Vaccine against human papillomavirus (HPV) as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology of human papilloma and virus, applied in the fields of genetic engineering and vaccinology, can solve problems such as high production costs, unfavorable allergic reactions, loss of plasmids, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0084] Preparation and fermentation production of engineering bacteria
[0085] The inventive point of the present invention mainly lies in the transformed HPV L1 gene. As for the technologies such as inserting the transformed HPV L1 gene into a plasmid, transforming Pichia pastoris, engineering bacterium, fermentation of engineered bacterium, and separation of products, the conventional methods known in the art are basically carried out (for example, people such as Sambrook, Molecular Cloning: Conditions described in a laboratory manual (New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1989)).
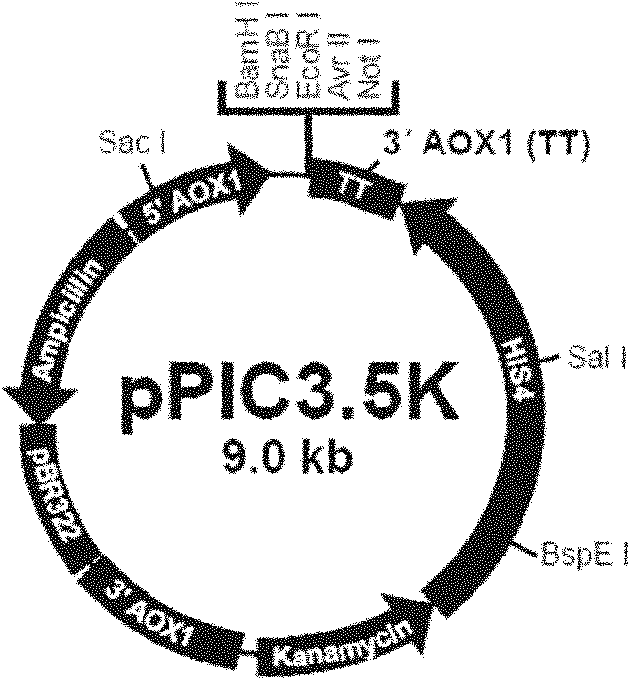
[0086] Usually, specific restriction sites can be introduced at the 5' end and 3' end of the optimized gene, and the optimized gene can be cloned into an expression vector (such as pPIC9, pPIC9K, etc.) by conventional methods of molecular cloning. Then, transform and integrate into the P. pastoris host cell chromosome. High-copy transformants were selected by conventional methods (suc...
Embodiment 1
[0146] Example 1. Construction of HPV52L1 Pichia pastoris expression system
[0147] 1. Obtaining the target gene
[0148] Optimized sequence: According to the amino acid sequence of natural HPV52L1, optimize the design according to the following factors: Pichia pastoris codon preference, A+T composition in the gene, G+C content, secondary structure of mRNA and translation initiation codon AUG flanking sequences, etc.
[0149] The nucleotide sequence of an optimized target gene is shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The amino acid sequence of the gene encoding HPV52L1 protein is shown in SEQ ID NO:2. The optimized gene (SEQ ID NO: 1) was artificially synthesized, and NotI and EcoRI restriction sites were introduced into its 5' end and 3' end respectively.
[0150] Control sequence 1: wild-type HPV52L1 gene (SEQ ID NO: 3), encoding the same HPV52L1 protein.
[0151] Control sequences 2 and 3: nucleotide sequences (SEQ ID NO: 4 and 21) generated by optimizing only according to the codon b...
Embodiment 2
[0165] Example 2. Construction of HPV58L1 Pichia pastoris expression system
[0166] Example 1 was repeated with the difference that the coding sequence of HPV52 L1 was replaced with the following coding sequence of HPV58 L1:
[0167] The nucleotide sequence of the optimized HPV58 L1 target gene is shown in SEQ ID NO:5. The amino acid sequence of the gene encoding HPV58L1 protein is shown in SEQ ID NO:6. The optimized gene (SEQID NO: 5) was artificially synthesized, and NotI and EcoRI restriction sites were introduced at its 5' end and 3' end, respectively.
[0168] Control sequence 4: wild-type HPV58L1 gene (SEQ ID NO: 7), encoding the same HPV58L1 protein.
[0169] Control sequences 5 and 6: nucleotide sequences (SEQ ID NO: 8 and 22) generated by optimizing only according to the codon bias principle of Pichia pastoris, encoding the same HPV58L1 protein. The control sequence is fully synthesized, and enzyme cutting sites are introduced at both ends.
[0170] As a result, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| antibody titer | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com