Method for removing nickel in chemical nickel-plating wastewater
A technology for nickel waste water and waste water, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, water/sewage multi-stage treatment, etc., can solve problems such as cumbersome operation and management, treatment compliance, and environmental protection pressure of enterprises, and achieve simple operation process, The effect of low pretreatment requirements and shortened work cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
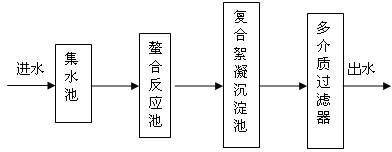
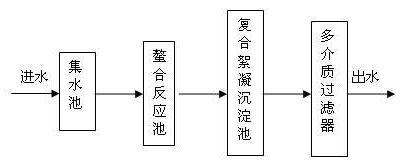
[0028] Collect the nickel waste water in the sump, the waste water is pressed into the chelation tank by the pump, the pH value of the waste water is controlled to be 8 with 30% sodium hydroxide, and the chelating agent is dropped into the chelating tank, and the weight ratio of the chelating agent to the waste water is 1:3500, the chelating agent includes 30 parts of mercaptan, 30 parts of sodium sulfide, and 40 parts of polymerized sodium dithiocarbamate, then add 1.8t of zeolite, 1.2t of shells, hydraulic retention for 30mins, and the wastewater after the chelation reaction flows into the composite flocculation sedimentation In the pool, put polymeric magnesium-aluminum sulfate composite flocculant into the composite flocculation sedimentation tank, the weight ratio of polymeric magnesium-aluminum composite flocculant to wastewater is 1:2000, polymeric magnesium-aluminum sulfate includes 98 parts of polyaluminum sulfate, 2 parts of polymagnesium sulfate, The hydraulic retent...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Collect the nickel waste water in the sump, the waste water is pressed into the chelation tank by the pump, and the pH value of the waste water is controlled with 30% sodium hydroxide to be 9, and the chelating agent is dropped into the chelating tank, and the weight ratio of the chelating agent to the waste water is 1:1500, the chelating agent includes 5 parts of mercaptan, 5 parts of sodium sulfide, and 90 parts of polymerized sodium dithiocarbamate, then add 2.4t of zeolite, 0.6t of shells, hydraulic retention for 1h, and the wastewater after the chelation reaction flows into the composite flocculation sedimentation In the pool, put polymeric magnesium-aluminum sulfate composite flocculant into the composite flocculation sedimentation tank, the weight ratio of polymeric magnesium-aluminum composite flocculant to wastewater is 1:3000, polymeric magnesium-aluminum sulfate includes 50 parts of polyaluminum sulfate, 50 parts of polymagnesium sulfate, The hydraulic retenti...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Collect the nickel waste water in the sump, the waste water is pressed into the chelation tank by the pump, the pH value of the waste water is controlled to be 8.5 with 30% sodium hydroxide, and the chelating agent is dropped into the chelating tank, and the weight ratio of the chelating agent to the waste water is 1:2500, the chelating agent includes 15 parts of mercaptan, 15 parts of sodium sulfide, and 70 parts of polymerized sodium dithiocarbamate, then add 1.5t of zeolite, 1.5t of shells, hydraulic retention for 75mins, and the wastewater after the chelation reaction flows into the composite flocculation sedimentation In the pool, put polymeric magnesium-aluminum sulfate composite flocculant into the composite flocculation sedimentation tank, the weight ratio of polymeric magnesium-aluminum composite flocculant to wastewater is 1:2500, polymeric magnesium-aluminum sulfate includes 70 parts of polyaluminum sulfate, 30 parts of polymagnesium sulfate, The hydraulic ret...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com