Method for manufacturing secondary battery and secondary battery
A secondary battery and manufacturing method technology, applied in the direction of lithium batteries, final product manufacturing, battery pack components, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in forming uniform bending and reduction in mechanical strength of thin foils
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0074] (1) Production of positive plate
[0075] First, 85 parts by weight of lithium cobaltate powder was prepared as a positive electrode active material, 10 parts by weight of carbon powder was prepared as a conductive material, and 5 parts by weight of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVdF) was prepared as a binder. Then, the prepared positive electrode active material, conductive material and binding material are mixed to prepare the positive electrode mixture coating.
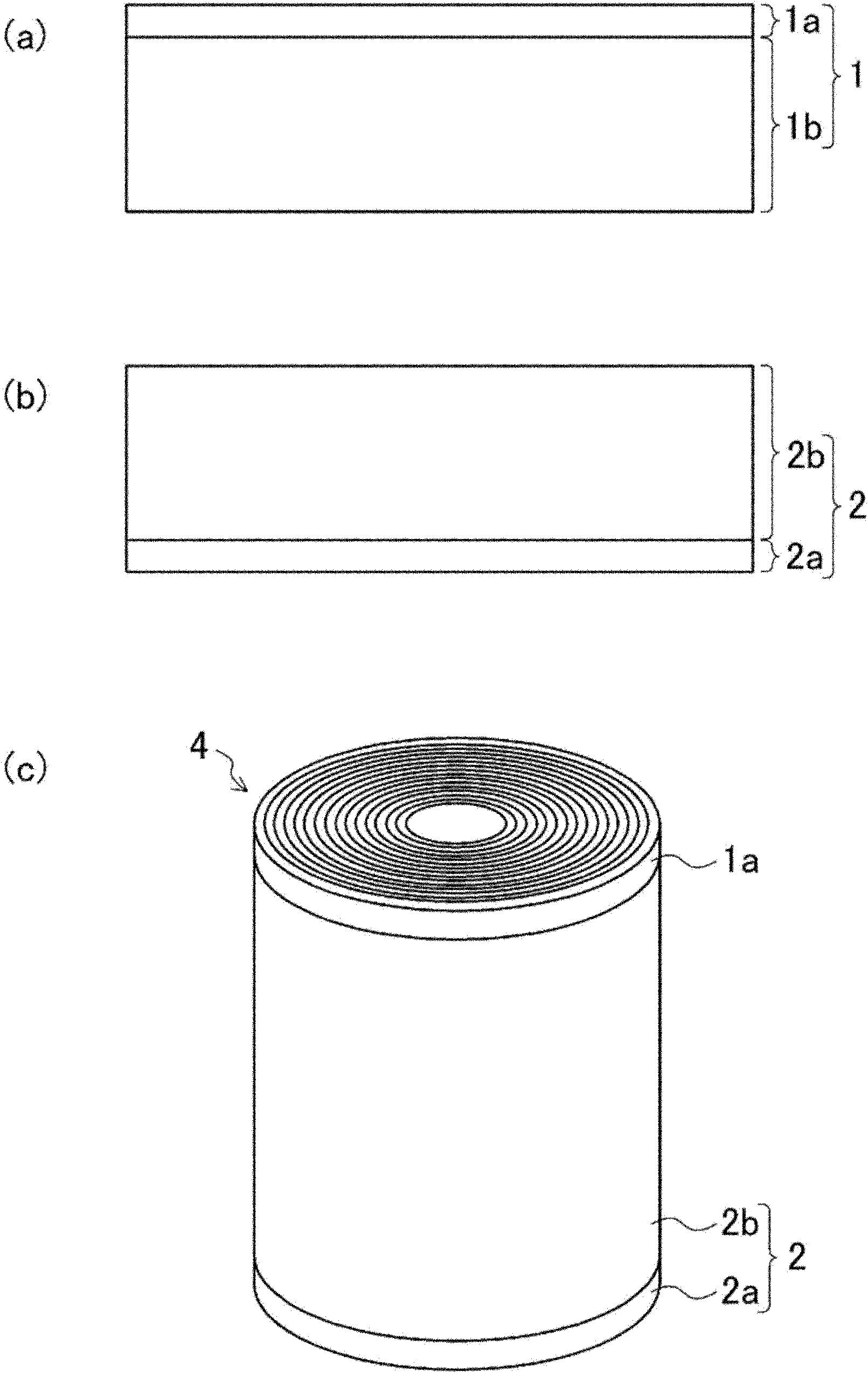
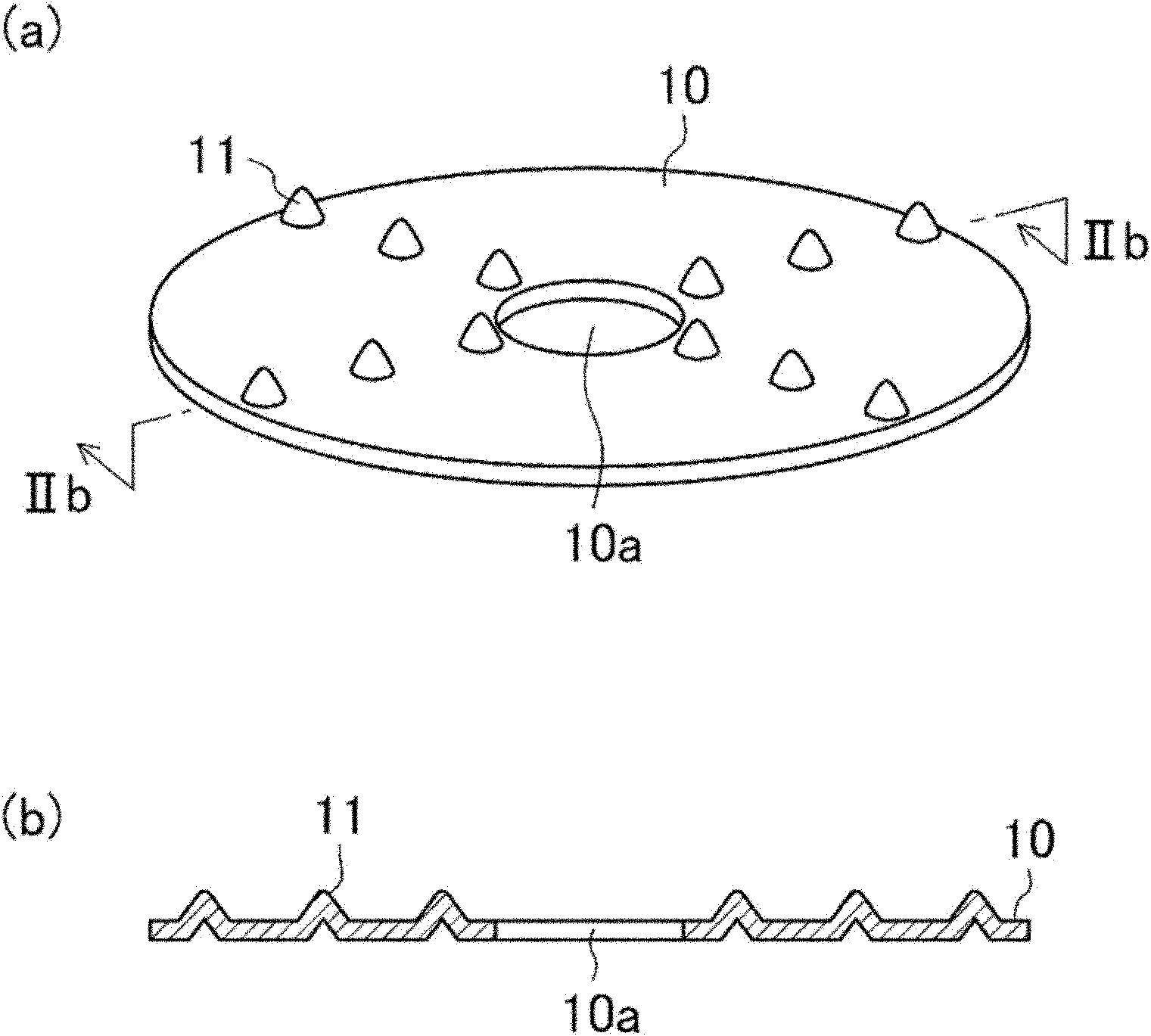
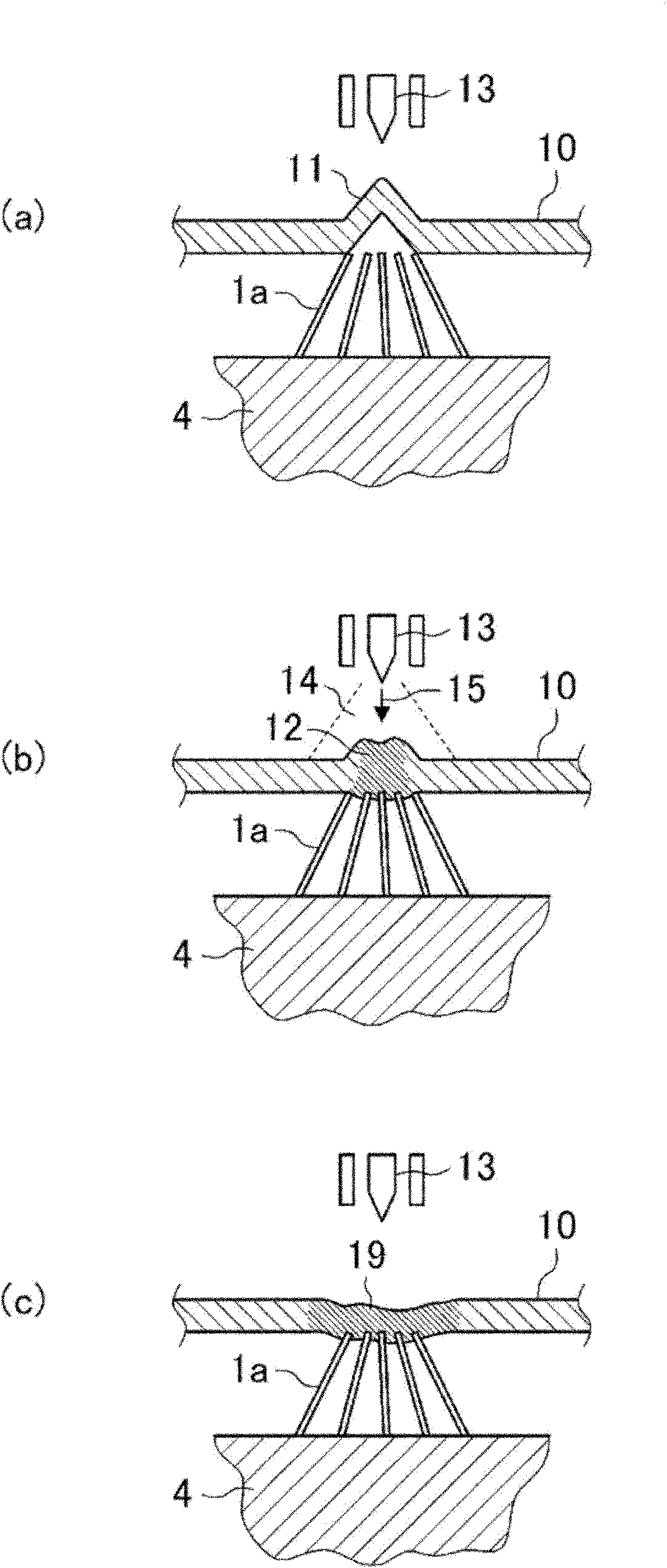
[0076] Next, the positive electrode mixture paint was applied to both surfaces of the positive electrode current collector of an aluminum foil having a thickness of 15 μm and a width of 56 mm, and the positive electrode mixture paint was dried. Then, the positive electrode mixture layer 1 b coated with the positive electrode mixture paint was rolled to form a positive electrode plate 1 with a thickness of 150 μm. At this time, the width of the positive electrode mixture layer 1 b was 50 mm, and the width of the ...
Embodiment 2
[0094] (1) Production of positive plate
[0095] First, 85 parts by weight of lithium cobaltate powder was prepared as a positive electrode active material, 10 parts by weight of carbon powder was prepared as a conductive material, and 5 parts by weight of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVdF) was prepared as a binder. Then, the prepared positive electrode active material, conductive material, and binder were mixed to prepare a positive electrode mixture coating.
[0096] Next, the positive electrode mixture paint was applied to both surfaces of the positive electrode current collector of an aluminum foil having a thickness of 15 μm and a width of 83 mm. After the positive electrode mixture paint was dried, the positive electrode mixture layer 1 b was rolled to produce a positive electrode plate 1 with a thickness of 83 μm. At this time, the width of the positive electrode mixture layer 1 b was 77 mm, and the width of the non-coated portion 1 a of the positive electrode mixture was ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com