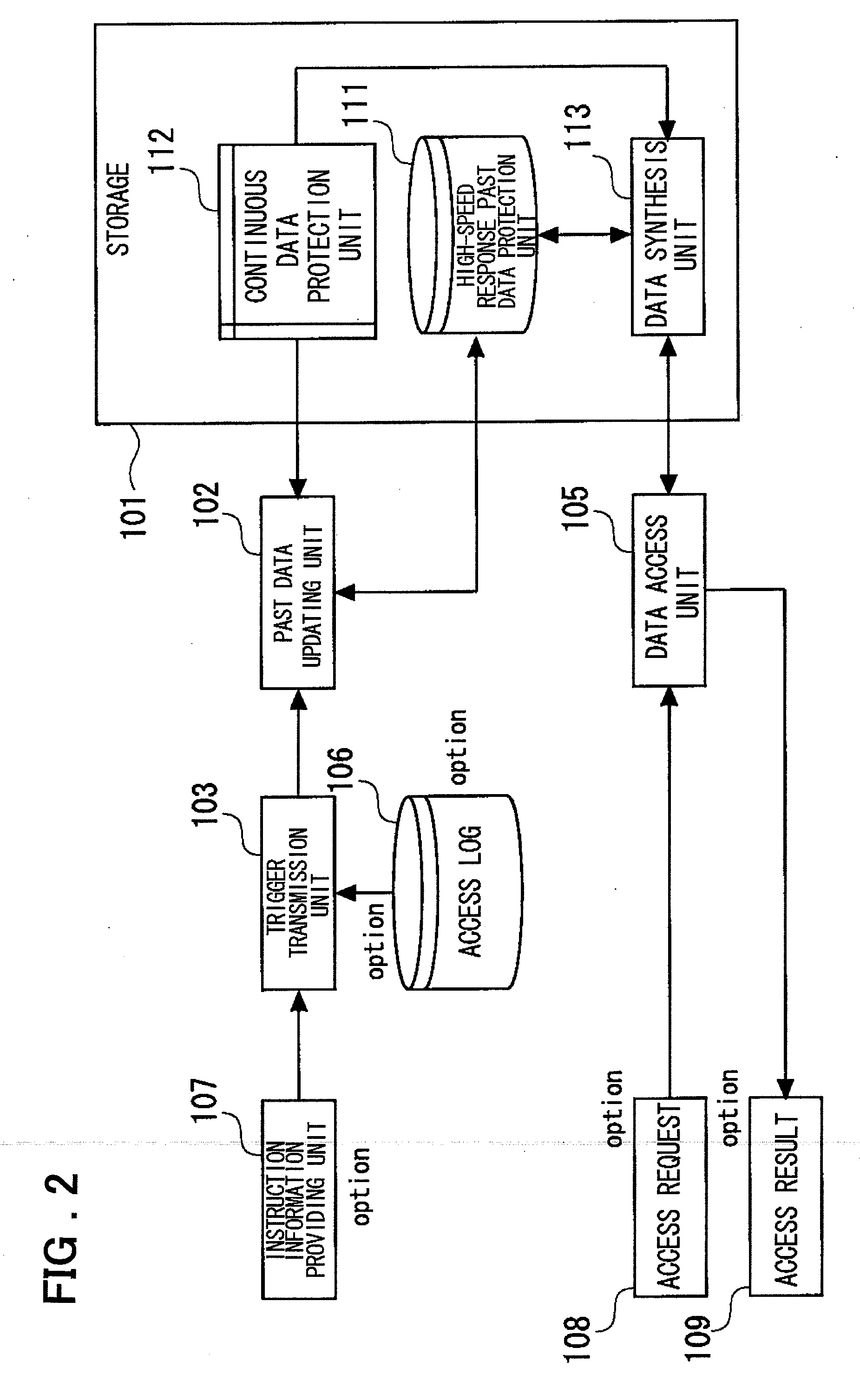
InactiveUS20080154914A1Access to the past data can be thereby sped upError detection/correctionAutomatic cassette changing arrangementsData storingData store
Disclosed is a system including a storage that includes a high-speed response past data protection unit that holds high-speed response past data, a continuous data protection unit that performs continuous data protection, a data synthesis unit that synthesizes data using the data in the high-speed response past data protection unit and data in the continuous data protection unit, and a past data updating unit that creates data corresponding to a predetermined trigger in advance. The past data updating unit restores the data corresponding to the predetermined trigger in advance. The data synthesis unit returns the high-speed response past data stored and held in the high-speed response past data protection unit. For a request to access data other than the one at the predetermined trigger, the data synthesis unit returns the data synthesized.
Owner:NEC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com