Slow wave structure based on semiconductor-filled metal waveguide structure
A slow-wave structure and metal-filled technology, applied in the field of slow-wave structures, can solve the problems of increasing electromagnetic wave scattering loss, difficulty in the preparation of slow-wave devices, and difficulty in preparation, achieving good loss characteristics, easy design and processing, and solving the problem of preparation. difficult effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
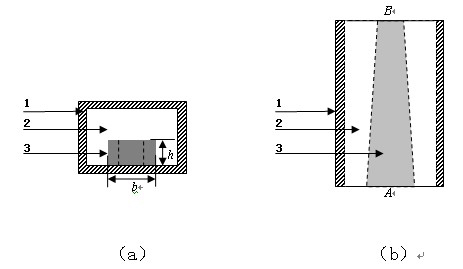
[0029] refer to figure 1 , a slow-wave waveguide based on a semiconductor-filled metal waveguide structure, comprising a rectangular metal waveguide wall 1 , a tapered semiconductor dielectric quadrangular prism 3 and air 2 . The length and width of the metal waveguide section are 80 and 40 . Height of pyramid-shaped semiconductor dielectric h Constant along the longitudinal direction, it is 16 , only the width b It becomes smaller along the longitudinal direction, and its material is germanium. Where A is the incident port of the electromagnetic wave. The present invention is a gradually tapered waveguide structure with the same structural parameters in the waveguide direction, rather than a periodic structure, and the structure of the present invention is much simpler than other slow wave structures.
[0030] In this embodiment, when the electromagnetic wave propagates along the waveguide structure, the energy flow transmitted in the air gap layer gradually increas...
Embodiment 2
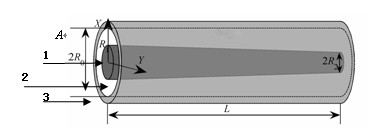
[0032] refer to image 3 , a slow-wave structure based on a semiconductor-filled metal waveguide structure, including a circular metal waveguide wall 1, air 2 and a tapered gallium arsenide semiconductor strip 3. The radius of GaAs semiconductor dielectric changes from the longitudinal direction, R 1 =0.23mm,R 2 =0.21mm,L=12mm,R 0 =0.4mm.
[0033] Electromagnetic waves flow from the wide port of the semiconductor A incident, propagates along the waveguide. Since the semiconductor near the port is wider, the guided wave has a larger group velocity. With the propagation of the guided wave, the average energy flow in the air is gradually close to the value in the semiconductor, the group velocity of the guided wave is gradually reduced, and the energy of the electromagnetic wave is gradually concentrated and strengthened. The corresponding part of the waveguide increases to the strongest, and electromagnetic waves of different frequencies will be enhanced in different parts ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com