Nitrogen responsive early nodulin gene
A specific, amino acid technology, applied in genetic engineering, climate change adaptation, sugar derivatives, etc., can solve problems such as lack of
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0112] For the preparation of OsENOD93 overexpressing plants, introduction of polynucleotides into plant cells is accomplished by one of several techniques known in the art, including but not limited to electroporation or chemical transformation (see, e.g., Ausubel, ed. (1994) Current Protocols in Molecular Biology, John Wiley and Sons, Inc., Indianapolis, Indiana). Markers that confer resistance to toxic substances are used in the identification of transformed cells (cells that have taken up and expressed the test polynucleotide sequence) from non-transformed cells (those cells that do not contain or express the test polynucleotide sequence) useful in. In one aspect of the invention, genes are useful as markers for assessing the introduction of DNA into plant cells. A transgenic plant, transformed plant, or stably transformed plant, or any cell, tissue or seed of the foregoing, refers to a plant in which exogenous polynucleotides have been incorporated or integrated into pla...
Embodiment 1
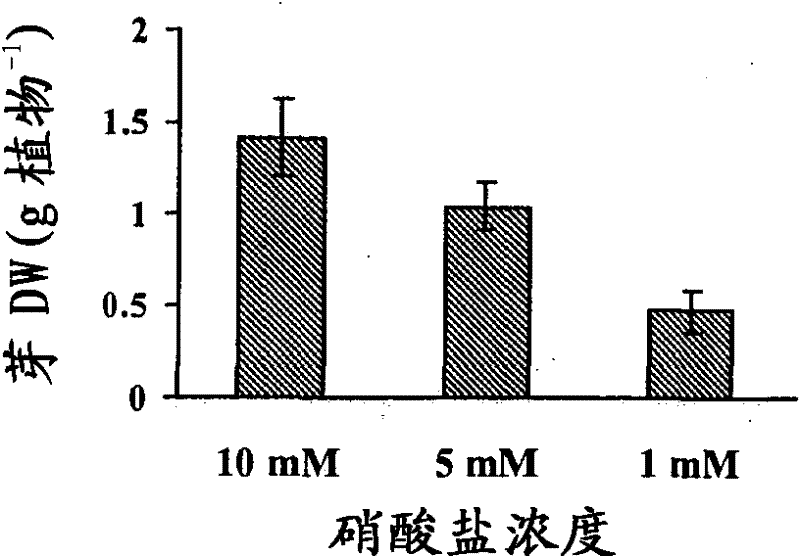
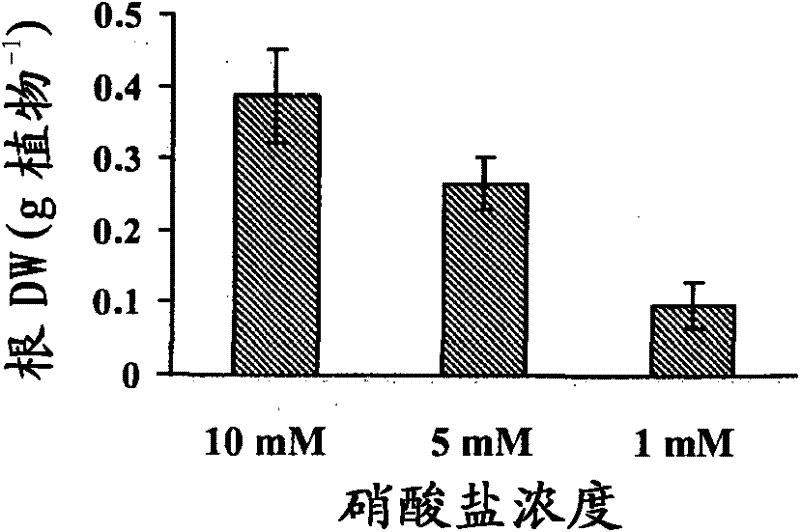
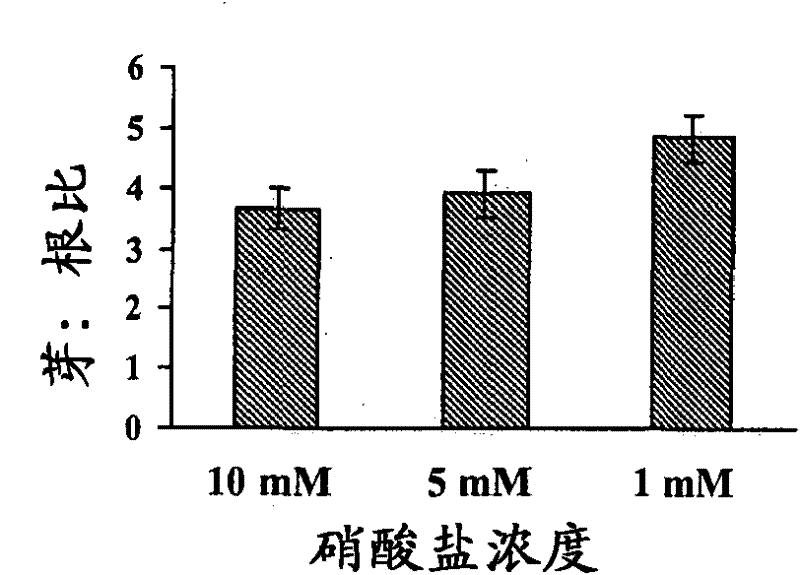
[0171] [Example 1: Changes in biomass in plants exposed to different nitrogen levels]
[0172] Wild-type Japanese rice (Oryza sativa Japonica) var. Donjin plants were grown in a mixture of sphagnum moss and vermiculite (1:4) (SunGro Horticulture Canada Ltd. BC, Canada) with varying amounts of nitrate added once a week. Nutrient solution until harvest. Nutrient solution containing 4mM MgSO 4 , 5mM KCl, 5mM CaCl 2 , 1mMKH 2 PO 4 , 0.1mM Fe-EDTA, 0.5mM MES (pH6.0), 9μM MnSO 4 , 0.7 μM ZnSO 4 , 0.3 μM CuSO 4 , 46 μM NaB 4 o 7 and 0.2μM (NH 4 ) 6 Mo 7 o 2 . 10 mM nitrate was used as high nitrogen condition, 5 mM nitrate as medium nitrogen, and 1 mM nitrate as low nitrogen. Plants are grown under 16 hours light at 28~30℃(-400μmolm -2 the s -1 ) and 4 weeks in a growth room at 22-24°C for 8 hours in the dark. Shoots and roots were harvested independently, and differences in biomass were assessed as growth markers.
Embodiment 2
[0174] [Example 2: Response to nitrogen deficiency]
[0175] Wild-type Japanese rice (Oryza sativa Japonica) var. Donjin plants were grown as described in Example 1. Yellowing of leaves and presence of purple flavonoid anthocyanins are some typical responses of plants when N deficiency occurs (Diaz U, et al, Plant and Cell Physiology, 2006, 47:74-83). The relative anthocyanin content was analyzed based on the method described by Neff and Chory (Neff MM & Chory J, Plant Physiol, 1998, 118:27-35). Total chlorophyll was either measured using a Minolta SPAD 502DL chlorophyll meter (Tokyo, Japan), or extracted by ethanol and tested by a spectrophotometer according to Kirk (Kirk, JTO, Planta, Berl, 1968, 78:200). The levels of chlorophyll and anthocyanins in leaves were similar under high and medium nitrogen conditions. Under low nitrogen conditions, plants were not distinctly yellow or purple, although chlorophyll decreased and anthocyanins increased significantly compared to hig...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| affinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com